A Z-axis Quartz Cross-fork Micromachined Gyroscope Based on Shear Stress Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
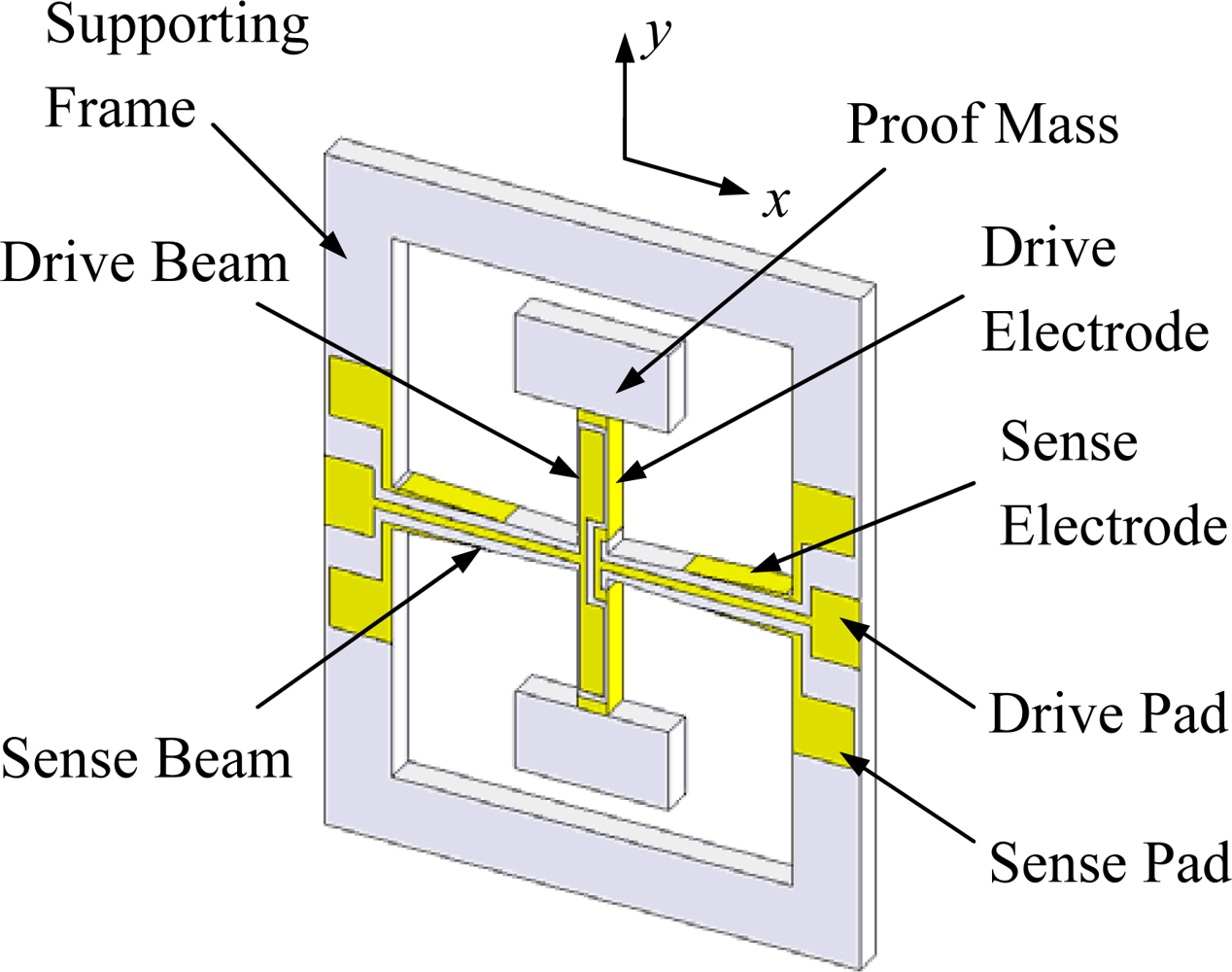
2. Design Concept
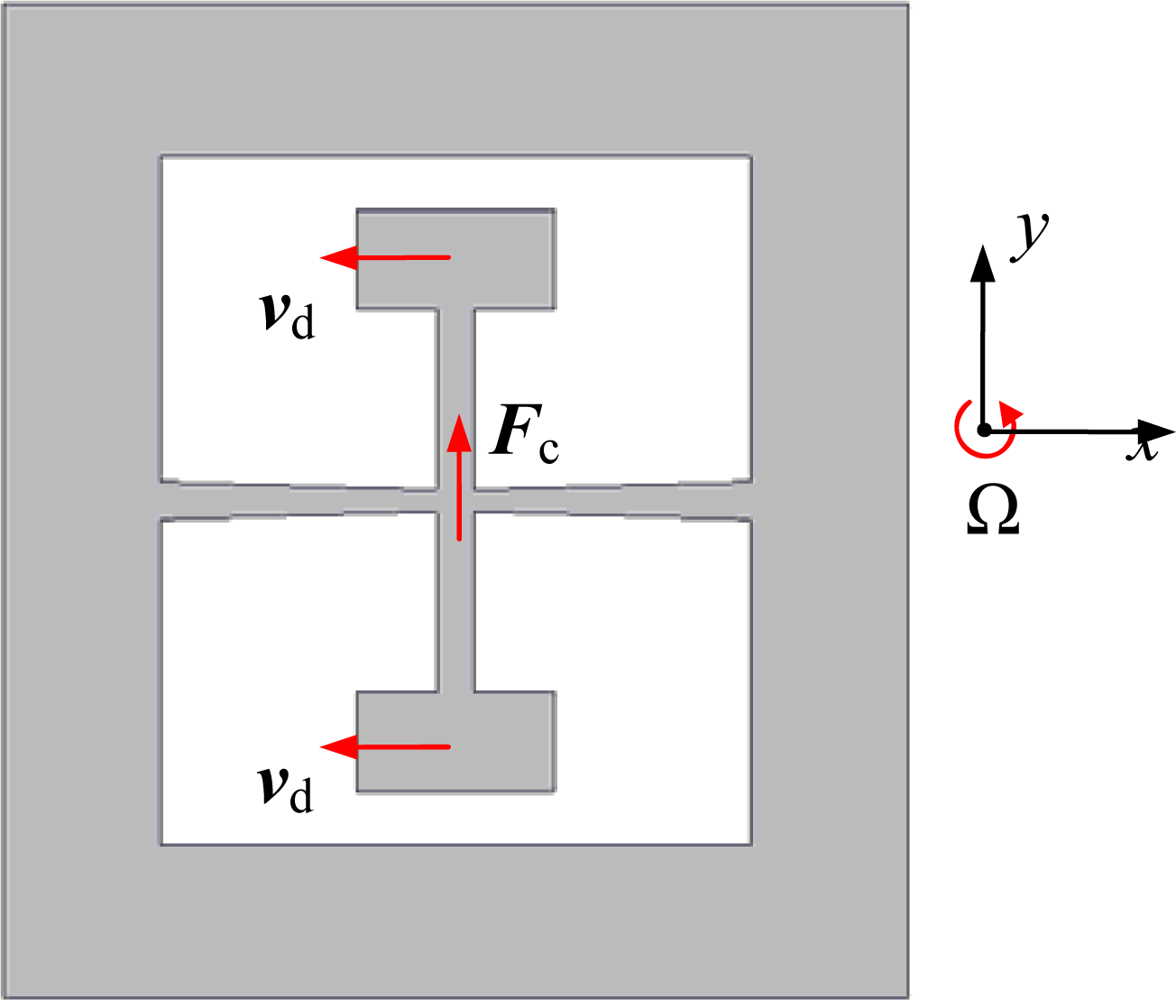
2.1. Working Principle
2.2. Electrodes Design
2.3. Structure Design
- A pair of sense electrodes is formed on the sidewalls of the sense beam independently. This electrode layout is easy to be prepared by aperture masks.
- As both the drive mode and the sense mode are vibrating in the structure plane, air damping is slide-film damping. Therefore, it is easy to obtain a high quality factor.
- For quartz material, the piezoelectric coefficient d26 between shear stress T6 and electric displacement D2 is the largest of all, and the Coriolis’ force is detected by this coefficient. Thus, the sensor inherently has sufficient sensitivity.
- In order to increase the sensitivity of the gyroscope, a pair of proof masses is introduced and a tapered sense beam has been designed.
3. Fabrication
4. Readout Circuit
5. Experimental Results
5.1. Mode Test
5.2. Coriolis’ Force Test
5.3. Performance Test
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References and Notes
- Dixon, R.H.; Bouchaud, J. Markets and applications for MEMS inertial sensors. Proc. SPIE 2006, 6113, 06:1–06:13. [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg, M.S.; Kourepenis, A. Error sources in in-plane silicon tuning-fork MEMS gyroscopes. J. Microelectromech. Syst 2006, 15, 479–491. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, B.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, T.; Baek, S.S. Dynamic characteristics of vertically coupled structures and the design of a decoupled micro gyroscope. Sensors 2009, 9, 5952–5967. [Google Scholar]
- Closkey, R.M.; Challoner, A.D. Modeling, identification, and control of micro-sensor prototypes. Proceedings of the American Control conference, Boston, MA, USA, June 2004; pp. 9–24.
- Soderkvist, J. Micromachined vibrating gyroscopes. Proc. SPIE 1996, 2882, 152–160. [Google Scholar]
- Megherbi, S.; Levy, R.; Parrain, F.; Mathias, H.; Traon, O.L.; Janiaud, D.; Gilles, J.P. Behavioral modelling of vibrating piezoelectric micro-gyro sensor and detection electronics. Proceedings of the International Conference on Thermal Mechanical and Multi-Physics Simulation Experiments in Microelectronics and Micro-Systems, London, UK, April 2007; pp. 1–4.
- Jaffe, R.; Simshauser, S.; Madni, A.M. Quartz dual axis rate sensor. Proceedings of the IEEE Position, Location, and Navigation Symposium, San Diego, CA, USA, April 2006; pp. 26–35.
- Kikuchi, T.; Gouji, S.; Tai, T.; Hayashi, S.; Okada, N.; Tani, M.; Ishikawa, S.; Yokoi, S.; Enokijima, T.; Kawamura, Y. Miniaturized quartz vibratory gyrosensor with hammer-headed arms. Proceedings of the IEEE International Ultrasonincs Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control Joint 50th Anniversary Conference, Montreal, Canada, August 2004; pp. 330–333.
- Madni, A.M.; Costlow, L.E.; Smith, M.W. The μGyro: a quartz MEMS automotive gyroscope. Proceedings of the SAE World Congress, Detroit, MI, USA, April 2006.
- Gupta, P.K.; Jenson, C.E. Rotation rate sensor with center mounted tuning fork. U.S. Patent 5,396,144, 1995.
- Knowles, S.J. Inertial rate sensor tuning fork. U.S. Patent 6,262,520, 2001.
- Soderkvist, J. Piezoelectric beams and vibrating angular rate sensors. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Contr 1991, 38, 271–280. [Google Scholar]
- Madni, A.M.; Wan, L.A.; Hammons, S. A microelectromechanical quartz rotational rate sensor for inertial applications. Proceedings of the IEEE Aerospace Applications Conference, New York, NY, USA, February 1996; pp. 315–332.
- Senturia, S.D. Microsystem Design; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Boston, MA, USA, 2000; p. 582. [Google Scholar]
- Uehara, H.; Ohtsuka, T.; Inoue, T. Miniaturized angular rate sensor with laminated quartz tuning fork. Proceedings of the IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium and Exposition, Vancouver, Canada, August 2005; pp. 886–891.
- Ohtsuka, T.; Inoue, T.; Yoshimatsu, M.; Matsudo, H.; Okazaki, M. Development of an ultra-small angular rate sensor element with a laminated quartz tuning fork. Proceedings of the IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium and Exposition, Miami, FL, USA, June 2006; pp. 129–132.
- Sato, K.; Ono, A.; Tomikawa, Y. Experimental study of gyro sensor using double-ended tuning fork quartz resonator. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys 2004, 43, 3000–3003. [Google Scholar]
- Soderkvist, J. An analysis of space-dependent electric fields used in exciting flexural vibartions of piezoelectric beams. Meas. Sci. Technol 1990, 1, 731–737. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Z.K. Piezoelectric Quartz Crystal; Defense Industry Press: Beijing, China, 1980; pp. 68–99. [Google Scholar]
- Hibbeler, R.C. Mechanics of Materials; George, D.A., Ed.; Pearson Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2005; p. 294. [Google Scholar]
- Timoshenko, S.P.; Gere, J.M. Mechanics of Materials; Van Nostrand Reinhold Company: New York, NY, USA, 1973; pp. 156–158. [Google Scholar]
- Schofield, A.R.; Trusov, A.A.; Shkel, A.M. Design trade-offs of micromachined gyroscope concept allowing interchangeable operation in both robust and precision modes. Proceedings of the Transducers, Denver, CO, USA, June 2009; pp. 1952–1955.
- Rangsten, P.; Hedlund, C.; Katardjiev, I.V.; Backlund, Y. Etch rates of crystallographic planes in z-cut quartz—experiments and simulation. J. Micromech. Microeng 1998, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.F. Piezoelectric Vibration; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1989; p. 51. [Google Scholar]

















| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Thickness (mm) | 0.50 |
| Mass width (mm) | 1.30 |
| Mass length (mm) | 2.50 |
| Drive beam width (mm) | 0.48 |
| Drive beam length (mm) | 5.00 |
| Sense beam length (mm) | 7.48 |
| Sense beam width (mm) | 0.50 |
| Sense beam taper (degree) | 1.64 |
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, L.; Wu, X.; Li, S.; Wang, H.; Su, J.; Dong, P. A Z-axis Quartz Cross-fork Micromachined Gyroscope Based on Shear Stress Detection. Sensors 2010, 10, 1573-1588. https://doi.org/10.3390/s100301573
Xie L, Wu X, Li S, Wang H, Su J, Dong P. A Z-axis Quartz Cross-fork Micromachined Gyroscope Based on Shear Stress Detection. Sensors. 2010; 10(3):1573-1588. https://doi.org/10.3390/s100301573
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Liqiang, Xuezhong Wu, Shengyi Li, Haoxu Wang, Jianbin Su, and Peitao Dong. 2010. "A Z-axis Quartz Cross-fork Micromachined Gyroscope Based on Shear Stress Detection" Sensors 10, no. 3: 1573-1588. https://doi.org/10.3390/s100301573
APA StyleXie, L., Wu, X., Li, S., Wang, H., Su, J., & Dong, P. (2010). A Z-axis Quartz Cross-fork Micromachined Gyroscope Based on Shear Stress Detection. Sensors, 10(3), 1573-1588. https://doi.org/10.3390/s100301573




