Effect of Saliva Collection Methods on the Detection of Periodontium-Related Genetic and Epigenetic Biomarkers—A Pilot Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Periodontal Status of Participants
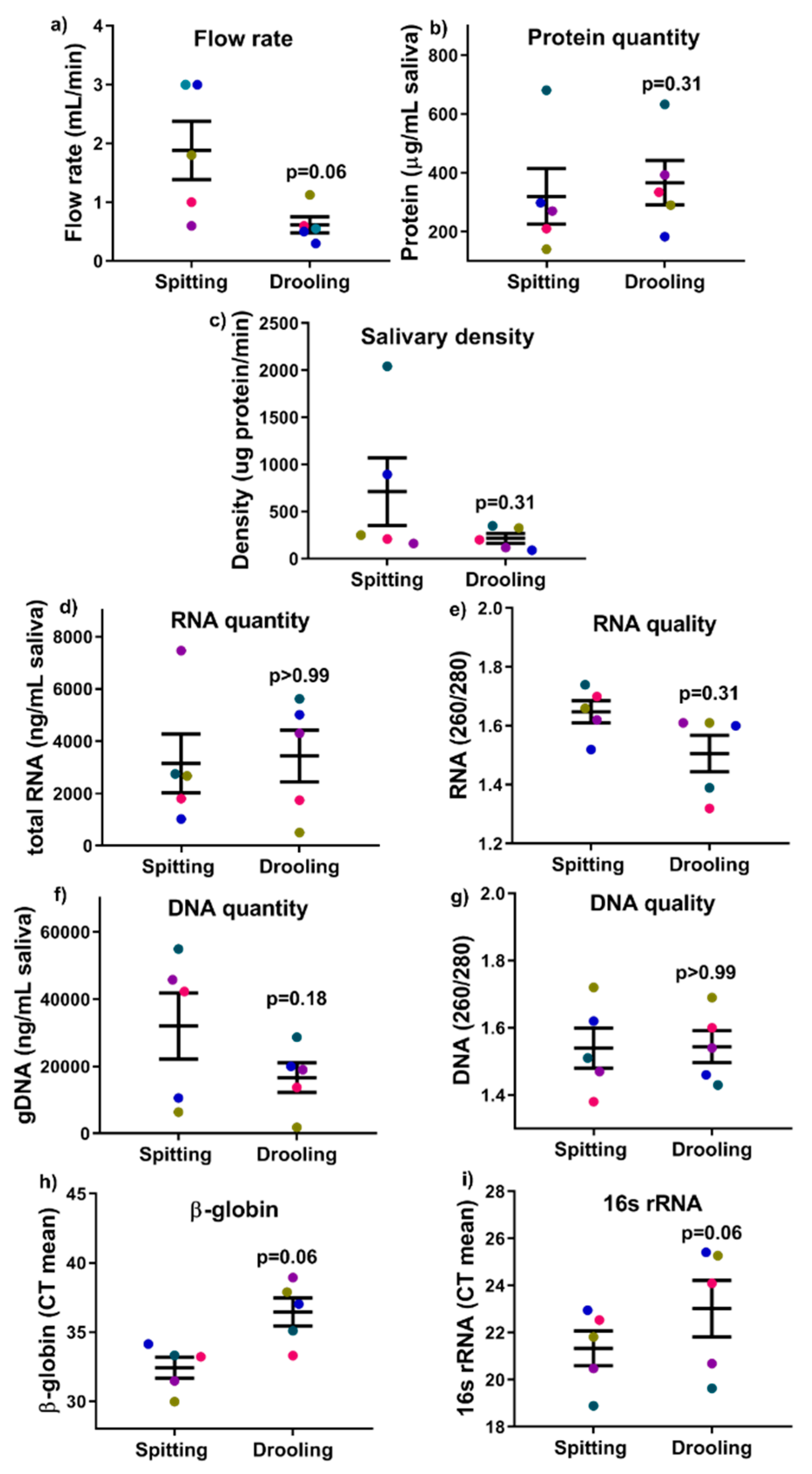
2.2. Salivary Flow Rate, DNA/RNA/Protein Quantity and Quality
2.3. Osteogenic and Wnt Pathway-Related Gene Expression
2.4. DNA and RNA Methylation Epigenetic Factors Changes
2.5. Four Periodontium-Associated DNA Methylation Levels in Saliva from Different Collection Methods
2.6. Correlation between Gene Methylation Levels and Clinical Parameter
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Participant and Saliva Sample Collection
4.2. Salivary RNA Extraction Using a Trizol™ Method
4.3. Salivary gDNA Isolation Using Trizol
4.4. Salivary Protein Isolation and Quantification
4.5. gDNA Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
4.6. mRNA Expression for Osteogenic, Wnt-Related Genes and DNA/RNA Methylation Regulators
4.7. Bisulfite Conversion and Quantitative Methylation-Specific PCR (qMSP)
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Humphrey, S.P.; Williamson, R.T. A review of saliva: Normal composition, flow, and function. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2001, 85, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podzimek, S.; Vondrackova, L.; Duskova, J.; Janatova, T.; Broukal, Z. Salivary Markers for Periodontal and General Diseases. Dis. Markers 2016, 2016, 9179632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellagambi, F.G.; Degano, I.; Ghimenti, S.; Lomonaco, T.; Dini, V.; Romanelli, M.; Mastorci, F.; Gemignani, A.; Salvo, P.; Fuoco, R.; et al. Determination of salivary alpha-amylase and cortisol in psoriatic subjects undergoing the Trier Social Stress Test. Microchem. J. 2018, 136, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimenti, S.; Lomonaco, T.; Onor, M.; Murgia, L.; Paolicchi, A.; Fuoco, R.; Ruocco, L.; Pellegrini, G.; Trivella, M.G.; Di Francesco, F. Measurement of warfarin in the oral fluid of patients undergoing anticoagulant oral therapy. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomonaco, T.; Ghimenti, S.; Piga, I.; Biagini, D.; Onor, O.; Fuoco, R.; Paolicchi, A.; Ruocco, L.; Pellegrini, G.; Trivella, M.G.; et al. Monitoring of warfarin therapy: Preliminary results from a longitudinal pilot study. Microchem. J. 2018, 136, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agha-Hosseini, F.; Mirzaii-Dizgah, I.; Mirjalili, N. Relationship of stimulated whole saliva cortisol level with the severity of a feeling of dry mouth in menopausal women. Gerodontology 2012, 29, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henson, B.S.; Wong, D.T. Collection, storage, and processing of saliva samples for downstream molecular applications. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 666, 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- Pfaffe, T.; Cooper-White, J.; Beyerlein, P.; Kostner, K.; Punyadeera, C. Diagnostic potential of saliva: Current state and future applications. Clin. Chem. 2011, 57, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, B.L.; Cooper-White, J.; Punyadeera, C.K. Saliva proteome research: Current status and future outlook. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2013, 33, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worthman, C.M.; Stallings, J.F.; Hofman, L.F. Sensitive salivary estradiol assay for monitoring ovarian function. Clin. Chem. 1990, 36, 1769–1773. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, C.K.; Christodoulides, N.J.; Floriano, P.N.; Miller, C.S.; Ebersole, J.L.; Weigum, S.E.; McDevitt, J.; Redding, S.W. Current development of saliva/oral fluid-based diagnostics. Tex. Dent. J. 2010, 127, 651–661. [Google Scholar]
- Esser, D.; Alvarez-Llamas, G.; de Vries, M.P.; Weening, D.; Vonk, R.J.; Roelofsen, H. Sample Stability and Protein Composition of Saliva: Implications for Its Use as a Diagnostic Fluid. Biomark. Insights 2008, 3, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wren, M.E.; Shirtcliff, E.A.; Drury, S.S. Not all biofluids are created equal: Chewing over salivary diagnostics and the epigenome. Clin. Ther. 2015, 37, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomonaco, T.; Ghimenti, S.; Biagini, D.; Bramanti, E.; Onor, M.; Bellagambi, F.G.; Fuoco, R.; di Francesco, F. The effect of sampling procedures on the urate in oral fluid and lactate concentration in oral fluid. Microchem. J. 2018, 136, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomonaco, T.; Lomonaco, T.; Ghimenti, S.; Piga, I.; Biagini, D.; Onor, M.; Fuoco, R.; di Francesco, F. Influence of sampling on the determination of warfarin and warfarin alcohols in oral fluid. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, G. Gingival crevicular fluid as a periodontal diagnostic indicator- II: Inflammatory mediators, host-response modifiers and chair side diagnostic aids. J. Med. Life 2013, 6, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Giannobile, W.V.; Beikler, T.; Kinney, J.S.; Ramseier, C.A.; Morelli, T.; Wong, D.T. Saliva as a diagnostic tool for periodontal disease: Current state and future directions. Periodontology 2009, 50, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justino, A.B.; Teixeira, R.R.; Peixoto, L.G.; Jaramillo, O.L.B.; Espindola, F.S. Effect of saliva collection methods and oral hygiene on salivary biomarkers. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2017, 77, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michishige, F.; Kanno, K.; Yoshinaga, S.; Hinode, D.; Takehisa, Y.; Yasuoka, S. Effect of saliva collection method on the concentration of protein components in saliva. J. Med. Investig. 2006, 53, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohamed, R.; Campbell, J.L.; Cooper-White, J.; Dimeski, G.; Punyadeera, C. The impact of saliva collection and processing methods on CRP, IgE, and Myoglobin immunoassays. Clin. Transl. Med. 2012, 1, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapp-Santos, K.J.; Altamura, L.A.; Norris, S.L.; Lugo-Roman, L.A.; Rico, P.J.; Hofer, C.C. Comparison of Saliva Collection Methods for the Determination of Salivary Cortisol Levels in Rhesus Macaques (Macaca mulatta), Cynomolgus Macaques (Macaca fascicularis), and African Green Monkeys (Chlorocebus aethiops). J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2017, 56, 181–189. [Google Scholar]
- Yamuna, P.K.; Muthu, P.K. Methods of collection of saliva—A Review. Int. J. Oral Health Dent. 2017, 3, 149–153. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, Y.; Totsika, M.; Punyadeera, M.M.C. The saliva microbiome profiles are minimally affected by collection method or DNA extraction protocols. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; Li, Y.; Robertson, K.D. DNA methylation: Superior or subordinate in the epigenetic hierarchy? Genes Cancer 2011, 2, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominissini, D.; Moshitch-Moshkovitz, S.; Schwartz, S.; Salmon-Divon, M.; Ungar, L.; Osenberg, S.; Cesarkas, K.; Jacob-Hirsch, J.; Amariglio, N.; Kupiec, M.; et al. Topology of the human and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-seq. Nature 2012, 485, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, M.; Eggert, C.; Kaplick, P.M.; Eder, M.; Röh, S.; Tietze, L.; Namendorf, C.; Arloth, J.; Weber, P.; Rex-Haffner, M.; et al. The Role of m(6)A/m-RNA Methylation in Stress Response Regulation. Neuron 2018, 99, 389.e9–403.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desrosiers, R.; Friderici, K.; Rottman, F. Identification of methylated nucleosides in messenger RNA from Novikoff hepatoma cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1974, 71, 3971–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traube, F.R.; Carell, T. The chemistries and consequences of DNA and RNA methylation and demethylation. RNA Biol. 2017, 14, 1099–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torres, I.O.; Fujimori, D.G. Functional coupling between writers, erasers and readers of histone and DNA methylation. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2015, 35, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gillette, T.G.; Hill, J.A. Readers, writers, and erasers: Chromatin as the whiteboard of heart disease. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapple, I.L.C.; Mealey, B.L.; Van Dyke, T.E.; Bartold, P.M.; Dommisch, H.; Eickholz, P.; Geisinger, M.L.; Genco, R.J.; Glogauer, M.; Goldstein, M.; et al. Periodontal health and gingival diseases and conditions on an intact and a reduced periodontium: Consensus report of workgroup 1 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant. Diseases and Conditions. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. 1), S74–S84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, E. The Scientific Basis of Oral Health Education. J. Orthod. 2015, 42, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, R. The scientific basis of oral health education. Community Dent Health 2004, 21, 131–133. [Google Scholar]
- Sreebny, L.M.; Valdini, A. Xerostomia: A neglected symptom. Arch. Intern. Med. 1987, 147, 1333–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Wu, C.; Chang, J.; Xiao, Y. The cementogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament cells via the activation of Wnt/beta-catenin signalling pathway by Li+ ions released from bioactive scaffolds. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 6370–6379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooker, S.M.; Liu, B.; Helms, J.A. Role of Wnt signaling in the biology of the periodontium. Dev. Dyn. 2010, 239, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Ivanovski, S.; Crawford, R.; Xiao, Y. Activation of the Canonical Wnt Signaling Pathway Induces Cementum Regeneration. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2015, 30, 1160–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaenisch, R.; Young, R. Stem cells, the molecular circuitry of pluripotency and nuclear reprogramming. Cell 2008, 132, 567–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Sun, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, E.; Ma, Z.; Xu, W.; Li, H.; Qiu, M.; Xu, Y.; Xia, W.; et al. Roles of RNA methylation by means of N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A) in human cancers. Cancer Lett. 2017, 408, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, Y.K.; Hong, H.S.; Lee, W.K.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, D.S. Increased Methylation of Interleukin 6 Gene Is Associated with Obesity in Korean Women. Mol. Cells 2015, 38, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nilsson, E.; Jansson, P.A.; Perfilyev, A.; Volkov, P.; Pedersen, M.; Svensson, M.K.; Poulsen, P.; Ribel-Madsen, R.; Pedersen, N.L.; Almgren, P.; et al. Altered DNA methylation and differential expression of genes influencing metabolism and inflammation in adipose tissue from subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2014, 63, 2962–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, S.J.; Aubourg, G.; Sorial, A.K.; Almarza, D.; Tselepi, M.; Deehan, D.J.; Reynard, L.N.; Loughlin, J. Identification of a novel, methylation-dependent, RUNX2 regulatory region associated with osteoarthritis risk. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 27, 3464–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo-Jousse, V.; Garcia-Diaz, D.F.; Codner, E.; Pérez-Bravo, F. Epigenetics in type 1 diabetes: TNFa gene promoter methylation status in Chilean patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, 1861–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, N.F.; Damm, G.R.; Andia, D.C.; Salmon, C.; Nociti, F.H., Jr.; Line, S.R.; de Souza, A.P. DNA methylation status of the IL8 gene promoter in oral cells of smokers and non-smokers with chronic periodontitis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2009, 36, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefani, F.A.; Viana, M.B.; Dupim, A.C.; Brito, J.A.; Gomez, R.S.; da Costa, J.E.; Moreira, P.R. Expression, polymorphism and methylation pattern of interleukin-6 in periodontal tissues. Immunobiology 2013, 218, 1012–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.P.; Barros, S.P.; Moretti, A.J.; Yu, N.; Zhou, J.; Preisser, J.S.; Niculescu, M.D.; Offenbacher, S. Epigenetic Regulation of TNFA Expression in Periodontal Disease. J. Periodontol. 2013, 84, 1606–1616. [Google Scholar]
- Andia, D.C.; de Oliveira, N.F.; Casarin, R.C.; Casati, M.Z.; Line, S.R.; de Souza, A.P. DNA methylation status of the IL8 gene promoter in aggressive periodontitis. J. Periodontol. 2010, 81, 1336–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asa’ad, F.; Bollati, V.; Pagni, G.; Castilho, R.M.; Rossi, E.; Pomingi, F.; Tarantini, L.; Consonni, D.; Giannobile, W.V.; Rasperini, G. Evaluation of DNA methylation of inflammatory genes following treatment of chronic periodontitis: A pilot case-control study. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, P.; Cooper-White, J.; Punyadeera, C. High-yield RNA-extraction method for saliva. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 1118–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.C.; Dahiya, R. MethPrimer: Designing primers for methylation PCRs. Bioinformatics 2002, 18, 1427–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Gender | Age | PPD | BOP | Collection Method | Ethnicity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | F | 33 | <4 mm | 27% | Spitting, drooling | Asian |
| 2 | M | 29 | <4 mm | 41% | Spitting, drooling | Asian |
| 3 | M | 38 | <4 mm | 14% | Spitting, drooling | Caucasian |
| 4 | F | 38 | <4 mm | 10% | Spitting, drooling | Asian |
| 5 | M | 24 | <4 mm | 6% | Spitting, drooling | Caucasian |
| Spitting | Drooling | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 9 | 4 |
| 2 | 9 | 2 |
| 3 | 9 | 3 |
| 4 | 9 | 1 |
| 5 | 9 | 1 |
| Gene | Forward (5′-3′) | Reverse (5′-3′) | Product (bp) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RUNX2 | M pair | AGATTTCGTTCGGTAGTCGG | CTCACGTCGCTCATTTTACC | 257 |
| U pair | AGATTTTGTTTGGTAGTTGG | CTCACATCACTCATTTTACC | 257 | |
| CEMP1 | M pair | TTACGAGGTGTAGAGGTTCGG | ACTCTCAAAACTAATAAAAATAACCCGT | 200 |
| U pair | TTATGAGGTGTAGAGGTTTGGA | ACTCTCAAAACTAATAAAAATAACCCATTT | 200 | |
| IL 6 | M pair | GAGTTTATCGGGAACGAAAG | CTCCCTCACACAAAACTCGAC | 133 |
| U pair | GAGTTTATTGGGAATGAAAG | CCCTCACACAAAACTCAACC | 131 | |
| TNF α | M pair | GCGATGGAGAAGAAATCGAG | AACAACTACCTTTATATATCCCTAAAACG | 153 |
| U pair | TGATGGAGAAGAAATTGAGAT | AACTACCTTTATATATCCCTAAAACAAAAA | 149 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, P.; Ivanovski, S. Effect of Saliva Collection Methods on the Detection of Periodontium-Related Genetic and Epigenetic Biomarkers—A Pilot Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4729. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194729
Han P, Ivanovski S. Effect of Saliva Collection Methods on the Detection of Periodontium-Related Genetic and Epigenetic Biomarkers—A Pilot Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(19):4729. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194729
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Pingping, and Sašo Ivanovski. 2019. "Effect of Saliva Collection Methods on the Detection of Periodontium-Related Genetic and Epigenetic Biomarkers—A Pilot Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 19: 4729. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194729
APA StyleHan, P., & Ivanovski, S. (2019). Effect of Saliva Collection Methods on the Detection of Periodontium-Related Genetic and Epigenetic Biomarkers—A Pilot Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(19), 4729. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194729






