The Role of Exo-miRNAs in Cancer: A Focus on Therapeutic and Diagnostic Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
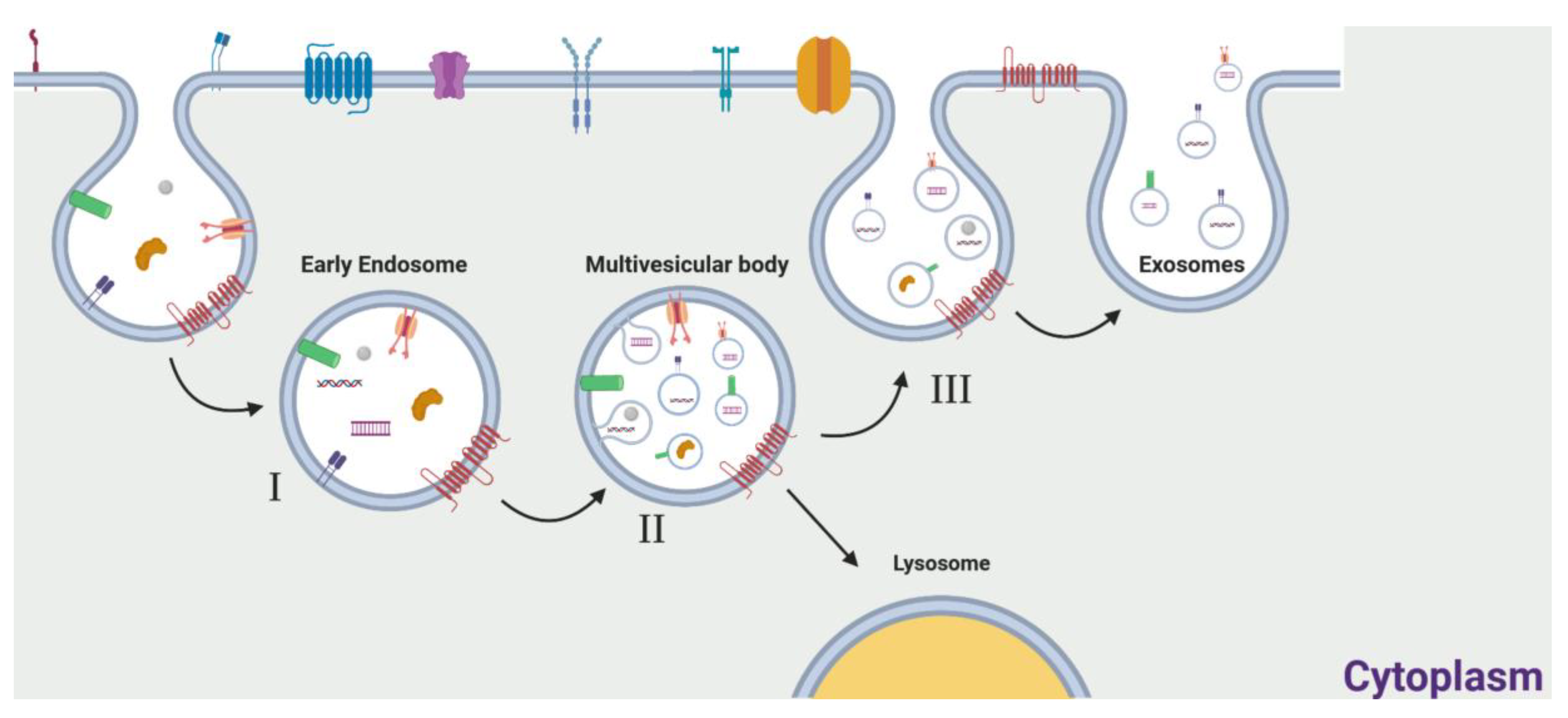
2. Exosomes: General Features
The Role of Exosomes in Cancer
3. MiRNA and Exosomes
3.1. Extracellular miRNAs
3.2. Passive and Selective Release of miRNAs from Cells to Exosomes
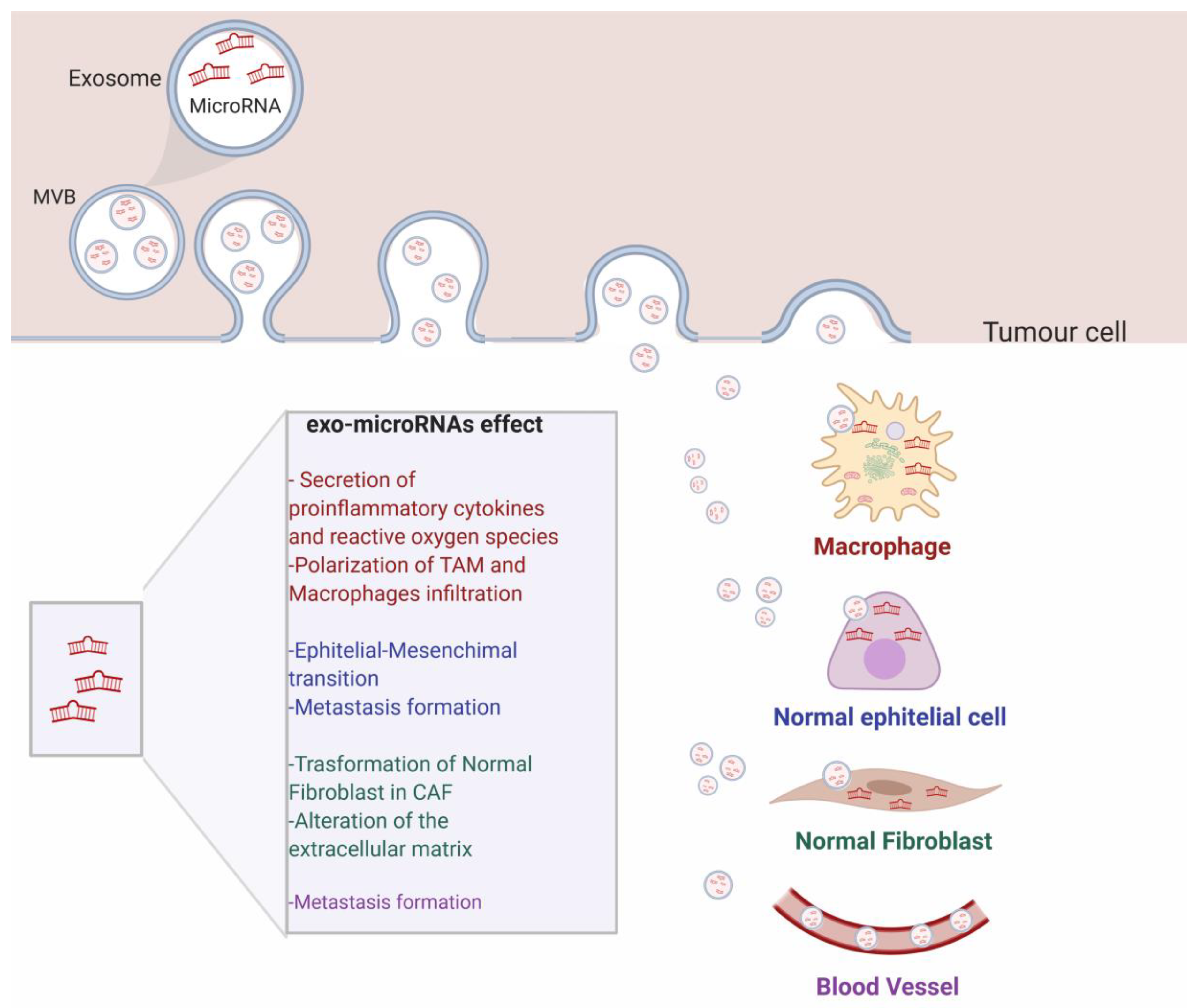
3.3. Exosomal miRNAs Involvement in Cancer
4. Exosomal miRNAs as Biomarkers in Diagnosis and Prognosis in Cancer
5. Exosomal miRNA-Based Therapy
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rak, J. Extracellular vesicles—Biomarkers and effectors of the cellular interactome in cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2013, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Niel, G.; D’Angelo, G.; Raposo, G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, M.; Raposo, G.; Thery, C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 30, 255–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, H.; Drummen, G.P.; Mathivanan, S. Focus on Extracellular Vesicles: Introducing the Next Small Big Thing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuana, Y.; Sturk, A.; Nieuwland, R. Extracellular vesicles in physiological and pathological conditions. Blood Rev. 2013, 27, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fiore, D.; Donnarumma, E.; Roscigno, G.; Iaboni, M.; Russo, V.; Affinito, A.; Adamo, A.; De Martino, F.; Quintavalle, C.; Romano, G.; et al. miR-340 predicts glioblastoma survival and modulates key cancer hallmarks through down-regulation of NRAS. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 19531–19547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pekarsky, Y.; Balatti, V.; Palamarchuk, A.; Rizzotto, L.; Veneziano, D.; Nigita, G.; Rassenti, L.Z.; Pass, H.I.; Kipps, T.J.; Liu, C.G.; et al. Dysregulation of a family of short noncoding RNAs, tsRNAs, in human cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 5071–5076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quintavalle, C.; Donnarumma, E.; Iaboni, M.; Roscigno, G.; Garofalo, M.; Romano, G.; Fiore, D.; De Marinis, P.; Croce, C.M.; Condorelli, G. Effect of miR-21 and miR-30b/c on TRAIL-induced apoptosis in glioma cells. Oncogene 2013, 32, 4001–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintavalle, C.; Garofalo, M.; Zanca, C.; Romano, G.; Iaboni, M.; De Caro, M.D.; Martinez-Montero, J.C.; Incoronato, M.; Nuovo, G.; Croce, C.M.; et al. miR-221/222 overexpession in human glioblastoma increases invasiveness by targeting the protein phosphate PTP mu. Oncogene 2012, 31, 858–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintavalle, C.; Mangani, D.; Roscigno, G.; Romano, G.; Diaz-Lagares, A.; Iaboni, M.; Donnarumma, E.; Fiore, D.; De Marinis, P.; Soini, Y.; et al. miR-221/222 Target the DNA Methyltransferase MGMT in Glioma Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roscigno, G.; Puoti, I.; Giordano, I.; Donnarumma, E.; Russo, V.; Affinito, A.; Adamo, A.; Quintavalle, C.; Todaro, M.; Vivanco, M.D.; et al. MiR-24 induces chemotherapy resistance and hypoxic advantage in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 19507–19521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roscigno, G.; Quintavalle, C.; Donnarumma, E.; Puoti, I.; Diaz-Lagares, A.; Iaboni, M.; Fiore, D.; Russo, V.; Todaro, M.; Romano, G.; et al. MiR-221 promotes stemness of breast cancer cells by targeting DNMT3b. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Pol, E.; Boing, A.N.; Harrison, P.; Sturk, A.; Nieuwland, R. Classification, functions, and clinical relevance of extracellular vesicles. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 676–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarroya-Beltri, C.; Baixauli, F.; Gutierrez-Vazquez, C.; Sanchez-Madrid, F.; Mittelbrunn, M. Sorting it out: Regulation of exosome loading. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2014, 28, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Niel, G.; Porto-Carreiro, I.; Simoes, S.; Raposo, G. Exosomes: A common pathway for a specialized function. J. Biochem. 2006, 140, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hessvik, N.P.; Llorente, A. Current knowledge on exosome biogenesis and release. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarroya-Beltri, C.; Gutierrez-Vazquez, C.; Sanchez-Cabo, F.; Perez-Hernandez, D.; Vazquez, J.; Martin-Cofreces, N.; Martinez-Herrera, D.J.; Pascual-Montano, A.; Mittelbrunn, M.; Sanchez-Madrid, F. Sumoylated hnRNPA2B1 controls the sorting of miRNAs into exosomes through binding to specific motifs. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, T.; Deng, C.X. Current Progresses of Exosomes as Cancer Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riches, A.; Campbell, E.; Borger, E.; Powis, S. Regulation of exosome release from mammary epithelial and breast cancer cells—A new regulatory pathway. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 1025–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, J.; Cao, D.; You, Y.; Shen, K.; Peng, P. Regulation of exosomes released from normal ovarian epithelial cells and ovarian cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, H.W.; Michael, M.Z.; Gleadle, J.M. Hypoxic enhancement of exosome release by breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parolini, I.; Federici, C.; Raggi, C.; Lugini, L.; Palleschi, S.; De Milito, A.; Coscia, C.; Iessi, E.; Logozzi, M.; Molinari, A.; et al. Microenvironmental pH is a key factor for exosome traffic in tumor cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 34211–34222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budnik, V.; Ruiz-Canada, C.; Wendler, F. Extracellular vesicles round off communication in the nervous system. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2016, 17, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taraboletti, G.; D’Ascenzo, S.; Giusti, I.; Marchetti, D.; Borsotti, P.; Millimaggi, D.; Giavazzi, R.; Pavan, A.; Dolo, V. Bioavailability of VEGF in tumor-shed vesicles depends on vesicle burst induced by acidic pH. Neoplasia 2006, 8, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, H.; Xiong, C.; Liu, Y. Hypoxic glioblastoma release exosomal VEGF-A induce the permeability of blood-brain barrier. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 502, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skog, J.; Wurdinger, T.; van Rijn, S.; Meijer, D.H.; Gainche, L.; Sena-Esteves, M.; Curry, W.T., Jr.; Carter, B.S.; Krichevsky, A.M.; Breakefield, X.O. Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumor growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 1470–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Nedawi, K.; Meehan, B.; Micallef, J.; Lhotak, V.; May, L.; Guha, A.; Rak, J. Intercellular transfer of the oncogenic receptor EGFRvIII by microvesicles derived from tumor cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Chen, M.; Jiang, R.; Guo, Y.; Wu, M.; Zhang, X. Exosome-related tumor microenvironment. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 3084–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Domenis, R.; Cesselli, D.; Toffoletto, B.; Bourkoula, E.; Caponnetto, F.; Manini, I.; Beltrami, A.P.; Ius, T.; Skrap, M.; Di Loreto, C.; et al. Systemic T Cells Immunosuppression of Glioma Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Is Mediated by Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.; Qu, J.L.; Zhang, Y.; Che, X.F.; Cheng, Y.; Fan, Y.B.; Zhang, S.M.; Na, D.; Liu, Y.P.; Qu, X.J. Gastric cancer-derived exosomes promote peritoneal metastasis by destroying the mesothelial barrier. FEBS Lett. 2017, 591, 2167–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.T.; Qi, C.S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Gao, J.; Wu, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhao, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, X.J.; et al. Malignant ascites-derived exosomes promote peritoneal tumor cell dissemination and reveal a distinct miRNA signature in advanced gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 2019, 457, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, J.J.; Lin, X.J.; Tang, X.Y.; Zheng, T.T.; Lin, Y.Y.; Hua, K.Q. Exosomal Metastasis-Associated Lung Adenocarcinoma Transcript 1 Promotes Angiogenesis and Predicts Poor Prognosis in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 1960–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Lu, Y.; Xu, Y.C.; Hou, S.Z.; Huang, J.L.; Wang, B.; Zhao, J.Y.; Xia, S.L.; Fan, S.J.; Yu, X.T.; et al. Exosomal transfer of miR-501 confers doxorubicin resistance and tumorigenesis via targeting of BUD in gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 2019, 459, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Wei, Q.; Koay, E.J.; Liu, Y.; Ning, B.; Bernard, P.W.; Zhang, N.; Han, H.Y.; Katz, M.H.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Chemoresistance Transmission via Exosome-Mediated EphA2 Transfer in Pancreatic Cancer. Theranostics 2018, 8, 5986–5994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, J.A.; Krichevsky, A.M.; Kosik, K.S. MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 6029–6033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yuan, L.; Luo, J.; Gao, J.; Guo, J.; Xie, X. MiR-34a inhibits proliferation and migration of breast cancer through down-regulation of Bcl-2 and SIRT1. Clin. Exp. Med. 2013, 13, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buechner, J.; Tomte, E.; Haug, B.H.; Henriksen, J.R.; Lokke, C.; Flaegstad, T.; Einvik, C. Tumour-suppressor microRNAs let-7 and mir-101 target the proto-oncogene MYCN and inhibit cell proliferation in MYCN-amplified neuroblastoma. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Ba, Y.; Ma, L.; Cai, X.; Yin, Y.; Wang, K.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Guo, X.; et al. Characterization of microRNAs in serum: A novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noferesti, S.S.; Sohel, M.M.; Hoelker, M.; Salilew-Wondim, D.; Tholen, E.; Looft, C.; Rings, F.; Neuhoff, C.; Schellander, K.; Tesfaye, D. Controlled ovarian hyperstimulation induced changes in the expression of circulatory miRNA in bovine follicular fluid and blood plasma. J. Ovarian Res. 2015, 8, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, J.D.; Chevillet, J.R.; Kroh, E.M.; Ruf, I.K.; Pritchard, C.C.; Gibson, D.F.; Mitchell, P.S.; Bennett, C.F.; Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E.L.; Stirewalt, D.L.; et al. Argonaute2 complexes carry a population of circulating microRNAs independent of vesicles in human plasma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5003–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chim, S.S.; Shing, T.K.; Hung, E.C.; Leung, T.Y.; Lau, T.K.; Chiu, R.W.; Lo, Y.M. Detection and characterization of placental microRNAs in maternal plasma. Clin. Chem. 2008, 54, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mause, S.F.; Weber, C. Microparticles: Protagonists of a novel communication network for intercellular information exchange. Circ. Res. 2010, 107, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callis, T.E.; Pandya, K.; Seok, H.Y.; Tang, R.H.; Tatsuguchi, M.; Huang, Z.P.; Chen, J.F.; Deng, Z.; Gunn, B.; Shumate, J.; et al. MicroRNA-208a is a regulator of cardiac hypertrophy and conduction in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 2772–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zernecke, A.; Bidzhekov, K.; Noels, H.; Shagdarsuren, E.; Gan, L.; Denecke, B.; Hristov, M.; Koppel, T.; Jahantigh, M.N.; Lutgens, E.; et al. Delivery of microRNA-126 by apoptotic bodies induces CXCL12-dependent vascular protection. Sci. Signal. 2009, 2, ra81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valadi, H.; Ekstrom, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjostrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lotvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hunter, M.P.; Ismail, N.; Zhang, X.; Aguda, B.D.; Lee, E.J.; Yu, L.; Xiao, T.; Schafer, J.; Lee, M.L.; Schmittgen, T.D.; et al. Detection of microRNA expression in human peripheral blood microvesicles. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pigati, L.; Yaddanapudi, S.C.; Iyengar, R.; Kim, D.J.; Hearn, S.A.; Danforth, D.; Hastings, M.L.; Duelli, D.M. Selective release of microRNA species from normal and malignant mammary epithelial cells. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squadrito, M.L.; Baer, C.; Burdet, F.; Maderna, C.; Gilfillan, G.D.; Lyle, R.; Ibberson, M.; De Palma, M. Endogenous RNAs Modulate MicroRNA Sorting to Exosomes and Transfer to Acceptor Cells. Cell Rep. 2014, 8, 1432–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mittelbrunn, M.; Gutierrez-Vazquez, C.; Villarroya-Beltri, C.; Gonzalez, S.; Sanchez-Cabo, F.; Gonzalez, M.A.; Bernad, A.; Sanchez-Madrid, F. Unidirectional transfer of microRNA-loaded exosomes from T cells to antigen-presenting cells. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batagov, A.O.; Kuznetsov, V.A.; Kurochkin, I.V. Identification of nucleotide patterns enriched in secreted RNAs as putative cis-acting elements targeting them to exosome nano-vesicles. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, N.; Iguchi, H.; Yoshioka, Y.; Takeshita, F.; Matsuki, Y.; Ochiya, T. Secretory mechanisms and intercellular transfer of microRNAs in living cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 17442–17452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momose, F.; Seo, N.; Akahori, Y.; Sawada, S.; Harada, N.; Ogura, T.; Akiyoshi, K.; Shiku, H. Guanine-Rich Sequences Are a Dominant Feature of Exosomal microRNAs across the Mammalian Species and Cell Types. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, D.J.; Franklin, J.L.; Dou, Y.; Liu, Q.; Higginbotham, J.N.; Demory Beckler, M.; Weaver, A.M.; Vickers, K.; Prasad, N.; Levy, S.; et al. KRAS-dependent sorting of miRNA to exosomes. eLife 2015, 4, e07197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnarumma, E.; Fiore, D.; Nappa, M.; Roscigno, G.; Adamo, A.; Iaboni, M.; Russo, V.; Affinito, A.; Puoti, I.; Quintavalle, C.; et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts release exosomal microRNAs that dictate an aggressive phenotype in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 19592–19608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Li, Z.; Yu, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Ji, W.; Xia, W.; Lu, S. Exosomal miR-499a-5p promotes cell proliferation, migration and EMT via mTOR signaling pathway in lung adenocarcinoma. Exp. Cell Res. 2019, 379, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarzenbach, H. The clinical relevance of circulating, exosomal miRNAs as biomarkers for cancer. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2015, 15, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Yao, J.; Lowery, F.J.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, W.C.; Li, P.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; et al. Microenvironment-induced PTEN loss by exosomal microRNA primes brain metastasis outgrowth. Nature 2015, 527, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zha, W.; Zhang, W. Exosomal miR-660-5p promotes tumor growth and metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer. J. BUON 2019, 24, 599–607. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, J.C.; Lima, N.D.S.; Sarian, L.O.; Matheu, A.; Ribeiro, M.L.; Derchain, S.F.M. Exosome-mediated breast cancer chemoresistance via miR-155 transfer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Sun, S.; Li, Z.; Yang, Q.; Li, B.; Zhu, S.; Wang, L.; Wu, J.; Yuan, J.; Wang, C.; et al. Breast cancer-released exosomes trigger cancer-associated cachexia to promote tumor progression. Adipocyte 2019, 8, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paggetti, J.; Haderk, F.; Seiffert, M.; Janji, B.; Distler, U.; Ammerlaan, W.; Kim, Y.J.; Adam, J.; Lichter, P.; Solary, E.; et al. Exosomes released by chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells induce the transition of stromal cells into cancer-associated fibroblasts. Blood 2015, 126, 1106–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Luo, F.; Wang, B.R.; Li, H.Q.; Xu, Y.; Liu, X.L.; Shi, L.; Lu, X.L.; Xu, W.C.; Lu, L.; et al. STAT3-regulated exosomal miR-21 promotes angiogenesis and is involved in neoplastic processes of transformed human bronchial epithelial cells. Cancer Lett. 2016, 370, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, G.M.; Liu, Y.; Fang, X.; Liu, Y.H.; Fang, L.; Lin, L.J.; Liu, X.M.; Wang, N.P. Tumor-derived microRNA-494 promotes angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer. Angiogenesis 2015, 18, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Title, A.C.; Hong, S.J.; Pires, N.D.; Hasenohrl, L.; Godbersen, S.; Stokar-Regenscheit, N.; Bartel, D.P.; Stoffel, M. Genetic dissection of the miR-200-Zeb1 axis reveals its importance in tumor differentiation and invasion. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, M.T.N.; Hamar, P.; Guo, C.Y.; Basar, E.; Perdigao-Henriques, R.; Balaj, L.; Lieberman, J. miR-200-containing extracellular vesicles promote breast cancer cell metastasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 5109–5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.Y.; Fong, M.Y.; Min, Y.F.; Somlo, G.; Liu, L.; Palomares, M.R.; Yu, Y.; Chow, A.; O’Connor, S.T.F.; Chin, A.R.; et al. Cancer-Secreted miR-105 Destroys Vascular Endothelial Barriers to Promote Metastasis. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 501–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fabbri, M.; Paone, A.; Calore, F.; Galli, R.; Gaudio, E.; Santhanam, R.; Lovat, F.; Fadda, P.; Mao, C.; Nuovo, G.J.; et al. MicroRNAs bind to Toll-like receptors to induce prometastatic inflammatory response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E2110–E2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klibi, J.; Niki, T.; Riedel, A.; Pioche-Durieu, C.; Souquere, S.; Rubinstein, E.; Moulec, S.L.E.; Guigay, J.; Hirashima, M.; Guemira, F.; et al. Blood diffusion and Th1-suppressive effects of galectin-9-containing exosomes released by Epstein-Barr virus-infected nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Blood 2009, 113, 1957–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Chen, J.H.; Zhou, L.J.; Chen, W.C.; Ding, G.P.; Cao, L.P. Pancreatic cancer derived exosomes regulate the expression of TLR4 in dendritic cells via miR-203. Cell Immunol. 2014, 292, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okoye, I.S.; Coomes, S.M.; Pelly, V.S.; Czieso, S.; Papayannopoulos, V.; Tolmachova, T.; Seabra, M.C.; Wilson, M.S. MicroRNA-Containing T-Regulatory-Cell-Derived Exosomes Suppress Pathogenic T Helper 1 Cells. Immunity 2014, 41, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakano, T.; Chen, I.H.; Wang, C.C.; Chen, P.J.; Tseng, H.P.; Huang, K.T.; Hu, T.H.; Li, L.C.; Goto, S.; Cheng, Y.F.; et al. Circulating exosomal miR-92b: Its role for cancer immunoediting and clinical value for prediction of posttransplant hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence. Am. J. Transplant. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Pochampally, R.; Watabe, K.; Lu, Z.H.; Mo, Y.Y. Exosome-mediated transfer of miR-10b promotes cell invasion in breast cancer. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Cao, T.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, F.; Shi, Y.; Xia, J.; Wang, Z.P. miR-223 Regulates Cell Proliferation and Invasion via Targeting PDS5B in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Mol. Ther. Nucl. Acids 2019, 14, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fu, X.; Liu, M.; Qu, S.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, T.; Wen, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; et al. Exosomal microRNA-32-5p induces multidrug resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma via the PI3K/AKT pathway. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.H.; Zhong, M.Z.; Zeng, S.; Wang, L.Y.; Liu, P.; Xiao, X.Y.; Liu, Y.P. Exosome-derived miRNAs as predictive biomarkers for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma chemotherapy resistance. Epigenomics 2019, 11, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Yang, F.; Zhang, T.Z.; Wang, W.; Xi, W.J.; Li, Y.F.; Zhang, D.; Huo, Y.; Zhang, J.N.; Yang, A.G.; et al. MiR-9 promotes tumorigenesis and angiogenesis and is activated by MYC and OCT4 in human glioma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.X.; Liao, J.; Xie, M.; Gao, Z.K.; Wang, X.H.; Zhang, Y.; Shang, M.H.; Yin, L.H.; Pu, Y.P.; Liu, R. miR-93-5p Transferred by Exosomes Promotes the Proliferation of Esophageal Cancer Cells via Intercellular Communication by Targeting PTEN. BioMed Environ. Sci. 2018, 31, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valencia, K.; Luis-Ravelo, D.; Bovy, N.; Anton, I.; Martinez-Canarias, S.; Zandueta, C.; Ormazabal, C.; Struman, I.; Tabruyn, S.; Rebmann, V.; et al. miRNA cargo within exosome-like vesicle transfer influences metastatic bone colonization. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 8, 689–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Q.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Sun, P.; Xiang, R.; Yang, S. Exosomal miR-451a Functions as a Tumor Suppressor in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting LPIN1. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 53, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, J.; Liu, Q.H.; Wang, F.; Tan, J.J.; Deng, Y.Q.; Peng, X.H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, B.; Xu, X.; Li, X.P. Exosomal miR-9 inhibits angiogenesis by targeting MDK and regulating PDK/AKT pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizoguchi, A.; Takayama, A.; Arai, T.; Kawauchi, J.; Sudo, H. MicroRNA-8073: Tumor suppressor and potential therapeutic treatment. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0209750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakravan, K.; Babashah, S.; Sadeghizadeh, M.; Mowla, S.J.; Mossahebi-Mohammadi, M.; Ataei, F.; Dana, N.; Javan, M. MicroRNA-100 shuttled by mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes suppresses in vitro angiogenesis through modulating the mTOR/HIF-1 alpha/VEGF signaling axis in breast cancer cells. Cell Oncol. 2017, 40, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munson, P.B.; Hall, E.M.; Farina, N.H.; Pass, H.I.; Shukla, A. Exosomal miR-16-5p as a target for malignant mesothelioma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Gui, S.; Liu, Y.W.; Qiu, X.Y.; Zhang, G.Z.; Zhang, X.A.; Pan, J.; Fan, J.; Qi, S.T.; Qiu, B.H. Exosomes derived from microRNA-199a-overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells inhibit glioma progression by down-regulating AGAP2. Aging 2019, 11, 5300–5318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gold, P.; Freedman, S.O. Demonstration of Tumor-Specific Antigens in Human Colonic Carcinomata by Immunological Tolerance and Absorption Techniques. J. Exp. Med. 1965, 121, 439–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulasingam, V.; Pavlou, M.P.; Diamandis, E.P. Integrating high-throughput technologies in the quest for effective biomarkers for ovarian cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Filant, J.; Moxley, K.M.; Sood, A.; McMeekin, S.; Ramesh, R. Exosomes: A Role for Naturally Occurring Nanovesicles in Cancer Growth, Diagnosis and Treatment. Curr. Gene Ther. 2015, 15, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.Y.; Zhou, Y.X.; Lu, J.F.; Bai, Y.F.; Xie, X.Y.; Lu, Z.H. miRNA in Plasma Exosome is Stable under Different Storage Conditions. Molecules 2014, 19, 1568–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koga, Y.; Yasunaga, M.; Moriya, Y.; Akasu, T.; Fujita, S.; Yamamoto, S.; Matsumura, Y. Exosome can prevent RNase from degrading microRNA in feces. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2011, 2, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chugh, P.; Dittmer, D.P. Potential pitfalls in microRNA profiling. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2012, 3, 601–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, P.T.; Baldwin, D.A.; Scearce, L.M.; Oberholtzer, J.C.; Tobias, J.W.; Mourelatos, Z. Microarray-based, high-throughput gene expression profiling of microRNAs. Nat. Methods 2004, 1, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Lan, W.; Miller, D. Next-Generation Sequencing for MicroRNA Expression Profile. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1617, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.C.; Chen, Y.F.; Chen, H.B.; Fei, S.R.; Chen, D.D.; Cai, X.N.; Liu, L.; Lin, B.C.; Su, H.F.; Zhao, L.H.; et al. Evaluation of Tumor-Derived Exosomal miRNA as Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers for Early-Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Using Next-Generation Sequencing. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 5311–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihelich, B.L.; Dambal, S.; Lin, S.X.; Nonn, L. miR-182, of the miR-183 cluster family, is packaged in exosomes and is detected in human exosomes from serum, breast cells and prostate cells. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 1197–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, R.; Wang, P.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Chen, J.X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.Z.; Zhang, C.G.; Jiang, T.; Li, W.B.; Ding, W.; et al. Exosomal levels of miRNA-21 from cerebrospinal fluids associated with poor prognosis and tumor recurrence of glioma patients. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 26971–26981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.Y.; Yuan, T.Z.; Liang, M.H.; Du, M.J.; Xia, S.; Dittmar, R.; Wang, D.; See, W.; Costello, B.A.; Quevedo, F.; et al. Exosomal miR-1290 and miR-375 as Prognostic Markers in Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2015, 67, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannafon, B.N.; Trigoso, Y.D.; Calloway, C.L.; Zhao, Y.D.; Lum, D.H.; Welm, A.L.; Zhao, Z.J.; Blick, K.E.; Dooley, W.C.; Ding, W.Q. Plasma exosome microRNAs are indicative of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. BCR 2016, 18, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.; Moallem, R.; Hassanian, S.M.; Sadeghzade, M.; Mardani, R.; Ferns, G.A.; Khazaei, M.; Avan, A. Tumor-derived exosomes: Potential biomarkers and therapeutic target in the treatment of colorectal cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 12422–12432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Kamohara, H.; Kinoshita, K.; Kurashige, J.; Ishimoto, T.; Iwatsuki, M.; Watanabe, M.; Baba, H. Clinical impact of serum exosomal microRNA-21 as a clinical biomarker in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Am. Cancer Soc. 2013, 119, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, C.L.A.; Co, N.N.; Tsuruga, T.; Yeung, T.L.; Kwan, S.Y.; Leung, C.S.; Li, Y.; Lu, E.S.; Kwan, K.; Wong, K.K.; et al. Exosomal transfer of stroma-derived miR21 confers paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer cells through targeting APAF1. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaoka, R.; Iinuma, H.; Dejima, H.; Sakai, T.; Uehara, H.; Matsutani, N.; Kawamura, M. Usefulness of Plasma Exosomal MicroRNA-451a as a Noninvasive Biomarker for Early Prediction of Recurrence and Prognosis of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncology 2018, 94, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Iinuma, H.; Umemoto, Y.; Yanagisawa, T.; Matsumoto, A.; Jinno, H. Exosome-encapsulated microRNA-223-3p as a minimally invasive biomarker for the early detection of invasive breast cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 9584–9592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, F.M.; Qing, Q.; Pan, Q.; Hu, M.; Yu, H.M.; Yue, X. Serum exosomal miR-301a as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for human glioma. Cell. Oncol. 2018, 41, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.D.; Muller, V.; Milde-Langosch, K.; Trillsch, F.; Pantel, K.; Schwarzenbach, H. Diagnostic and prognostic relevance of circulating exosomal miR-373, miR-200a, miR-200b and miR-200c in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 16923–16935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eichelser, C.; Stuckrath, I.; Muller, V.; Milde-Langosch, K.; Wikman, H.; Pantel, K.; Schwarzenbach, H. Increased serum levels of circulating exosomal microRNA-373 in receptor-negative breast cancer patients. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 9650–9663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejima, H.; Iinuma, H.; Kanaoka, R.; Matsutani, N.; Kawamura, M. Exosomal microRNA in plasma as a non-invasive biomarker for the recurrence of non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmittgen, T.D. Exosomal miRNA Cargo as Mediator of Immune Escape Mechanisms in Neuroblastoma. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 1293–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Usman, W.M.; Pham, T.C.; Kwok, Y.Y.; Vu, L.T.; Ma, V.; Peng, B.; Chan, Y.S.; Wei, L.; Chin, S.M.; Azad, A.; et al. Efficient RNA drug delivery using red blood cell extracellular vesicles. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, S.; Li, P.; Zheng, C.; Zhou, X.; Tao, Y.; Chen, X.; Sun, L.; Wang, A.; et al. Blockage of transferred exosome-shuttled miR-494 inhibits melanoma growth and metastasis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, A.; Takahashi, Y.; Nishikawa, M.; Sano, K.; Morishita, M.; Charoenviriyakul, C.; Saji, H.; Takakura, Y. Accelerated growth of B16BL6 tumor in mice through efficient uptake of their own exosomes by B16BL6 cells. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 1803–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Tu, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J. Inhibition of multiple myelomaderived exosomes uptake suppresses the functional response in bone marrow stromal cell. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Exosomal Mir | Tumor | Effect | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oncogenic mir | |||
| miR-10b | Breast cancer | Invasion ↑ | [72] |
| miR-223 | Pancreatic cancer | Invasion↑ | [73] |
| miR-32-5p | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Drug resistance ↑ | [74] |
| miR-99a-5p, miR-125b-5p | Large B-cell lymphoma | Drug resistance ↑ | [75] |
| miR-9 | Glioma | Angiogenesis ↑ | [76] |
| miR-93-5p | Oesophageal cancer | Growth ↑ | [77] |
| miR-21,miR-378e,miR-143 | Breast Cancer | EMT and stemness ↑ | [54] |
| Oncosuppressor MIR | |||
| miR-192 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Metastasis ↓ | [78] |
| miR-451a | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Apoptosis ↑, Angiogenesis ↓ | [79] |
| miR-9 | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | Angiogenesis ↓ | [80] |
| miR-8073 | Colorectal cancer | Growth ↓ | [81] |
| miR-100 | Breast cancer | Angiogenesis ↓ | [82] |
| miR-16-5p | Mesothelioma | Growth ↓, migration ↓, invasion ↓ | [83] |
| miR-199a | Glioma | Growth ↓, migration ↓, invasion ↓ | [84] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ingenito, F.; Roscigno, G.; Affinito, A.; Nuzzo, S.; Scognamiglio, I.; Quintavalle, C.; Condorelli, G. The Role of Exo-miRNAs in Cancer: A Focus on Therapeutic and Diagnostic Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4687. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194687
Ingenito F, Roscigno G, Affinito A, Nuzzo S, Scognamiglio I, Quintavalle C, Condorelli G. The Role of Exo-miRNAs in Cancer: A Focus on Therapeutic and Diagnostic Applications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(19):4687. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194687
Chicago/Turabian StyleIngenito, Francesco, Giuseppina Roscigno, Alessandra Affinito, Silvia Nuzzo, Iolanda Scognamiglio, Cristina Quintavalle, and Gerolama Condorelli. 2019. "The Role of Exo-miRNAs in Cancer: A Focus on Therapeutic and Diagnostic Applications" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 19: 4687. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194687
APA StyleIngenito, F., Roscigno, G., Affinito, A., Nuzzo, S., Scognamiglio, I., Quintavalle, C., & Condorelli, G. (2019). The Role of Exo-miRNAs in Cancer: A Focus on Therapeutic and Diagnostic Applications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(19), 4687. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194687






