Identification and Clinical Validation of a Novel 4 Gene-Signature with Prognostic Utility in Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
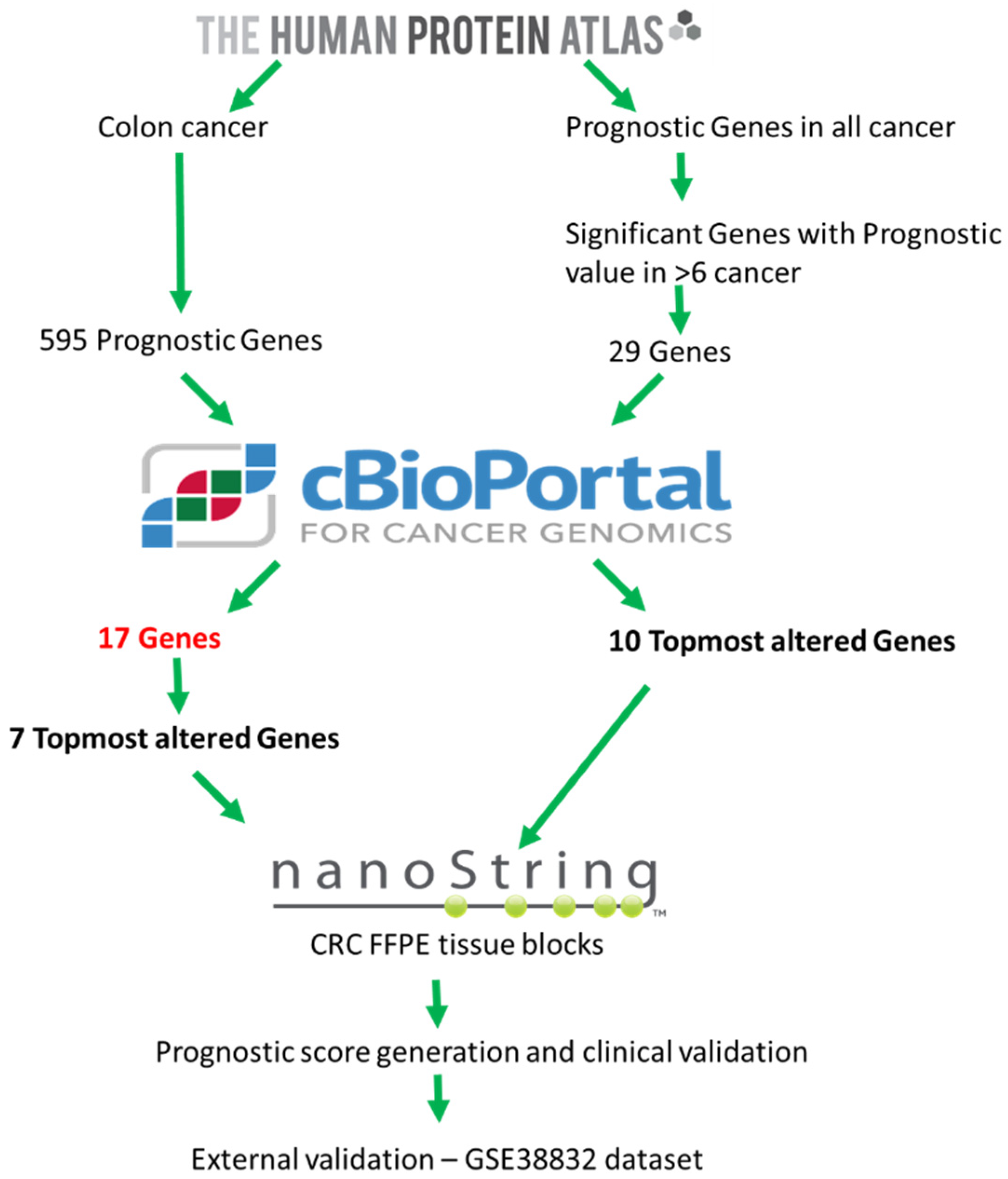
2.1. Exploratory Analysis to Build 17-Gene Panel
2.2. Clinicopathological Characteristics of CRC Patients
2.3. Univariate, Multivariate Analysis and Generation of Prognostic Score
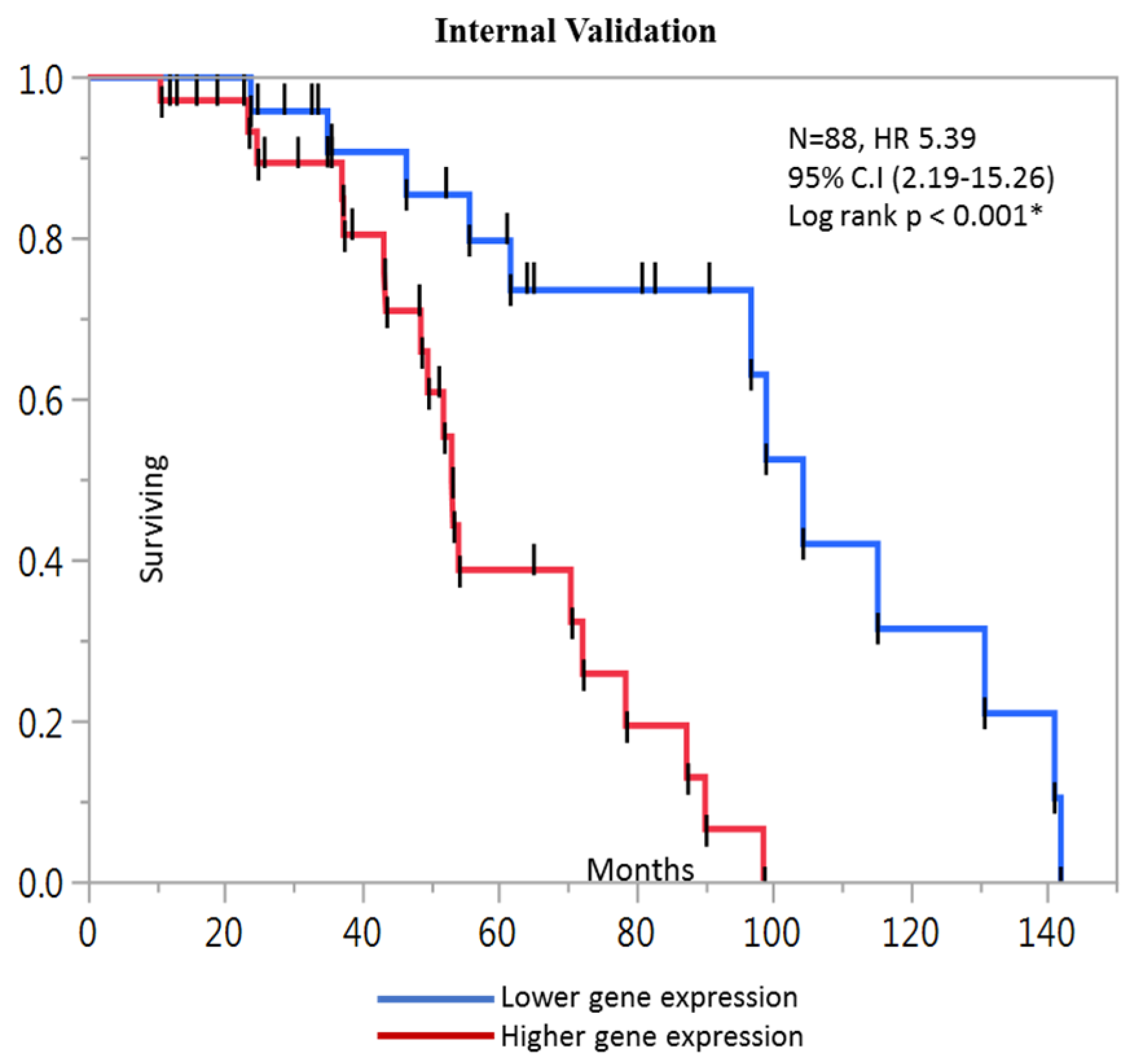
2.4. Kaplan-Meier Analysis
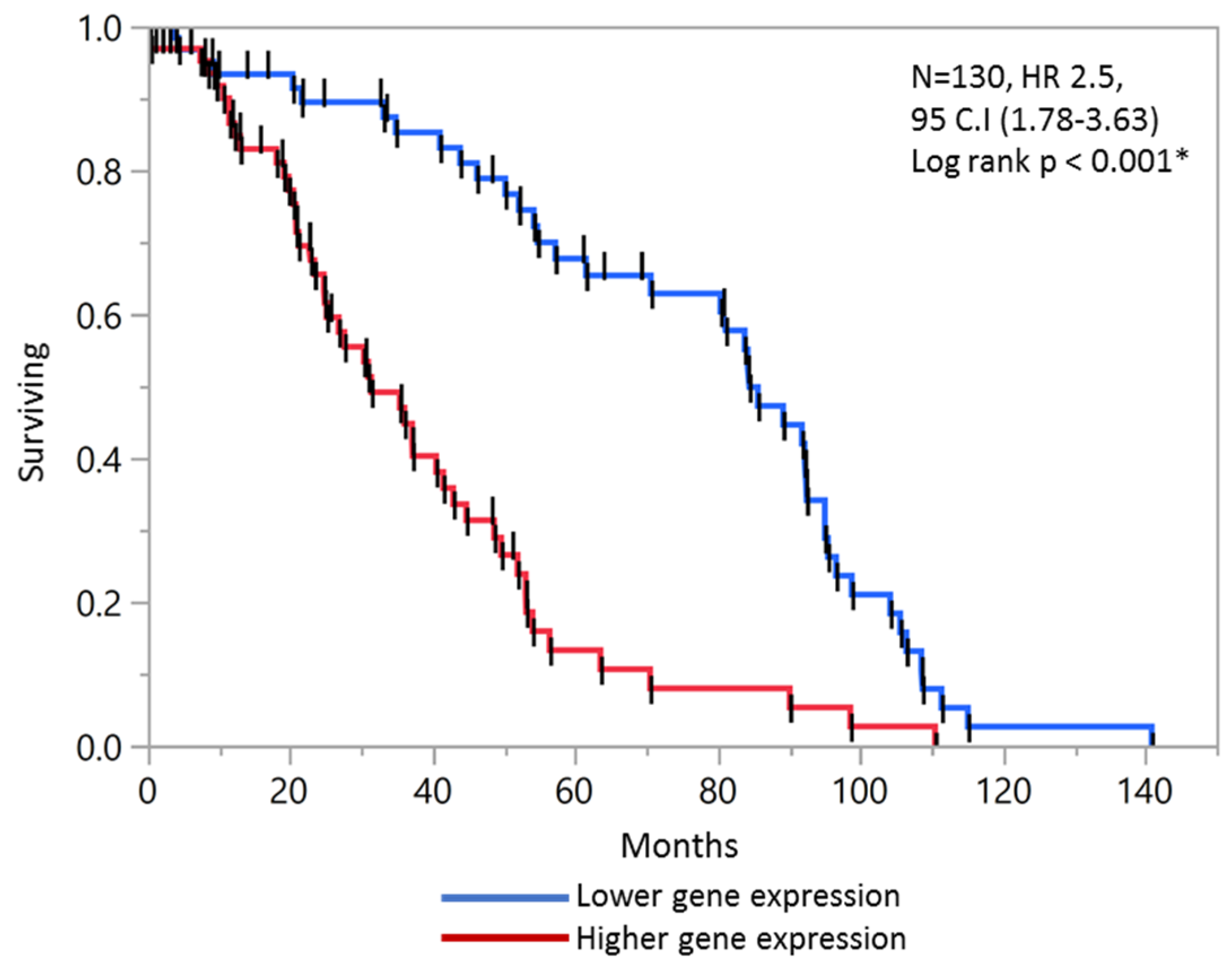
2.5. External Validation of Prognostic Score with GEO Microarray Dataset and ROC analysis
2.6. Validation of Prognostic Score in Combined Stage II and Stage III Patients
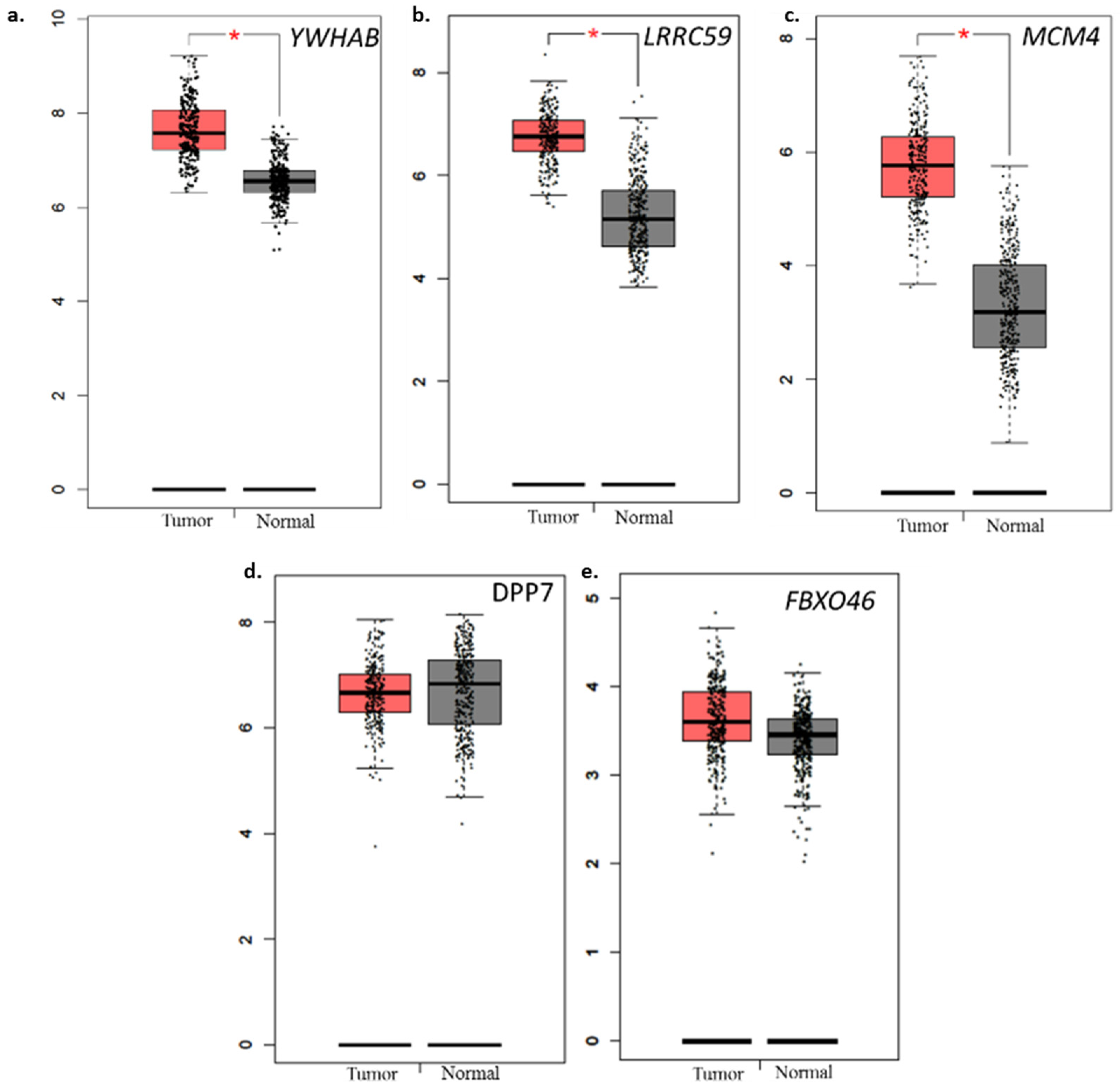
2.7. Comparison with Normal TCGA Datasets
2.8. Biological Features of Significant Genes Found in This Panel
2.9. Correlation Cluster of Expressed Genes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Source and Generation of 17-Gene Panel
4.2. Patient Characteristics
4.3. FFPE Tissue Sectioning and H&E Staining
4.4. RNA Isolation
4.5. Quantification of mRNA Molecules Using Nanostring Platform
4.6. mRNA Expression Data Normalization
4.7. Correlation Analysis and Gene Expression Comparison with Normal Tissue
4.8. Construction and Validation of a 4 Gene Prognostic Model
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fedewa, S.A.; Ahnen, D.J.; Meester, R.G.S.; Barzi, A.; Jemal, A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcker Espersen, M.L.; Linnemann, D.; Christensen, I.J.; Alamili, M.; Troelsen, J.T.; Hogdall, E. SOX9 expression predicts relapse of stage II colon cancer patients. Hum. Pathol 2016, 52, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zuo, S.; Dai, G.; Ren, X. Identification of a 6-gene signature predicting prognosis for colorectal cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, U.; Frankenberger, C.; Yun, J.; Bevilacqua, E.; Caldas, C.; Chin, S.F.; Rueda, O.M.; Reinitz, J.; Rosner, M.R. A prognostic gene signature for metastasis-free survival of triple negative breast cancer patients. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.H.; Jiao, J.W.; Zhang, H.F.; Li, C.Q.; Zhao, J.M.; Liao, L.D.; Wu, J.Y.; Wu, B.L.; Wu, Z.Y.; Wang, S.H.; et al. A three-gene signature from protein-protein interaction network of LOXL2- and actin-related proteins for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma prognosis. Cancer Med. 2017, 6, 1707–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connell, M.J.; Lavery, I.; Yothers, G.; Paik, S.; Clark-Langone, K.M.; Lopatin, M.; Watson, D.; Baehner, F.L.; Shak, S.; Baker, J.; et al. Relationship between tumor gene expression and recurrence in four independent studies of patients with stage II/III colon cancer treated with surgery alone or surgery plus adjuvant fluorouracil plus leucovorin. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 3937–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, R.D.; Bylesjo, M.; Kerr, P.; Davison, T.; Black, J.M.; Kay, E.W.; Holt, R.J.; Proutski, V.; Ahdesmaki, M.; Farztdinov, V.; et al. Development and independent validation of a prognostic assay for stage II colon cancer using formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 4620–4626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, R.; Roepman, P.; Capella, G.; Moreno, V.; Simon, I.; Dreezen, C.; Lopez-Doriga, A.; Santos, C.; Marijnen, C.; Westerga, J.; et al. Gene expression signature to improve prognosis prediction of stage II and III colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Sun, X.; Ge, W.; Qian, Y.; Bai, R.; Zheng, S. A seven-gene signature predicts overall survival of patients with colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 95054–95065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Narzo, A.F.; Tejpar, S.; Rossi, S.; Yan, P.; Popovici, V.; Wirapati, P.; Budinska, E.; Xie, T.; Estrella, H.; Pavlicek, A.; et al. Test of four colon cancer risk-scores in formalin fixed paraffin embedded microarray gene expression data. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Jensen, M.A.; Zenklusen, J.C. A Practical Guide to The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1418, 111–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlen, M.; Zhang, C.; Lee, S.; Sjostedt, E.; Fagerberg, L.; Bidkhori, G.; Benfeitas, R.; Arif, M.; Liu, Z.; Edfors, F.; et al. A pathology atlas of the human cancer transcriptome. Science 2017, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E.; et al. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, pl1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastassiou, D.; Rumjantseva, V.; Cheng, W.; Huang, J.; Canoll, P.D.; Yamashiro, D.J.; Kandel, J.J. Human cancer cells express Slug-based epithelial-mesenchymal transition gene expression signature obtained in vivo. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandres, E.; Malumbres, R.; Cubedo, E.; Honorato, B.; Zarate, R.; Labarga, A.; Gabisu, U.; Sola, J.J.; Garcia-Foncillas, J. A gene signature of 8 genes could identify the risk of recurrence and progression in Dukes’ B colon cancer patients. Oncol. Rep. 2007, 17, 1089–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhu, J.; Deane, N.G.; Lewis, K.B.; Padmanabhan, C.; Washington, M.K.; Ciombor, K.K.; Timmers, C.; Goldberg, R.M.; Beauchamp, R.D.; Chen, X. Evaluation of frozen tissue-derived prognostic gene expression signatures in FFPE colorectal cancer samples. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrier, A.; Roser, F.; Boelle, P.Y.; Franc, B.; Tse, C.; Brault, D.; Lacaine, F.; Houry, S.; Callard, P.; Penna, C.; et al. Prognosis of stage II colon cancer by non-neoplastic mucosa gene expression profiling. Oncogene 2007, 26, 2642–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlos-Suarez, A.; Barriga, F.M.; Jung, P.; Iglesias, M.; Cespedes, M.V.; Rossell, D.; Sevillano, M.; Hernando-Momblona, X.; da Silva-Diz, V.; Munoz, P.; et al. The intestinal stem cell signature identifies colorectal cancer stem cells and predicts disease relapse. Cell Stem Cell 2011, 8, 511–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Li, C.; Kang, B.; Gao, G.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z. GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W98–W102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consortium, G.T. The Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) project. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Downey, T.; Eu, K.W.; Koh, P.K.; Cheah, P.Y. A ’metastasis-prone’ signature for early-stage mismatch-repair proficient sporadic colorectal cancer patients and its implications for possible therapeutics. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2010, 27, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santarius, T.; Shipley, J.; Brewer, D.; Stratton, M.R.; Cooper, C.S. A census of amplified and overexpressed human cancer genes. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, Y.; Sorensen, V.; Skjerpen, C.S.; Haugsten, E.M.; Jin, Y.; Walchli, S.; Olsnes, S.; Wiedlocha, A. Nuclear import of exogenous FGF1 requires the ER-protein LRRC59 and the importins Kpnalpha1 and Kpnbeta1. Traffic 2012, 13, 650–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korc, M.; Friesel, R.E. The role of fibroblast growth factors in tumor growth. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2009, 9, 639–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choy, B.; LaLonde, A.; Que, J.; Wu, T.; Zhou, Z. MCM4 and MCM7, potential novel proliferation markers, significantly correlated with Ki-67, Bmi1, and cyclin E expression in esophageal adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and precancerous lesions. Hum. Pathol. 2016, 57, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danilov, A.V.; Danilova, O.V.; Brown, J.R.; Rabinowitz, A.; Klein, A.K.; Huber, B.T. Dipeptidyl peptidase 2 apoptosis assay determines the B-cell activation stage and predicts prognosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Exp. Hematol. 2010, 38, 1167–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.P.; Liu, P.; Nelson, J.; Hamilton, R.L.; Bhargava, R.; Michalopoulos, G.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, J.; Ma, D.; Pennathur, A.; et al. Identification of recurrent fusion genes across multiple cancer types. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xicola, R.M.; Manojlovic, Z.; Augustus, G.J.; Kupfer, S.S.; Emmadi, R.; Alagiozian-Angelova, V.; Triche, T., Jr.; Salhia, B.; Carpten, J.; Llor, X.; et al. Lack of APC somatic mutation is associated with early-onset colorectal cancer in African Americans. Carcinogenesis 2018, 39, 1331–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.; Wang, H.; Tong, Y.; Yin, H.; Wang, D.; Yan, Z.; Liang, Y.; Wu, D.; Su, Q. The function of BTG3 in colorectal cancer cells and its possible signaling pathway. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 144, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wen, G.; Ding, M.; Pan, J.Y.; Yu, M.L.; Zhao, F.; Weng, X.L.; Du, J.L. Comparative proteomic analysis of colon cancer cell HCT-15 in response to all-trans retinoic acid treatment. Protein Pept. Lett. 2012, 19, 1272–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, H.; Kurozumi, S.; Kijima, Y.; Idichi, T.; Shinden, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Arai, T.; Maemura, K.; Fujii, T.; Horiguchi, J.; et al. Molecular pathogenesis of triple-negative breast cancer based on microRNA expression signatures: Antitumor miR-204-5p targets AP1S3. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 63, 1197–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallai, R.; Bhaskar, A.; Barnett-Bernodat, N.; Gallo-Ebert, C.; Pusey, M.; Nickels, J.T., Jr.; Rice, L.M. Leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 59 mediates nuclear import of cancerous inhibitor of PP2A in prostate cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 6383–6390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigola, J.; Remus, D.; Mehanna, A.; Diffley, J.F. ATPase-dependent quality control of DNA replication origin licensing. Nature 2013, 495, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mele, D.A.; Bista, P.; Baez, D.V.; Huber, B.T. Dipeptidyl peptidase 2 is an essential survival factor in the regulation of cell quiescence. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 2425–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frescas, D.; Pagano, M. Deregulated proteolysis by the F-box proteins SKP2 and beta-TrCP: Tipping the scales of cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 438–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Li, Y.; Xue, D.; Liu, Y. PCMT1 is an unfavorable predictor and functions as an oncogene in bladder cancer. IUBMB Life 2018, 70, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, D.; Atkin, W.; Lenz, H.J.; Lynch, H.T.; Minsky, B.; Nordlinger, B.; Starling, N. Colorectal cancer. Lancet 2010, 375, 1030–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, I.B.; Tan, P. Genetics: An 18-gene signature (ColoPrint(R)) for colon cancer prognosis. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 8, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindarajan, R.; Posey, J.; Chao, C.Y.; Lu, R.; Jadhav, T.; Javed, A.Y.; Javed, A.; Mahmoud, F.A.; Osarogiagbon, R.U.; Manne, U. A comparison of 12-gene colon cancer assay gene expression in African American and Caucasian patients with stage II colon cancer. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Deng, J.; Wei, X.; Yuan, W.; Ma, J. Integrated analysis of competing endogenous RNA networks revealing five prognostic biomarkers associated with colorectal cancer. J. Cell Biochem. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; He, M.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, C.; Wei, S.; Bian, X.; Christopher, O.; Xie, L. The Prognostic and Clinicopathological Roles of PD-L1 Expression in Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.H.; Zhou, H.; Cooper, L.; Huang, J.L.; Zhu, S.B.; Zhao, X.X.; Ding, H.; Pan, Y.L.; Rong, L. LAYN Is a Prognostic Biomarker and Correlated With Immune Infiltrates in Gastric and Colon Cancers. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zou, S.; Guan, X.; Wang, M.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Li, C.; Lin, H.; Liu, X.; Yang, R.; et al. Apolipoprotein E Overexpression Is Associated With Tumor Progression and Poor Survival in Colorectal Cancer. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Cui, D.; Liu, G.; Xu, H.; Peng, X.; Duan, J.; Liu, L. Cancer stem cell associated eight gene-based signature predicts clinical outcomes of colorectal cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Zhu, X.; Yan, T.; Yu, C.; Shen, C.; Hu, Y.; Hong, J.; Chen, H.; Fang, J.Y. Recurrence-associated gene signature optimizes recurrence-free survival prediction of colorectal cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2017, 11, 1544–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandimalla, R.; Ozawa, T.; Gao, F.; Wang, X.; Goel, A.; T1 Colorectal Cancer Study Group. Gene Expression Signature in Surgical Tissues and Endoscopic Biopsies Identifies High-Risk T1 Colorectal Cancers. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 2338–2341.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, M.M. Digital multiplexed gene expression analysis using the NanoString nCounter system. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldman-Jones, M.H.; Brant, R.; Rooney, C.; Geh, C.; Emery, H.; Harbron, C.G.; Wappett, M.; Sharpe, A.; Dymond, M.; Barrett, J.C.; et al. Evaluating Robustness and Sensitivity of the NanoString Technologies nCounter Platform to Enable Multiplexed Gene Expression Analysis of Clinical Samples. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2587–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| S.No | Gene Symbol | Entrez Gene ID | Cytoband | Gene Title | Median Gene Expression, TPM (Transcripts per million) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tumor (n = 275) | Normal (n = 349) | |||||
| Genes selected from TPA and cBioportal | ||||||
| 1 | PI4K2B | 55300 | 4p15.2 | Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase type 2 beta | 0.05 | 0 |
| 2 | PBXIP1 | 57326 | 1q21.3 | Pre-B-cell leukemia homeobox interacting protein 1 | 31.3 | 75.75 |
| 3 | CHEK1 | 1111 | 11q24.2 | Checkpoint kinase 1 | 18.12 | 2.5 |
| 4 | DLAT | 1737 | 11q23.1 | Dihydrolipoamide S-acetyltransferase | 23.51 | 15.09 |
| 5 | FAM50A | 9130 | Xq28 | Family with sequence similarity 50, member A | 66.45 | 62.17 |
| 6 | KDM4B | 23030 | 19p13.3 | Lysine (K)-specific demethylase 4B | 9.39 | 12.39 |
| 7 | DPP7/2 | 29952 | 9q34.3 | Dipeptidyl-peptidase 7 | 100.63 | 113.3 |
| Genes selected from prognostic significance in multiple cancers | ||||||
| 8 | YWHAB | 7529 | 20q13.1 | Tryptophan 5-monooxygenase activation protein, beta | 190.47 | 93.05 |
| 9 | DSG2 | 1829 | 18q12.1 | Desmoglein 2 | 76.26 | 3.67 |
| 10 | PCMT1 | 5110 | 6q25.1 | Protein-L-isoaspartate (D-aspartate) O-methyltransferase | 48.97 | 38.82 |
| 11 | MCM4 | 4173 | 8q11.2 | Minichromosome maintenance complex component 4 | 53.46 | 8.09 |
| 12 | AGFG1 | 3267 | 2q36.3 | ArfGAP with FG repeats 1 | 45.46 | 24.07 |
| 13 | E2F1 | 1869 | 20q11.2 | E2F transcription factor 1 | 13.51 | 2.13 |
| 14 | LRRC59 | 55379 | 17q21.33 | Leucine rich repeat containing 59 | 107.08 | 34.6 |
| 15 | SLAMF6 | 114836 | 1q23.2 | SLAM family member 6 | 1.38 | 0.82 |
| 16 | FBXO46 | 23403 | 19q13.3 | F-box protein 46 | 11.1 | 9.98 |
| 17 | ITGA5 | 3678 | 12q11-q13 | Integrin alpha 5 | 21.76 | 191.95 |
| Clinical Parameters | No. of Patients | Percentage of Patients (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Age | ||
| <68 y | 27 | 30.68 |
| >68 y | 61 | 69.32 |
| Gender | ||
| Male | 37 | 42.05 |
| Female | 51 | 57.95 |
| Stage - AJCC | ||
| I | 14 | 15.91 |
| II | 30 | 34.09 |
| III | 26 | 29.55 |
| IV | 18 | 20.45 |
| Grade | ||
| I - Well differentiated | 18 | 20.45 |
| II: Intermediate differentiated | 40 | 45.45 |
| III: Poorly differentiated | 23 | 26.14 |
| IV: Undifferentiated | 7 | 7.95 |
| Distant Metastasis | ||
| Yes | 33 | 37.5 |
| No | 54 | 61.36 |
| Vital Status | ||
| Dead | 57 | 64.77 |
| Alive | 31 | 35.23 |
| Ethnicity | ||
| Caucasian | 47 | 53.41 |
| African-American | 38 | 43.18 |
| Alcohol Use | ||
| No Usage | 67 | 76.14 |
| Users | 20 | 22.73 |
| Tobacco Use | ||
| No | 56 | 63.64 |
| Yes | 32 | 36.36 |
| Chemotherapy after surgery | ||
| Administered | 26 | 29.54 |
| Not administered | 62 | 70.45 |
| Family History | ||
| No | 41 | 46.59 |
| Yes | 35 | 39.77 |
| Months survival (median) | ||
| Dead | 11.8 months | |
| Alive | 54.1 months | |
| Gene | Univariate | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Ratio | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| CHEK1 | 0.66 | 0.31–1.37 | 0.26 |
| DLAT | 0.7 | 0.33–1.48 | 0.35 |
| DPP7/2 | 0.38 | 0.14–0.89 | 0.02 |
| FAM50A | 0.5 | 0.19–1.45 | 0.2 |
| KDMB | 0.72 | 0.31–1.57 | 0.41 |
| PBXIP1 | 1.14 | 0.51–2.66 | 0.74 |
| PI4K2B | 1.09 | 0.52–2.38 | 0.8 |
| DSG | 1.3 | 0.66–2.93 | 0.39 |
| E2F | 1.77 | 0.79–4.05 | 0.15 |
| MCM4 | 2.69 | 1.19–6.35 | 0.01 |
| PCMT1 | 0.66 | 0.30–1.41 | 0.28 |
| YWHAB | 3.76 | 1.58–9.66 | 0.001 |
| AGFG1 | 0.8 | 0.39–1.82 | 0.65 |
| FBXO46 | 1.4 | 0.65–2.94 | 0.37 |
| ITGA5 | 0.71 | 0.34–1.48 | 0.37 |
| LRRC59 | 2.32 | 1.09–5.35 | 0.02 |
| SLAMF6 | 1 | 0.50–2.45 | 0.81 |
| Variable | Univariate | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Ratio | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Prognostic score (composite DPP7/2, YWHAB, MCM4 and FBXO46) | 5.39 | 2.19–15.26 | <0.001 * |
| Age (>68, <68 years) | 0.78 | 0.37–1.66 | 0.51 |
| Gender (Male, Female) | 0.95 | 0.45–2.06 | 0.89 |
| Stage (III + IV, I + II) | 2.9 | 1.39–6.36 | <0.001 * |
| Grade (III, I + II) | 1.79 | 0.73–5.3 | 0.2 |
| Ethnicity (African-American, Caucasian) | 0.9 | 0.41–2.07 | 0.81 |
| Alcohol consumption (Yes, No) | 0.6 | 0.26–1.55 | 0.27 |
| Tobacco smoking (Yes, No) | 0.58 | 0.25–1.23 | 0.16 |
| Variable | Multivariate | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Ratio | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Prognostic score (composite DPP7/2, YWHAB, MCM4 and FBXO46) | 3.42 | 1.71–7.94 | <0.001 * |
| Age (>68, <68 years) | 1.05 | 0.35–3.19 | 0.92 |
| Gender (Male, Female) | 2.34 | 0.62–9.37 | 0.20 |
| Stage (III + IV, I + II) | 4.56 | 1.33–19.15 | 0.01 * |
| Grade (III, I + II) | 0.19 | 0.02–1.18 | 0.07 |
| Ethnicity (African-American, Caucasian) | 2.89 | 0.69–12.47 | 0.14 |
| Alcohol consumption (Yes, No) | 7.38 | 1.58–38.14 | 0.01 * |
| Tobacco smoking (Yes, No) | 0.08 | 0.01–0.31 | 0.01 * |
| Gene | Function and Role in Cancer | References |
|---|---|---|
| YWHAB | Signal transduction and cell cycle, genetically altered in multiple cancers | [22,23] |
| MCM4 | Essential role in DNA replication, dysregulation found in several cancers. | [24,25] |
| DPP7/2 | Inhibition of DPP7/2 has been linked with apoptosis through c-Myc and p53 related pathways | [26] |
| FBXO46 | Deregulated cell cycle, cancer biogenesis | [27] |
| LRRC59 | Essential for nuclear import of Fibroblast growth factor 1, FGF promotes angiogenesis with VEGF | [24,28] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahluwalia, P.; Mondal, A.K.; Bloomer, C.; Fulzele, S.; Jones, K.; Ananth, S.; Gahlay, G.K.; Heneidi, S.; Rojiani, A.M.; Kota, V.; et al. Identification and Clinical Validation of a Novel 4 Gene-Signature with Prognostic Utility in Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3818. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153818
Ahluwalia P, Mondal AK, Bloomer C, Fulzele S, Jones K, Ananth S, Gahlay GK, Heneidi S, Rojiani AM, Kota V, et al. Identification and Clinical Validation of a Novel 4 Gene-Signature with Prognostic Utility in Colorectal Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(15):3818. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153818
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhluwalia, Pankaj, Ashis K. Mondal, Chance Bloomer, Sadanand Fulzele, Kimya Jones, Sudha Ananth, Gagandeep K. Gahlay, Saleh Heneidi, Amyn M. Rojiani, Vamsi Kota, and et al. 2019. "Identification and Clinical Validation of a Novel 4 Gene-Signature with Prognostic Utility in Colorectal Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 15: 3818. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153818
APA StyleAhluwalia, P., Mondal, A. K., Bloomer, C., Fulzele, S., Jones, K., Ananth, S., Gahlay, G. K., Heneidi, S., Rojiani, A. M., Kota, V., & Kolhe, R. (2019). Identification and Clinical Validation of a Novel 4 Gene-Signature with Prognostic Utility in Colorectal Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(15), 3818. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153818






