Modulating Expression of Thioredoxin Interacting Protein (TXNIP) Prevents Secondary Damage and Preserves Visual Function in a Mouse Model of Ischemia/Reperfusion
Abstract
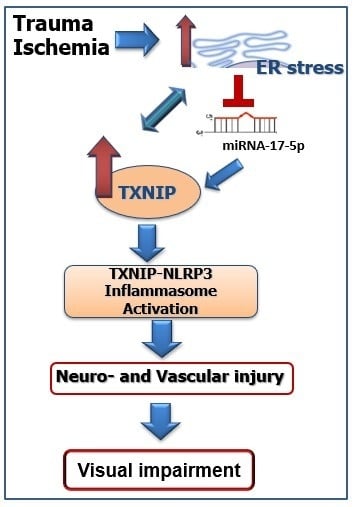
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Ocular Ischemia-Triggered Oxidative Stress and TXNIP Expression That Was Sustained for 14 Days
2.2. Ocular Ischemia-Triggered Activation of Glial Müller Cells That Was Sustained for 14 Days
2.3. IR Injury and Hypoxia-Triggered ER Stress Markers and Suppressed miR-17-5p Expression
2.3.1. Hypoxia-Triggered ER Stress Markers and Suppressed miR-17-5p Expression In-Vitro
2.3.2. Deletion of TXNIP Prevents IR Injury-Mediated ER Stress and Dysregulation of miR-17-5p In-Vivo
2.4. IR Injury and Hypoxia-Triggered NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and IL-1β Expression
2.4.1. Hypoxia-Triggered NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and IL-1β Expression In-Vitro
2.4.2. Deletion of TXNIP-Prevented IR-Induced Expression of Inflammatory Mediators In-Vivo
2.5. Deletion of TXNIP Prevented IR-Mediated Gliosis and Neuronal Cell Death Post-IR Injury
2.6. Deletion of TXNIP-Prevented IR-Mediated Neuro and Vascular Degeneration Post-IR Injury
2.7. Intervention Prevented Sustained Expression of TXNIP, ER-Stress and JNK Activation
2.8. Modulation of TXNIP Expression Improved Visual Function after IR Injury
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Retinal Ischemia-Reperfusion
4.3. Intravitreal Injection of TXNIP Antisense Oligomers (ASO)
4.4. Real-Time Quantitative PCR and MicroRNA Detection
4.5. Western Blotting
4.6. Isolation of Retinal Vasculature and Determination of Occluded (Acellular) Capillaries
4.7. Immunostaining of Glial Activation Using GFAP and Colocalization Studies
4.8. Müller Cell Culture
4.9. Slot Blot Analysis
4.10. ELISA
4.11. Visual Assessment
4.12. Terminal dUTP Nick End-Labeling (TUNEL) Analysis
4.13. Quantification of Total Neuronal Cells in Ganglion Cell Layer (GCL)
4.14. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATF-6 | activating transcription factor 6 |
| ASK-1 | Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 |
| ASO | Antisense Oligomers |
| CHOP | C/EBP-homologous protein |
| ER | Endoplasmic Reticulum |
| ELISA | Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| 4-HNE | 4-hydroxynenoal |
| IR | Ischemia Reperfusion |
| IRE-1α | inositol-requiring enzyme-1-alpha |
| IOP | Intraocular pressure |
| miR- | MicroRNA |
| NLRP3 | NOD-like Receptor Pyrin Domain Containing 3 |
| PERK | RNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR)-like ER kinase |
| TXNIP | Thioredoxin Interacting protein |
| TUNEL | Terminal dUTP nick end-labeling |
| UPR | Unfolded protein response |
References
- Simo, R.; Stitt, A.W.; Gardner, T.W. Neurodegeneration in diabetic retinopathy: Does it really matter? Diabetologia 2018, 61, 1902–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.; McGuire, P.G. Retinal and choroidal angiogenesis: Pathophysiology and strategies for inhibition. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2003, 22, 721–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, L.A. Neuroprotection in optic neuropathy. Asia Pac. J. Ophthalmol. (Phila.) 2018, 7, 246–250. [Google Scholar]
- Adornetto, A.; Russo, R.; Parisi, V. Neuroinflammation as a target for glaucoma therapy. Neural Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.Y.; Fu, Z.J.; Lo, A.C. Hypoxia-induced oxidative stress in ischemic retinopathy. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2012, 2012, 426769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, K.; Kecova, H.; Hernandez-Merino, E.; Kardon, R.H.; Harper, M.M. Retinal ganglion cell damage in an experimental rodent model of blast-mediated traumatic brain injury. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 3440–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junn, E.; Han, S.H.; Im, J.Y.; Yang, Y.; Cho, E.W.; Um, H.D.; Kim, D.K.; Lee, K.W.; Han, P.L.; Rhee, S.G.; et al. Vitamin d3 up-regulated protein 1 mediates oxidative stress via suppressing the thioredoxin function. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 6287–6295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.S.; Jung, J.E.; Narasimhan, P.; Sakata, H.; Chan, P.H. Induction of thioredoxin-interacting protein is mediated by oxidative stress, calcium, and glucose after brain injury in mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 46, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lerner, A.G.; Upton, J.P.; Praveen, P.V.; Ghosh, R.; Nakagawa, Y.; Igbaria, A.; Shen, S.; Nguyen, V.; Backes, B.J.; Heiman, M.; et al. Ire1alpha induces thioredoxin-interacting protein to activate the nlrp3 inflammasome and promote programmed cell death under irremediable er stress. Cell Metab. 2012, 16, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coucha, M.; Mohamed, I.N.; Elshaer, S.L.; Mbata, O.; Bartasis, M.L.; El-Remessy, A.B. High fat diet dysregulates microrna-17-5p and triggers retinal inflammation: Role of endoplasmic-reticulum-stress. World J. Diabetes 2017, 8, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Fu, N.; Yang, P. Mir-17 downregulation by high glucose stabilizes thioredoxin-interacting protein and removes thioredoxin inhibition on ask1 leading to apoptosis. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 150, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetz, C.; Papa, F.R. The unfolded protein response and cell fate control. Mol. Cell 2018, 69, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, K.; Wang, J.J.; Zhang, S.X. The unfolded protein response signaling and retinal Müller cell metabolism. Neural Regen. Res. 2018, 13, 1861–1870. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, I.N.; Ishrat, T.; Fagan, S.C.; El-Remessy, A.B. Role of inflammasome activation in the pathophysiology of vascular diseases of the neurovascular unit. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2015, 22, 1188–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, I.N.; Hafez, S.S.; Fairaq, A.; Ergul, A.; Imig, J.D.; El-Remessy, A.B. Thioredoxin-interacting protein is required for endothelial nlrp3 inflammasome activation and cell death in a rat model of high-fat diet. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elshaer, S.L.; Mohamed, I.N.; Coucha, M.; Altantawi, S.; Eldahshan, W.; Bartasi, M.L.; Shanab, A.Y.; Lorys, R.; El-Remessy, A.B. Deletion of txnip mitigates high-fat diet-impaired angiogenesis and prevents inflammation in a mouse model of critical limb ischemia. Antioxidants 2017, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, A.A.; Brown, R.E. Age-related changes in visual acuity, learning and memory in c57bl/6j and dba/2j mice. Neurobiol. Aging 2007, 28, 1577–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Gong, B.; Hatala, D.A.; Kern, T.S. Retinal ischemia and reperfusion causes capillary degeneration: Similarities to diabetes. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsaid, M.A.; Matragoon, S.; El-Remessy, A.B. Thioredoxin-interacting protein expression is required for vegf-mediated angiogenic signal in endothelial cells. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 2199–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Qi, Y.; Yang, X. Neuroprotective effects of crocin against oxidative stress induced by ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat retina. Ophthalmic Res. 2015, 54, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Du, G.; Wang, D.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, G.; Jiang, H. Overexpression of heme oxygenase-1 in mesenchymal stem cells augments their protection on retinal cells in vitro and attenuates retinal ischemia/reperfusion injury in vivo against oxidative stress. Stem Cells Int. 2017, 2017, 4985323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Gayyar, M.M.; Abdelsaid, M.A.; Matragoon, S.; Pillai, B.A.; El-Remessy, A.B. Thioredoxin interacting protein is a novel mediator of retinal inflammation and neurotoxicity. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 164, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El-Azab, M.F.; Baldowski, B.R.; Mysona, B.A.; Shanab, A.Y.; Mohamed, I.N.; Abdelsaid, M.A.; Matragoon, S.; Bollinger, K.E.; Saul, A.; El-Remessy, A.B. Deletion of thioredoxin-interacting protein preserves retinal neuronal function by preventing inflammation and vascular injury. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 1299–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ren, X.; Lu, H.; Wang, N.; Zhang, C.; Ji, Y.; Cui, S.; Dong, Y.; Yang, K.; Du, M.; Diao, F.; et al. Thioredoxin is implicated in the antiapoptotic effects of grape seed proanthocyanidin extract during hyperglycemia. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 7731–7737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Tong, N.; Gong, Y.; Qiu, Q.; Yin, L.; Lv, X.; Wu, X. Valproate protects the retina from endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis after ischemia-reperfusion injury. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 504, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhu, X.; Fang, F.; Jiang, D.; Tang, L. Down-regulation of grp78 enhances apoptosis via chop pathway in retinal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Neurosci. Lett. 2014, 575, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Miao, L.; Liang, F.; Liu, X.; Xu, L.; Teng, X.; Wang, Q.; Ridder, W.H., 3rd; Shindler, K.S.; Sun, Y.; et al. Neuroprotection by eif2alpha-chop inhibition and xbp-1 activation in eae/optic neuritiss. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hata, M.; Ikeda, H.O.; Kikkawa, C.; Iwai, S.; Muraoka, Y.; Hasegawa, T.; Kakizuka, A.; Yoshimura, N. Kus121, a vcp modulator, attenuates ischemic retinal cell death via suppressing endoplasmic reticulum stress. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Xia, F.; Ha, Y.; Zhu, S.; Li, Y.; Folorunso, O.; Pashaei-Marandi, A.; Lin, P.Y.; Tilton, R.G.; Pierce, A.P.; et al. Neuroprotective effects of hsf1 in retinal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2019, 60, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlin, B.A.; Feenstra, D.J.; Mohr, S. Müller cells and diabetic retinopathy. Vision Res. 2017, 139, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.R.; Kim, J.H.; Park, H.L.; Park, C.K. Ischemia reperfusion injury triggers tnfalpha induced-necroptosis in rat retina. Curr. Eye Res. 2017, 42, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Zhuang, J.; Hu, P.; Ye, W.; Chen, S.; Pang, Y.; Li, N.; Deng, C.; Zhang, X. Resveratrol delays retinal ganglion cell loss and attenuates gliosis-related inflammation from ischemia-reperfusion injury. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, 3879–3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimouchi, A.; Yokota, H.; Ono, S.; Matsumoto, C.; Tamai, T.; Takumi, H.; Narayanan, S.P.; Kimura, S.; Kobayashi, H.; Caldwell, R.B.; et al. Neuroprotective effect of water-dispersible hesperetin in retinal ischemia reperfusion injury. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 60, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, D.C.; Bordone, M.P.; Chianelli, M.S.; Rosenstein, R.E. Retinal neuroprotection against ischemia-reperfusion damage induced by postconditioning. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 3922–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Chen, C.; McLaughlin, T.; Wang, Y.; Le, Y.Z.; Wang, J.J.; Zhang, S.X. Loss of x-box binding protein 1 in Müller cells augments retinal inflammation in a mouse model of diabetes. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, T.S.; Lee, I.; Huttemann, M.; Kumar, A.; Nantwi, K.D.; Singh, L.P. Txnip links innate host defense mechanisms to oxidative stress and inflammation in retinal Müller glia under chronic hyperglycemia: Implications for diabetic retinopathy. Exp. Diabetes Res. 2012, 2012, 438238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Zhu, X.; Guo, B.; Zheng, T.; Ren, J.; Zeng, W.; Chen, X.; Ke, M. Unfolded protein response pathways correlatively modulate endoplasmic reticulum stress responses in rat retinal Müller cells. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 2019, 9028483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Dixon, B.J.; Doycheva, D.M.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Q.; He, Y.; Guo, Z.; Nowrangi, D.; Flores, J.; et al. Ire1alpha inhibition decreased txnip/nlrp3 inflammasome activation through mir-17-5p after neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in rats. J. Neuroinflammation 2018, 15, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.W.; Zhang, J.; Ancrum, T.; Manevich, Y.; Townsend, D.M.; Tew, K.D. Glutathione s-transferase p-mediated protein s-glutathionylation of resident endoplasmic reticulum proteins influences sensitivity to drug-induced unfolded protein response. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2017, 26, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsaid, M.A.; El-Remessy, A.B. S-glutathionylation of lmw-ptp regulates vegf-mediated fak activation and endothelial cell migration. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 4751–4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, L.; Devi, T.S.; Hosoya, K.; Terasaki, T.; Singh, L.P. Thioredoxin interacting protein (txnip) induces inflammation through chromatin modification in retinal capillary endothelial cells under diabetic conditions. J. Cell. Physiol. 2009, 221, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trueblood, K.E.; Mohr, S.; Dubyak, G.R. Purinergic regulation of high-glucose-induced caspase-1 activation in the rat retinal Müller cell line rmc-1. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2011, 301, C1213–C1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duvigneau, J.C.; Luis, A.; Gorman, A.M.; Samali, A.; Kaltenecker, D.; Moriggl, R.; Kozlov, A.V. Crosstalk between inflammatory mediators and endoplasmic reticulum stress in liver diseases. Cytokine 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gessner, D.K.; Grone, B.; Couturier, A.; Rosenbaum, S.; Hillen, S.; Becker, S.; Erhardt, G.; Reiner, G.; Ringseis, R.; Eder, K. Dietary fish oil inhibits pro-inflammatory and er stress signalling pathways in the liver of sows during lactation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishrat, T.; Mohamed, I.N.; Pillai, B.; Soliman, S.; Fouda, A.Y.; Ergul, A.; El-Remessy, A.B.; Fagan, S.C. Thioredoxin-interacting protein: A novel target for neuroprotection in experimental thromboembolic stroke in mice. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 51, 766–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wang, L.; Huang, K.; Zheng, L. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in retinal vascular degeneration: Protective role of resveratrol. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 3241–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, T.; Verkman, A.S. Aquaporin-4 gene disruption in mice protects against impaired retinal function and cell death after ischemia. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 4477–4483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, R.; Coucha, M.; Elshaer, S.L.; Artham, S.; Lemtalsi, T.; El-Remessy, A.B. Inducible overexpression of endothelial prongf as a mouse model to study microvascular dysfunction. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 746–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsaid, M.A.; Pillai, B.A.; Matragoon, S.; Prakash, R.; Al-Shabrawey, M.; El-Remessy, A.B. Early intervention of tyrosine nitration prevents vaso-obliteration and neovascularization in ischemic retinopathy. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 332, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matragoon, S.; Al-Gayyar, M.M.; Mysona, B.A.; Abdelsaid, M.A.; Pillai, B.A.; Neet, K.E.; Fagan, S.C.; El-Remessy, A.B. Electroporation-mediated gene delivery of cleavage-resistant pro-nerve growth factor causes retinal neuro- and vascular degeneration. Mol. Vis. 2012, 18, 2993–3003. [Google Scholar]










| Gene | Forward | Reverse |
|---|---|---|
| 18 S | CGCGGTTCTATTTTGTTGGT | AGTCGGCATCGTTTATGGTC |
| IRE1α | GGGTTGCTGTCGTGCCTCGAG | TGGGGGCCTTCCAGCAAAGGA |
| TXNIP | AAGCTGTCCTCAGTCAGAGGCAAT | ATGACTTTCTTGGAGCCAGGGACA |
| Antibody | Source | Catalogue # | Company |
|---|---|---|---|
| TXNIP TXNIP | Monoclonal Polyclonal | K0205-3 403700 | MBL Abacus ALS Australia Invitrogen-Thermo-Fischer Scientific, Waltham, MA |
| NLRP-3 | Polyclonal | LS-B4321 | LifeSpan Biosciences, Inc, Seatle, WA |
| IL1β | Polyclonal | ab9722 | Abcam, Cambridge, MA |
| TNF-a | Polyclonal | ab9635 | Abcam, Cambridge, MA |
| Tubulin | Monoclonal | ab4074 | Abcam, Cambridge, MA |
| GAPDH | Polyclonal | 5174 | Cell Signaling Tech, Danvers, MA |
| CHOP | Polyclonal | 3082 | Cell Signaling Tech, Danvers, MA |
| Antibody | Source | Catalogue # | Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|
| TXNIP | Polyclonal | 403700 | 1:100 |
| Glutamine Synthetase (GS) | Monoclonal | MA5-27749 | 1:100 |
| Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein (GFAP) | Polyclonal | PA5-16291 | 1:200 |
| Oregon green-Conjugated secondary antibody | Goat anti-rabbit | O-11038 | 1:500 |
| Texas red-Conjugated secondary antibody | Goat anti-mouse | T-862 | 1:500 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coucha, M.; Shanab, A.Y.; Sayed, M.; Vazdarjanova, A.; El-Remessy, A.B. Modulating Expression of Thioredoxin Interacting Protein (TXNIP) Prevents Secondary Damage and Preserves Visual Function in a Mouse Model of Ischemia/Reperfusion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3969. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20163969
Coucha M, Shanab AY, Sayed M, Vazdarjanova A, El-Remessy AB. Modulating Expression of Thioredoxin Interacting Protein (TXNIP) Prevents Secondary Damage and Preserves Visual Function in a Mouse Model of Ischemia/Reperfusion. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(16):3969. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20163969
Chicago/Turabian StyleCoucha, Maha, Ahmed Y. Shanab, Mohamed Sayed, Almira Vazdarjanova, and Azza B. El-Remessy. 2019. "Modulating Expression of Thioredoxin Interacting Protein (TXNIP) Prevents Secondary Damage and Preserves Visual Function in a Mouse Model of Ischemia/Reperfusion" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 16: 3969. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20163969
APA StyleCoucha, M., Shanab, A. Y., Sayed, M., Vazdarjanova, A., & El-Remessy, A. B. (2019). Modulating Expression of Thioredoxin Interacting Protein (TXNIP) Prevents Secondary Damage and Preserves Visual Function in a Mouse Model of Ischemia/Reperfusion. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(16), 3969. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20163969