Proinflammatory Markers, Chemokines, and Enkephalin in Patients Suffering from Dry Eye Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical Analysis
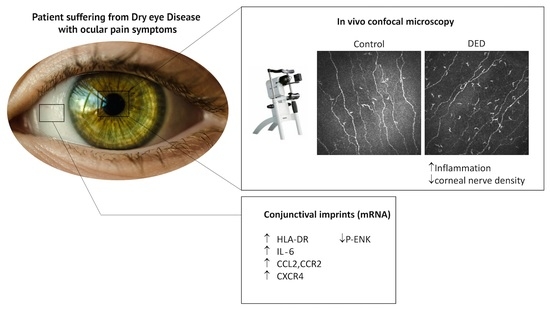
2.2. In Vivo Confocal Microscopy Analysis
2.3. Changes in Inflammatory Markers, Chemokines and Their Receptors, and Enkephalin mRNA Levels in Conjunctival Imprint Samples
2.4. Changes in Cell Morphology and in Inflammatory Markers in Conjunctiva-Derived Epithelial Cells Exposed to a Hyperosmolar Condition
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. In Vivo Confocal Microscopy
4.3. Conjunctival Impression Cytology
4.4. WKD Cell Lines
4.5. Hyperosmolar Condition and Cell Stimulation Protocol
4.6. RT-qPCR Analysis
4.7. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deschamps, N.; Ricaud, X.; Rabut, G.; Labbe, A.; Baudouin, C.; Denoyer, A. The impact of dry eye disease on visual performance while driving. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2013, 156, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labbe, A.; Wang, Y.X.; Jie, Y.; Baudouin, C.; Jonas, J.B.; Xu, L. Dry eye disease, dry eye symptoms and depression: The beijing eye study. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2013, 97, 1399–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiffman, R.M.; Walt, J.G.; Jacobsen, G.; Doyle, J.J.; Lebovics, G.; Sumner, W. Utility assessment among patients with dry eye disease. Ophthalmology 2003, 110, 1412–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, B.D.; Crews, L.A.; Messmer, E.M.; Foulks, G.N.; Nichols, K.K.; Baenninger, P.; Geerling, G.; Figueiredo, F.; Lemp, M.A. Correlations between commonly used objective signs and symptoms for the diagnosis of dry eye disease: Clinical implications. Acta Ophthalmol. 2014, 92, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bron, A.J.; de Paiva, C.S.; Chauhan, S.K.; Bonini, S.; Gabison, E.E.; Jain, S.; Knop, E.; Markoulli, M.; Ogawa, Y.; Perez, V.; et al. Tfos dews ii pathophysiology report. Ocul. Surf. 2017, 15, 438–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brignole-Baudouin, F.; Riancho, L.; Ismail, D.; Deniaud, M.; Amrane, M.; Baudouin, C. Correlation between the inflammatory marker HLA-DR and signs and symptoms in moderate to severe dry eye disease. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 2438–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, K.S.; Mok, J.W.; Kim, J.Y.; Rho, C.R.; Joo, C.K. Correlations between tear cytokines, chemokines, and soluble receptors and clinical severity of dry eye disease. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 5443–5450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reaux-Le Goazigo, A.; Rivat, C.; Kitabgi, P.; Pohl, M.; Melik Parsadaniantz, S. Cellular and subcellular localization of cxcl12 and cxcr4 in rat nociceptive structures: Physiological relevance. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2012, 36, 2619–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Steenwinckel, J.; Auvynet, C.; Sapienza, A.; Reaux-Le Goazigo, A.; Combadiere, C.; Melik Parsadaniantz, S. Stromal cell-derived CCL2 drives neuropathic pain states through myeloid cell infiltration in injured nerve. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 45, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Steenwinckel, J.; Reaux-Le Goazigo, A.; Pommier, B.; Mauborgne, A.; Dansereau, M.A.; Kitabgi, P.; Sarret, P.; Pohl, M.; Melik Parsadaniantz, S. CCL2 released from neuronal synaptic vesicles in the spinal cord is a major mediator of local inflammation and pain after peripheral nerve injury. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 5865–5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melik Parsadaniantz, S.; Rivat, C.; Rostene, W.; Reaux-Le Goazigo, A. Opioid and chemokine receptor crosstalk: A promising target for pain therapy? Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basso, L.; Boue, J.; Mahiddine, K.; Blanpied, C.; Robiou-du-Pont, S.; Vergnolle, N.; Deraison, C.; Dietrich, G. Endogenous analgesia mediated by cd4(+) t lymphocytes is dependent on enkephalins in mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roques, B.P.; Fournie-Zaluski, M.C.; Wurm, M. Inhibiting the breakdown of endogenous opioids and cannabinoids to alleviate pain. Nature reviews. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 292–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, C.; Kuchler, S. Targeting inflammation and wound healing by opioids. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 34, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poras, H.; Bonnard, E.; Dange, E.; Fournie-Zaluski, M.C.; Roques, B.P. New orally active dual enkephalinase inhibitors (DENKIs) for central and peripheral pain treatment. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 5748–5763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, C.; Kuchler, S. Non-analgesic effects of opioids: Peripheral opioid effects on inflammation and wound healing. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 6053–6069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marfurt, C.F.; Cox, J.; Deek, S.; Dvorscak, L. Anatomy of the human corneal innervation. Exp. Eye Res. 2010, 90, 478–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belmonte, C.; Nichols, J.J.; Cox, S.M.; Brock, J.A.; Begley, C.G.; Bereiter, D.A.; Dartt, D.A.; Galor, A.; Hamrah, P.; Ivanusic, J.J.; et al. Tfos dews ii pain and sensation report. Ocul. Surf. 2017, 15, 404–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta, M.C.; Luna, C.; Quirce, S.; Belmonte, C.; Gallar, J. Changes in sensory activity of ocular surface sensory nerves during allergic keratoconjunctivitis. PAIN 2013, 154, 2353–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barabino, S.; Montaldo, E.; Solignani, F.; Valente, C.; Mingari, M.C.; Rolando, M. Immune response in the conjunctival epithelium of patients with dry eye. Exp. Eye Res. 2010, 91, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baudouin, C.; Liang, H.; Bremond-Gignac, D.; Hamard, P.; Hreiche, R.; Creuzot-Garcher, C.; Warnet, J.M.; Brignole-Baudouin, F. CCR 4 and CCR 5 expression in conjunctival specimens as differential markers of T(H)1/T(H)2 in ocular surface disorders. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 116, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivat, C.; Sebaihi, S.; van Steenwinckel, J.; Fouquet, S.; Kitabgi, P.; Pohl, M.; Melik Parsadaniantz, S.; Reaux-Le Goazigo, A. Src family kinases involved in CXCL12-induced loss of acute morphine analgesia. Brain Behav. Immun. 2014, 38, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, S.; Chauhan, S.K.; Zhang, Q.; Dana, R. Amelioration of murine dry eye disease by topical antagonist to chemokine receptor 2. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2009, 127, 882–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, J.W.; Guida, M.P.; Warren, J.; Amat, J.; Brosnan, C.F. Localization of monocyte chemoattractant peptide-1 expression in the central nervous system in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and trauma in the rat. J. Immunol. 1996, 156, 3017–3023. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wilson, N.M.; Jung, H.; Ripsch, M.S.; Miller, R.J.; White, F.A. Cxcr4 signaling mediates morphine-induced tactile hyperalgesia. Brain Behav. Immun. 2011, 25, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieckow, J.; Brandt, W.; Hattermann, K.; Schob, S.; Schulze, U.; Mentlein, R.; Ackermann, P.; Sel, S.; Paulsen, F.P. CXCR4 and CXCR7 Mediate TFF3-Induced Cell Migration Independently From the ERK1/2 Signaling Pathway. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Martín, L.; Estecha, A.; Samaniego, R.; Sánchez-Ramón, S.; Vega, M.Á.; Sánchez-Mateos, P. The chemokine CXCL12 regulates monocyte-macrophage differentiation and RUNX3 expression. Blood 2011, 117, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farris, R.L. Tear osmolarity—A new gold standard? Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1994, 350, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gilbard, J.P.; Farris, R.L.; Santamaria, J., 2nd. Osmolarity of tear microvolumes in keratoconjunctivitis sicca. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1978, 96, 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clouzeau, C.; Godefroy, D.; Riancho, L.; Rostene, W.; Baudouin, C.; Brignole-Baudouin, F. Hyperosmolarity potentiates toxic effects of benzalkonium chloride on conjunctival epithelial cells in vitro. Mol. Vis. 2012, 18, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Warcoin, E.; Clouzeau, C.; Roubeix, C.; Raveu, A.L.; Godefroy, D.; Riancho, L.; Baudouin, C.; Brignole-Baudouin, F. Hyperosmolarity and benzalkonium chloride differently stimulate inflammatory markers in conjunctiva-derived epithelial cells in vitro. Ophthalmic Res. 2017, 58, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabo, I.; Chen, X.H.; Xin, L.; Adler, M.W.; Howard, O.M.; Oppenheim, J.J.; Rogers, T.J. Heterologous desensitization of opioid receptors by chemokines inhibits chemotaxis and enhances the perception of pain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 10276–10281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Geller, E.B.; Rogers, T.J.; Adler, M.W. Rapid heterologous desensitization of antinociceptive activity between mu or delta opioid receptors and chemokine receptors in rats. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2007, 88, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabot, P.J.; Carter, L.; Schafer, M.; Stein, C. Methionine-enkephalin-and dynorphin a-release from immune cells and control of inflammatory pain. PAIN 2001, 93, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, M.; Carter, L.; Stein, C. Interleukin 1 beta and corticotropin-releasing factor inhibit pain by releasing opioids from immune cells in inflamed tissue. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 4219–4223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousa, S.A.; Shakibaei, M.; Sitte, N.; Schafer, M.; Stein, C. Subcellular pathways of beta-endorphin synthesis, processing, and release from immunocytes in inflammatory pain. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 1331–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stapleton, F.; Alves, M.; Bunya, V.Y.; Jalbert, I.; Lekhanont, K.; Malet, F.; Na, K.S.; Schaumberg, D.; Uchino, M.; Vehof, J.; et al. TFOS DEWS II epidemiology report. Ocul. Surf. 2017, 15, 334–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiffman, R.M.; Christianson, M.D.; Jacobsen, G.; Hirsch, J.D.; Reis, B.L. Reliability and validity of the Ocular Surface Disease Index. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2000, 118, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bron, A.J.; Evans, V.E.; Smith, J.A. Grading of corneal and conjunctival staining in the context of other dry eye tests. Cornea 2003, 22, 640–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labbe, A.; Liang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Baudouin, C.; Sun, X. Corneal nerve structure and function in patients with non-sjogren dry eye: Clinical correlations. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 5144–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, L.; Diebold, Y.; Calonge, M.; Gao, J.; Stern, M.E.; Beuerman, R.W. Comparison of gene expression profiles of conjunctival cell lines with primary cultured conjunctival epithelial cells and human conjunctival tissue. Gene Expr. 2009, 14, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.; Ren, Y.; Reinach, P.S.; Xiao, B.; Lu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Qu, J.; Chen, W. Reactive oxygen species activated NLRP3 inflammasomes initiate inflammation in hyperosmolarity stressed human corneal epithelial cells and environment-induced dry eye patients. Exp. Eye Res. 2015, 134, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Parameters | Control | DED | p-Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 50.7 ± 24.0 | 50.6 ± 19.6 | 0.98 |
| Sex, female/male (%) | 60/40 | 72/28 | |
| Symptoms (years) | 0 ± 0 | 5.0 ± 4.7 | <0.01 |
| OSDI score | 6.2 ± 4.4 | 67.8 ± 21.4 | <0.01 |
| Schirmer test (mm) | 24.7 ± 4.1 | 12.5 ± 8.8 | <0.02 |
| Break-up time (s) | 14.4 ± 2.3 | 5.4 ± 3.3 | <0.01 |
| Oxford score | 0 ± 0 | 1.4 ± 1.6 | <0.01 |
| Assessment of pain (/10) | 0 ± 0 | 6.1 ± 2.9 | <0.01 |
| IVCM Parameters | Control | DED | p-Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Subbasal dendritic cell density (c/mm2) | 49.2 ± 43.7 | 103.5 ± 84.5 | <0.01 |
| Nerve density (mm/mm2) | 20.3 ± 3.3 | 16.5 ± 3.4 | <0.01 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nicolle, P.; Liang, H.; Reboussin, E.; Rabut, G.; Warcoin, E.; Brignole-Baudouin, F.; Melik-Parsadaniantz, S.; Baudouin, C.; Labbe, A.; Reaux-Le Goazigo, A. Proinflammatory Markers, Chemokines, and Enkephalin in Patients Suffering from Dry Eye Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041221
Nicolle P, Liang H, Reboussin E, Rabut G, Warcoin E, Brignole-Baudouin F, Melik-Parsadaniantz S, Baudouin C, Labbe A, Reaux-Le Goazigo A. Proinflammatory Markers, Chemokines, and Enkephalin in Patients Suffering from Dry Eye Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(4):1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041221
Chicago/Turabian StyleNicolle, Pierre, Hong Liang, Elodie Reboussin, Ghislaine Rabut, Elise Warcoin, Françoise Brignole-Baudouin, Stéphane Melik-Parsadaniantz, Christophe Baudouin, Antoine Labbe, and Annabelle Reaux-Le Goazigo. 2018. "Proinflammatory Markers, Chemokines, and Enkephalin in Patients Suffering from Dry Eye Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 4: 1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041221
APA StyleNicolle, P., Liang, H., Reboussin, E., Rabut, G., Warcoin, E., Brignole-Baudouin, F., Melik-Parsadaniantz, S., Baudouin, C., Labbe, A., & Reaux-Le Goazigo, A. (2018). Proinflammatory Markers, Chemokines, and Enkephalin in Patients Suffering from Dry Eye Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(4), 1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041221