Acidic Chitinase-Chitin Complex Is Dissociated in a Competitive Manner by Acetic Acid: Purification of Natural Enzyme for Supplementation Purposes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
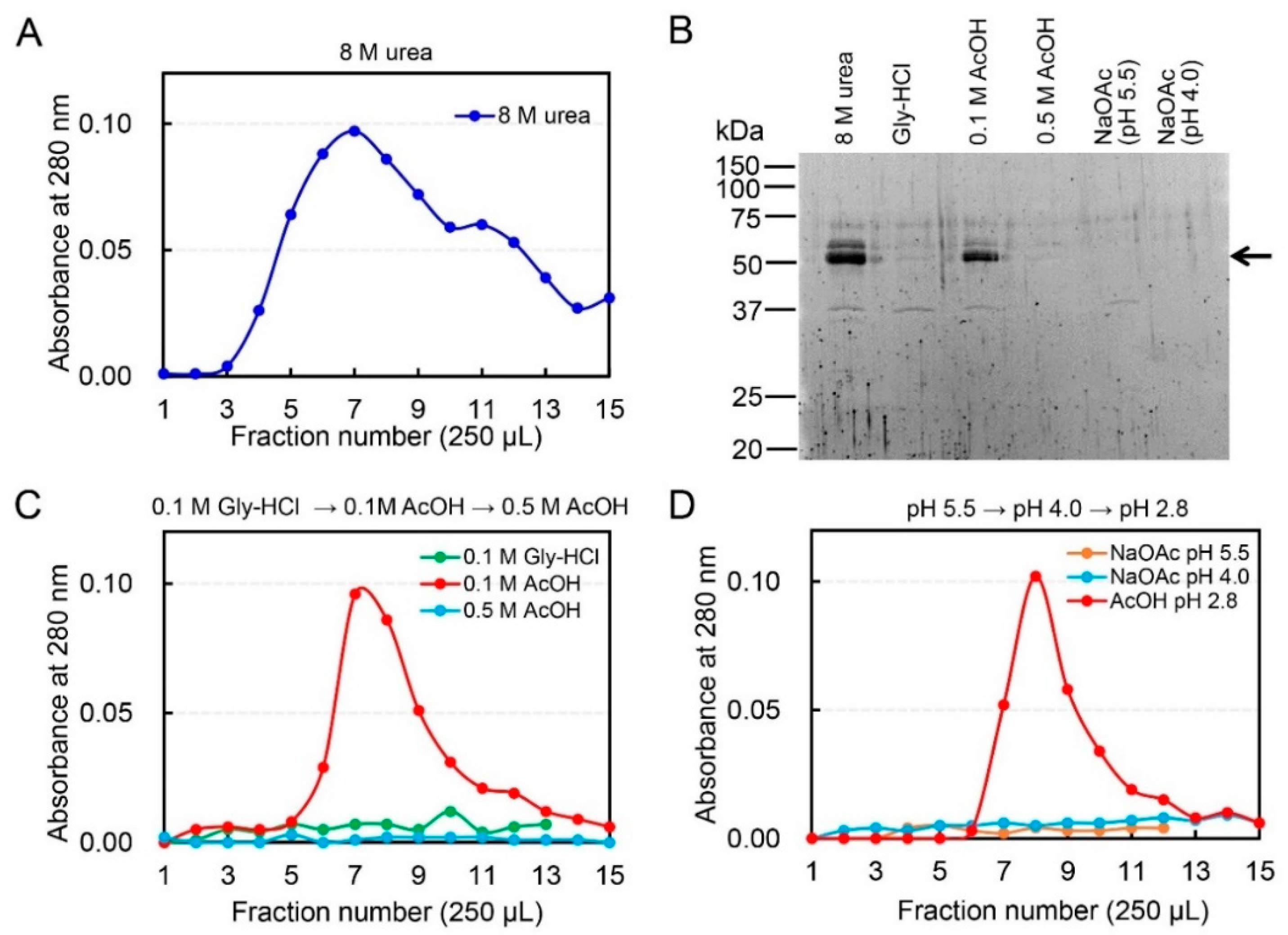
2.1. Dissociation of Chicken Chia–Chitin Complex by 0.1 M Acetic Acid
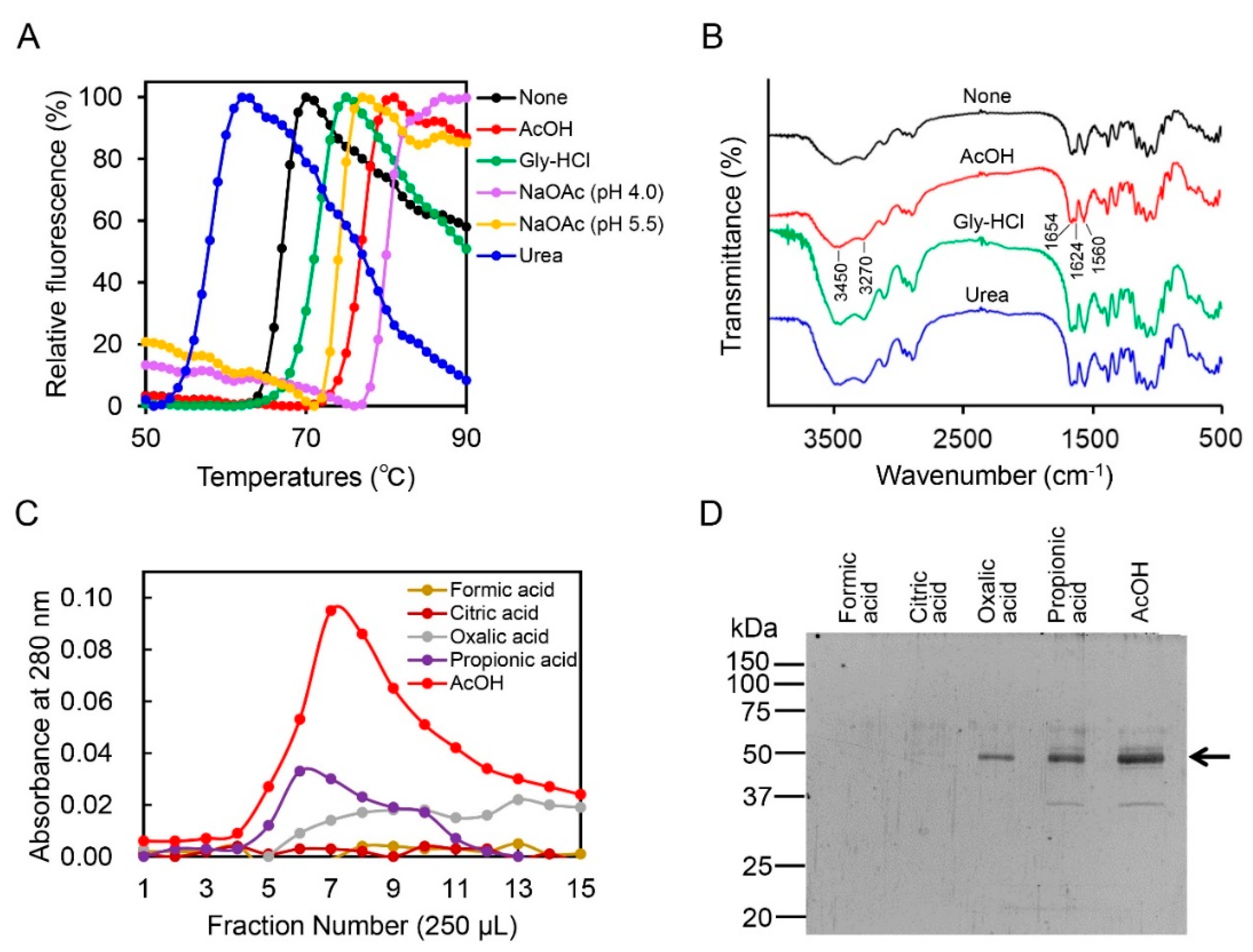
2.2. Acetic Acid Is Suitable for Chicken Chia Elution from Chitin Column without Acid Denaturation
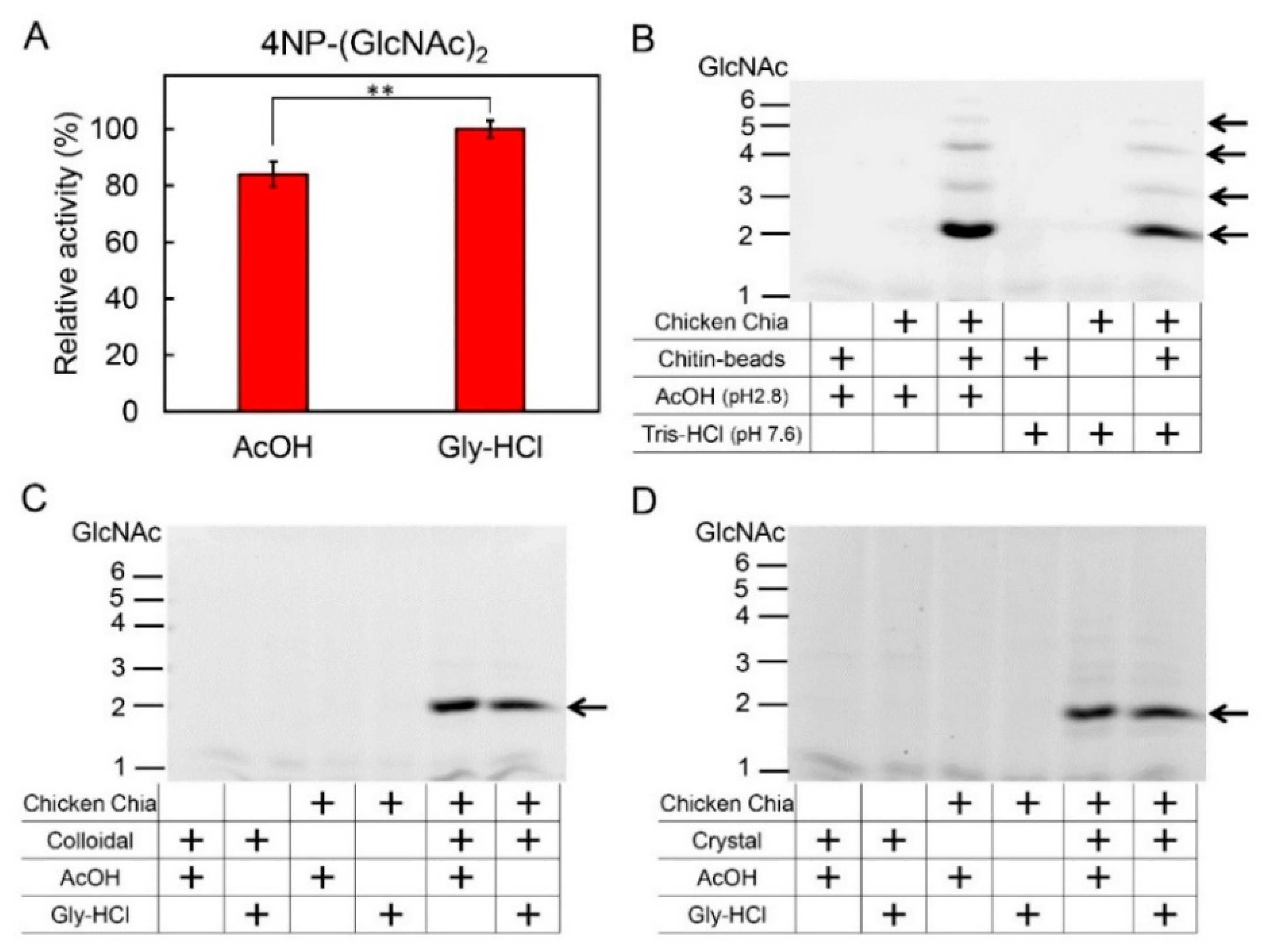
2.3. Effect of Acetic Acid on Chitin Degradation by Chicken Chia Enzyme
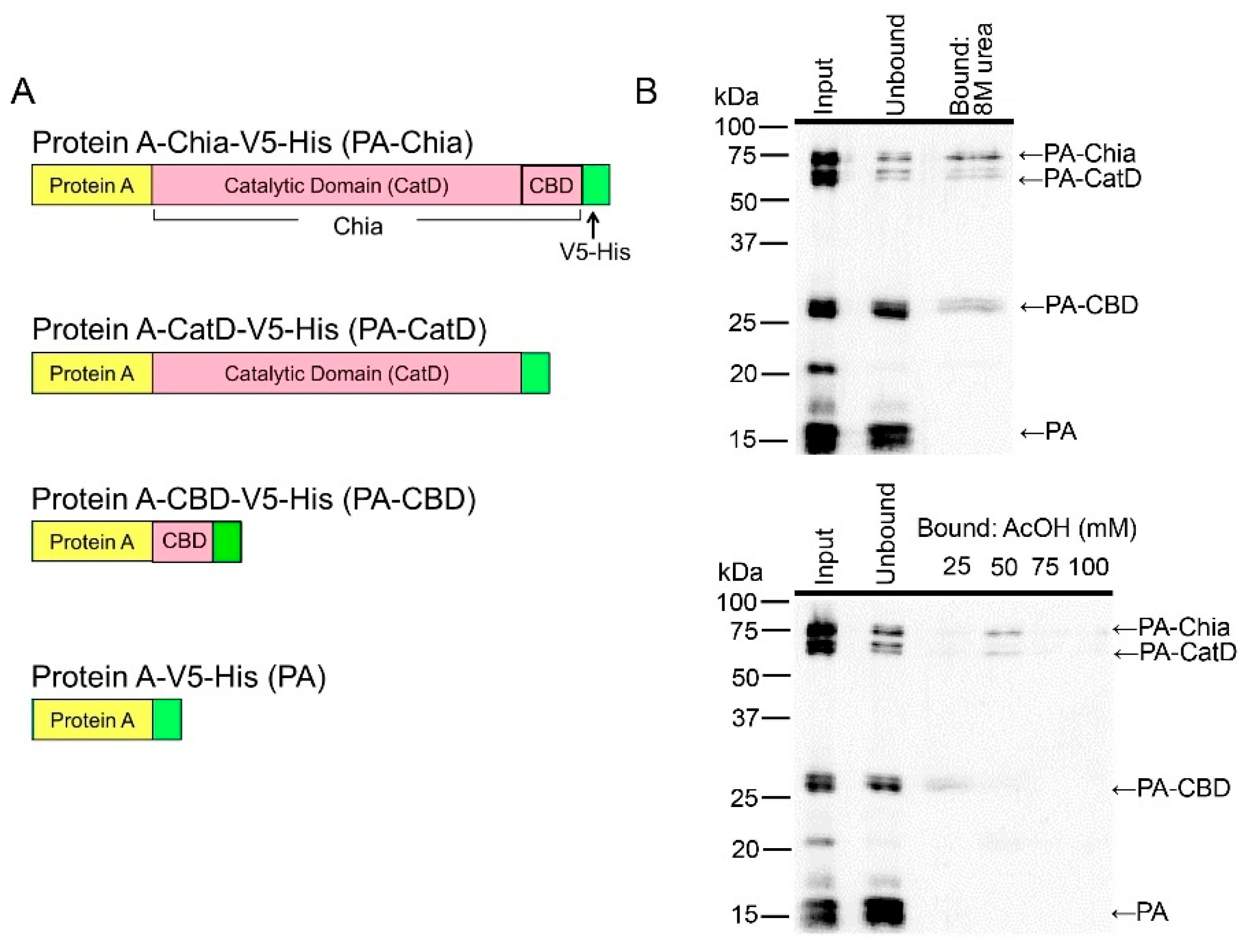
2.4. CatD and CBD of Chicken Chia Bind with Chitin Column, Which Were Eluted by Acetic Acid
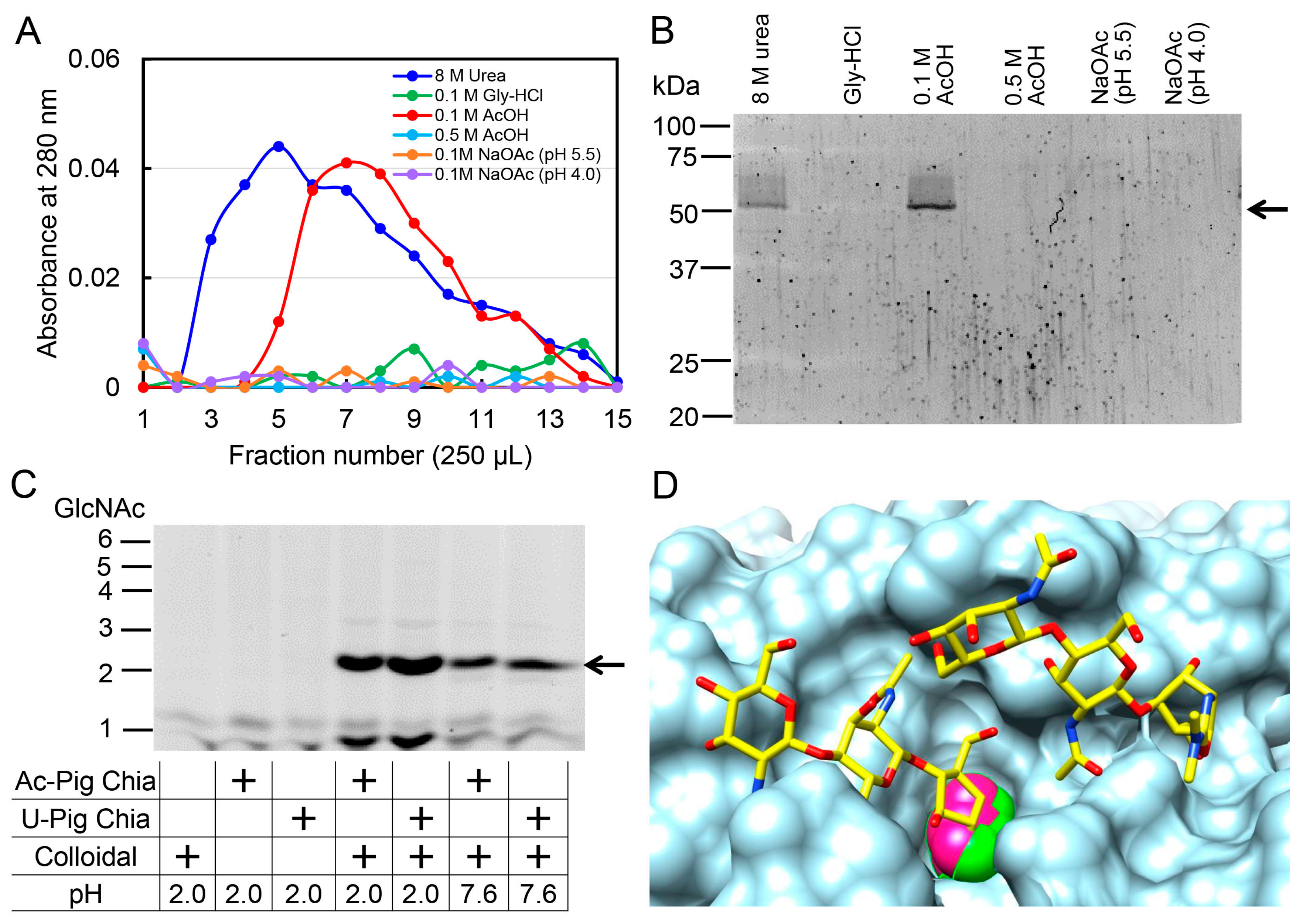
2.5. Pig Chia Purification from Stomach Tissues Using a Chitin Column and Acetic Acid
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chicken Glandular Stomach and Pig Stomach Tissues
4.2. Preparation of Soluble Proteins from Chicken Glandular Stomach and Pig Stomach
4.3. Elution of Chia Proteins from Chitin Column
4.4. Purification of Chicken and Pig Chia Using 8 M Urea or 0.1 M Acetic Acid
4.5. SDS-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis and SYPRO Ruby Staining
4.6. Differential Scanning Fluorimetry
4.7. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
4.8. Chitinase Enzymatic Assays
4.9. Degradation of Chitin Beads, Colloidal and Crystalline Chitin Substrates by Chia
4.10. E. coli Expression Vectors and Preparation of Recombinant Fusion Proteins
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khoushab, F.; Yamabhai, M. Chitin research revisited. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1988–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueter, C.L.; Specht, C.A.; Levitz, S.M. Innate sensing of chitin and chitosan. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wysokowski, M.; Petrenko, I.; Stelling, A.L.; Stawski, D.; Jesionowski, T.; Ehrlich, H. Poriferan chitin as a versatile template for extreme biomimetics. Polymers 2015, 7, 235–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minke, R.; Blackwell, J. The structure of alpha-chitin. J. Mol. Biol. 1978, 120, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, J.C.; Salaün, F.; Giraud, S.; Ferri, A.; Chen, G.; Guan, J. Solubility of chitin: Solvents, solution behaviors and their related mechanisms, solubility of polysaccharides, dr. Zhenbo xu (ed.). Biochem. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2017, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussink, A.P.; Speijer, D.; Aerts, J.M.; Boot, R.G. Evolution of mammalian chitinase(-like) members of family 18 glycosyl hydrolases. Genetics 2007, 177, 959–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, B.E.; Stougaard, J.; Spaink, H.P. Keeping track of the growing number of biological functions of chitin and its interaction partners in biomedical research. Glycobiology 2015, 25, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.G.; Da Silva, C.A.; Dela Cruz, C.S.; Ahangari, F.; Ma, B.; Kang, M.J.; He, C.H.; Takyar, S.; Elias, J.A. Role of chitin and chitinase/chitinase-like proteins in inflammation, tissue remodeling, and injury. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2011, 73, 479–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boot, R.G.; Blommaart, E.F.; Swart, E.; Ghauharali-van der Vlugt, K.; Bijl, N.; Moe, C.; Place, A.; Aerts, J.M. Identification of a novel acidic mammalian chitinase distinct from chitotriosidase. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 6770–6778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boot, R.G.; Bussink, A.P.; Verhoek, M.; de Boer, P.A.; Moorman, A.F.; Aerts, J.M. Marked differences in tissue-specific expression of chitinases in mouse and man. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2005, 53, 1283–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno, M.; Tsuda, K.; Sakaguchi, M.; Sugahara, Y.; Oyama, F. Chitinase mRNA levels by quantitative pcr using the single standard DNA: Acidic mammalian chitinase is a major transcript in the mouse stomach. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashimura, A.; Okawa, K.; Ishikawa, K.; Kida, Y.; Iwabuchi, K.; Matsushima, Y.; Sakaguchi, M.; Sugahara, Y.; Oyama, F. Protein A-mouse acidic mammalian chitinase-V5-His expressed in periplasmic space of Escherichia coli possesses chitinase functions comparable to CHO-expressed protein. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno, M.; Togashi, Y.; Tsuda, K.; Okawa, K.; Kamaya, M.; Sakaguchi, M.; Sugahara, Y.; Oyama, F. Quantification of chitinase mRNA levels in human and mouse tissues by real-time PCR: Species-specific expression of acidic mammalian chitinase in stomach tissues. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashimura, A.; Kimura, M.; Okawa, K.; Suzuki, H.; Ukita, A.; Wakita, S.; Okazaki, K.; Ohno, M.; Bauer, P.O.; Sakaguchi, M.; et al. Functional properties of the catalytic domain of mouse acidic mammalian chitinase expressed in Escherichia coli. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 4028–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno, M.; Kimura, M.; Miyazaki, H.; Okawa, K.; Onuki, R.; Nemoto, C.; Tabata, E.; Wakita, S.; Kashimura, A.; Sakaguchi, M.; et al. Acidic mammalian chitinase is a proteases-resistant glycosidase in mouse digestive system. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabata, E.; Kashimura, A.; Wakita, S.; Ohno, M.; Sakaguchi, M.; Sugahara, Y.; Kino, Y.; Matoska, V.; Bauer, P.O.; Oyama, F. Gastric and intestinal proteases resistance of chicken acidic chitinase nominates chitin-containing organisms for alternative whole edible diets for poultry. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabata, E.; Kashimura, A.; Wakita, S.; Ohno, M.; Sakaguchi, M.; Sugahara, Y.; Imamura, Y.; Seki, S.; Ueda, H.; Matoska, V.; et al. Protease resistance of porcine acidic mammalian chitinase under gastrointestinal conditions implies that chitin-containing organisms can be sustainable dietary resources. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Zheng, T.; Homer, R.J.; Kim, Y.K.; Chen, N.Y.; Cohn, L.; Hamid, Q.; Elias, J.A. Acidic mammalian chitinase in asthmatic TH2 inflammation and IL-13 pathway activation. Science 2004, 304, 1678–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reese, T.A.; Liang, H.E.; Tager, A.M.; Luster, A.D.; Van Rooijen, N.; Voehringer, D.; Locksley, R.M. Chitin induces accumulation in tissue of innate immune cells associated with allergy. Nature 2007, 447, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bierbaum, S.; Nickel, R.; Koch, A.; Lau, S.; Deichmann, K.A.; Wahn, U.; Superti-Furga, A.; Heinzmann, A. Polymorphisms and haplotypes of acid mammalian chitinase are associated with bronchial asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 172, 1505–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seibold, M.A.; Reese, T.A.; Choudhry, S.; Salam, M.T.; Beckman, K.; Eng, C.; Atakilit, A.; Meade, K.; Lenoir, M.; Watson, H.G.; et al. Differential enzymatic activity of common haplotypic versions of the human acidic mammalian chitinase protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 19650–19658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okawa, K.; Ohno, M.; Kashimura, A.; Kimura, M.; Kobayashi, Y.; Sakaguchi, M.; Sugahara, Y.; Kamaya, M.; Kino, Y.; Bauer, P.O.; et al. Loss and gain of human acidic mammalian chitinase activity by nonsynonymous SNPs. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 3183–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucolo, C.; Musumeci, M.; Maltese, A.; Drago, F.; Musumeci, S. Effect of chitinase inhibitors on endotoxin-induced uveitis (EIU) in rabbits. Pharmacol. Res. 2008, 57, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musumeci, M.; Aragona, P.; Bellin, M.; Maugeri, F.; Rania, L.; Bucolo, C.; Musumeci, S. Acidic mammalian chitinase in dry eye conditions. Cornea 2009, 28, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucolo, C.; Musumeci, M.; Musumeci, S.; Drago, F. Acidic mammalian chitinase and the eye: Implications for ocular inflammatory diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2011, 2, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozzarini, E.; Bellin, M.; Norberto, L.; Polese, L.; Musumeci, S.; Lanfranchi, G.; Paoletti, M.G. Chit1 and AMCase expression in human gastric mucosa: Correlation with inflammation and Helicobacter pylori infection. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 21, 1119–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nookaew, I.; Thorell, K.; Worah, K.; Wang, S.; Hibberd, M.L.; Sjovall, H.; Pettersson, S.; Nielsen, J.; Lundin, S.B. Transcriptome signatures in Helicobacter pylori-infected mucosa identifies acidic mammalian chitinase loss as a corpus atrophy marker. BMC Med. Genom. 2013, 6, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Dyken, S.J.; Liang, H.E.; Naikawadi, R.P.; Woodruff, P.G.; Wolters, P.J.; Erle, D.J.; Locksley, R.M. Spontaneous chitin accumulation in airways and age-related fibrotic lung disease. Cell 2017, 169, 497.e413–509.e413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabata, E.; Kashimura, A.; Kikuchi, A.; Masuda, H.; Miyahara, R.; Hiruma, Y.; Wakita, S.; Ohno, M.; Sakaguchi, M.; Sugahara, Y.; et al. Chitin digestibility is dependent on feeding behaviors, which determine acidic chitinase mrna levels in mammalian and poultry stomachs. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheba, B. Microbial chitinases purification: Conventional protocols and affinity based strategies. World J. Fish Mar. Sci. 2015, 7, 458–461. [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda, M.; Miyauchi, K.; Matsumiya, M. Purification and characterization of a 56 kda chitinase isozyme (PaChiB) from the stomach of the silver croaker, Pennahia argentatus. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2012, 76, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taira, T.; Ohdomari, A.; Nakama, N.; Shimoji, M.; Ishihara, M. Characterization and antifungal activity of gazyumaru (Ficus microcarpa) latex chitinases: Both the chitin-binding and the antifungal activities of class I chitinase are reinforced with increasing ionic strength. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2005, 69, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, M.; Ikegami, T.; Seino, S.; Ohuchi, N.; Fukada, H.; Sugiyama, J.; Shirakawa, M.; Watanabe, T. Expression and characterization of the chitin-binding domain of chitinase A1 from Bacillus circulans WL-12. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 3045–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobo, M.D.; Silva, F.D.; Landim, P.G.; da Cruz, P.R.; de Brito, T.L.; de Medeiros, S.C.; Oliveira, J.T.; Vasconcelos, I.M.; Pereira, H.D.; Grangeiro, T.B. Expression and efficient secretion of a functional chitinase from Chromobacterium violaceum in Escherichia coli. BMC Biotechnol. 2013, 13, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gupta, R.; Deswal, R. Refolding of beta-stranded class I chitinases of Hippophae rhamnoides enhances the antifreeze activity during cold acclimation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91723. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, M.; Morimatsu, M.; Yamashita, T.; Iwanaga, T.; Syuto, B. A novel serum chitinase that is expressed in bovine liver. FEBS Lett. 2001, 506, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheba, B.A.; Zaghloul, T.I.; EL-Mahdy, A.R.; HishamEL-Massry, M. Affinity purification and immobilization of chitinase from Bacillus sp.R2. Procedia Technol. 2015, 19, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onaga, S.; Taira, T. A new type of plant chitinase containing LysM domains from a fern (Pteris ryukyuensis): Roles of LysM domains in chitin binding and antifungal activity. Glycobiology 2008, 18, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niesen, F.H.; Berglund, H.; Vedadi, M. The use of differential scanning fluorimetry to detect ligand interactions that promote protein stability. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2212–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Sun, J.; Yu, L.; Zhang, C.; Bi, J.; Zhu, F.; Qu, M.; Jiang, C.; Yang, Q. Extraction and characterization of chitin from the beetle Holotrichia parallela motschulsky. Molecules 2012, 17, 4604–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, P. The use of polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis for the high-resolution separation of reducing saccharides labelled with the fluorophore 8-aminonaphthalene-1,3,6-trisulphonic acid. Detection of picomolar quantities by an imaging system based on a cooled charge-coupled device. Biochem. J. 1990, 270, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wakita, S.; Kimura, M.; Kato, N.; Kashimura, A.; Kobayashi, S.; Kanayama, N.; Ohno, M.; Honda, S.; Sakaguchi, M.; Sugahara, Y.; et al. Improved fluorescent labeling of chitin oligomers: Chitinolytic properties of acidic mammalian chitinase under somatic tissue pH conditions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 164, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tjoelker, L.W.; Gosting, L.; Frey, S.; Hunter, C.L.; Trong, H.L.; Steiner, B.; Brammer, H.; Gray, P.W. Structural and functional definition of the human chitinase chitin-binding domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henrissat, B. A classification of glycosyl hydrolases based on amino acid sequence similarities. Biochem. J. 1991, 280 Pt 2, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantarel, B.L.; Coutinho, P.M.; Rancurel, C.; Bernard, T.; Lombard, V.; Henrissat, B. The Carbohydrate-Active EnZymes database (CAZy): An expert resource for Glycogenomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D233–D238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, Y.C.; Wu, Y.J.; Chiang, T.Y.; Kuo, C.Y.; Shrestha, K.L.; Chao, C.F.; Huang, Y.C.; Chuankhayan, P.; Wu, W.G.; Li, Y.K.; et al. Crystal structures of Bacillus cereus NCTU2 chitinase complexes with chitooligomers reveal novel substrate binding for catalysis: A chitinase without chitin binding and insertion domains. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 31603–31615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payne, C.M.; Baban, J.; Horn, S.J.; Backe, P.H.; Arvai, A.S.; Dalhus, B.; Bjoras, M.; Eijsink, V.G.; Sorlie, M.; Beckham, G.T.; et al. Hallmarks of processivity in glycoside hydrolases from crystallographic and computational studies of the Serratia marcescens chitinases. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 36322–36330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, F.V.; Houston, D.R.; Boot, R.G.; Aerts, J.M.; Sakuda, S.; van Aalten, D.M. Crystal structures of allosamidin derivatives in complex with human macrophage chitinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 20110–20116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boland, J.S.; Davidson, P.M.; Weiss, J. Enhanced inhibition of Escherichia coli O157:H7 by lysozyme and chelators. J. Food Prot. 2003, 66, 1783–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattengale, P.K.; Stewart, T.A.; Leder, A.; Sinn, E.; Muller, W.; Tepler, I.; Schmidt, E.; Leder, P. Animal models of human disease. Pathology and molecular biology of spontaneous neoplasms occurring in transgenic mice carrying and expressing activated cellular oncogenes. Am. J. Pathol. 1989, 135, 39–61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Litten-Brown, J.C.; Corson, A.M.; Clarke, L. Porcine models for the metabolic syndrome, digestive and bone disorders: A general overview. Animal 2010, 4, 899–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, B.; Neises, G. ‘Human’ insulin versus animal insulin in people with diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2003, CD003816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, M.; Shimodaira, S.; Ishida, S.N.; Amemiya, M.; Honda, S.; Sugahara, Y.; Oyama, F.; Kawakita, M. Identification of GH15 family thermophilic archaeal trehalases that function within a narrow acidic-pH range. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 4920–4931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tabata, E.; Kashimura, A.; Wakita, S.; Sakaguchi, M.; Sugahara, Y.; Imamura, Y.; Shimizu, H.; Matoska, V.; Bauer, P.O.; Oyama, F. Acidic Chitinase-Chitin Complex Is Dissociated in a Competitive Manner by Acetic Acid: Purification of Natural Enzyme for Supplementation Purposes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020362
Tabata E, Kashimura A, Wakita S, Sakaguchi M, Sugahara Y, Imamura Y, Shimizu H, Matoska V, Bauer PO, Oyama F. Acidic Chitinase-Chitin Complex Is Dissociated in a Competitive Manner by Acetic Acid: Purification of Natural Enzyme for Supplementation Purposes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(2):362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020362
Chicago/Turabian StyleTabata, Eri, Akinori Kashimura, Satoshi Wakita, Masayoshi Sakaguchi, Yasusato Sugahara, Yasutada Imamura, Hideaki Shimizu, Vaclav Matoska, Peter O. Bauer, and Fumitaka Oyama. 2018. "Acidic Chitinase-Chitin Complex Is Dissociated in a Competitive Manner by Acetic Acid: Purification of Natural Enzyme for Supplementation Purposes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 2: 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020362
APA StyleTabata, E., Kashimura, A., Wakita, S., Sakaguchi, M., Sugahara, Y., Imamura, Y., Shimizu, H., Matoska, V., Bauer, P. O., & Oyama, F. (2018). Acidic Chitinase-Chitin Complex Is Dissociated in a Competitive Manner by Acetic Acid: Purification of Natural Enzyme for Supplementation Purposes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(2), 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020362




