Urinary Human Epididymis Secretory Protein 4 as a Useful Biomarker for Subclinical Acute Rejection Three Months after Kidney Transplantation
Abstract
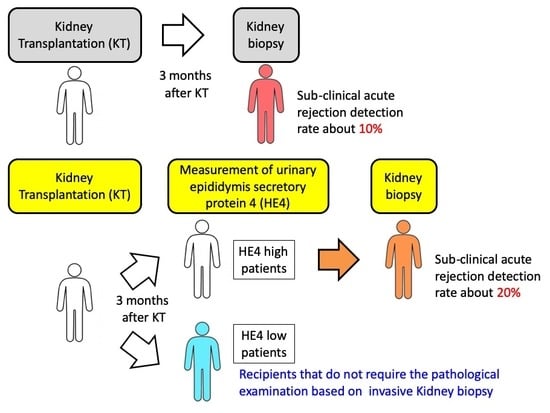
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patient Characteristics
2.2. Diagnostic Ability of Urinary Biomarkers
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Subjects
4.2. Urine samples
4.3. Diagnostic Criteria SubAR and Data Collection
4.4. Statistical Analyses
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nankivell, B.J.; Chapman, J.R. The significance of subclinical rejection and the value of protocol biopsies. Am. J. Transplant. 2006, 6, 2006–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kee, T.Y.; Chapman, J.R.; O’Connell, P.J.; Fung, C.L.; Allen, R.D.; Kable, K.; Vitalone, M.J.; Nankivell, B.J. Treatment of subclinical rejection diagnosed by protocol biopsy of kidney transplants. Transplantation 2006, 82, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heilman, R.L.; Devarapalli, Y.; Chakkera, H.A.; Mekeel, K.L.; Moss, A.A.; Mulligan, D.C.; Mazur, M.J.; Hamawi, K.; Williams, J.W.; Reddy, K.S. Impact of subclinical inflammation on the development of interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy in kidney transplant recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 2010, 10, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosio, F.G.; Grande, J.P.; Larson, T.S.; Gloor, J.M.; Velosa, J.A.; Textor, S.C.; Griffin, M.D.; Stegall, M.D. Kidney allograft fibrosis and atrophy early after living donor transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2005, 5, 1130–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nankivell, B.J.; Borrows, R.J.; Fung, C.L.; O’Connell, P.J.; Chapman, J.R.; Allen, R.D. Delta analysis of posttransplantation tubulointerstitial damage. Transplantation 2004, 78, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rush, D.; Jeffery, J.; Trpkov, K.; Solez, K.; Gough, J. Effect of subclinical rejection on renal allograft histology and function at 6 months. Transplant. Proc. 1996, 28, 494–495. [Google Scholar]
- Shishido, S.; Asanuma, H.; Nakai, H.; Mori, Y.; Satoh, H.; Kamimaki, I.; Hataya, H.; Ikeda, M.; Honda, M.; Hasegawa, A. The impact of repeated subclinical acute rejection on the progression of chronic allograft nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, 1046–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rush, D.N.; Jeffery, J.R.; Gough, J. Sequential protocol biopsies in renal transplant patients. Clinico-pathological correlations using the Banff schema. Transplantation 1995, 59, 511–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, G.P.; Shah, S.V. Autophagy in acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 779–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, X.P.; Yi, Z.W. Efficacy of antisense monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) in a rat model of mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis. Ren. Fail. 2013, 35, 1418–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishihara, K.; Masuda, S.; Shinke, H.; Ozawa, A.; Ichimura, T.; Yonezawa, A.; Nakagawa, S.; Inui, K.; Bonventre, J.V.; Matsubara, K. Urinary chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 (monocyte chemotactic protein-1) as a tubular injury marker for early detection of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 85, 570–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maatman, R.G.; van de Westerlo, E.M.; van Kuppevelt, T.H.; Veerkamp, J.H. Molecular identification of the liver- and the heart-type fatty acid-binding proteins in human and rat kidney. Use of the reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction. Biochem. J. 1992, 288, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ichikawa, D.; Kamijo-Ikemori, A.; Sugaya, T.; Shibagaki, Y.; Yasuda, T.; Hoshino, S.; Katayama, K.; Igarashi-Migitaka, J.; Hirata, K.; Kimura, K. Human liver-type fatty acid-binding protein protects against tubulointerstitial injury in aldosterone-induced renal injury. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2015, 308, F114–F121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasilewska, A.; Zoch-Zwierz, W.; Taranta-Janusz, K.; Michaluk-Skutnik, J. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL): A new marker of cyclosporine nephrotoxicity? Pediatr. Nephrol. 2010, 25, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, J.; Dent, C.; Tarabishi, R.; Mitsnefes, M.M.; Ma, Q.; Kelly, C.; Ruff, S.M.; Zahedi, K.; Shao, M.; Bean, J.; et al. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a biomarker for acute renal injury after cardiac surgery. Lancet 2005, 365, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedjic, J.; Aichinger, M.; Emmerich, J.; Mizushima, N.; Klein, L. Autophagy in thymic epithelium shapes the T-cell repertoire and is essential for tolerance. Nature 2008, 455, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsuchimoto, A.; Shinke, H.; Uesugi, M.; Kikuchi, M.; Hashimoto, E.; Sato, T.; Ogura, Y.; Hata, K.; Fujimoto, Y.; Kaido, T.; et al. Urinary Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin: A Useful Biomarker for Tacrolimus-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Liver Transplant Patients. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clauss, A.; Lilja, H.; Lundwall, A. A locus on human chromosome 20 contains several genes expressing protease inhibitor domains with homology to whey acidic protein. Biochem. J. 2002, 368, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- LeBleu, V.S.; Teng, Y.; O’Connell, J.T.; Charytan, D.; Muller, G.A.; Muller, C.A.; Sugimoto, H.; Kalluri, R. Identification of human epididymis protein-4 as a fibroblast-derived mediator of fibrosis. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wan, J.; Wang, Y.; Cai, G.; Liang, J.; Yue, C.; Wang, F.; Song, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, M.; Luo, J.; et al. Elevated serum concentrations of HE4 as a novel biomarker of disease severity and renal fibrosis in kidney disease. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 67748–67759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, T.; Li, Y. Human Epididymis Protein 4 as a Potential Biomarker of Chronic Kidney Disease in Female Patients With Normal Ovarian Function. Lab. Med. 2017, 48, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, B., Jr.; Krasznai, Z.T.; Balla, H.; Csoban, M.; Antal-Szalmas, P.; Hernadi, Z.; Kappelmayer, J. Elevated human epididymis protein 4 concentrations in chronic kidney disease. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2012, 49, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, S.; Nishihara, K.; Miyata, H.; Shinke, H.; Tomita, E.; Kajiwara, M.; Matsubara, T.; Iehara, N.; Igarashi, Y.; Yamada, H.; et al. Molecular Markers of Tubulointerstitial Fibrosis and Tubular Cell Damage in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bingle, C.D.; Vyakarnam, A. Novel innate immune functions of the whey acidic protein family. Trends. Immunol. 2008, 29, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Sun, Y.; Cai, X.; Fu, G. The diagnostic value of human epididymis protein 4 as a novel biomarker in patients with renal dysfunction. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, M.; Lowe, D.; Cobbold, M.; Higgins, R.; Briggs, D.; Inston, N.; Ready, A.R. The use of NGAL and IP-10 in the prediction of early acute rejection in highly sensitized patients following HLA-incompatible renal transplantation. Transpl. Int. 2014, 27, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kohei, J.; Ishida, H.; Tanabe, K.; Tsuchiya, K.; Nitta, K. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin is a sensitive biomarker for the early diagnosis of acute rejection after living-donor kidney transplantation. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2013, 45, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyne, N.; Kemmner, S.; Schneider, C.; Nadalin, S.; Konigsrainer, A.; Haring, H.U. Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin accurately detects acute allograft rejection among other causes of acute kidney injury in renal allograft recipients. Transplantation 2012, 93, 1252–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Qian, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Du, Y.; Dai, H.; Qian, J.; Yan, Y. Autophagy protects renal tubular cells against ischemia / reperfusion injury in a time-dependent manner. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 36, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondylis, V.; van Nispen Tot Pannerden, H.E.; van Dijk, S.; Ten Broeke, T.; Wubbolts, R.; Geerts, W.J.; Seinen, C.; Mutis, T.; Heijnen, H.F. Endosome-mediated autophagy: An unconventional MIIC-driven autophagic pathway operational in dendritic cells. Autophagy 2013, 9, 861–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.K.; Lund, J.M.; Ramanathan, B.; Mizushima, N.; Iwasaki, A. Autophagy-dependent viral recognition by plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Science 2007, 315, 1398–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pua, H.H.; He, Y.W. Maintaining T lymphocyte homeostasis: Another duty of autophagy. Autophagy 2007, 3, 266–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degli Esposti, D.; Sebagh, M.; Pham, P.; Reffas, M.; Pous, C.; Brenner, C.; Azoulay, D.; Lemoine, A. Ischemic preconditioning induces autophagy and limits necrosis in human recipients of fatty liver grafts, decreasing the incidence of rejection episodes. Cell Death Dis. 2011, 2, e111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, M.A.; Vaidya, V.S.; Waikar, S.S.; Collings, F.B.; Sunderland, K.E.; Gioules, C.J.; Bonventre, J.V. Urinary liver-type fatty acid-binding protein predicts adverse outcomes in acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2010, 77, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Portilla, D.; Dent, C.; Sugaya, T.; Nagothu, K.K.; Kundi, I.; Moore, P.; Noiri, E.; Devarajan, P. Liver fatty acid-binding protein as a biomarker of acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, J.; Wang, F.; Wan, J.; Ye, Z.; Huang, C.; Cai, Y.; Liu, M.; Wu, B.Q.; Li, L. Serum human epididymis secretory protein 4 as a potential biomarker of renal fibrosis in kidney transplantation recipients. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 483, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colvin, R.B.; Cohen, A.H.; Saiontz, C.; Bonsib, S.; Buick, M.; Burke, B.; Carter, S.; Cavallo, T.; Haas, M.; Lindblad, A.; et al. Evaluation of pathologic criteria for acute renal allograft rejection: Reproducibility, sensitivity, and clinical correlation. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1997, 8, 1930–1941. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo, S.; Imai, E.; Horio, M.; Yasuda, Y.; Tomita, K.; Nitta, K.; Yamagata, K.; Tomino, Y.; Yokoyama, H.; Hishida, A. Revised equations for estimated GFR from serum creatinine in Japan. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2009, 53, 982–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristics | No-SubAR (n = 69) | subAR (n = 11) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recipient age (years) | 42.9 ± 12.7 | 53.8 ± 14.7 | 0.019 |
| Recipient sex (male/female) | 43/26 | 5/6 | NS |
| Primary disease (n) | NS | ||
| Glomerulonephritis | 25 (36.2) | 5 (45.5) | |
| Diabetes | 17 (24.6) | 4 (36.4) | |
| Polycystic kidney disease | 4 (5.8) | 2 (18.2) | |
| Others | 23 (33.3) | 0 (0.0) | |
| ABO blood group match (n) | NS | ||
| Identical | 45 (65.2) | 6 (54.5) | |
| Compatible | 10 (14.5) | 2 (18.2) | |
| Incompatible | 14 (20.3) | 3 (27.3) | |
| Preoperative Scr (mg/dL) | 8.5 ± 4.1 | 8.9 ± 2.9 | NS |
| Preoperative BUN (mg/dL) | 59.0 ± 21.2 | 61.4 ± 20.2 | NS |
| Preoperative eGFR (mL/min/1.73m2) | 7.6 ± 4.6 | 5.7 ± 2.7 | NS |
| AUC (95% CI) | Cut-off Value | Sensitivity (95% CI) | Specificity (95% CI) | Positive Predictive Value | Negative Predictive Value | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LC3 (pg/mg creatinine) | 0.725 (0.554–0.895) | 517.9 | 0.64 (0.31–0.89) | 0.78 (0.67–0.87) | 0.32 | 0.93 | 0.01725 |
| MCP-1(pg/mg creatinine) | 0.688 (0.539–0.837) | 226.0 | 0.82 (0.48–0.98) | 0.57 (0.44–0.68) | 0.23 | 0.95 | 0.04655 |
| L-FABP (ng/mg creatinine) | 0.606 (0.446–0.767) | 7.6 | 0.09 (0.00–0.41) | 0.88 (0.78–0.94) | 0.15 | 1.00 | 0.2608 |
| NGAL (ng/mg creatinine) | 0.715 (0.589–0.842) | 12.8 | 1.00 (0.72–1.00) | 0.48 (0.36–0.60) | 0.23 | 1.00 | 0.0224 |
| HE4 (ng/mg creatinine) | 0.808 (0.700–0.916) | 789.1 | 1.00 (0.72–1.00) | 0.54 (0.41–0.66) | 0.26 | 1.00 | 0.001113 |
| AUC (95% CI) | Cut-off Value | Sensitivity (95% CI) | Specificity (95% CI) | Positive Predictive Value | Negative Predictive Value | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LC3 (pg/mg creatinine) | 0.584 (0.339–0.829) | 131.7 | 1.00 (0.48–1.00) | 0.24 (0.15–0.35) | 0.08 | 1.00 | 0.5313 |
| MCP-1 (pg/mg creatinine) | 0.632 (0.365–0.899) | 417.9 | 0.60 (0.15–0.95) | 0.76 (0.65–0.85) | 0.14 | 0.97 | 0.3252 |
| L-FABP (ng/mg creatinine) | 0.600 (0.388–0.812) | 7.2 | 0.20 (0.00–0.71) | 0.86 (0.76–0.93) | 0.07 | 1.00 | 0.4561 |
| NGAL (ng/mg creatinine) | 0.867 (0.745–0.989) | 23.0 | 1.00 (0.48–1.00) | 0.72 (0.60–0.82) | 0.19 | 1.00 | 0.006299 |
| HE4 (ng/mg creatinine) | 0.875 (0.731–1.018) | 1165.6 | 0.80 (0.28–0.99) | 0.84 (0.74–0.91) | 0.25 | 0.98 | 0.005248 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tajima, S.; Fu, R.; Shigematsu, T.; Noguchi, H.; Kaku, K.; Tsuchimoto, A.; Okabe, Y.; Masuda, S. Urinary Human Epididymis Secretory Protein 4 as a Useful Biomarker for Subclinical Acute Rejection Three Months after Kidney Transplantation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4699. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194699
Tajima S, Fu R, Shigematsu T, Noguchi H, Kaku K, Tsuchimoto A, Okabe Y, Masuda S. Urinary Human Epididymis Secretory Protein 4 as a Useful Biomarker for Subclinical Acute Rejection Three Months after Kidney Transplantation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(19):4699. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194699
Chicago/Turabian StyleTajima, Soichiro, Rao Fu, Tomohiro Shigematsu, Hiroshi Noguchi, Keizo Kaku, Akihiro Tsuchimoto, Yasuhiro Okabe, and Satohiro Masuda. 2019. "Urinary Human Epididymis Secretory Protein 4 as a Useful Biomarker for Subclinical Acute Rejection Three Months after Kidney Transplantation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 19: 4699. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194699
APA StyleTajima, S., Fu, R., Shigematsu, T., Noguchi, H., Kaku, K., Tsuchimoto, A., Okabe, Y., & Masuda, S. (2019). Urinary Human Epididymis Secretory Protein 4 as a Useful Biomarker for Subclinical Acute Rejection Three Months after Kidney Transplantation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(19), 4699. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194699