Additive Pharmacological Interaction between Cisplatin (CDDP) and Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors (HDIs) in MDA-MB-231 Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Cells with Altered Notch1 Activity—An Isobolographic Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
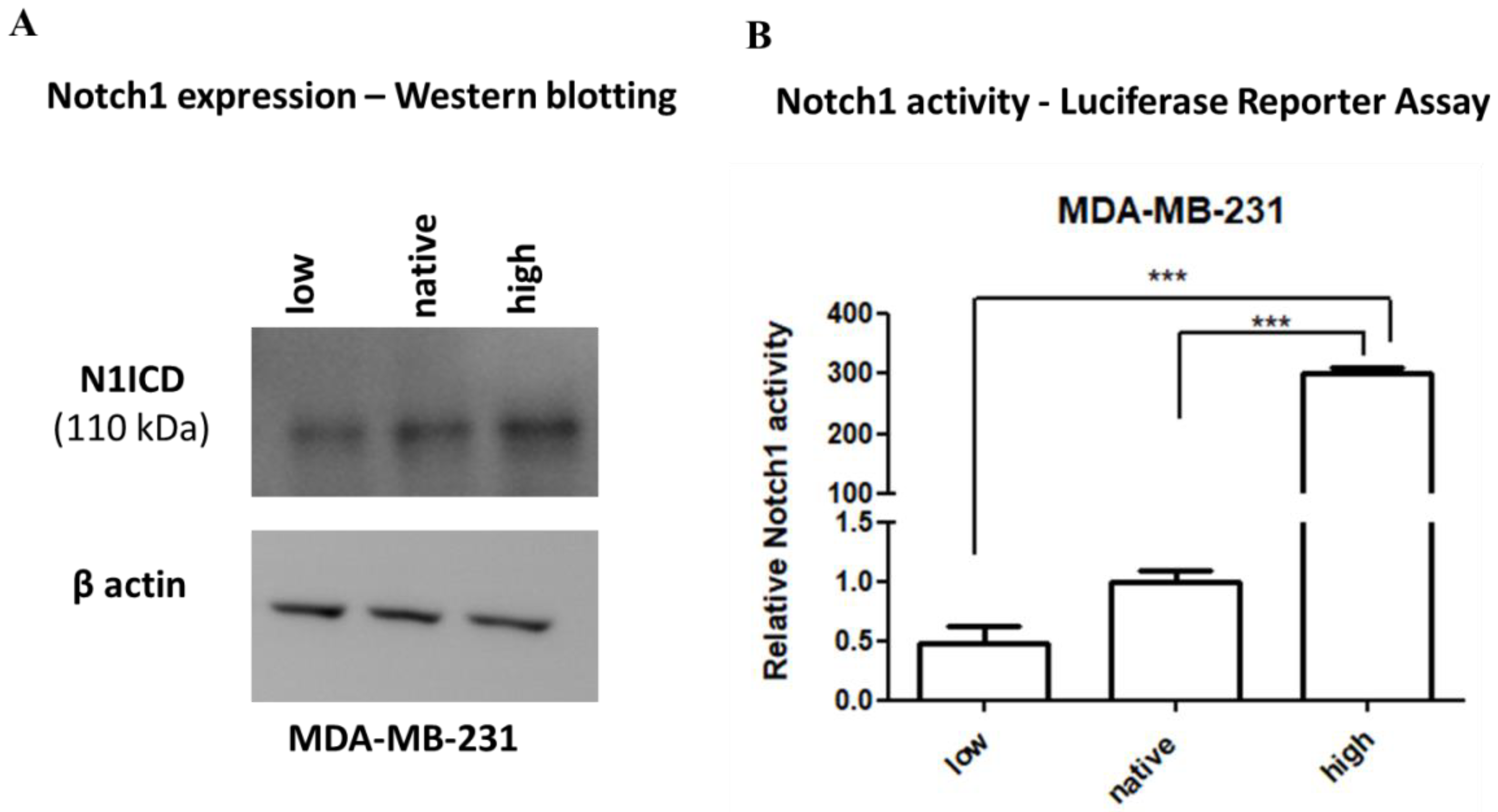
2.1. Expression and Activity of Notch1
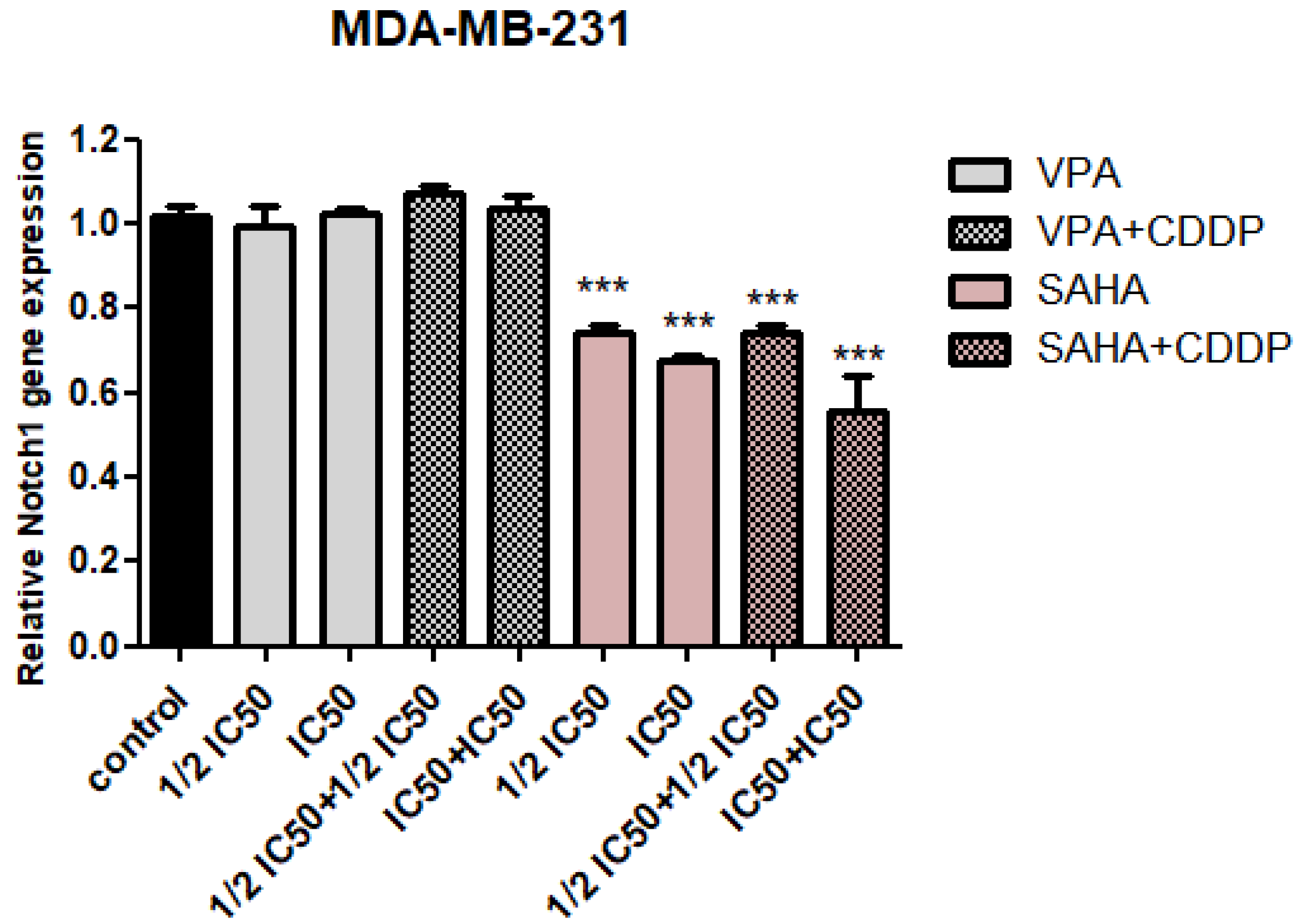
2.2. Assessment of Notch1 Gene Expression Changes after HDIs and CDDP Treatment
2.3. Dose-Dependent Growth Inhibition of Native and Transfected MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells after CDDP and HDIs Treatment
2.4. Effect of SAHA and VPA on The Anti-Proliferative Effects of CDDP in The MDA-MB-231 Cell Line with Increased Activity of The Notch 1 (Notch1highMDA-MB-231)
2.5. Effect of SAHA and VPA on The Anti-Proliferative Effects of CDDP in The MDA-MB-231 Cell Line with Decreased Activity of The Notch 1 (Notch1lowMDA-MB-231)
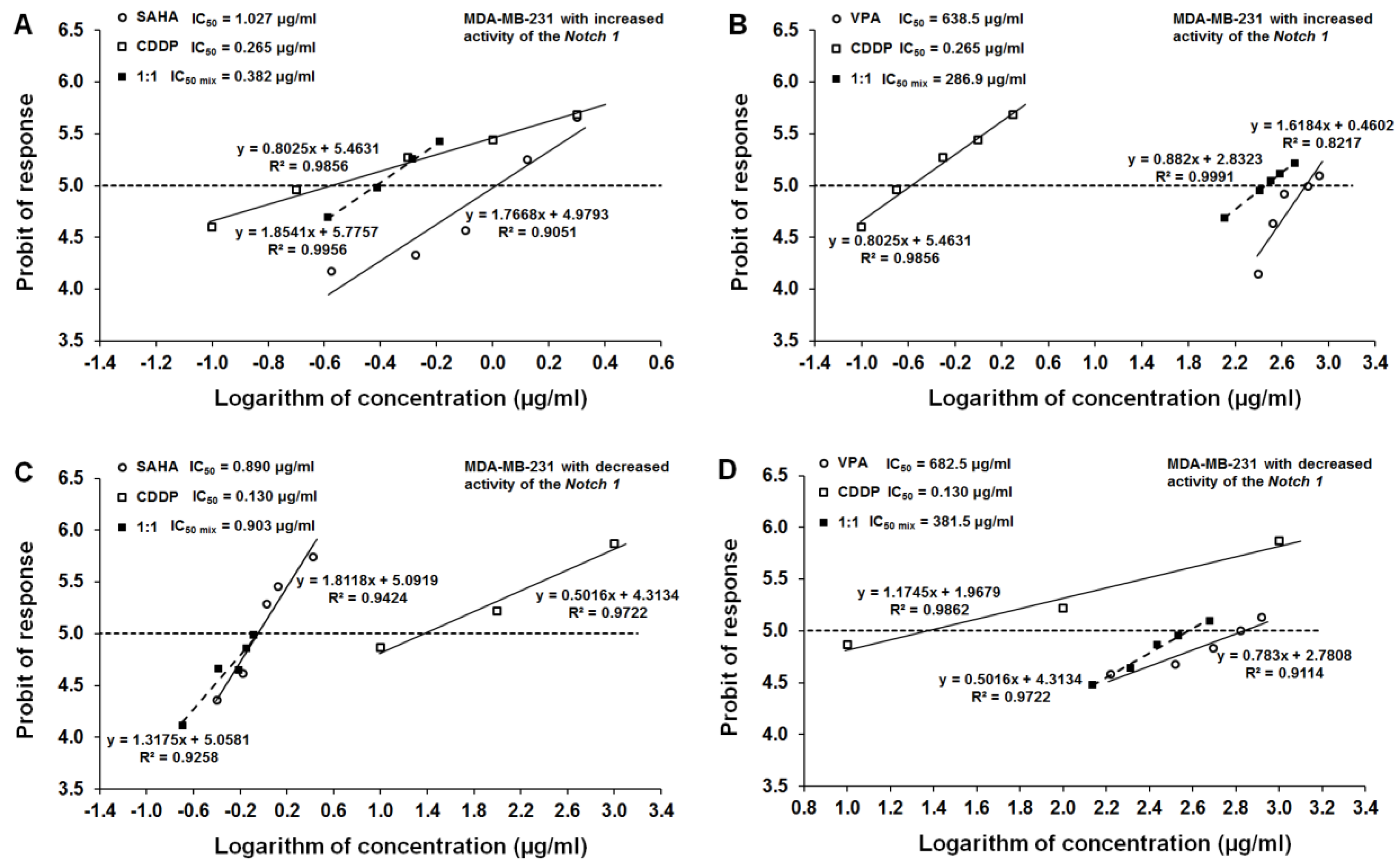
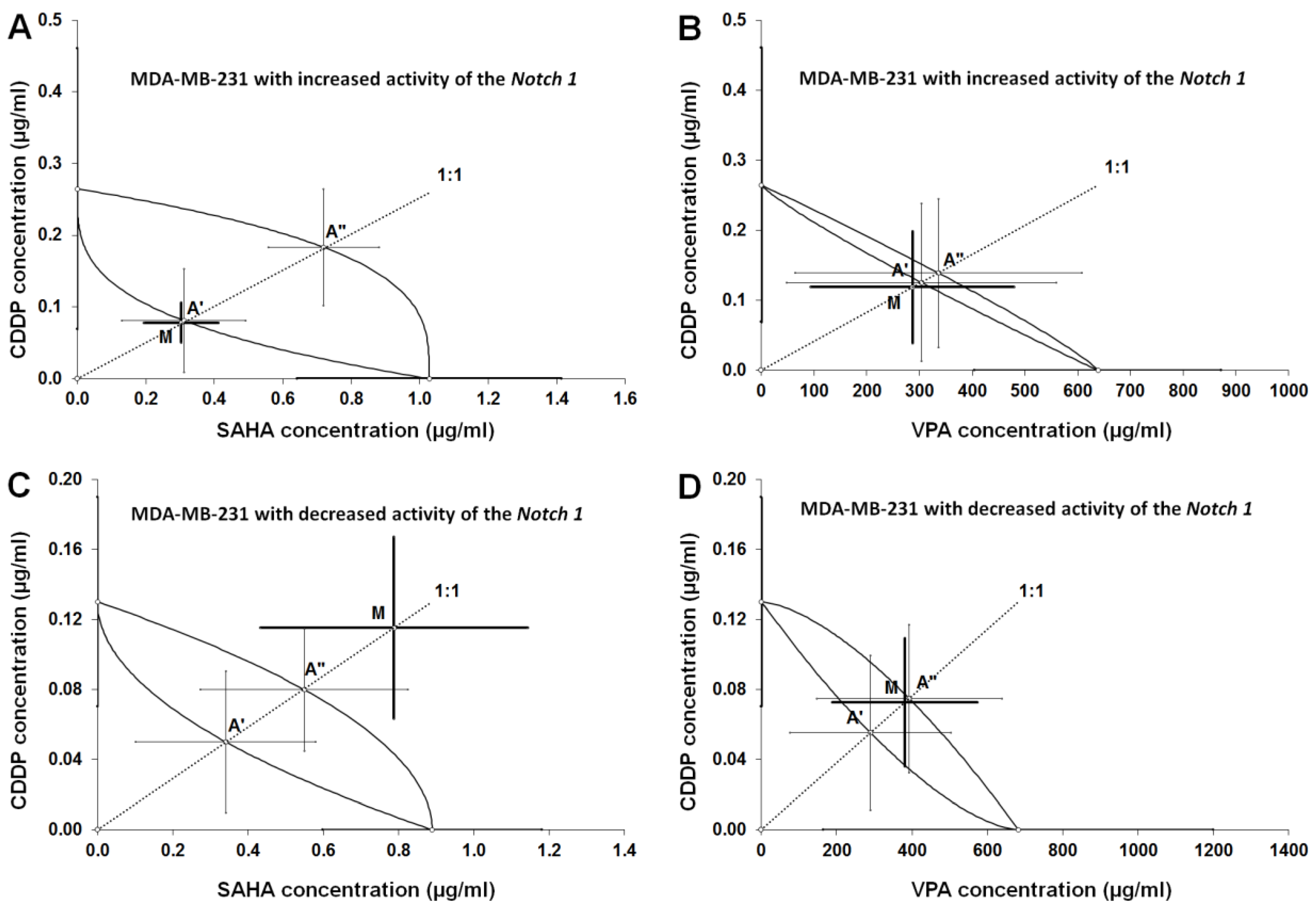
2.6. Type I Isobolographic Analysis of Interaction for The Combinations of CDDP with SAHA and VPA in The MDA-MB-231 Cell Line with Increased Activity of The Notch 1 (Notch1highMDA-MB-231)
2.7. Type I Isobolographic Analysis of Interaction for The Combinations of CDDP with SAHA and VPA in The MDA-MB-231 Cell Line with Decreased Activity of The Notch 1 (Notch1lowMDA-MB-231)
2.8. Analysis of The Types of Pharmacological Interaction between CDDP and HDIs in The MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells with Altered Notch1 Activity with Reference to Native MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
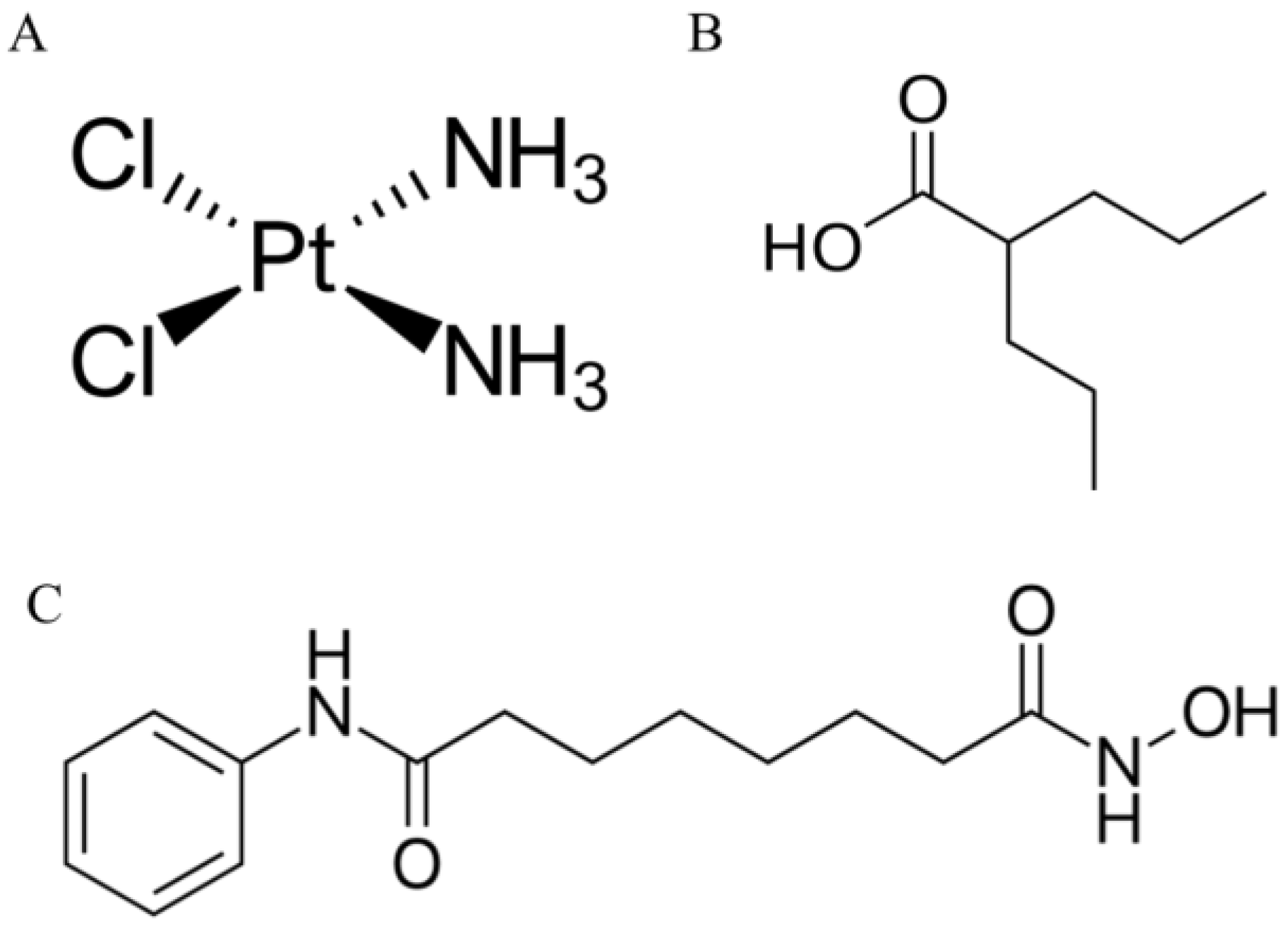
4.1. Drugs
4.2. Cell Lines
4.3. Transfection Procedure and Development of Breast Cancer Cell Lines with Decreased (Notch1low) and Increased (Notch1high) Notch1 Activity
4.4. Protein Extraction and Western Blotting Analysis
4.5. Luciferase Reporter Assay
4.6. RNA Isolation and cDNA Synthesis
4.7. Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
4.8. Cell Viability Assay
4.9. Isobolographic Analysis of Pharmacological Interactions between HDIs and CDDP
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| BC | Breast cancer |
| CBF1 | Centromere-binding protein 1 |
| CDDP | Cisplatin |
| CSL | CBF1/Su(H)/Lag-1 |
| DCIs | Ductal carcinoma in situ |
| DRRCs | Log-probit dose–response relationship curves |
| Dll | Delta like ligand |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| dnCSL | Dominant negative CSL |
| DSL | Delta, Serrate, Lag2 |
| ER | Estrogen receptor |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| GSIs | γ-secretase inhibitors |
| HAT | Histone acetyltransferase |
| HDIs | Histone deacetylase inhibitors |
| HER2 | Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 |
| HES1 | HES family bHLH transcription factor 1 |
| IDCs | Invasive ductal carcinomas |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| ILCs | Invasive lobular carcinomas |
| KDM5A | Lysine-specific demethylase 5A |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| NICD | Intracellular domain of Notch receptor |
| PCAF | Acetyltransferase p300/CBP associated factor |
| PBS | Phosphate buffered saline |
| PR | Progesteron receptor |
| RBP-Jk | Recombination signal binding protein for immunoglobulin kappa |
| SAHA | Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid |
| SHARP | SMART/HDAC1-associated repressor protein |
| SCLC | Small-cell lung carcinoma |
| SDS | Sodium dodecyl sulfate |
| S.E.M. | Standard error |
| SIRT1 | Sirtuin 1 |
| TNBC | Triple negative breast cancer |
| VPA | Valproic acid |
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 144, 1941–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Li, T.; Bai, Z.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhan, J.; Shi, B. Breast cancer intrinsic subtype classification, clinical use and future trends. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 2929–2943. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- O’Reilly, E.A.; Gubbins, L.; Sharma, S.; Tully, R.; Guang, M.H.Z.; Weiner-Gorzel, K.; McCaffrey, J.; Harrison, M.; Furlong, F.; Kell, M.; et al. The fate of chemoresistance in triple negative breast cancer (TNBC). BBA Clin. 2015, 3, 257–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strati, T.-M.; Kotoula, V.K.I.; Manousou, K.; Papadimitriou, C.; Lazaridis, G.; Lakis, S.; Pentheroudakis, G.; Pectasides, D.; Pazarli, E.; Christodoulou, C.; et al. Prognostic subcellular Notch2, Notch3 and Jagged1 localization patterns in early triple-negative breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Liu, Q.; Chen, S.; Shao, Z. Cisplatin versus carboplatin in combination with paclitaxel as neoadjuvant regimen for triple negative breast cancer. Onco. Targets. Ther. 2017, 10, 5739–5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, R.C.; Lippard, S.J. Structure of duplex DNA containing the cisplatin 1,2-{Pt(NH3)2}2+-d(GpG) cross-link at 1.77 Å resolution. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2010, 104, 902–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, S.; Bernard Tchounwou, P. Cisplatin in cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 740, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Yu, J.; Gui, G.; Chen, Y.; Huang, R.; Jiang, L.; Kwong, J.S.W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L. Cisplatin for testicular germ cell tumors: A rapid review. J. Evid. Based. Med. 2016, 9, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Reed, E.; Li, Q.Q. Molecular basis of cellular response to cisplatin chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2004, 12, 955–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckstein, N. Platinum resistance in breast and ovarian cancer cell lines. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 30, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caramelo, O.; Silva, C.; Caramelo, F.; Frutuoso, C.; Almeida-Santos, T. The effect of neoadjuvant platinum-based chemotherapy in BRCA mutated triple negative breast cancers-systematic review and meta-analysis. Hered. Cancer Clin. Pract. 2019, 17, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrisi, R.; Zuradelli, M.; Agostinetto, E.; Masci, G.; Losurdo, A.; De Sanctis, R.; Santoro, A. Platinum salts in the treatment of BRCA-associated breast cancer: A true targeted chemotherapy? Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2019, 135, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reedijk, J. Platinum anticancer coordination compounds: Study of DNA binding inspires new drug design. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 2009, 1303–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, I.; Topcul, M.R. In vitro antiproliferative effects of nab-paclitaxel with liposomal cisplatin on MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 breast cancer cell lines. J. BUON 2017, 22, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kelland, L. The resurgence of platinum-based cancer chemotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oun, R.; Moussa, Y.E.; Wheate, N.J. The side effects of platinum-based chemotherapy drugs: A review for chemists. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 6645–6653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cepeda, V.; Fuertes, M.A.; Castilla, J.; Alonso, C.; Quevedo, C.; Pérez, J.M. Biochemical mechanisms of cisplatin cytotoxicity. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2007, 7, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavoshi, H.; Vahedian, V.; Saghaei, S.; Pirouzpanah, M.B.; Raeisi, M.; Samadi, N. Adjuvant therapy with silibinin improves the efficacy of paclitaxel and cisplatin in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2017, 18, 2243–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Chen, W.; Li, H.; Li, M.; Li, L. The histone acetylation modifications of breast cancer and their therapeutic implications. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2018, 24, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licciardello, M.P.; Müllner, M.K.; Dürnberger, G.; Kerzendorfer, C.; Boidol, B.; Trefzer, C.; Sdelci, S.; Berg, T.; Penz, T.; Schuster, M.; et al. NOTCH1 activation in breast cancer confers sensitivity to inhibition of SUMOylation. Oncogene 2015, 34, 3780–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wawruszak, A.; Kalafut, J.; Okon, E.; Czapinski, J.; Halasa, M.; Przybyszewska, A.; Miziak, P.; Okla, K.; Rivero-Muller, A.; Stepulak, A. Histone deacetylase inhibitors and phenotypical transformation of cancer cells. Cancers 2019, 11, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hałasa, M.; Wawruszak, A.; Przybyszewska, A.; Jaruga, A.; Guz, M.; Kałafut, J.; Stepulak, A.; Cybulski, M. H3K18Ac as a marker of cancer progression and potential target of anti-cancer therapy. Cells 2019, 8, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedele, P.; Orlando, L.; Cinieri, S. Targeting triple negative breast cancer with histone deacetylase inhibitors. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2017, 26, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, L.J.; Zhao, F.; Wang, M.; Swaby, R.F.; Sparano, J.A.; Meropol, N.J.; Bhalla, K.N.; Pellegrino, C.M.; Katherine Alpaugh, R.; Falkson, C.I.; et al. A phase I/II study of suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) in combination with trastuzumab (Herceptin) in patients with advanced metastatic and/or local chest wall recurrent HER2-amplified breast cancer: A trial of the ECOG-ACRIN cancer research group. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 165, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aztopal, N.; Erkisa, M.; Erturk, E.; Ulukaya, E.; Tokullugil, A.H.; Ari, F. Valproic acid, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, induces apoptosis in breast cancer stem cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 280, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.J.; Wang, Y.S.; Gu, W.P.; Zhao, X. The role and possible molecular mechanism of valproic acid in the growth of MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Croat. Med. J. 2017, 58, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wawruszak, A.; Luszczki, J.J.; Grabarska, A.; Gumbarewicz, E.; Dmoszynska-Graniczka, M.; Polberg, K.; Stepulak, A. Assessment of interactions between cisplatin and two histone deacetylase inhibitors in mcf7, t47d and mda-mb-231 human breast cancer cell lines–an isobolographic analysis. PloS ONE 2015, 10, e0143013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.; Jin, H.; Roy, M.; Ma, A.L.; Gong, S.; Jaskula-Sztul, R.; Chen, H. Antineoplastic effects of histone deacetylase inhibitors in neuroendocrine cancer cells are mediated through transcriptional regulation of Notch1 by activator protein 1. Cancer Med. 2017, 6, 2142–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Previs, R.A.; Coleman, R.L.; Harris, A.L.; Sood, A.K. Molecular pathways: Translational and therapeutic implications of the notch signaling pathway in cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 955–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhao, F.; Lu, J.; Li, T.; Yang, H.; Wu, C.; Liu, Y. Notch-1 signaling promotes the malignant features of human breast cancer through NF-κB activation. PloS ONE 2014, 9, e95912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, J.N.; Rutkovsky, A.C.; Giordano, A. Mechanisms of resistance in estrogen receptor positive breast cancer: Overcoming resistance to tamoxifen/aromatase inhibitors. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2018, 41, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braune, E.B.; Tsoi, Y.L.; Phoon, Y.P.; Landor, S.; Silva Cascales, H.; Ramsköld, D.; Deng, Q.; Lindqvist, A.; Lian, X.; Sahlgren, C.; et al. Loss of CSL unlocks a hypoxic response and enhanced tumor growth potential in breast cancer cells. Stem Cell Rep. 2016, 6, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, G.; Tian, Y.; Lu, C.; Guo, H.; Zhao, X.; Guo, Y.; Wang, L.; Du, Q.; Liu, C. Effects of notch-1 down-regulation on malignant behaviors of breast cancer stem cells. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Medical Sci.] 2014, 34, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Zhang, M.; Wu, H.; Xu, H.; Han, N.; Chu, Q.; Yu, S.; Chen, Y.; Wu, K. Expression of Notch1 correlates with breast cancer progression and prognosis. PloS ONE 2015, 10, e0131689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Yang, Y.; Lv, J.; Sun, L.; Liu, M. Valproic acid exhibits different cell growth arrest effect in three HPV-positive/negative cervical cancer cells and possibly via inducing Notch1 cleavage and E6 downregulation. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 49, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.; Mackey, L.V.; Coy, D.H.; Yu, C.Y.; Sun, L. The histone deacetylase inhibitor vaproic acid induces cell growth arrest in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via suppressing notch signaling. J. Cancer 2015, 6, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landor, S.K.J.; Mutvei, A.P.; Mamaeva, V.; Jin, S.; Busk, M.; Borra, R.; Gronroos, T.J.; Kronqvist, P.; Lendahl, U.; Sahlgren, C.M. Hypo-and hyperactivated Notch signaling induce a glycolytic switch through distinct mechanisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 18814–18819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tallarida, R.J. Revisiting the isobole and related quantitative methods for assessing drug synergism. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 342, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, B.S.; Sharma, S.C.; Chanana, P.; Jhamb, S. Systemic treatment strategies for triple-negative breast cancer. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 5, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumbarewicz, E.; Luszczki, J.J.; Wawruszak, A.; Dmoszynska-Graniczka, M.; Grabarska, A.J.; Jarząb, A.M.; Polberg, K.; Stepulak, A. Isobolographic analysis demonstrates additive effect of cisplatin and HDIs combined treatment augmenting their anti-cancer activity in lung cancer cell lines. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 6, 2831–2845. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grabarska, A.; Łuszczki, J.J.; Nowosadzka, E.; Gumbarewicz, E.; Jeleniewicz, W.; Dmoszyńska-Graniczka, M.; Kowalczuk, K.; Kupisz, K.; Polberg, K.; Stepulak, A. Histone deacetylase inhibitor SAHA as potential targeted therapy agent for larynx cancer cells. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarząb, A.; Łuszczki, J.J.; Guz, M.; Gumbarewicz, E.; Polberg, K.; Stepulak, A. Additive interaction of cisplatin and histone deacetylase inhibitors combined treatment in rhabdomyosarcoma cells–An isobolographic analysis. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Qiao, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, R.J.; Wang, L.H.; Zhao, L.; Yan, L.N.; Zhang, Z.H.; Hao, C.L. Effects of VPA on the expression of notch signaling pathway in multiple myeloma RPMI 8226 cell line. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 2016, 24, 1449–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, J.T.; Hottinger, D.G.; Kunnimalaiyaan, M.; Chen, H. Histone deacetylase inhibitors upregulate Notch-1 and inhibit growth in pheochromocytoma cells. Surgery 2008, 144, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenblatt, D.Y.; Vaccaro, A.M.; Jaskula-Sztul, R.; Ning, L.; Haymart, M.; Kunnimalaiyaan, M.; Chen, H. Valproic acid activates Notch-1 Signaling and regulates the neuroendocrine phenotype in carcinoid cancer cells. Oncologist 2007, 12, 942–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockhausen, M.T.; Sjölund, J.; Manetopoulos, C.; Axelson, H. Effects of the histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid on Notch signalling in human neuroblastoma cells. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 92, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenblatt, D.Y.; Cayo, M.A.; Adler, J.T.; Ning, L.; Haymart, M.R.; Kunnimalaiyaan, M.; Chen, H. Valproic acid activates Notch1 signaling and induces apoptosis in medullary thyroid cancer cells. Ann. Surg. 2008, 247, 1036–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; He, Q.; Tsai, C.; Lei, J.; Chen, J.; Vienna Makcey, L.; Coy, D.H. HDAC inhibitors suppressed small cell lung cancer cell growth and enhanced the suppressive effects of receptor-targeting cytotoxins via upregulating somatostatin receptor II. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Paryan, M.; Tavakoli, R.; Rad, S.M.A.H.; Feizi, N.; Kamani, F.; Mostafavi, E.; Mohammadi-Yeganeh, S. Over-expression of NOTCH1 as a biomarker for invasive breast ductal carcinoma. 3 Biotech. 2016, 6, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Fan, H.; Xu, J.; Zhao, E. Prognostic implication of NOTCH1 in early stage oral squamous cell cancer with occult metastases. Clin. Oral Investig. 2018, 22, 1131–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inamura, N.; Kimura, T.; Wang, L.; Yanagi, H.; Tsuda, M.; Tanino, M.; Nishihara, H.; Fukuda, S.; Tanaka, S. Notch1 regulates invasion and metastasis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by inducing EMT through c-Myc. Auris Nasus Larynx 2017, 44, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, A.N.; Mc-Dermott, N.; Meunier, A.; Marignol, L. NUMB inhibition of NOTCH signalling as a therapeutic target in prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2014, 11, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamaeva, V.; Niemi, R.; Beck, M.; Özliseli, E.; Desai, D.; Landor, S.; Gronroos, T.; Kronqvist, P.; Pettersen, I.K.N.; Mc-Cormack, E.; et al. Inhibiting notch activity in breast cancer stem cells by glucose functionalized nanoparticles carrying γ-secretase inhibitors. Mol. Ther. 2016, 24, 926–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Cell Line | CDDP | SAHA | VPA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Notch1highMDA-MB-231 | 0.265 | 1.027 | 638.5 |
| MDA-MB-231 | 3.614 | 0.577 | 267.0 |
| Notch1lowMDA-MB-231 | 0.130 | 0.890 | 628.5 |
| Cell Line | Notch1 Activity | Combination | IC50 mix (μg/mL) | nmix | L IC50 add (μg/mL) | nadd | U IC50 Add (μg/mL) | nadd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Notch1highMDA-MB-231 | Increased | CDDP+SAHA | 0.382 ± 0.137 | 24 | 0.392 ± 0.253 | 50 | 0.902 ± 0.244 | 50 |
| Notch1highMDA-MB-231 | Increased | CDDP+VPA | 286.9 ± 193.2 | 30 | 303.5 ± 255.7 | 56 | 336.0 ± 272.0 | 56 |
| Notch1lowMDA-MB-231 | Decreased | CDDP+SAHA | 0.903 ± 0.407 | 30 | 0.391 ± 0.279 | 50 | 0.629 ± 0.310 | 50 |
| Notch1lowMDA-MB-231 | Decreased | CDDP+VPA | 381.5 ± 192.9 | 30 | 289.7 ± 214.5 | 56 | 392.8 ± 246.0 | 56 |
| Combination | Notch1highMDA-MB-231 | Notch1lowMDA-MB-231 | MDA-MB-231native [28] |
|---|---|---|---|
| CDDP/VPA | additivity | additivity | antagonism |
| CDDP/SAHA | additivity | additivity with tendency towards antagonism | additivity |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wawruszak, A.; Luszczki, J.J.; Kalafut, J.; Okla, K.; Halasa, M.; Rivero-Muller, A.; Stepulak, A. Additive Pharmacological Interaction between Cisplatin (CDDP) and Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors (HDIs) in MDA-MB-231 Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Cells with Altered Notch1 Activity—An Isobolographic Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3663. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153663
Wawruszak A, Luszczki JJ, Kalafut J, Okla K, Halasa M, Rivero-Muller A, Stepulak A. Additive Pharmacological Interaction between Cisplatin (CDDP) and Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors (HDIs) in MDA-MB-231 Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Cells with Altered Notch1 Activity—An Isobolographic Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(15):3663. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153663
Chicago/Turabian StyleWawruszak, Anna, Jarogniew J. Luszczki, Joanna Kalafut, Karolina Okla, Marta Halasa, Adolfo Rivero-Muller, and Andrzej Stepulak. 2019. "Additive Pharmacological Interaction between Cisplatin (CDDP) and Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors (HDIs) in MDA-MB-231 Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Cells with Altered Notch1 Activity—An Isobolographic Analysis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 15: 3663. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153663
APA StyleWawruszak, A., Luszczki, J. J., Kalafut, J., Okla, K., Halasa, M., Rivero-Muller, A., & Stepulak, A. (2019). Additive Pharmacological Interaction between Cisplatin (CDDP) and Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors (HDIs) in MDA-MB-231 Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Cells with Altered Notch1 Activity—An Isobolographic Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(15), 3663. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153663






