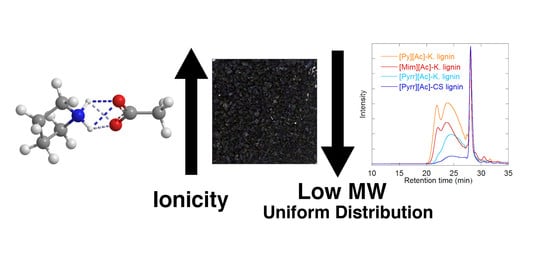
Protic Ionic Liquids for Lignin Extraction—A Lignin Characterization Study
Abstract
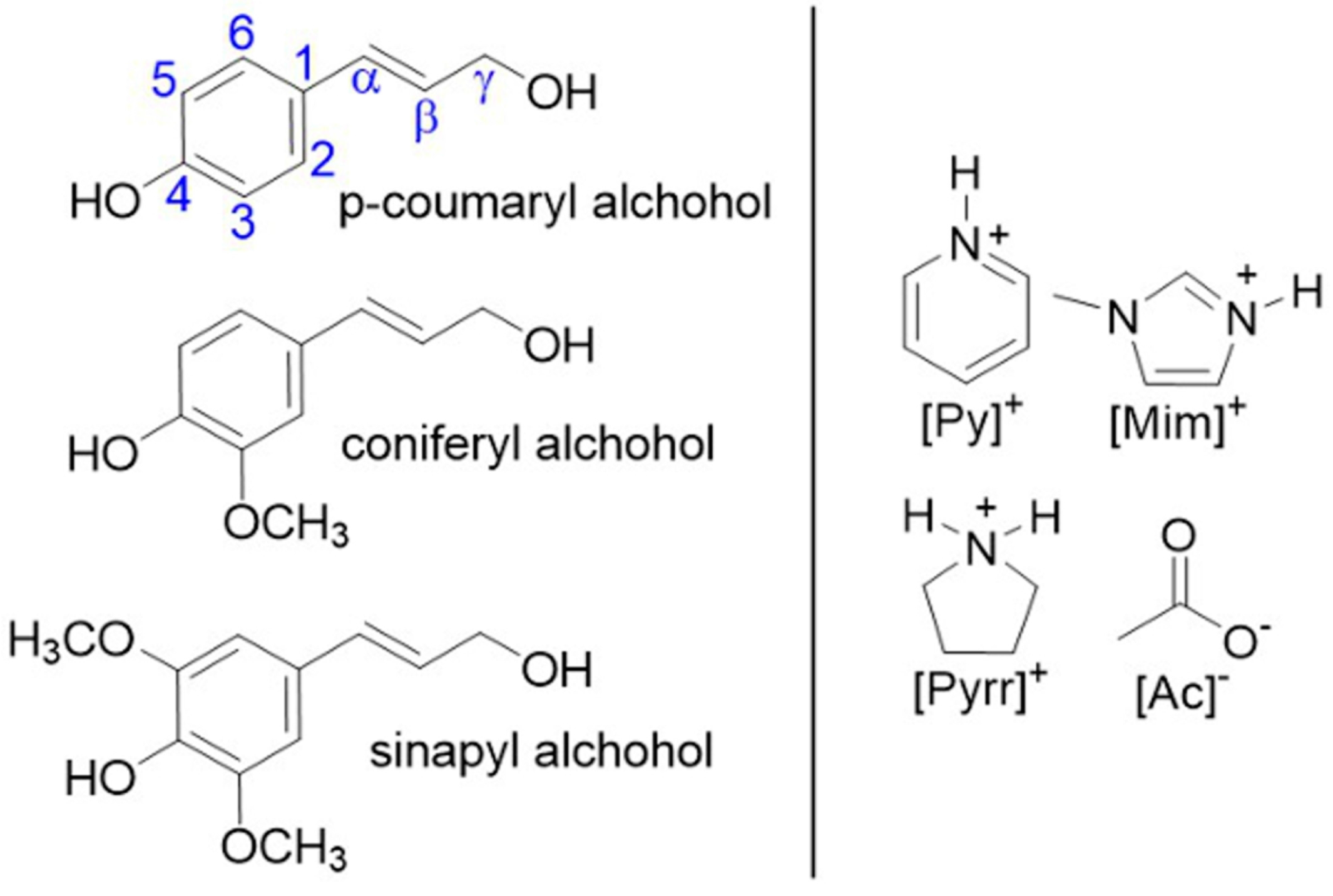
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Lignin Fragmentation (MWD)
2.2. Elemental Analysis
2.3. Lignin FT-IR Analyses
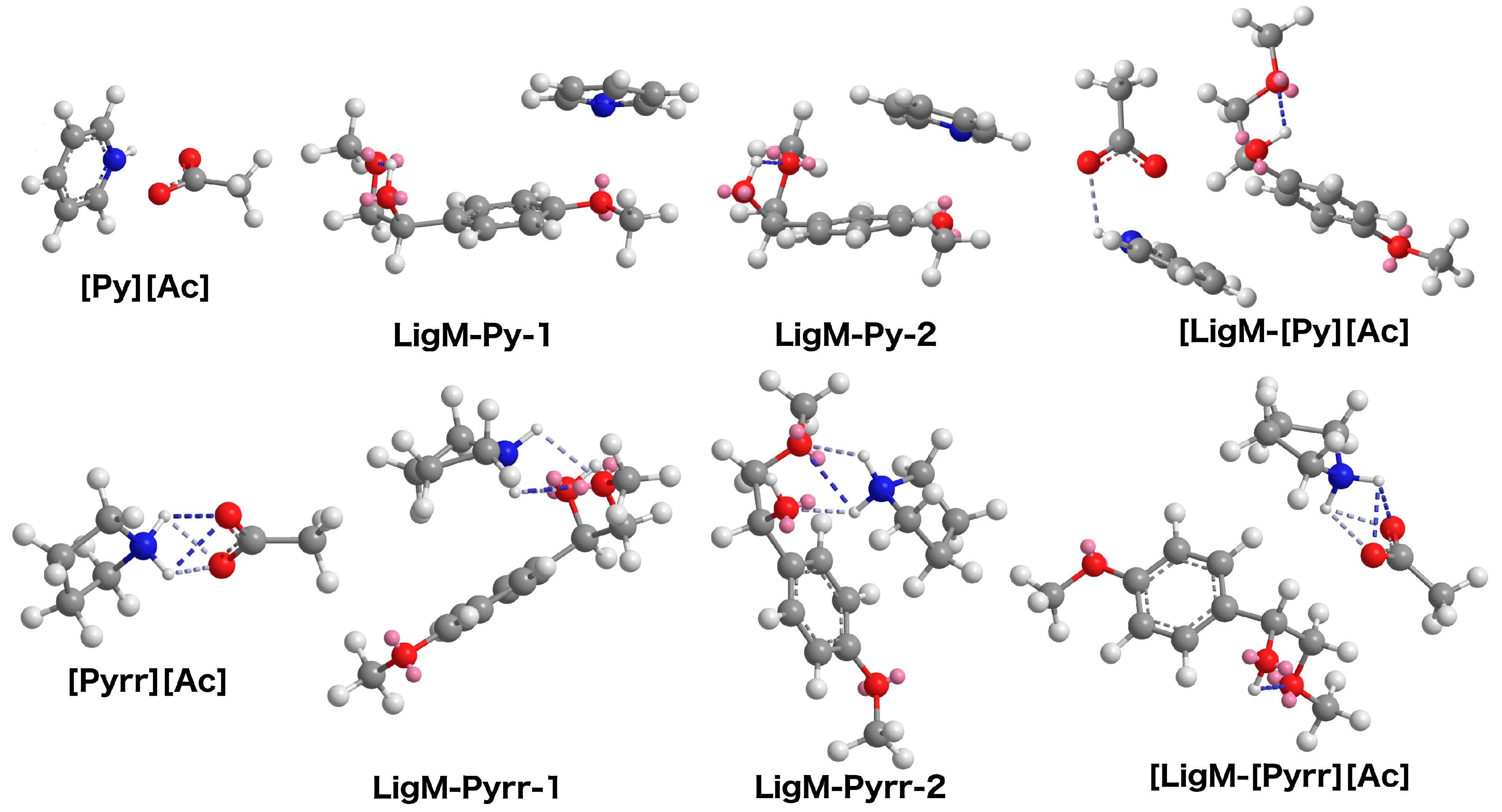
2.4. Energy Minimization (MM2 Analyses)
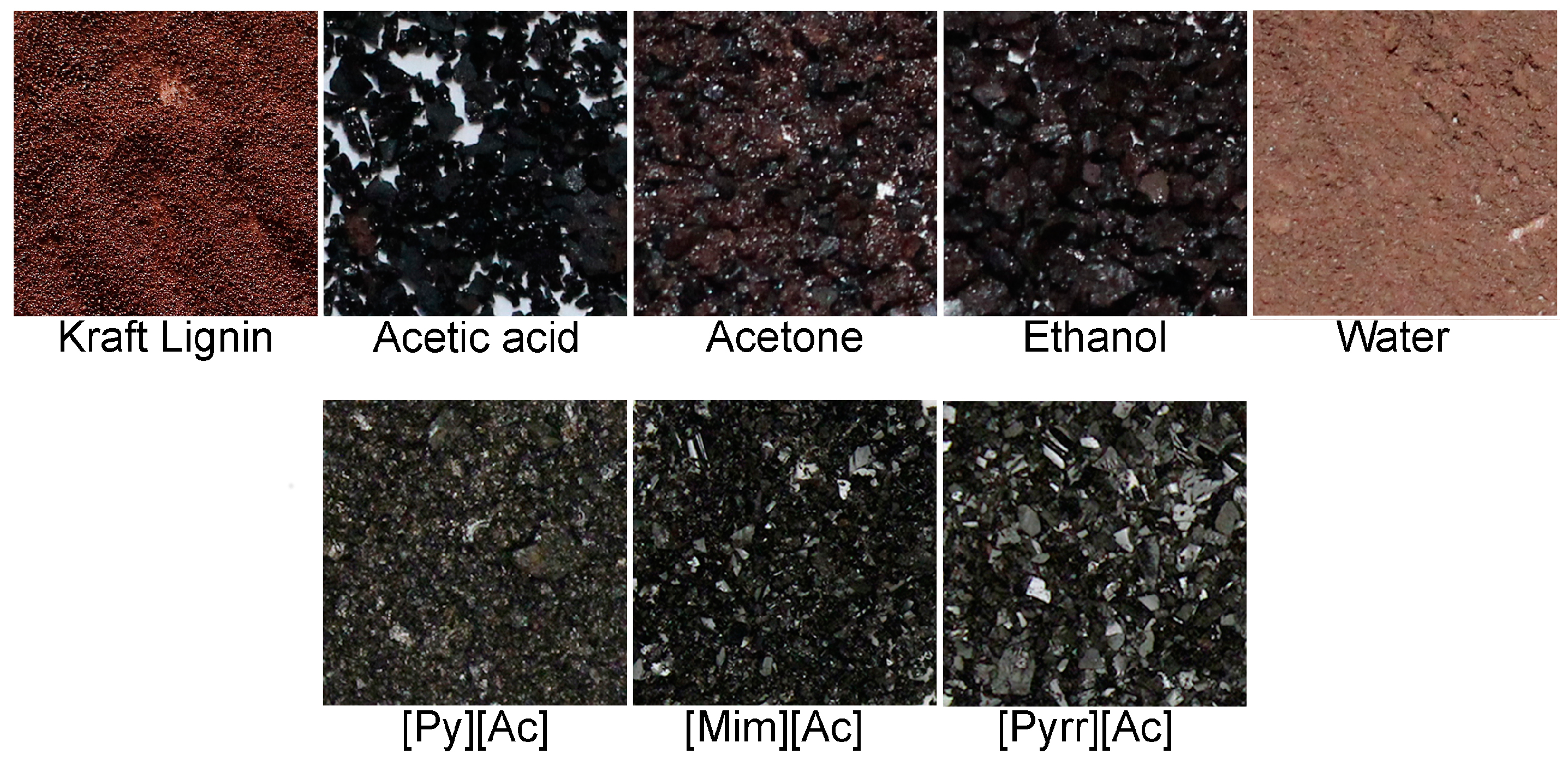
2.5. Effect of the Solvent Type on Lignin Regeneration
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Lignin Extraction and Recovery from Biomass (Corn Stover)
3.2. Molecular Weight Determination (Lignin Acetylation)
3.3. Molecular Weight Determination (Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC))
3.4. Elemental Analyses
3.5. FT-IR Spectroscopy
3.6. MM2 Analyses
3.7. Lignin Solubility and Regeneration in Various Solvents
3.8. Imaging
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PIL | protic ionic liquid |
| [Py][Ac] | pyridinium acetate |
| [Mim][Ac] | 1-methylimidazolium acetate |
| [Pyrr][Ac] | pyrrolidinium acetate |
| MWD | molecular weight distribution |
| DOU | degree of unsaturation |
| CS | corn stover |
| K. lignin | kraft lignin |
| MM2 | molecular mechanics 2 |
| %e | lignin extraction efficiency |
References
- Stewart, D. Lignin as a base material for materials applications: Chemistry, application and economics. Ind. Crops Prod. 2008, 27, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norgren, M.; Edlund, H. Lignin: Recent advances and emerging applications. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 19, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, R.; Jastrzebski, R.; Clough, M.T.; Ralph, J.; Kennema, M.; Bruijnincx, P.C.A.; Weckhuysen, B.M. Paving the Way for Lignin Valorisation: Recent Advances in Bioengineering, Biorefining and Catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 8164–8215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadla, J.F.; Kubo, S. Lignin-based polymer blends: Analysis of intermolecular interactions in lignin–synthetic polymer blends. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2004, 35, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainka, H.; Täger, O.; Körner, E.; Hilfert, L.; Busse, S.; Edelmann, F.T.; Herrmann, A.S. Lignin—An alternative precursor for sustainable and cost-effective automotive carbon fiber. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2015, 4, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aili, M.; Wuqing, D.; Chengqian, L.; Jie, C. Characterization of lignin and study on mechanical properties of lignin/PVC blends. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Biobase Material Science and Engineering, Changsha, China, 21–23 October 2012; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Tucker, M.; Ji, Y. Recent Development in Chemical Depolymerization of Lignin: A Review. Available online: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/jac/2013/838645/ (accessed on 18 October 2017).
- Kumar, P.; Barrett, D.M.; Delwiche, M.J.; Stroeve, P. Methods for pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for efficient hydrolysis and biofuel production. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 3713–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, L.; Xu, S.; Shi, J. Catalytic oxidation and depolymerization of lignin in aqueous ionic liquid. Front. Energy Res. 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, T.; Shu, R.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Fu, J.; Ma, L. Hydrothermal depolymerization of lignin: Understanding the structural evolution. BioResources 2014, 9, 7162–7175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Li, C.; Xu, G.; Ma, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y. Depolymerization of lignin via a non-precious Ni–Fe alloy catalyst supported on activated carbon. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 1895–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picart, P.; Liu, H.; Grande, P.M.; Anders, N.; Zhu, L.; Klankermayer, J.; Leitner, W.; de María, P.D.; Schwaneberg, U.; Schallmey, A. Multi-step biocatalytic depolymerization of lignin. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 6277–6287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanmolee, W.; Daorattanachai, P.; Laosiripojana, N. Depolymerization of organosolv lignin to valuable chemicals over homogeneous and heterogeneous acid catalysts. Energy Procedia 2016, 100, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Dueñas, F.J.; Martínez, Á.T. Microbial degradation of lignin: How a bulky recalcitrant polymer is efficiently recycled in nature and how we can take advantage of this. Microb. Biotechnol. 2009, 2, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Gregorio, G.F.; Prado, R.; Vriamont, C.; Erdocia, X.; Labidi, J.; Hallett, J.P.; Welton, T. Oxidative depolymerization of lignin using a novel polyoxometalate-protic ionic liquid system. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 6031–6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, B.E.; Moreira, M.J. Freeze-Explosion Technique for Increasing Cellulose Hydrolysis. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Biotechnology in Energy Production and Conservation, Gatlinburg, TN, USA, 11 May 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Chakar, F.; Ragauskas, A. Review of current and future softwood kraft lignin process chemistry. Ind. Crops Prod. 2004, 20, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amen-Chen, C.; Pakdel, H.; Roy, C. Production of monomeric phenols by thermochemical conversion of biomass: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 79, 277–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sarkanen, S. Alkylated kraft lignin-based thermoplastic blends with aliphatic polyesters. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 9707–9715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashtban, M.; Schraft, H.; Syed, T.A.; Qin, W. Fungal biodegradation and enzymatic modification of lignin. Int. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 1, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Achinivu, E.C.; Howard, R.M.; Li, G.; Gracz, H.; Henderson, W.A. Lignin extraction from biomass with protic ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 1114–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschwend, F.J.V.; Brandt, A.; Chambon, C.L.; Tu, W.-C.; Weigand, L.; Hallett, J.P. Pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass with low-cost ionic liquids. J. Vis. Exp. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, C.L.B.; e Silva, L.M.A.; Rodrigues, T.H.S.; Félix, A.K.N.; de Santiago-Aguiar, R.S.; Canuto, K.M.; Rocha, M.V.P. Pretreatment of cashew apple bagasse using protic ionic liquids: Enhanced enzymatic hydrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 224, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, E.G.A.; Pin, T.C.; Rabelo, S.C.; Costa, A.C. Evaluation of the use of protic ionic liquids on biomass fractionation. Fuel 2017, 206, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, E.; da Costa, A.C.; Aznar, M. Use of protic ionic liquids as biomass pretreatment for lignocellulosic ethanol production. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2014, 37, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt-Talbot, A.; Gschwend, F.J.V.; Fennell, P.S.; Lammens, T.M.; Tan, B.; Weale, J.; Hallett, J.P. An economically viable ionic liquid for the fractionation of lignocellulosic biomass. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 3078–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, T.; Kait, C.F.; Regupathi, I.; Murugesan, T. Dissolution of kraft lignin using Protic Ionic Liquids and characterization. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 84, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, T.; Kait, C.F.; Murugesan, T. Effect of temperature on molecular weight distribution of pyridinium acetate treated kraft lignin. Procedia Eng. 2016, 148, 1363–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.-L.; Yuan, T.-Q.; Sun, S.-L.; Xu, F.; Sun, R.-C. Understanding the chemical transformations of lignin during ionic liquid pretreatment. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathitsuksanoh, N.; Holtman, K.M.; Yelle, D.J.; Morgan, T.; Stavila, V.; Pelton, J.; Blanch, H.; Simmons, B.A.; George, A. Lignin fate and characterization during ionic liquid biomass pretreatment for renewable chemicals and fuels production. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 1236–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Xu, Y.; Yu, C. The isolation and characterization of lignin of kenaf fiber. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 114, 1896–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, N.E.E.; Yuan, Q.; Huang, F. Characterization of alkaline lignins for use in phenol-formaldehyde and epoxy resins. BioResources 2011, 6, 2647–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, S.C.; McDonald, A.G. Chemical and thermal characterization of three industrial lignins and their corresponding lignin esters. BioResources 2010, 5, 990–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, L.M.; Hayes, D.G.; Womac, A.R.; Labbe, N. Simplified determination of lignin content in hard and soft woods via UV-spectrophotometric analysis of biomass dissolved in ionic liquids. BioResources 2010, 5, 1366–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Kim, J.S.; Sunwoo, C.; Lee, Y.Y. Pretreatment of corn stover by aqueous ammonia. Bioresour. Technol. 2003, 90, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, X. Influence of biopretreatment on the character of corn stover lignin as shown by thermogravimetric and chemical structural analyses. BioResources 2010, 5, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Rivera, J.; Terrazas, T. Lignin analysis by HPLC and FTIR. In Xylem; Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 193–211. ISBN 978-1-4939-6720-9. [Google Scholar]
- Tolbert, A.; Akinosho, H.; Khunsupat, R.; Naskar, A.K.; Ragauskas, A.J. Characterization and analysis of the molecular weight of lignin for biorefining studies. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefin. 2014, 8, 836–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, M.; Minami, E.; Yamauchi, K.; Kawamoto, H.; Saka, S. Characterization of the precipitated lignin from Japanese beech as treated by semi-flow hot-compressed water. Holzforschung 2017, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoia, L.; Salanti, A.; Tolppa, E.-L.; Ballabio, D.; Orlandi, M. Valorization of side-streams from a SSF biorefinery plant: Wheat straw lignin purification study. BioResources 2017, 12, 1680–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, J.-Y.; Youn, H.J.; Choi, J.W. Fractionation of lignin macromolecules by sequential organic solvents systems and their characterization for further valuable applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepto, R.F.T. Dispersity in polymer science (IUPAC Recommendations 2009). Pure Appl. Chem. 2009, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkert, A.; Ang, K.L.; Marsh, K.N.; Pang, S. Density, viscosity and electrical conductivity of protic alkanolammonium ionic liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 5136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brogan, A.P.S.; Hallett, J.P. Solubilizing and stabilizing proteins in anhydrous ionic liquids through formation of protein–polymer surfactant nanoconstructs. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 4494–4501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, F.G.; Soares, A.K.; Santaella, S.T.; e Silva, L.M.; Canuto, K.M.; Cáceres, C.A.; de Freitas Rosa, M.; de Andrade Feitosa, J.P.; Leitão, R.C. Optimization of the acetosolv extraction of lignin from sugarcane bagasse for phenolic resin production. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 96, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badertscher, M.; Bischofberger, K.; Munk, M.E.; Pretsch, E. A novel formalism to characterize the degree of unsaturation of organic molecules. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2001, 41, 889–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, W.; Ding, Z.; Liu, J.; Song, Q.; Xia, X.; Gao, H.; Wang, H.; Gu, W. Mechanism of lignin dissolution and regeneration in ionic liquid. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 6393–6403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janesko, B.G. Modeling interactions between lignocellulose and ionic liquids using DFT-D. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 11393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkert, U.; Allinger, N.L. Molecular Mechanics ACS Monograph 177; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1982; 107p. [Google Scholar]
- Schnur, D.M.; Grieshaber, M.V.; Bowen, J.P. Development of an internal searching algorithm for parameterization of the MM2/MM3 force fields. J. Comput. Chem. 1991, 12, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, E.; Allinger, N.L. Molecular mechanics calculations (MM2) on aliphatic nitriles. J. Mol. Struct. THEOCHEM 1989, 188, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allinger, N.L. Conformational analysis. 130. MM2. A hydrocarbon force field utilizing V1 and V2 torsional terms. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1977, 99, 8127–8134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| PIL | Mn | Mw | Mw/Mn |
|---|---|---|---|
| K. Lignin (Indulin AT) | 1600 | 6500 | 4.06 |
| [Py][Ac]-K. lignin | 830 | 4983 | 6.00 |
| [Mim][Ac]-K. lignin | 646 | 3919 | 6.06 |
| [Pyrr][Ac]-K. lignin | 528 | 1797 | 3.40 |
| [Pyrr][Ac]-CS lignin | 330 | 900 | 2.73 |
| PIL | C (%) | H (%) | N (%) | Degree of Unsaturation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kraft lignin | 62.2 | 6.1 | 0.9 | 3 |
| [Py][Ac]-K. lignin | 63.7 | 5.8 | 1.4 | 3 |
| [Mim][Ac]-K. lignin | 63.5 | 6.0 | 3.7 | 3 |
| [Pyrr][Ac]-K. lignin | 64.5 | 7.2 | 4.0 | 3 |
| [Pyrr][Ac]-CS lignin | 52.1 | 10.3 | 10.1 | 1 |
| EF-CS | 43.0 | 5.7 | 0.9 | 2 |
| Approximate Band (cm−1) | Assignment |
|---|---|
| 3350–3400 | O–H stretching in hydroxyl groups |
| 2975, 2925 | C–H stretching in methyl and methylene groups, C–H stretching aromatic methoxyl groups |
| 2850 | –CH2– symmetry stretching in methyl and methylene groups |
| 1700–1725 | C=O stretching in unconjugated ketone, carbonyl, and ester groups |
| 1650 a | C=O stretching in conjugated ketone p-subst. Aryl ketones |
| 1600 b | Aromatic skeleton vibrations plus C=O stretching; S > G |
| 1500–1525 | Stretching of aromatic skeleton; G > S |
| 1450 | Aromatic skeletal vibrations C–H deformations (asymmetry in methyl group –CH3– and –CH2–) O–CH3 in-plane deformations. |
| 1375 | Aliphatic C–H stretching in methyl and phenol OH |
| 1325 a | (C–O of syringyl ring) S unit plus G unit condensed (G unit bound via position 5) |
| 1250 | C–O stretching of guaiacyl unit |
| 1225 | C–C plus C–O plus C=O stretching |
| 1125 a | Typical of S unit; also secondary alcohol and C=O stretch |
| 1050–1025 c | C–O of primary alcohol, C–O–C ether stretch, guaiacyl C–H |
| 875 c | C–H out of-plane vibrations in position 2, 5 and 6 of the guaiacyl units |
| 825 a | C–H out of plane in position 2 and 6 (syringyl units) |
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Achinivu, E.C. Protic Ionic Liquids for Lignin Extraction—A Lignin Characterization Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020428
Achinivu EC. Protic Ionic Liquids for Lignin Extraction—A Lignin Characterization Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(2):428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020428
Chicago/Turabian StyleAchinivu, Ezinne C. 2018. "Protic Ionic Liquids for Lignin Extraction—A Lignin Characterization Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 2: 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020428
APA StyleAchinivu, E. C. (2018). Protic Ionic Liquids for Lignin Extraction—A Lignin Characterization Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(2), 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020428