Proteomic Phosphosite Analysis Identified Crucial NPM-ALK-Mediated NIPA Serine and Threonine Residues
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Phosphorylation of NIPA in ALCL Cells Is Induced in an NPM-ALK-Dependent Manner
2.2. Proteomic Phosphosite Analysis Identified Five Crucial NPM-ALK-Induced NIPA Phosphosites
2.3. NPM-ALK-Mediated NIPA Phosphorylation Does Not Change the SCFNIPA-Complex Formation but Might Influence the NIPA Localization at the Nucleus
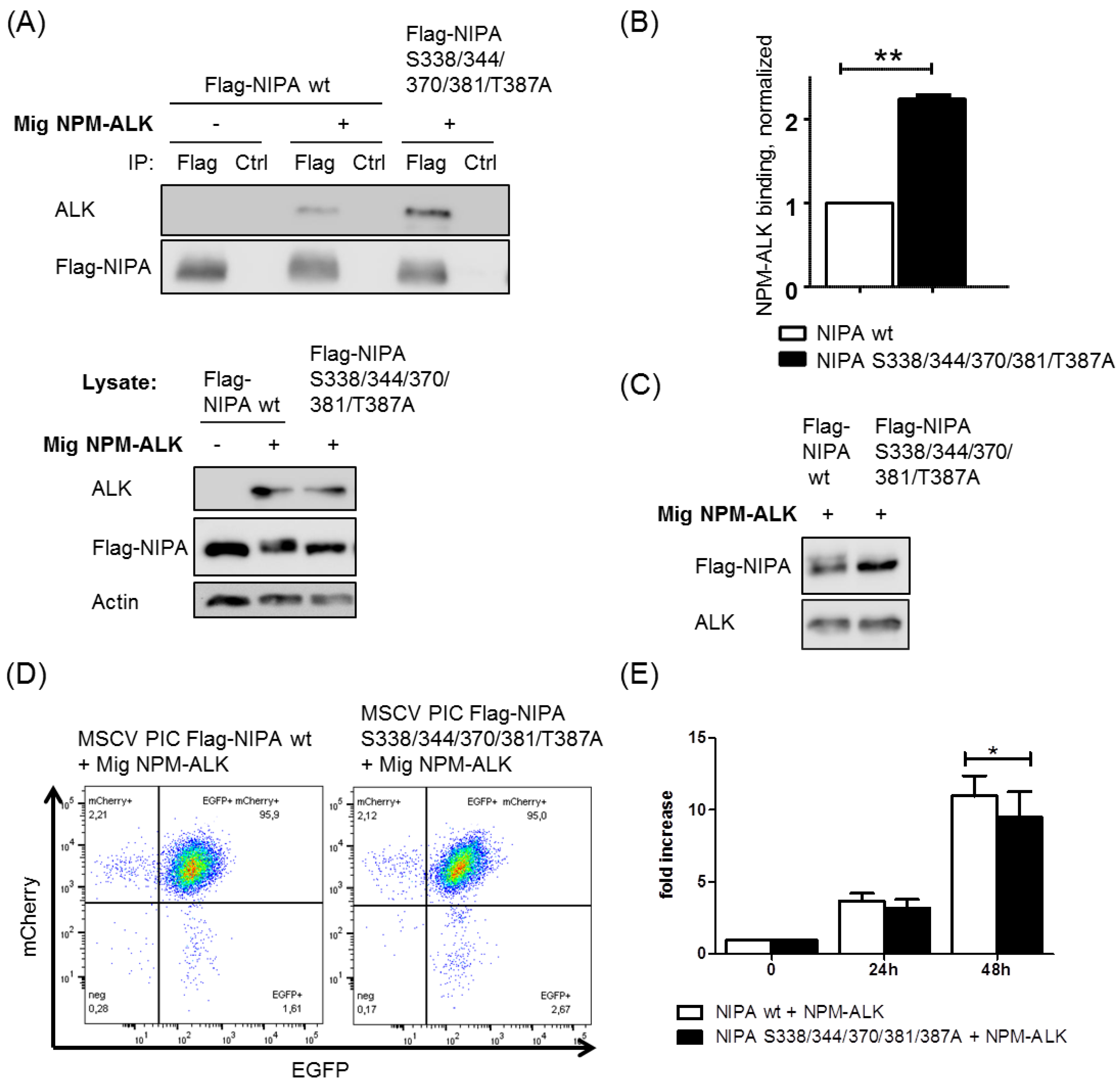
2.4. NIPA Phosphodeficiency Leads to Enhanced NPM-ALK Binding and Impaired Cell Proliferation in NPM-ALK-Positive Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plasmids
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Consensus Sequence Analysis
4.4. Flow Cytometry Analysis
4.5. Immunofluorescence Microscopy
4.6. Immunoprecipitation and Immunoblot
4.7. MTS Assay and Soft-Agar Assay
4.8. Proteomic Analysis
4.9. Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stein, H.; Mason, D.Y.; Gerdes, J.; O’Connor, N.; Wainscoat, J.; Pallesen, G.; Gatter, K.; Falini, B.; Delsol, G.; Lemke, H.; et al. The expression of the Hodgkin’s disease associated antigen Ki-1 in reactive and neoplastic lymphoid tissue: Evidence that Reed-Sternberg cells and histiocytic malignancies are derived from activated lymphoid cells. Blood 1985, 66, 848–858. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pileri, S.; Falini, B.; Delsol, G.; Stein, H.; Baglioni, P.; Poggi, S.; Martelli, M.F.; Rivano, M.T.; Mason, D.Y.; Stansfeld, A.G. Lymphohistiocytic T-cell lymphoma (anaplastic large cell lymphoma CD30+/Ki-1 + with a high content of reactive histiocytes). Histopathology 1990, 16, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreri, A.J.M.; Govi, S.; Pileri, S.A.; Savage, K.J. Anaplastic large cell lymphoma, ALK-positive. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2012, 83, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, S.W.; Kirstein, M.N.; Valentine, M.B.; Dittmer, K.G.; Shapiro, D.N.; Saltman, D.L.; Look, A.T. Fusion of a kinase gene, ALK, to a nucleolar protein gene, NPM, in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Science 1994, 263, 1281–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiarle, R.; Voena, C.; Ambrogio, C.; Piva, R.; Inghirami, G. The anaplastic lymphoma kinase in the pathogenesis of cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cussac, D.; Greenland, C.; Roche, S.; Bai, R.Y.; Duyster, J.; Morris, S.W.; Delsol, G.; Allouche, M.; Payrastre, B. Nucleophosmin-anaplastic lymphoma kinase of anaplastic large-cell lymphoma recruits, activates and uses pp60c-src to mediate its mitogenicity. Blood 2004, 103, 1464–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, H.M.; Lai, R. Pathobiology of ALK+ anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Blood 2007, 110, 2259–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inghirami, G.; Pileri, S.A. European T-Cell Lymphoma Study Group Anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 2011, 28, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Palmer, R.H.; Vernersson, E.; Grabbe, C.; Hallberg, B. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase: Signalling in development and disease. Biochem. J. 2009, 420, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, T.; Bai, R.Y.; Bassermann, F.; von Klitzing, C.; Klumpen, S.; Miething, C.; Morris, S.W.; Peschel, C.; Duyster, J. Identification and Characterization of a Nuclear Interacting Partner of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (NIPA). J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 30028–30036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassermann, F.; von Klitzing, C.; Münch, S.; Bai, R.Y.; Kawaguchi, H.; Morris, S.W.; Peschel, C.; Duyster, J. NIPA Defines an SCF-Type Mammalian E3 Ligase that Regulates Mitotic Entry. Cell 2005, 122, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illert, A.L.; Zech, M.; Moll, C.; Albers, C.; Kreutmair, S.; Peschel, C.; Bassermann, F.; Duyster, J. Extracellular Signal-regulated Kinase 2 (ERK2) Mediates Phosphorylation and Inactivation of Nuclear Interaction Partner of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (NIPA) at G2/M. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 37997–38005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassermann, F.; von Klitzing, C.; Illert, A.L.; Münch, S.; Morris, S.W.; Pagano, M.; Peschel, C.; Duyster, J. Multisite Phosphorylation of Nuclear Interaction Partner of ALK (NIPA) at G2/M Involves Cyclin B1/Cdk1. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 15965–15972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceccon, M.; Merlo, M.E.B.; Mologni, L.; Poggio, T.; Varesio, L.M.; Menotti, M.; Bombelli, S.; Rigolio, R.; Manazza, A.D.; Di Giacomo, F.; et al. Excess of NPM-ALK oncogenic signaling promotes cellular apoptosis and drug dependency. Oncogene 2016, 35, 3854–3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, M.T.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wasik, M.A. Nucleophosmin-anaplastic lymphoma kinase: The ultimate oncogene and therapeutic target. Blood 2017, 129, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, J.D.; Medeiros, L.J.; Rassidakis, G.Z.; Yared, M.A.; Tsioli, P.; Leventaki, V.; Schmitt-Graeff, A.; Herling, M.; Amin, H.M.; Lai, R. Differential expression and clinical significance of tyrosine-phosphorylated STAT3 in ALK+ and ALK- anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 3692–3699. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chiarle, R.; Simmons, W.J.; Cai, H.; Dhall, G.; Zamo, A.; Raz, R.; Karras, J.G.; Levy, D.E.; Inghirami, G. Stat3 is required for ALK-mediated lymphomagenesis and provides a possible therapeutic target. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaccarotella, E.; Pellegrino, E.; Ferracin, M.; Ferreri, C.; Cuccuru, G.; Liu, C.; Iqbal, J.; Cantarella, D.; Taulli, R.; Provero, P.; et al. STAT3-mediated activation of microRNA cluster 17~92 promotes proliferation and survival of ALK-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Haematologica 2014, 99, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sattu, K.; Hochgräfe, F.; Wu, J.; Umapathy, G.; Schönherr, C.; Ruuth, K.; Chand, D.; Witek, B.; Fuchs, J.; Li, P.K.; et al. Phosphoproteomic analysis of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) downstream signaling pathways identifies signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 as a functional target of activated ALK in neuroblastoma cells. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 5269–5282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasov, N.; Bonzheim, I.; Rudelius, M.; Klier, M.; Dau, T.; Angermeier, D.; Duyster, J.; Pittaluga, S.; Fend, F.; Raffeld, M.; et al. C/EBPβ expression in ALK-positive anaplastic large cell lymphomas is required for cell proliferation and is induced by the STAT3 signaling pathway. Haematologica 2010, 95, 760–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, R.Y.; Ouyang, T.; Miething, C.; Morris, S.W.; Peschel, C.; Duyster, J. Nucleophosmin-anaplastic lymphoma kinase associated with anaplastic large-cell lymphoma activates the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt antiapoptotic signaling pathway. Blood 2000, 96, 4319–4327. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hübinger, G.; Scheffrahn, I.; Müller, E.; Bai, R.; Duyster, J.; Morris, S.W.; Schrezenmeier, H.; Bergmann, L. The tyrosine kinase NPM-ALK, associated with anaplastic large cell lymphoma, binds the intracellular domain of the surface receptor CD30 but is not activated by CD30 stimulation. Exp. Hematol. 1999, 27, 1796–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.Y.; Dieter, P.; Peschel, C.; Morris, S.W.; Duyster, J. Nucleophosmin-anaplastic lymphoma kinase of large-cell anaplastic lymphoma is a constitutively active tyrosine kinase that utilizes phospholipase C-gamma to mediate its mitogenicity. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 6951–6961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Molavi, O.; Zhang, H.; Gupta, N.; Alshareef, A.; Bone, K.M.; Gopal, K.; Wu, F.; Lewis, J.T.; Douglas, D.N.; et al. STAT1 is phosphorylated and downregulated by the oncogenic tyrosine kinase NPM-ALK in ALK-positive anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Blood 2015, 126, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, S.; Hwang, S.; Basrur, V.; Conlon, K.; Fermin, D.; Wey, E.; Murga-Zamalloa, C.; Zeng, Z.; Zu, Y.; Elenitoba-Johnson, K.; et al. NPM-ALK signals through glycogen synthase kinase 3β to promote oncogenesis. Oncogene 2012, 31, 3733–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wu, F.; Wang, P.; Zhang, J.; Young, L.C.; Lai, R.; Li, L. Studies of phosphoproteomic changes induced by nucleophosmin-anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) highlight deregulation of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)/Fas/TNF-related apoptosis-induced ligand signaling pathway in ALK-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2010, 9, 1616–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenal, U.; Galperin, M.Y. Single domain response regulators: Molecular switches with emerging roles in cell organization and dynamics. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2009, 12, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Hwang, P.K.; Fletterick, R.J. Distinct phosphorylation signals converge at the catalytic center in glycogen phosphorylases. Structure 1997, 5, 1511–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illert, A.L.; Albers, C.; Kreutmair, S.; Leischner, H.; Peschel, C.; Miething, C.; Duyster, J. Grb10 is involved in BCR-ABL-positive leukemia in mice. Leukemia 2015, 29, 858–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illert, A.L.; Kawaguchi, H.; Antinozzi, C.; Bassermann, F.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; von Klitzing, C.; Hiwatari, M.; Peschel, C.; de Rooij, D.G.; Morris, S.W.; et al. Targeted inactivation of nuclear interaction partner of ALK disrupts meiotic prophase. Development 2012, 139, 2523–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundler, R.; Thiede, C.; Miething, C.; Steudel, C.; Peschel, C.; Duyster, J. Sensitivity toward tyrosine kinase inhibitors varies between different activating mutations of the FLT3 receptor. Blood 2003, 102, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borowicz, S.; Van Scoyk, M.; Avasarala, S.; Karuppusamy Rathinam, M.K.; Tauler, J.; Bikkavilli, R.K.; Winn, R.A. The Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 92, 51998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shevchenko, A.; Tomas, H.; Havlis, J.; Olsen, J.V.; Mann, M. In-gel digestion for mass spectrometric characterization of proteins and proteomes. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2856–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rappsilber, J.; Mann, M.; Ishihama, Y. Protocol for micro-purification, enrichment, pre-fractionation and storage of peptides for proteomics using StageTips. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 1896–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucci, S.; Mingirulli, N.; Wehbe, Z.; Dumit, V.I.; Kirschner, J.; Spiekerkoetter, U. Mitochondrial fatty acid biosynthesis and muscle fiber plasticity in very long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase-deficient mice. FEBS Lett. 2018, 592, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gengenbacher, A.; Müller-Rudorf, A.; Poggio, T.; Gräßel, L.; Dumit, V.I.; Kreutmair, S.; Lippert, L.J.; Duyster, J.; Illert, A.L. Proteomic Phosphosite Analysis Identified Crucial NPM-ALK-Mediated NIPA Serine and Threonine Residues. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4060. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20164060
Gengenbacher A, Müller-Rudorf A, Poggio T, Gräßel L, Dumit VI, Kreutmair S, Lippert LJ, Duyster J, Illert AL. Proteomic Phosphosite Analysis Identified Crucial NPM-ALK-Mediated NIPA Serine and Threonine Residues. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(16):4060. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20164060
Chicago/Turabian StyleGengenbacher, Anina, Alina Müller-Rudorf, Teresa Poggio, Linda Gräßel, Veronica I. Dumit, Stefanie Kreutmair, Lena J. Lippert, Justus Duyster, and Anna L. Illert. 2019. "Proteomic Phosphosite Analysis Identified Crucial NPM-ALK-Mediated NIPA Serine and Threonine Residues" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 16: 4060. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20164060
APA StyleGengenbacher, A., Müller-Rudorf, A., Poggio, T., Gräßel, L., Dumit, V. I., Kreutmair, S., Lippert, L. J., Duyster, J., & Illert, A. L. (2019). Proteomic Phosphosite Analysis Identified Crucial NPM-ALK-Mediated NIPA Serine and Threonine Residues. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(16), 4060. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20164060




