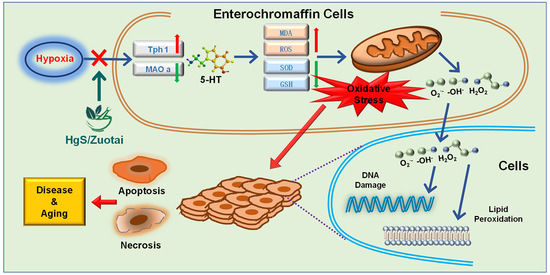
HgS Inhibits Oxidative Stress Caused by Hypoxia through Regulation of 5-HT Metabolism Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
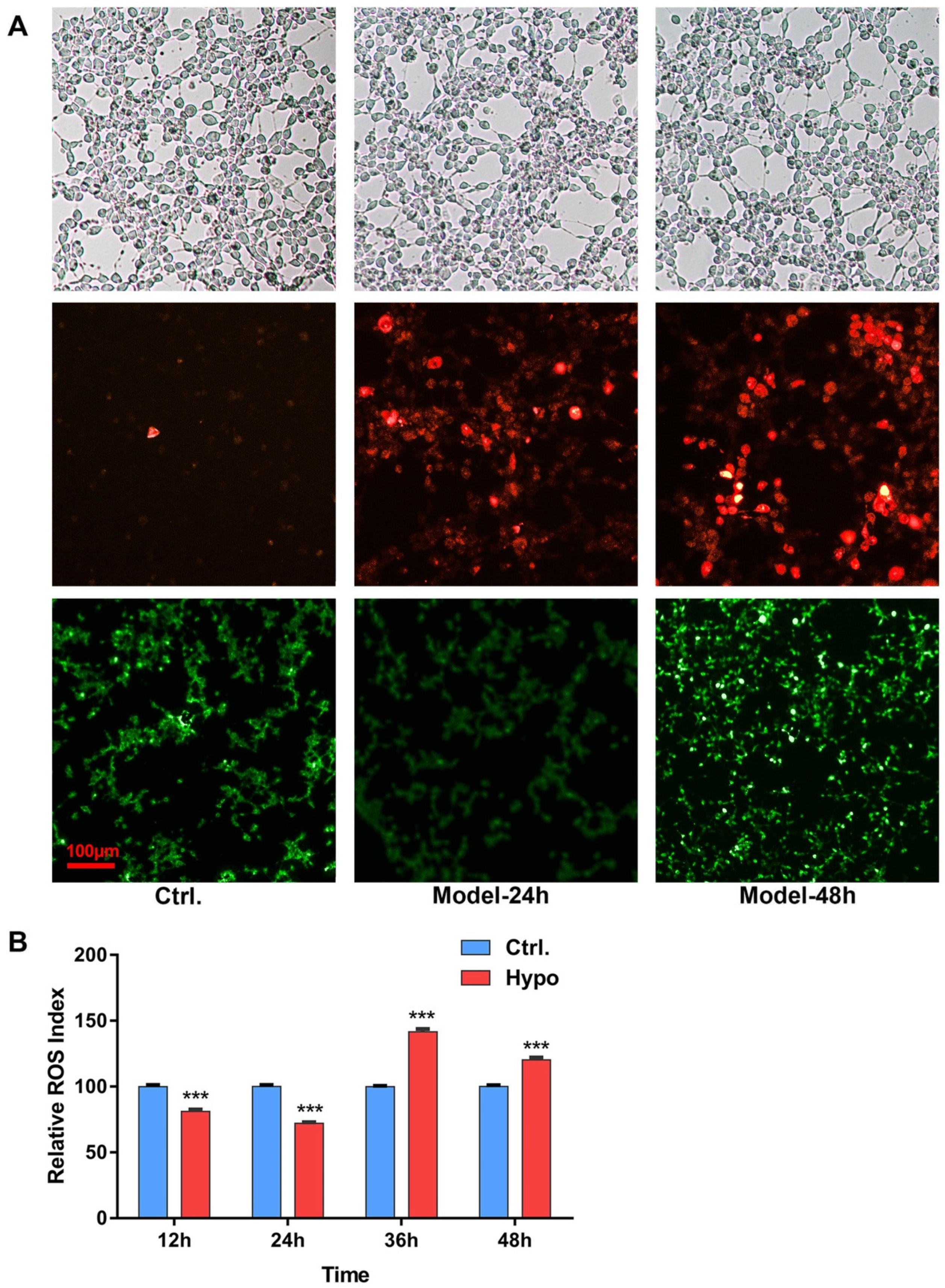
2.1. Relative ROS of RIN-14B Cells after Hypoxia Treatment
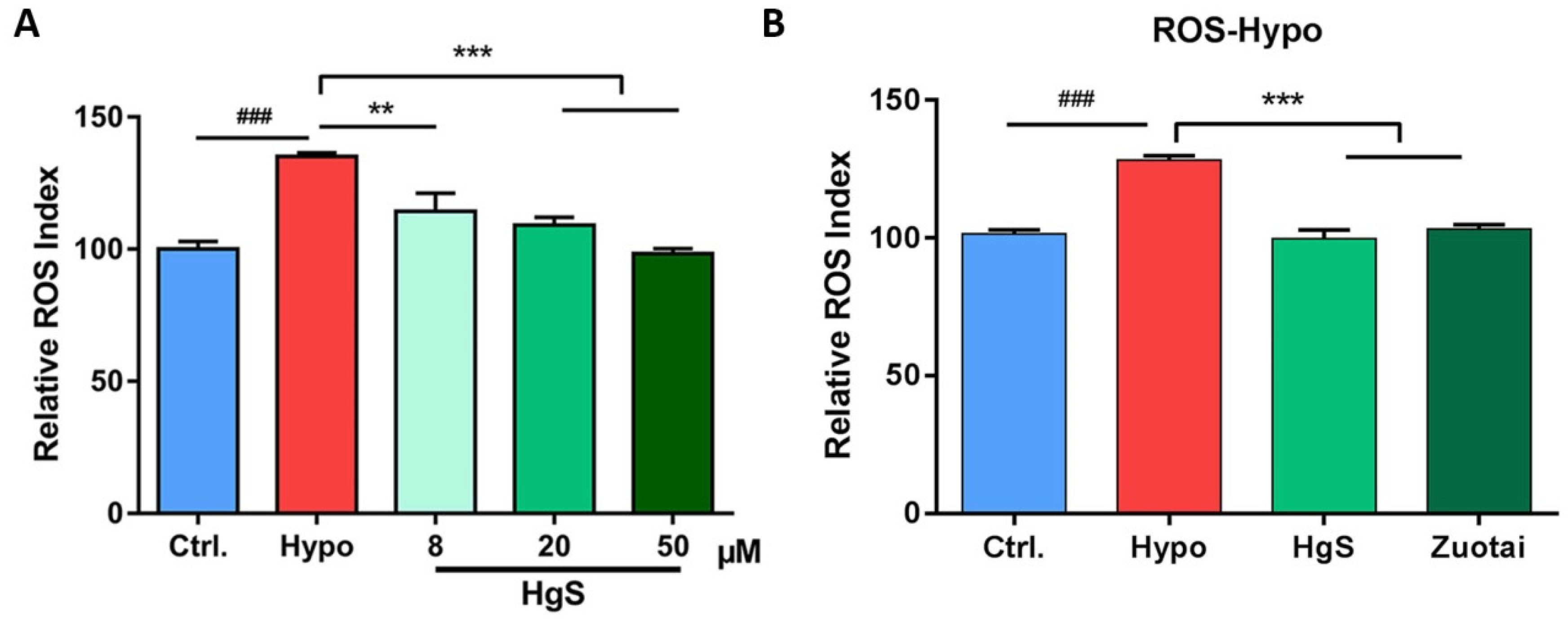
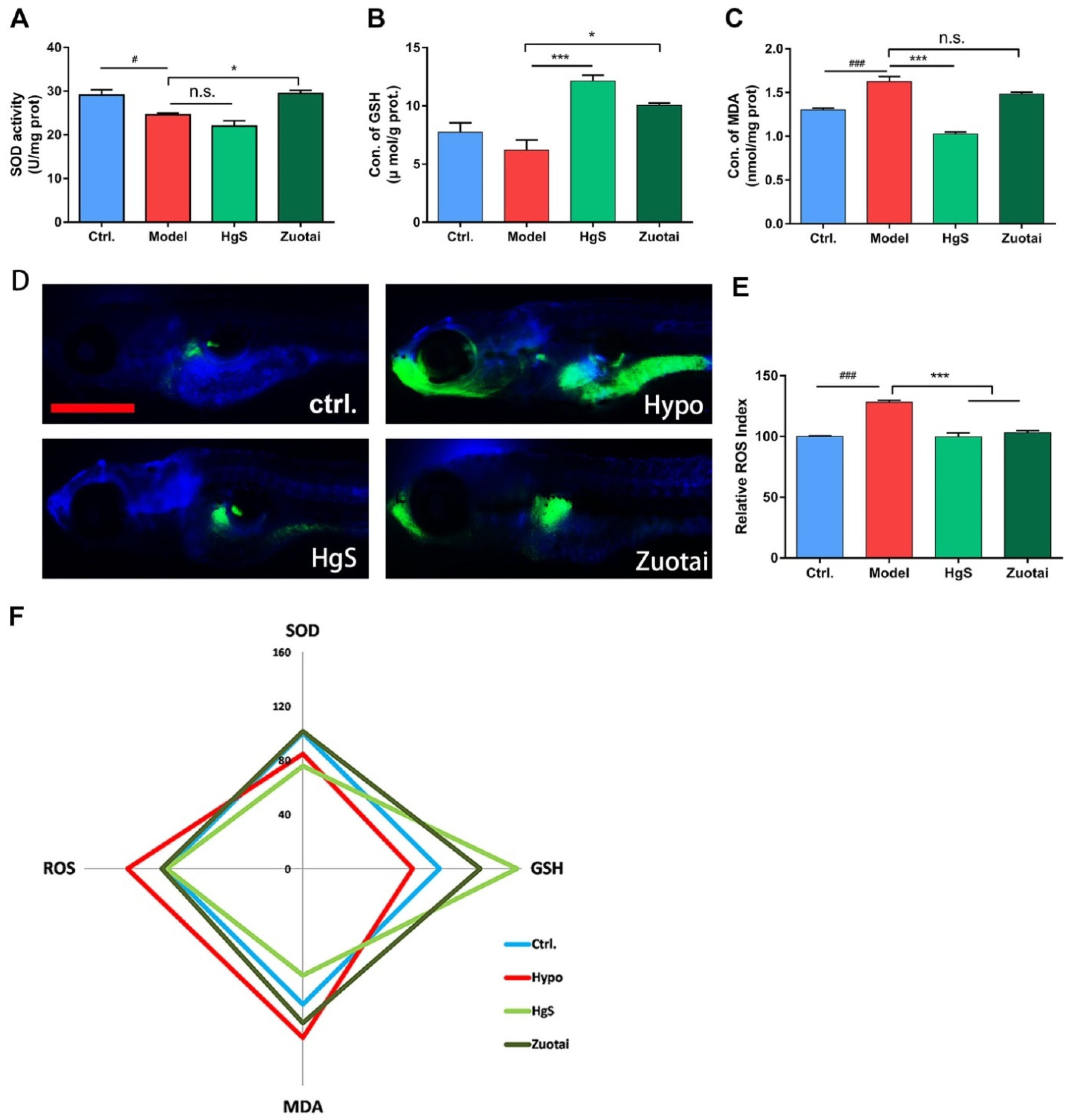
2.2. The Effects of HgS and Zuotai on Abnormal ROS Level of RIN-14B Cells
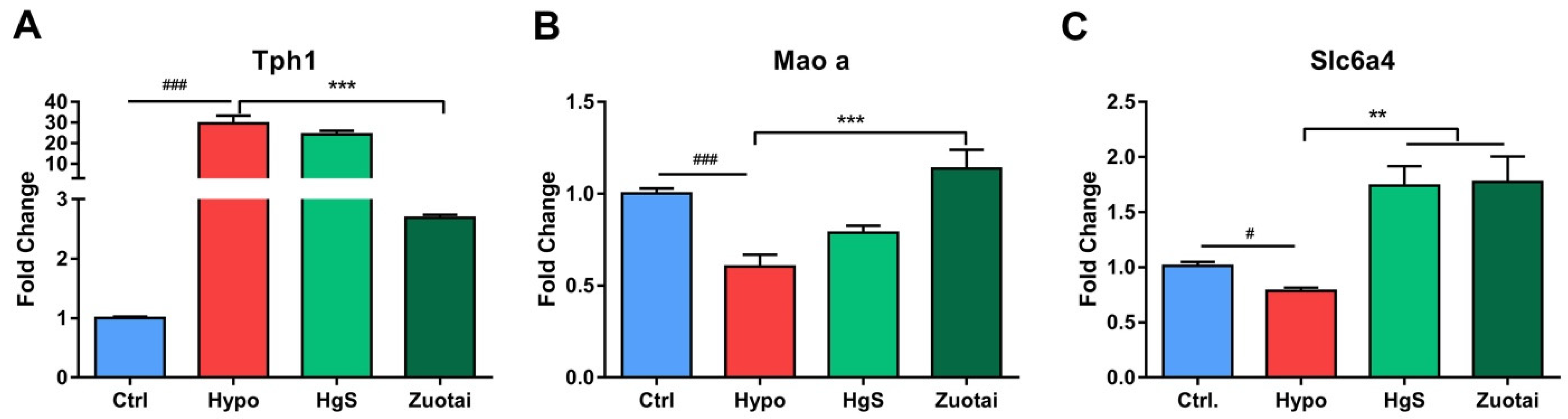
2.3. 5-HT Metabolism Pathway mRNA Expression in the RIN-14B
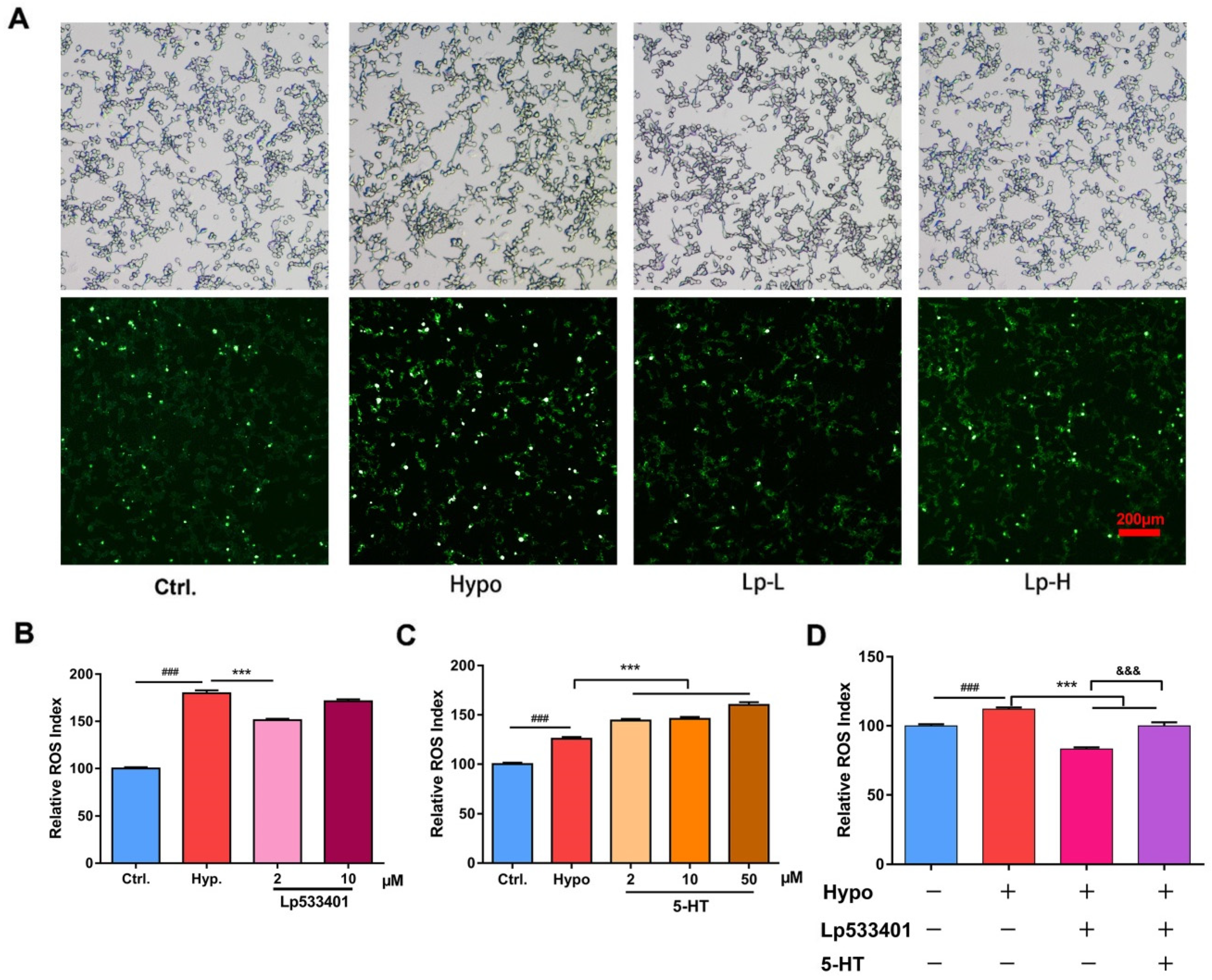
2.4. The 5-HT Metabolism Pathway Influenced the ROS Generation in RIN-14B Cells
2.5. HgS and Zuotai Regulated Redox State of Larval Zebrafish
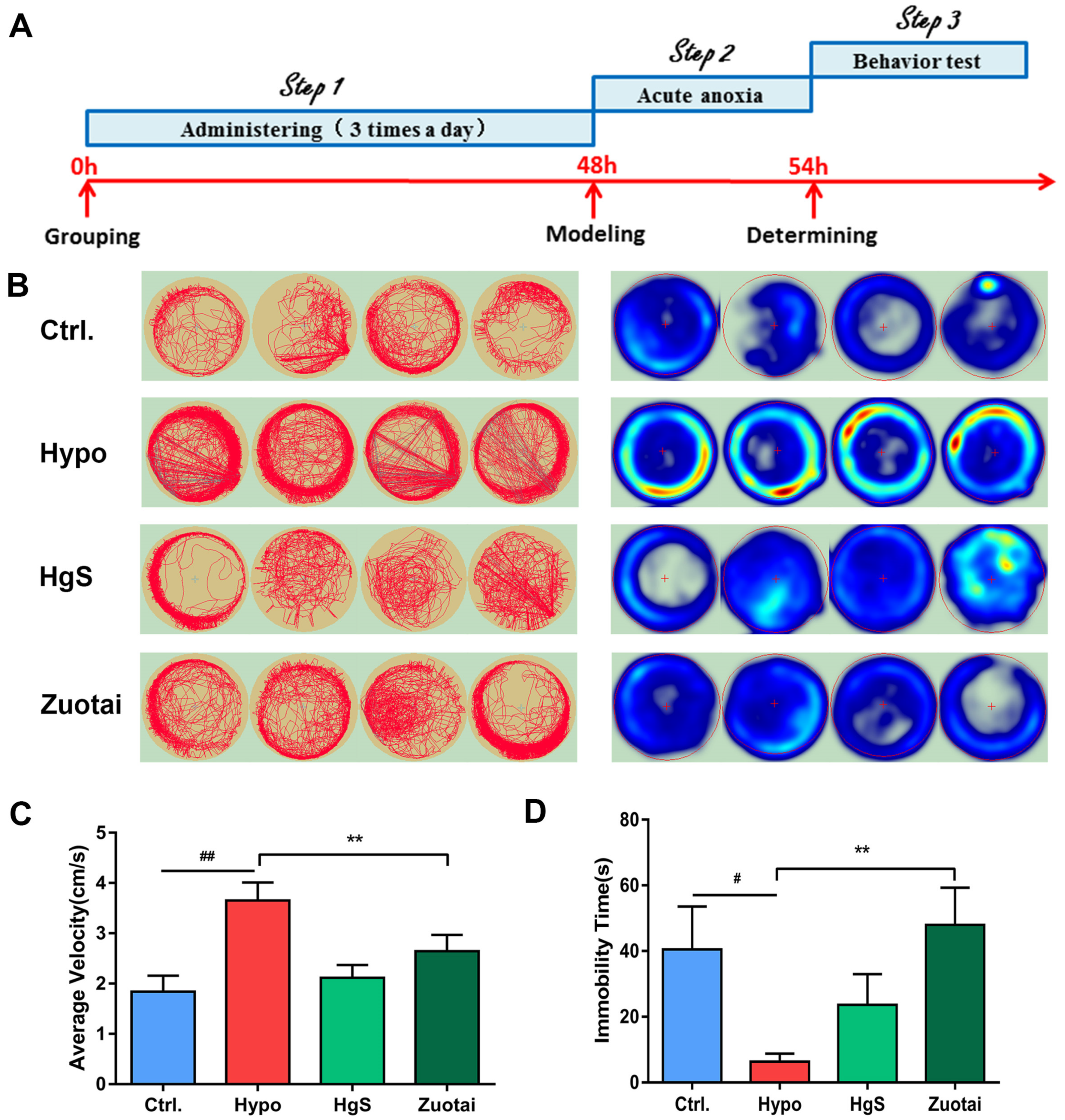
2.6. Effects of HgS and Zuotai on Larval Zebrafish Behavior
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Solution
4.2. Materials
4.3. Cell Culture and Treatments
4.4. Biochemical Measurement
4.5. Measurement of ROS Generation
4.6. Maintenance of Zebrafish and Treatments
4.7. Fluorescence Photography
4.8. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Studies
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| 5-HT | 5-hydroxytryptamine |
| IBD | inflammatory bowel disease |
| FBS | fetal bovine serum |
| SOD | superoxide dismutase |
| GSH | glutathione |
| MDA | malondialdehyde |
| Tph1 | Tryptophan hydroxylase-1 |
| Maoa | monoamine oxidase A |
| Slc6a4 | Solute Carrier Family 6 Member 4 |
| Ctrl. | control |
| Hypo | hypoxia group |
References
- Soria, R.; Julian, C.G.; Vargas, E.; Moore, L.G.; Giussani, D.A. Graduated effects of high-altitude hypoxia and highland ancestry on birth size. Pediatric Res. 2013, 74, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tianyi, W. Advances in High-Altitude Medicine and Hypoxic Physiology in China. Science 2012, 338, 1485. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, S.J.; Reichardt-Pascal, S.Y.; Vaughan, D.; Russell, G.I. Differential effect of ischaemia-reperfusion injury on anti-oxidant enzyme activity in the rat kidney. Exp. Nephrol. 1995, 3, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dosek, A.; Ohno, H.; Acs, Z.; Taylor, A.W.; Radak, Z. High altitude and oxidative stress. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2007, 158, 128–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiti, P.; Singh, S.B.; Sharma, A.K.; Muthuraju, S.; Banerjee, P.K.; Ilavazhagan, G. Hypobaric hypoxia induces oxidative stress in rat brain. Neurochem. Int. 2006, 49, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magalhaes, J.; Ascensao, A.; Viscor, G.; Soares, J.; Oliveira, J.; Marques, F.; Duarte, J. Oxidative Stress in Humans during and after 4 Hours of Hypoxia at a Simulated Altitude of 5500 m. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 2004, 75, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Lushchak, V.I.; Bagnyukova, T.V. Hypoxia induces oxidative stress in tissues of a goby, the rotan Perccottus glenii. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 148, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, J.D.A. The effect of hypoxia on monoamine synthesis, levels and metabolism in rat brain. J. Neurochem. 1973, 21, 783–790. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, C.S.; Li, J.J.; Tipoe, G.L.; Youdim, M.B.H.; Fung, M.L. Monoamine oxidase A upregulated by chronic intermittent hypoxia activates indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and neurodegeneration. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocito, A.; Dahm, F.; Jochum, W.; Jang, J.H.; Georgiev, P.; Bader, M.; Renner, E.L.; Clavien, P.A. Serotonin mediates oxidative stress and mitochondrial toxicity in a murine model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umbarkar, P.; Singh, S.; Arkat, S.; Bodhankar, S.L.; Lohidasan, S.; Sitasawad, S.L. Monoamine oxidase-A is an important source of oxidative stress and promotes cardiac dysfunction, apoptosis, and fibrosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 87, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valko, M.; Leibfritz, D.; Moncol, J.; Cronin, M.T.; Mazur, M.; Telser, J. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 44–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manolagas, S.C. From estrogen-centric to aging and oxidative stress: A revised perspective of the pathogenesis of osteoporosis. Endocr. Rev. 2010, 31, 266–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heistad, D.D.; Wakisaka, Y.; Miller, J.; Chu, Y.; Pena-Silva, R. Novel Aspects of Oxidative Stress in Cardiovascular Diseases. Circ. J. 2009, 73, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glover, L.E.; Colgan, S.P. Hypoxia and metabolic factors that influence inflammatory bowel disease pathogenesis. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 1748–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, E.P.; Crean, D. Hypoxia and inflammatory bowel disease. Microbes Infect. 2017, 19, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapalli, A.; Bertoni, S.; Arcaro, V.; Saccani, F.; Grandi, A.; Vivo, V.; Cantoni, A.M.; Barocelli, E. Dual Role of Endogenous Serotonin in 2,4,6-Trinitrobenzene Sulfonic Acid-Induced Colitis. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, I.M.; Ware, C.J.; da Roza Davis, J.M.; Cowen, P.J. Decreased 5-HT-mediated prolactin release in major depression. Br. J. Psychiatry 1992, 160, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kious, B.M.; Kondo, D.G.; Renshaw, P.F. Living High and Feeling Low: Altitude, Suicide, and Depression. Harv. Rev. Psychiatry 2018, 26, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shi, J.Z.; Yu, L.M.; Goyer, R.A.; Waalkes, M.P. Mercury in traditional medicines: Is cinnabar toxicologically similar to common mercurials? Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 2008, 233, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Nair, A.G.C.; Reddy, A.V.R.; Garg, A.N. Bhasmas: Unique ayurvedic metallic-herbal preparations, chemical characterization. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2006, 109, 231–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamath, S.U.; Pemiah, B.; Sekar, R.K.; Krishnaswamy, S.; Sethuraman, S.; Krishnan, U.M. Mercury-based traditional herbo-metallic preparations: A toxicological perspective. Arch. Toxicol. 2012, 86, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Lu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Yan, J.; Shi, J.; Liu, J. Role of cinnabar and realgar of WSHFD in protecting against LPS-induced neurotoxicity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 139, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafiujjaman, M.; Nurunnabi, M.; Saha, S.K.; Jahan, R.; Lee, Y.K.; Rahmatullah, M. Anticancer activity of Arkeshwara Rasa—A herbo-metallic preparation. Ayu 2015, 36, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mukhi, P.; Mohapatra, S.S.; Bhattacharjee, M.; Ray, K.K.; Muraleedharan, T.S.; Arun, A.; Sathyavathi, R.; Juluri, R.R.; Satyam, P.V.; Panda, A.K.; et al. Mercury based drug in ancient India: The red sulfide of mercury in nanoscale. J. Ayurveda Integr. Med. 2017, 8, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, X.; Zhang, B.; Yang, X.; Wang, K. The anxiolytic effect of cinnabar involves changes of serotonin levels. Eur. J. Pharm. 2007, 565, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, E.; Coon, J.T. Heavy metals in traditional Chinese medicines: A systematic review. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 70, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarkson, T.W.; Magos, L. The toxicology of mercury and its chemical compounds. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2006, 36, 609–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuu, J.J.; Liu, S.H.; Lin-Shiau, S.Y. Differential neurotoxic effects of methylmercury and mercuric sulfide in rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2007, 169, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.F.; Hsu, C.J.; Liu, S.H.; Lin-Shiau, S.Y. Exposure to low dose of cinnabar (a naturally occurring mercuric sulfide (HgS)) caused neurotoxicological effects in offspring mice. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 254582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, Z.B. An introduction of Zuotai in Tibetan patent medicine. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2013, 38, 1621–1623. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Wei, L.-X.; Wang, Q.; Lu, Y.-F.; Zhang, F.; Shi, J.-Z.; Li, C.; Cherian, M.G. A review of cinnabar (HgS) and/or realgar (As4S4)-containing traditional medicines. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 210, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.L.; Chen, H.J.; He, Q.Q.; Li, C.; Wei, L.X.; Shang, J. Evaluation of hepatotoxicity potential of a potent traditional Tibetan medicine Zuotai. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 234, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, V.K.; Balaji, S.; Suresh, P.S.; Liu, X.S.; Lu, X.; Li, Z.; Guo, X.E.; Mann, J.J.; Balapure, A.K.; Gershon, M.D.; et al. Pharmacological inhibition of gut-derived serotonin synthesis is a potential bone anabolic treatment for osteoporosis. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrmann, D.C.; Brune, B. Mitochondrial composition and function under the control of hypoxia. Redox Biol. 2017, 12, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, S.K.P. Modulating hypoxia-induced hepatocyte injury by affecting intracellular redox state. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 1995, 1269, 153–161. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbaum, D.M.; Kalberg, J.; Kessler, J.A. Superoxide dismutase ameliorates neuronal death from hypoxia in culture. Stroke 1994, 25, 857–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanraj, P.; Merola, A.J.; Wright, V.P.; Clanton, T.L. Antioxidants protect rat diaphragmatic muscle function under hypoxic conditions. J. Appl. Physiol. 1998, 84, 1960–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.K.; Patnaik, R.; Muresanu, D.F.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, H.S. Quercetin in hypoxia-induced oxidative stress: Novel target for neuroprotection. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2012, 102, 107–146. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jain, I.H.; Zazzeron, L.; Goli, R.; Alexa, K.; Schatzman-Bone, S.; Dhillon, H.; Goldberger, O.; Peng, J.; Shalem, O.; Sanjana, N.E.; et al. Hypoxia as a therapy for mitochondrial disease. Science 2016, 352, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandel, N.S.; Maltepe, E.; Goldwasser, E.; Mathieu, C.E.; Simon, M.C.; Schumacker, P.T. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species trigger hypoxia-induced transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 11715–11720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, D.M.; Davies, B.; Young, I.S. Intermittent hypoxic training implications for lipid peroxidation induced by acute normoxic exercise in active men. Clin. Sci. 2001, 101, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, X.; Zhang, B.; Yang, X.; Wang, K. Cinnabar is Different from Mercuric Chloride in Mercury Absorption and Influence on the Brain Serotonin Level. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 112, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, F.; Zhang, J. Metabolic Kinetics of 5-Hydroxytryptamine and the Research Targets of Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2014, 59, 2642–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abid, S.; Houssaini, A.; Chevarin, C.; Marcos, E.; Tissot, C.M.; Gary-Bobo, G.; Wan, F.; Mouraret, N.; Amsellem, V.; Dubois-Randé, J.L.; et al. Inhibition of gut- and lung-derived serotonin attenuates pulmonary hypertension in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2012, 303, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridovich, I. Superoxide dismutases. An adaptation to a paramagnetic gas. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 7761–7764. [Google Scholar]
- Meister, A. Selective modification of glutathione metabolism. Science 1983, 220, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liang, S.; He, J.; Bai, Y.; Niu, Y.; Tang, X.; Li, D.; Chen, Q. Oxidative stress and antioxidant status in a lizard Phrynocephalus vlangalii at different altitudes or acclimated to hypoxia. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2015, 190, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieschke, G.J.; Currie, P.D. Animal models of human disease: Zebrafish swim into view. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moussavi Nik, S.H.; Croft, K.; Mori, T.A.; Lardelli, M. The comparison of methods for measuring oxidative stress in zebrafish brains. Zebrafish 2014, 11, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, M.M.; Rico, E.P.; Cordova, S.D.; Pinto, C.B.; Blaser, R.E.; Dias, R.D.; Rosemberg, D.B.; Oliveira, D.L.; Souza, D.O. Evaluation of spontaneous recovery of behavioral and brain injury profiles in zebrafish after hypoxia. Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 253, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Gene Name | Forward Primer Sequence | Reverse Primer Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| Gapdh | TCTCTGCTCCTCCCTGTTC | ACACCGACCTTCACCATCT |
| Tph1 | GTCCCTCTCTTGGCTGAA | TGAACCGTCTCCTCTGAA |
| Maoa | AAGACACGCTCAGGAATG | TGAACCGTCTCCTCTGAA |
| Slc6a4(SERT) | AGCGATGTGAAGGAGATGCT | GGACGACATCCCTATGCAGT |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, Q.; Ma, J.; Kalavagunta, P.K.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, J.; Dong, J.; Ahmad, O.; Du, Y.; Wei, L.; Shang, J. HgS Inhibits Oxidative Stress Caused by Hypoxia through Regulation of 5-HT Metabolism Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061364
He Q, Ma J, Kalavagunta PK, Zhou L, Zhu J, Dong J, Ahmad O, Du Y, Wei L, Shang J. HgS Inhibits Oxidative Stress Caused by Hypoxia through Regulation of 5-HT Metabolism Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(6):1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061364
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Qiangqiang, Ji Ma, Praveen Kumar Kalavagunta, Liangliang Zhou, Junyi Zhu, Jing Dong, Owais Ahmad, Yuzhi Du, Lixin Wei, and Jing Shang. 2019. "HgS Inhibits Oxidative Stress Caused by Hypoxia through Regulation of 5-HT Metabolism Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 6: 1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061364
APA StyleHe, Q., Ma, J., Kalavagunta, P. K., Zhou, L., Zhu, J., Dong, J., Ahmad, O., Du, Y., Wei, L., & Shang, J. (2019). HgS Inhibits Oxidative Stress Caused by Hypoxia through Regulation of 5-HT Metabolism Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(6), 1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061364