Essential Role of Endothelial MCPIP in Vascular Integrity and Post-Ischemic Remodeling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
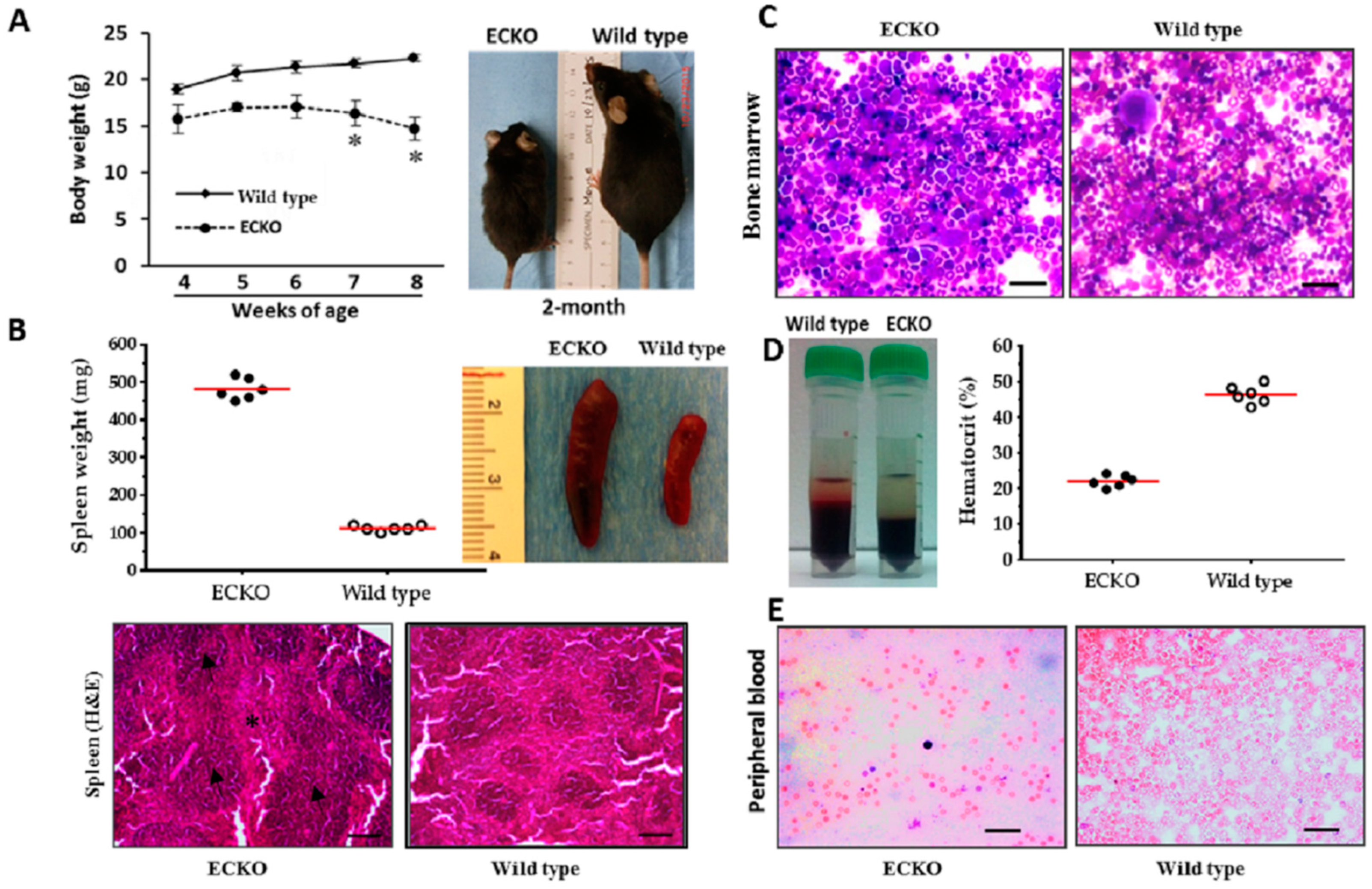
2.1. Endothelial-Specific MCPIP Deletion Leads to Systemic Inflammation and Growth Retardation
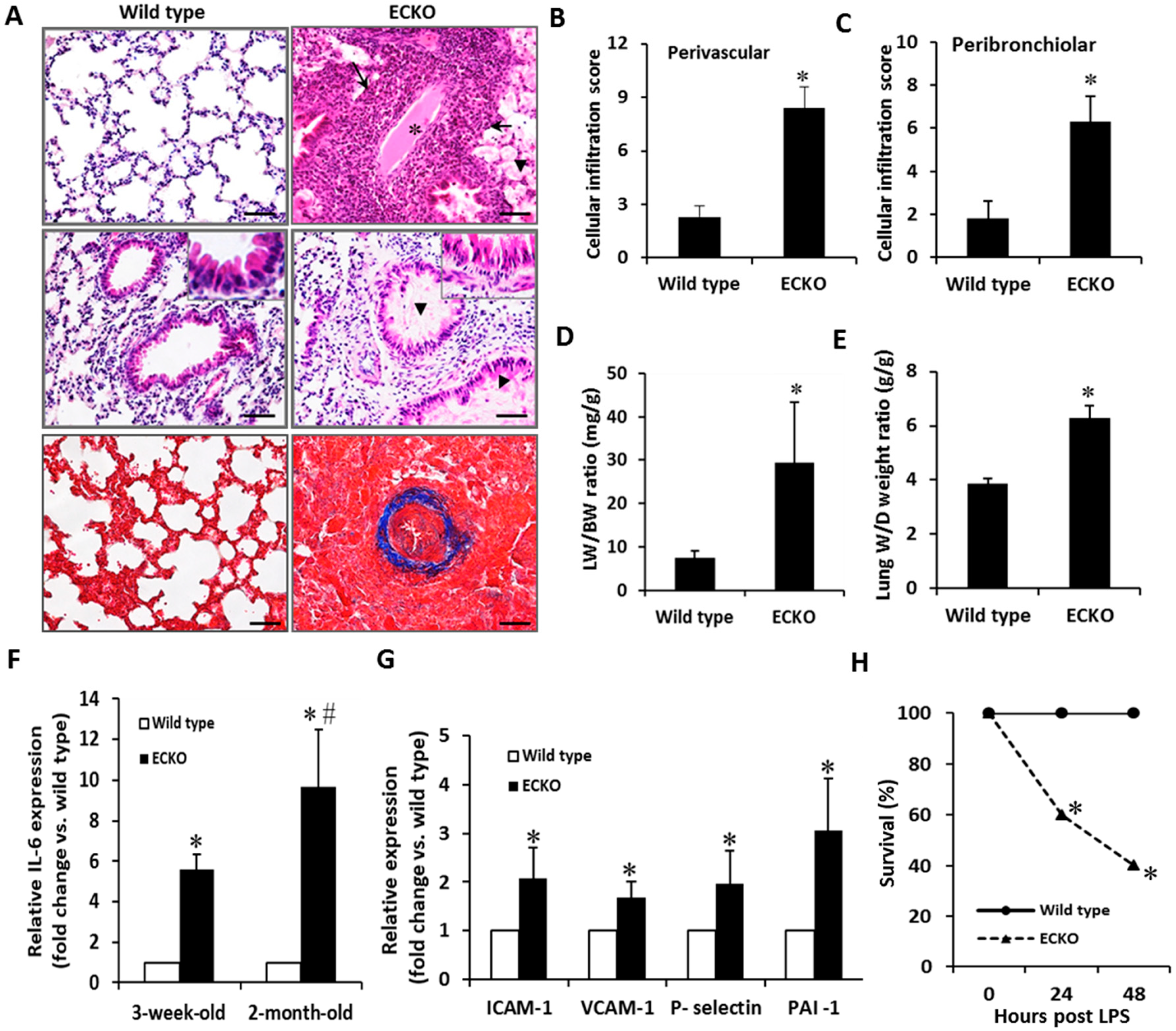
2.2. Endothelial-Specific MCPIP Deletion Leads to Vascular Leak and Systemic Coagulopathy
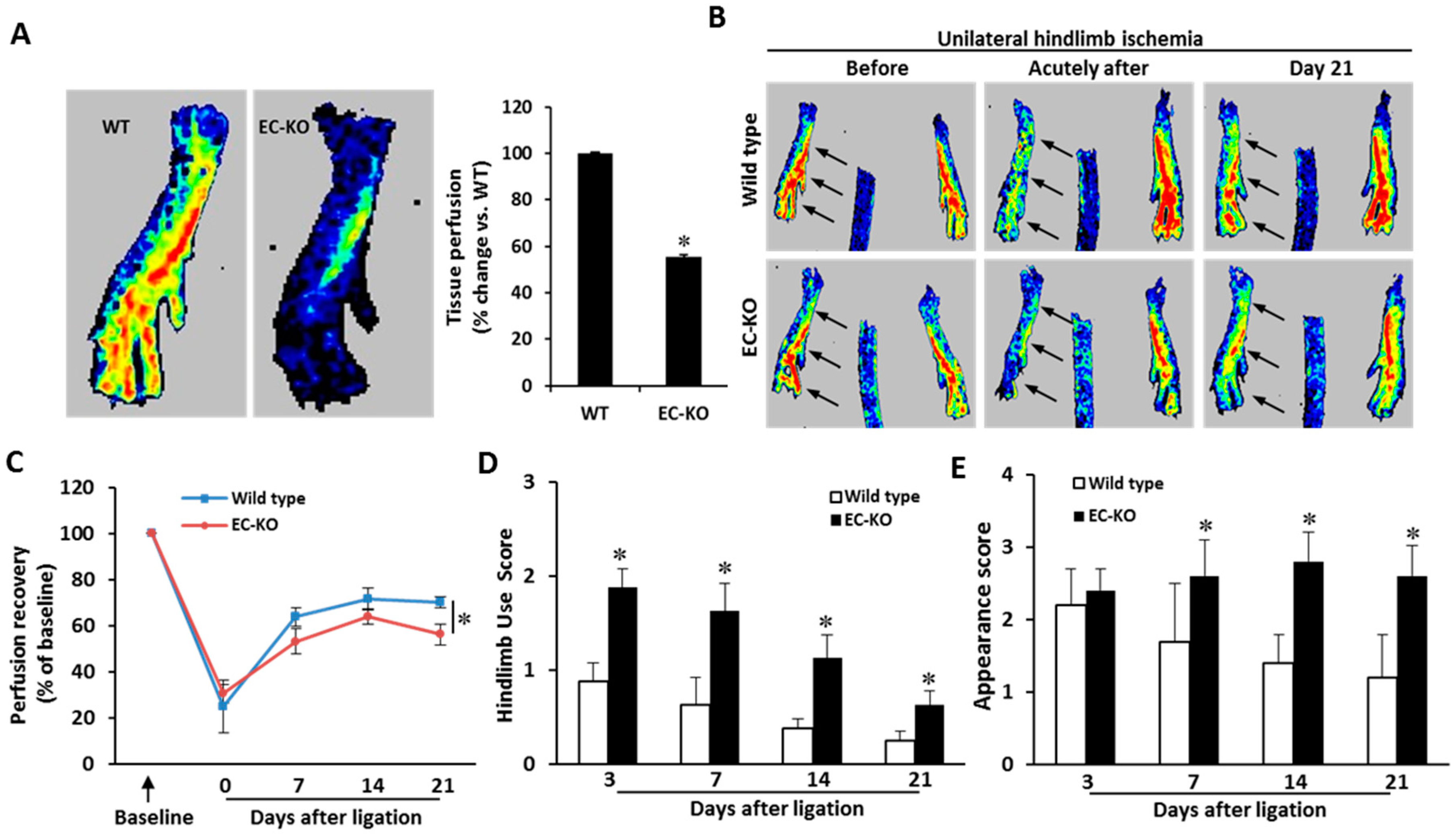
2.3. Endothelial-Specific MCPIP Deletion Impairs Tissue Perfusion and Post-Ischemic Angiogenesis
2.4. MCPIP Deficiency Induces NF-κB Activity and Pro-Inflammatory miRNAs in ECs In Vitro and In Vivo
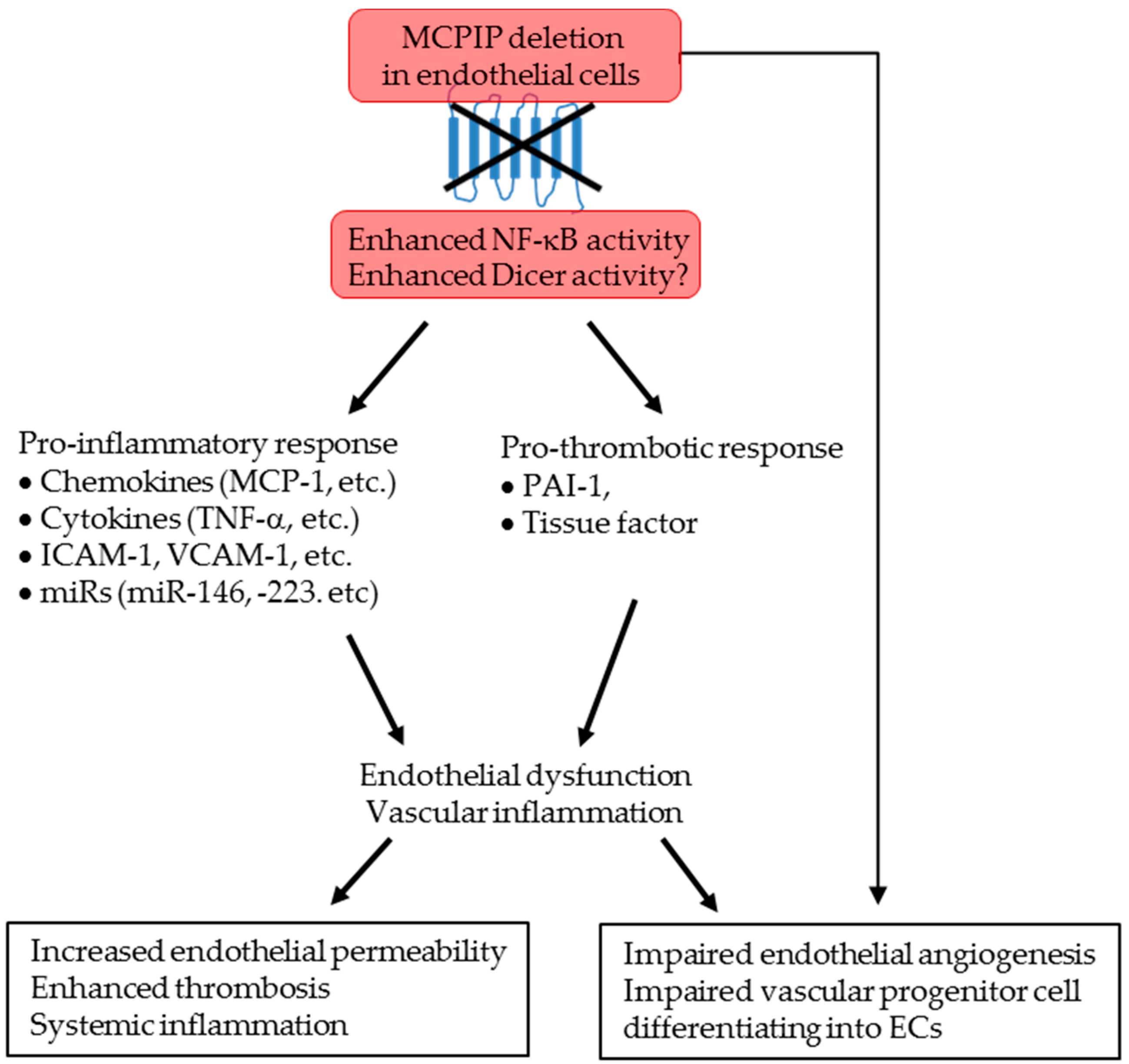
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. EC-Specific MCPIP Deletion in Mice
4.2. Vascular Permeability Assay In Vivo
4.3. Preparation of Bone Marrow and Blood Smears
4.4. Histological and Histomorphometric Assessment
4.5. Fluorescent Immunohistochemical Analysis
4.6. RNA Isolation and Quantitative Real-Time RT-PCR (qRT-PCR)
4.7. Knockdown Assays with siRNA
4.8. Western Blot Analysis
4.9. Ex Vivo Aortic Ring Assay
4.10. Hindlimb Ischemia Model and Assessment of Post-Ischemic Functional Recovery
4.11. Assessment of Blood Perfusion by Laser Doppler Imaging
4.12. Multiple Analytic Profiling on Serum
4.13. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MCPIP | MCP-1-induced protein |
| MCP-1 | Monocye chemoattractant protein 1 |
| ECs | Endothelial cells |
| ECKO | MCPIP endothelium conditional knockout |
| HUVECs | Human umbilical vein endothelial cells |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative reverse transcription-PCR |
| ICAM-1 | Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1 |
| VCAM-1 | Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 |
| PAI-1 | Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 |
| TF | Tissue factor |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| IL-1β | Interleukin 1 beta |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
References
- Weber, C.; Erl, W. Modulation of vascular cell activation, function, and apoptosis: Role of antioxidants and nuclear factor-kappa B. Curr. Top. Cell. Regul. 2000, 36, 217–235. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deanfield, J.E.; Halcox, J.P.; Rabelink, T.J. Endothelial function and dysfunction: Testing and clinical relevance. Circulation 2007, 115, 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pober, J.S.; Sessa, W.C. Evolving functions of endothelial cells in inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 803–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, M.; Nata, T.; Morishita, R.; Matsushita, H.; Nakagami, H.; Yamamoto, K.; Yamazaki, K.; Nakabayashi, M.; Ogihara, T.; Kaneda, Y. Endothelial apoptosis induced by oxidative stress through activation of NF-kappaB: Antiapoptotic effect of antioxidant agents on endothelial cells. Hypertension 2001, 38, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempe, S.; Kestler, H.; Lasar, A.; Wirth, T. NF-kappaB controls the global pro-inflammatory response in endothelial cells: Evidence for the regulation of a pro-atherogenic program. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 5308–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fish, J.E.; Cybulsky, M.I. Taming endothelial activation with a microRNA. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 1967–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamorro-Jorganes, A.; Araldi, E.; Suarez, Y. MicroRNAs as pharmacological targets in endothelial cell function and dysfunction. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 75, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, N. New paradigms in inflammatory signaling in vascular endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2014, 306, H317–H325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Azfer, A.; Niu, J.; Graham, S.; Choudhury, M.; Adamski, F.M.; Younce, C.; Binkley, P.F.; Kolattukudy, P.E. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 induces a novel transcription factor that causes cardiac myocyte apoptosis and ventricular dysfunction. Circ. Res. 2006, 98, 1177–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Saad, Y.; Lei, T.; Wang, J.; Qi, D.; Yang, Q.; Kolattukudy, P.E.; Fu, M. MCP-induced protein 1 deubiquitinates TRAF proteins and negatively regulates JNK and NF-kappaB signaling. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 2959–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, K.; Takeuchi, O.; Standley, D.M.; Kumagai, Y.; Kawagoe, T.; Miyake, T.; Satoh, T.; Kato, H.; Tsujimura, T.; Nakamura, H.; et al. Zc3h12a is an RNase essential for controlling immune responses by regulating mRNA decay. Nature 2009, 458, 1185–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uehata, T.; Akira, S. mRNA degradation by the endoribonuclease Regnase-1/ZC3H12a/MCPIP-1. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1829, 708–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.I.; Arase, M.; Matsuyama, H.; Choi, Y.L.; Ueno, T.; Mano, H.; Sugimoto, K.; Miyazono, K. MCPIP1 ribonuclease antagonizes dicer and terminates microRNA biogenesis through precursor microRNA degradation. Mol. Cell 2011, 44, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, A.V.; Amatya, N.; Chen, K.; Cruz, J.A.; Grover, P.; Whibley, N.; Conti, H.R.; Hernandez Mir, G.; Sirakova, T.; Childs, E.C.; et al. MCPIP1 Endoribonuclease Activity Negatively Regulates Interleukin-17-Mediated Signaling and Inflammation. Immunity 2015, 43, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Liang, J.; She, Z.G.; Cai, Y.; Wang, J.; Lei, T.; Stallcup, W.B.; Fu, M. MCP-induced protein 1 suppresses TNFalpha-induced VCAM-1 expression in human endothelial cells. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 3065–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Liang, X.; He, L.; Wen, W.; Zhao, S.; Wen, L.; Liu, Y.; Shyy, J.Y.; Yuan, Z. Endothelial dysfunction in rheumatoid arthritis: The role of monocyte chemotactic protein-1-induced protein. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 1384–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, J.; Azfer, A.; Zhelyabovska, O.; Fatma, S.; Kolattukudy, P.E. Monocyte chemotactic protein (MCP)-1 promotes angiogenesis via a novel transcription factor, MCP-1-induced protein (MCPIP). J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 14542–14551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alva, J.A.; Zovein, A.C.; Monvoisin, A.; Murphy, T.; Salazar, A.; Harvey, N.L.; Carmeliet, P.; Iruela-Arispe, M.L. VE-Cadherin-Cre-recombinase transgenic mouse: A tool for lineage analysis and gene deletion in endothelial cells. Dev. Dyn. 2006, 235, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, N.; Niu, J.; Saad, Y.; Kumar, S.; Sirakova, T.; Becerra, E.; Li, X.; Kolattukudy, P.E. Transcription factors STAT6 and KLF4 implement macrophage polarization via the dual catalytic powers of MCPIP. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 6011–6023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, T.C.; Anderson, M.E.; Moots, R.J. The many faces of interleukin-6: The role of IL-6 in inflammation, vasculopathy, and fibrosis in systemic sclerosis. Int. J. Rheumatol. 2011, 2011, 721608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestre, J.S.; Smadja, D.M.; Levy, B.I. Postischemic revascularization: From cellular and molecular mechanisms to clinical applications. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 1743–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Defelice, A.F.; Hanig, J.P.; Colatsky, T. Biomarkers of endothelial cell activation serve as potential surrogate markers for drug-induced vascular injury. Toxicol. Pathol. 2010, 38, 856–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, J.; Wang, K.; Graham, S.; Azfer, A.; Kolattukudy, P.E. MCP-1-induced protein attenuates endotoxin-induced myocardial dysfunction by suppressing cardiac NF-small ka, CyrillicB activation via inhibition of Ismall ka, CyrillicB kinase activation. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2011, 51, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, J.; Jin, Z.; Kim, H.; Kolattukudy, P.E. MCP-1-induced protein attenuates post-infarct cardiac remodeling and dysfunction through mitigating NF-κB activation and suppressing inflammation-associated microRNA expression. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2015, 110, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Wang, J.; Saad, Y.; Warble, L.; Becerra, E.; Kolattukudy, P.E. Participation of MCP-induced protein 1 in lipopolysaccharide preconditioning-induced ischemic stroke tolerance by regulating the expression of proinflammatory cytokines. J. Neuroinflamm. 2011, 8, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skalniak, L.; Dziendziel, M.; Jura, J. MCPIP1 contributes to the toxicity of proteasome inhibitor MG-132 in HeLa cells by the inhibition of NF-kappaB. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2014, 395, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.S.; Sivachandran, N.; Lau, A.; Boudreau, E.; Zhao, J.L.; Baltimore, D.; Delgado-Olguin, P.; Cybulsky, M.I.; Fish, J.E. MicroRNA-146 represses endothelial activation by inhibiting pro-inflammatory pathways. EMBO Mol. Med. 2013, 5, 1017–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, T.A.; Yamakuchi, M.; Ferlito, M.; Mendell, J.T.; Lowenstein, C.J. MicroRNA-126 regulates endothelial expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 1516–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fish, J.E.; Santoro, M.M.; Morton, S.U.; Yu, S.; Yeh, R.F.; Wythe, J.D.; Ivey, K.N.; Bruneau, B.G.; Stainier, D.Y.; Srivastava, D. miR-126 regulates angiogenic signaling and vascular integrity. Dev. Cell 2008, 15, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Chen, H.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, M.; Yao, G.; Yu, Y.; Qin, W.; Zeng, C.; Zen, K.; Liu, Z. MiR-223 downregulation promotes glomerular endothelial cell activation by upregulating importin alpha4 and alpha5 in IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2014, 85, 624–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, Y.; Fernandez-Hernando, C.; Pober, J.S.; Sessa, W.C. Dicer dependent microRNAs regulate gene expression and functions in human endothelial cells. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, 1164–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheloufi, S.; Dos Santos, C.O.; Chong, M.M.; Hannon, G.J. A dicer-independent miRNA biogenesis pathway that requires Ago catalysis. Nature 2010, 465, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohnsack, M.T.; Czaplinski, K.; Gorlich, D. Exportin 5 is a RanGTP-dependent dsRNA-binding protein that mediates nuclear export of pre-miRNAs. RNA 2004, 10, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boldin, M.P.; Baltimore, D. MicroRNAs, new effectors and regulators of NF-kappaB. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 246, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, B.; Cao, J.; Zhang, F.; Cui, H.; Teng, J.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Morehouse, C.; Jallal, B.; Tang, Y.; et al. Type I Interferon Inhibition of MicroRNA-146a Maturation Through Up-Regulation of Monocyte Chemotactic Protein-Induced Protein 1 in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 3209–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Chen, H.; Ren, J.; Geng, Q.; Song, J.; Lee, C.; Cao, C.; Zhang, J.; Xu, N. MicroRNA-223 inhibits tissue factor expression in vascular endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis 2014, 237, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabet, F.; Vickers, K.C.; Cuesta Torres, L.F.; Wiese, C.B.; Shoucri, B.M.; Lambert, G.; Catherinet, C.; Prado-Lourenco, L.; Levin, M.G.; Thacker, S.; et al. HDL-transferred microRNA-223 regulates ICAM-1 expression in endothelial cells. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, P.; Zhou, Z.; Natarelli, L.; Wei, Y.; Nazari-Jahantigh, M.; Zhu, M.; Grommes, J.; Steffens, S.; Weber, C.; Schober, A. Endothelial Dicer promotes atherosclerosis and vascular inflammation by miRNA-103-mediated suppression of KLF4. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, C.; Quach, J.M.; Walkley, C.R.; Lane, S.W.; Lo Celso, C.; Purton, L.E. Deciphering hematopoietic stem cells in their niches: A critical appraisal of genetic models, lineage tracing, and imaging strategies. Cell Stem Cell 2013, 13, 520–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Wang, K.; Zhelyabovska, O.; Saad, Y.; Kolattukudy, P.E. MCP-1-induced protein promotes endothelial-like and angiogenic properties in human bone marrow monocytic cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2013, 347, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.R.; Kim, E.; Abdel-Wahab, O. Femoral bone marrow aspiration in live mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalothorn, D.; Zhang, H.; Smith, J.E.; Edwards, J.C.; Faber, J.E. Chloride intracellular channel-4 is a determinant of native collateral formation in skeletal muscle and brain. Circ. Res. 2009, 105, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalothorn, D.; Clayton, J.A.; Zhang, H.; Pomp, D.; Faber, J.E. Collateral density, remodeling, and VEGF-A expression differ widely between mouse strains. Physiol. Genom. 2007, 30, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Wild Type (n =3) | ECKO (n = 3) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cytokines (pg/mL) | |||
| G-CSF | 228.7 ± 11.8 | 707.1 ± 8.2 | <0.0001 |
| M-CSF | 20.6 ± 9.8 | 59.1 ± 35.7 | 0.146 |
| IL-1β | 19.5 ± 7.1 | 30.2 ± 8.2 | 0.1627 |
| IL-2 | 19.2 ± 5.9 | 221.7 ± 18.8 | <0.0001 |
| IL-3 | 6.6 ± 2.8 | 18.5 ± 0.8 | 0.002 |
| IL-4 | 0.2 ± 0.03 | 3.8.7 ± 0.05 | <0.0001 |
| IL-5 | 5.8 ± 0.8 | 381.9 ± 8.4 | <0.0001 |
| IL-6 | 1.0 ± 0.7 | 22.8 ± 0.7 | <0.0001 |
| IL-7 | 8.1 ± 3.3 | 14.9 ± 1.1 | 0.027 |
| IL-10 | 6.6 ± 3.1 | 54.8 ± 16.3 | 0.007 |
| IL-12p40 | 29.8 ± 5.3 | 71.6 ± 10.7 | 0.003 |
| IL-13 | 62.6 ± 22.1 | 760.2 ± 102.1 | 0.0003 |
| IL-15 | 97.1 ± 67.7 | 127.6 ± 33.2 | 0.522 |
| IL-17 | 2.5 ± 0.4 | 6.0 ± 0.3 | 0.0003 |
| TNF-α | 16.1 ± 1.4 | 24.9 ± 5.2 | 0.047 |
| Chemokines (pg/mL) | |||
| CCL11 | 482.8 ± 72.1 | 1420.2 ± 126.2 | 0.0004 |
| CCL2/MCP-1 | 59.9 ± 6.7 | 96.6 ± 3.4 | 0.001 |
| MIP-1α | 46.7 ± 38.2 | 335.3 ± 39.2 | 0.0008 |
| MIP-1β | 11.4 ± 4.1 | 244.3 ± 40.5 | 0.0006 |
| CXCL9/MIG | 74.4 ± 8.6 | 143.9 ± 0.9 | 0.0002 |
| RANTES | 43.5 ± 8.1 | 76.4 ± 28.1 | 0.123 |
| Othrers (pg/mL) | |||
| KC | 83.6 ± 6.5 | 524.5 ± 23.5 | <0.0001 |
| LIX | 7302.1 ± 858.9 | 120 ± 45.3 | 0.0001 |
| IP-10 | 59.5 ± 6.7 | 3720.3 ± 212.3 | <0.0001 |
| LIF | 1.4 ± 0.9 | 3.4 ± 0.3 | 0.021 |
| VEGF | 1.0 ± 0.4 | 6.9 ± 0.4 | <0.0001 |
| PAI-1 | 4.6 ± 0.6 | 19.7 ± 0.8 | <0.0001 |
| sP-selectin | 166.8 ± 4.6 | 226.6 ± 6.9 | 0.0002 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, Z.; Niu, J.; Kapoor, N.; Liang, J.; Becerra, E.; Kolattukudy, P.E. Essential Role of Endothelial MCPIP in Vascular Integrity and Post-Ischemic Remodeling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20010172
Jin Z, Niu J, Kapoor N, Liang J, Becerra E, Kolattukudy PE. Essential Role of Endothelial MCPIP in Vascular Integrity and Post-Ischemic Remodeling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(1):172. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20010172
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Zhuqing, Jianli Niu, Nidhi Kapoor, Jian Liang, Edilu Becerra, and Pappachan E. Kolattukudy. 2019. "Essential Role of Endothelial MCPIP in Vascular Integrity and Post-Ischemic Remodeling" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 1: 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20010172
APA StyleJin, Z., Niu, J., Kapoor, N., Liang, J., Becerra, E., & Kolattukudy, P. E. (2019). Essential Role of Endothelial MCPIP in Vascular Integrity and Post-Ischemic Remodeling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(1), 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20010172





