Karyotypes and Sex Chromosomes in Two Australian Native Freshwater Fishes, Golden Perch (Macquaria ambigua) and Murray Cod (Maccullochella peelii) (Percichthyidae)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
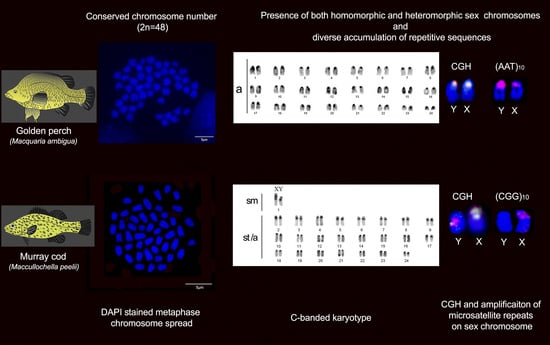
2.1. Karyotype and C-Banding of Golden Perch and Murray Cod
2.2. Intraspecies Comparative Genomic Hybridisation (CGH)
2.3. FISH Mapping of Telomeric Probe and Microsatellite Motifs
2.4. Immunofluorescence Detection of DNA Methylation
2.5. Cross-Species CGH
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Specimen Collection and Mitotic Chromosome Preparation
4.2. C-Banding
4.3. Genomic DNA Extraction
4.4. Comparative Genomic Hybridisation (CGH) and Cross-Species CGH
4.5. Probes for FISH (Fluorescence In Situ Hybridisation) Experiments
4.6. Immunofluorescence Detection of DNA Methylation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, A.; Sen, S. Chromosome Botany; Science Publishers: Enfield, CT, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Getlekha, N.; Cioffi, M.d.B.; Maneechot, N.; Bertollo, L.A.C.; Supiwong, W.; Tanomtong, A.; Molina, W.F. Contrasting evolutionary paths among Indo-Pacific Pomacentrus species promoted by extensive pericentric inversions and genome organization of repetitive sequences. Zebrafish 2018, 15, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubara, K.; Knopp, T.; Sarre, S.D.; Georges, A.; Ezaz, T. Karyotypic analysis and FISH mapping of microsatellite motifs reveal highly differentiated XX/XY sex chromosomes in the pink-tailed worm-lizard (Aprasia parapulchella, Pygopodidae, Squamata). Mol. Cytogenet. 2013, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ráb, P.; Yano, C.F.; Lavoué, S.; Jegede, O.I.; Bertollo, L.A.; Ezaz, T.; Majtánová, Z.; de Oliveira, E.A.; Cioffi, M.B. Karyotype and Mapping of Repetitive DNAs in the African Butterfly Fish Pantodon buchholzi, the Sole Species of the Family Pantodontidae. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2016, 149, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baroiller, J.-F.; D’Cotta, H.; Saillant, E. Environmental effects on fish sex determination and differentiation. Sex. Dev. 2009, 3, 118–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, T.B. Sex determination and primary sex differentiation in amphibians: Genetic and developmental mechanisms. J. Exp. Zool. 1998, 281, 373–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Nagahama, Y.; Nakamura, M. Diversity and Plasticity of Sex Determination and Differentiation in Fishes. Sex. Dev. 2013, 7, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baillie, J.; Hilton-Taylor, C.; Stuart, S.N. 2004 IUCN Red List of Threatened Species: A Global Species Assessment; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, J.S.; Grande, T.C.; Wilson, M.V. Fishes of the World; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; Lévêque, C.; Revenga, C.; Bos, R.; Caudill, C.; Chilton, J.; Douglas, E.; Meybeck, M.; Prager, D.; Balvanera, P. Fresh water. Ecosyst. Hum. Well-Being Curr. State Trends 2005, 1, 167–201. [Google Scholar]
- Bray, D.J. Temperate Basses, Percichthyidae in Fishes of Australia. Available online: https://australianmuseum.net.au/learn/animals/fishes/percichthyidae-australian-freshwater-basses-perches-and-cods/ (accessed on 25 June 2018).
- Allen, G.R.; Midgley, S.H.; Allen, M. Field Guide to the Freshwater Fishes of Australia; Western Australian Museum: Welshpool, WA, Australia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Lintermans, M. Fishes of the Murray-Darling Basin: An Introductory Guide; Murray-Darling Basin Commisssion: Canbera, ACT, Australia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Beheregaray, L.B.; Pfeiffer, L.V.; Attard, C.R.M.; Sandoval-Castillo, J.; Domingos, F.M.C.B.; Faulks, L.K.; Gilligan, D.M.; Unmack, P.J. Genome-wide data delimits multiple climate-determined species ranges in a widespread Australian fish, the golden perch (Macquaria ambigua). Mol. Phylogenet. Evolut. 2017, 111, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodrich, H. Mendelian inheritance in fish. Q. Rev. Biol. 1929, 4, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, M. Genetics of Platypoecilus III. Inheritance of Sex and Crossing over of the Sex Chromosomes in the Platyfish. Genetics 1937, 22, 376–392. [Google Scholar]
- Huxley, J.S. Note on an alternating preponderance of males and females in fish, and its possible significance. J. Genet. 1920, 10, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, R.H.; Nagahama, Y. Sex determination and sex differentiation in fish: An overview of genetic, physiological, and environmental influences. Aquaculture 2002, 208, 191–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira-Filho, O.; Bertollo, L.A.; Galetti Jr, P.M. Distribution of sex chromosome mechanisms in neotropical fish and description of a ZZ/ZW system in Parodon hilarii (Parodontidae). Caryologia 1993, 46, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinemann, M.; Steinemann, S.; Lottspeich, F. How Y chromosomes become genetically inert. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 5737–5741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.J.D. Animal Cytology and Evolution; CUP Archive: Cambridge, UK, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Ezaz, T.; Berra, T.M.; Graves, J.A.M. Karyotype of the Australian nurseryfish, Kurtus gulliveri (Kurtidae: Perciformes). Chromosome Sci. 2006, 9, 85–88. [Google Scholar]
- Majtánová, Z.; Moy, K.G.; Unmack, P.J.; Ráb, P.; Ezaz, T. Characterization of the karyotype and accumulation of repetitive sequences in Australian Darling hardyhead Craterocephalus amniculus (Atheriniformes, Teleostei). Peer J. Prepr. 2019, 7, e27688v27681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, R. Fish. Karyotypes: A Check List; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Betancur-R, R.; Wiley, E.O.; Arratia, G.; Acero, A.; Bailly, N.; Miya, M.; Lecointre, G.; Orti, G. Phylogenetic classification of bony fishes. BMC Evolut. Biol. 2017, 17, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barby, F.F.; Bertollo, L.A.C.; de Oliveira, E.A.; Yano, C.F.; Hatanaka, T.; Ráb, P.; Sember, A.; Ezaz, T.; Artoni, R.F.; Liehr, T. Emerging patterns of genome organization in Notopteridae species (Teleostei, Osteoglossiformes) as revealed by Zoo-FISH and Comparative Genomic Hybridization (CGH). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ráb, P.; Rábová, M.; Pereira, C.S.; Collares-Pereira, M.J.; Pelikánová, Š. Chromosome studies of European cyprinid fishes: Interspecific homology of leuciscine cytotaxonomic marker—The largest subtelocentric chromosome pair as revealed by cross-species painting. Chromosome Res. 2008, 16, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, P.F.; Ezaz, T.; de Bello Cioffi, M.; Jackson Almeida, B.; Feldberg, E. Evolutionary Insights of the ZW Sex Chromosomes in Snakes: A New Chapter Added by the Amazonian Puffing Snakes of the Genus Spilotes. Genes 2019, 10, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Near, T.J.; Sandel, M.; Kuhn, K.L.; Unmack, P.J.; Wainwright, P.C.; Smith, W.L. Nuclear gene-inferred phylogenies resolve the relationships of the enigmatic Pygmy Sunfishes, Elassoma (Teleostei: Percomorpha). Mol. Phylogenet. Evolut. 2012, 63, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, W.F. Chromosomal changes and stasis in marine fish groups. Fish. Cytogenet. 2007, 31, 69–110. [Google Scholar]
- Abramyan, J.; Ezaz, T.; Graves, J.A.M.; Koopman, P. Z and W sex chromosomes in the cane toad (Bufo marinus). Chromosome Res. 2009, 17, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida-Toledo, L.; Foresti, F.; Daniel, M.; Toledo-Filho, S. Sex chromosome evolution in fish: The formation of the neo-Y chromosome in Eigenmannia (Gymnotiformes). Chromosoma 2000, 109, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezaz, T.; Quinn, A.E.; Miura, I.; Sarre, S.D.; Georges, A.; Graves, J.A.M. The dragon lizard Pogona vitticeps has ZZ/ZW micro-sex chromosomes. Chromosome Res. 2005, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubara, K.; Sarre, S.D.; Georges, A.; Matsuda, Y.; Graves, J.A.M.; Ezaz, T. Highly differentiated ZW sex microchromosomes in the Australian Varanus species evolved through rapid amplification of repetitive sequences. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traut, W.; Winking, H. Meiotic chromosomes and stages of sex chromosome evolution in fish: Zebrafish, platyfish and guppy. Chromosome Res. 2001, 9, 659–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlesworth, B. The evolution of sex chromosomes. Science 1991, 251, 1030–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, J.A.M. Weird animal genomes and the evolution of vertebrate sex and sex chromosomes. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2008, 42, 565–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, H.J. A gene for the fourth chromosome of Drosophila. J. Exp. Zool. 1914, 17, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohno, S. Sex chromosome and sex-linked genes. Chromosoma 1967, 23, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas, N.L.; Al-Rikabi, A.B.; Bertollo, L.A.C.; Ezaz, T.; Yano, C.F.; de Oliveira, E.A.; Hatanaka, T.; de Bello Cioffi, M. Early stages of XY sex chromosomes differentiation in the fish Hoplias malabaricus (Characiformes, Erythrinidae) revealed by DNA repeats accumulation. Cur. Genomics 2018, 19, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezaz, T.; Deakin, J.E. Repetitive sequence and sex chromosome evolution in vertebrates. Adv. Evolut. Biol. 2014, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kejnovský, E.; Michalovova, M.; Steflova, P.; Kejnovska, I.; Manzano, S.; Hobza, R.; Kubat, Z.; Kovarik, J.; Jamilena, M.; Vyskot, B. Expansion of microsatellites on evolutionary young Y chromosome. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e45519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viana, P.F.; Ezaz, T.; Marajó, L.; Ferreira, M.; Zuanon, J.; Cioffi, M.B.; Bertollo, L.A.; Gross, M.C.; Feldberg, E. Genomic Organization of Repetitive DNAs and Differentiation of an XX/XY Sex Chromosome System in the Amazonian Puffer Fish, Colomesus asellus (Tetraodontiformes). Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2017, 153, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, C.F.; Bertollo, L.A.C.; Liehr, T.; Troy, W.P.; Cioffi, M.d.B. W chromosome dynamics in Triportheus species (Characiformes, Triportheidae): An ongoing process narrated by repetitive sequences. J. Hered. 2016, 107, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schartl, M. Sex chromosome evolution in non-mammalian vertebrates. Cur. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2004, 14, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volff, J.-N.; Nanda, I.; Schmid, M.; Schartl, M. Governing sex determination in fish: Regulatory putsches and ephemeral dictators. Sex. Dev. 2007, 1, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioffi, M.; Kejnovsky, E.; Bertollo, L. The chromosomal distribution of microsatellite repeats in the genome of the wolf fish Hoplias malabaricus, focusing on the sex chromosomes. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2011, 132, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, I.; Feichtinger, W.; Schmid, M.; Schröder, J.H.; Zischler, H.; Epplen, J.T. Simple repetitive sequences are associated with differentiation of the sex chromosomes in the guppy fish. J. Mol. Evolut. 1990, 30, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamble, T.; Geneva, A.J.; Glor, R.E.; Zarkower, D. Anolis sex chromosomes are derived from a single ancestral pair. Evolution 2014, 68, 1027–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokorná, M.; Kratochvíl, L.; Kejnovský, E. Microsatellite distribution on sex chromosomes at different stages of heteromorphism and heterochromatinization in two lizard species (Squamata: Eublepharidae: Coleonyx elegans and Lacertidae: Eremias velox). BMC Genet. 2011, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertollo, L.; Cioffi, M.; Moreira-Filho, O. Direct chromosome preparation from freshwater teleost fishes. In Fish Cytogenetic Techniques (Chondrichthyans and Teleosts); Ozouf-Costaz, C., Pisano, E., Foresti, F., Almeida Toledo, L.F., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Völker, M.; Ráb, P. Direct chromosome preparation from regenerating fish fin tissue. In Fish Cytogenetic Techniques (Ray-Fin Fishes and Chondrichthyans); Ozouf-Costaz, C., Pisano, E., Foresti, F., Almeida Toledo, L.F., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Salvadori, S.; Coluccia, E.; Deiana, A.M. C-Banding. In Fish Cytogenetic Techniques: Ray-Fin Fishes and Chondrichthyans; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 88–91. [Google Scholar]
- Ezaz, M.T.; McAndrew, B.; Penman, D. Spontaneous diploidization of the maternal chromosome set in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.) eggs. Aquac. Res. 2004, 35, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symonová, R.; Sember, A.; Majtánová, Z.; Ráb, P. Characterization of fish genomes by GISH and CGH. In Fish Cytogenetic Techniques: Ray-Fin Fishes and Chondrichthyans; Ozouf-Costaz, C., Pisano, E., Foresti, F., Almeida Toledo, L.F., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 118–131. [Google Scholar]
- Bonillo, C.; Coutanceau, J.; D’Cotta, H.; Ghigliotti, L.; Ozouf-Costaz, C.; Pisano, E. Standard fluorescence in situ hybridization procedures. In Fish Cytogenetic Techniques: Ray-Fin Fishes and Chondrichthyans; Ozouf-Costaz, C., Pisano, E., Foresti, F., Almeida Toledo, L.F., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 103–118. [Google Scholar]
- Domaschenz, R.; Livernois, A.M.; Rao, S.; Ezaz, T.; Deakin, J.E. Immunofluorescent staining reveals hypermethylation of microchromosomes in the central bearded dragon, Pogona vitticeps. Mol. Cytogenet. 2015, 8, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingles, E.D.; Deakin, J.E. Global DNA Methylation patterns on marsupial and devil facial tumour chromosomes. Mol. Cytogenet. 2015, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Golden Perch | Murray Cod | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | Male | Female | Male | |||||
| Number of individuals | Number of cells/each | Number of individuals | Number of cells/each | Number of individuals | Number of cells/each | Number of individuals | Number of cells/each | |
| Mitosis | 12 | 60 | 12 | 60 | 3 | 60 | 5 | 60 |
| Karyotyping | 5 | 20 | 5 | 20 | 3 | 20 | 5 | 20 |
| CGH | 3 | 20 | 3 | 20 | 3 | 20 | 3 | 20 |
| C-banding | 3 | 60 | 5 | 60 | 3 | 60 | 5 | 60 |
| FISH- telomeric probe | 3 | 20 | 3 | 20 | 3 | 20 | 3 | 20 |
| FISH-repetitive sequences | 3 | 20 | 3 | 20 | 3 | 20 | 3 | 20 |
| DNA methylation | 3 | 20 | 3 | 20 | 3 | 20 | 3 | 20 |
| Cross-species CGH | - | - | 1 | 20 | - | - | 1 | 20 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shams, F.; Dyer, F.; Thompson, R.; Duncan, R.P.; Thiem, J.D.; Majtánová, Z.; Ezaz, T. Karyotypes and Sex Chromosomes in Two Australian Native Freshwater Fishes, Golden Perch (Macquaria ambigua) and Murray Cod (Maccullochella peelii) (Percichthyidae). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4244. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174244
Shams F, Dyer F, Thompson R, Duncan RP, Thiem JD, Majtánová Z, Ezaz T. Karyotypes and Sex Chromosomes in Two Australian Native Freshwater Fishes, Golden Perch (Macquaria ambigua) and Murray Cod (Maccullochella peelii) (Percichthyidae). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(17):4244. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174244
Chicago/Turabian StyleShams, Foyez, Fiona Dyer, Ross Thompson, Richard P. Duncan, Jason D. Thiem, Zuzana Majtánová, and Tariq Ezaz. 2019. "Karyotypes and Sex Chromosomes in Two Australian Native Freshwater Fishes, Golden Perch (Macquaria ambigua) and Murray Cod (Maccullochella peelii) (Percichthyidae)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 17: 4244. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174244
APA StyleShams, F., Dyer, F., Thompson, R., Duncan, R. P., Thiem, J. D., Majtánová, Z., & Ezaz, T. (2019). Karyotypes and Sex Chromosomes in Two Australian Native Freshwater Fishes, Golden Perch (Macquaria ambigua) and Murray Cod (Maccullochella peelii) (Percichthyidae). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(17), 4244. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174244