Detectability of Absorption and Reduced Scattering Coefficients in Frequency-Domain Measurements Using a Realistic Head Phantom
Abstract
:1. Introduction
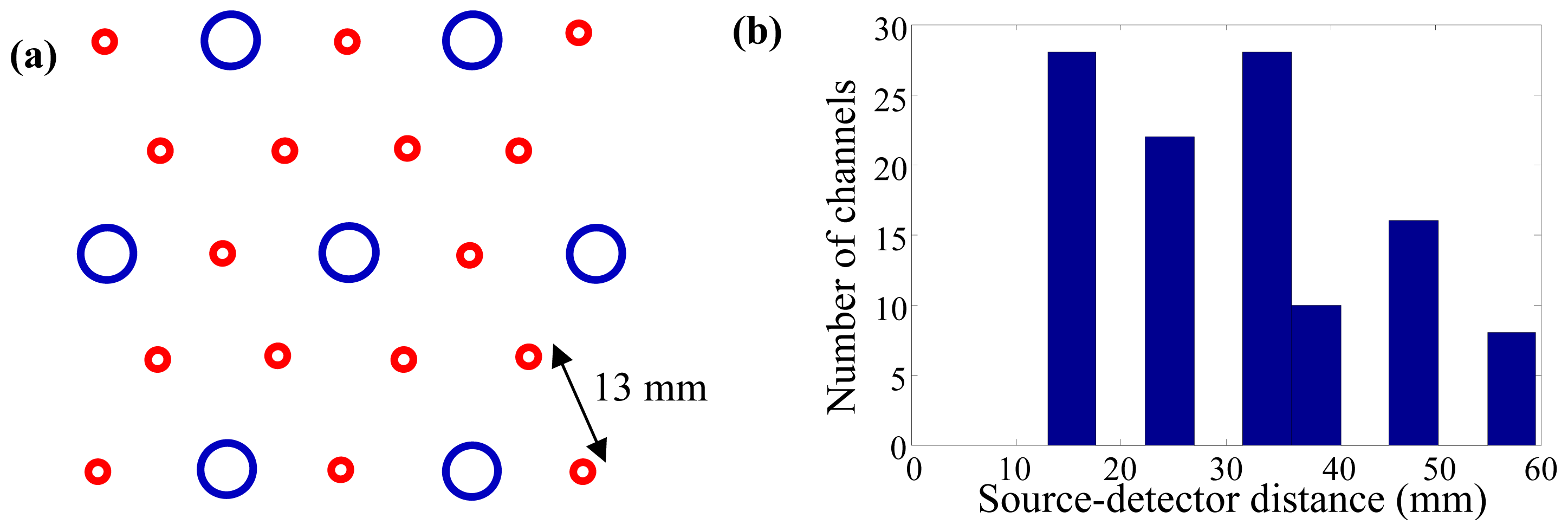
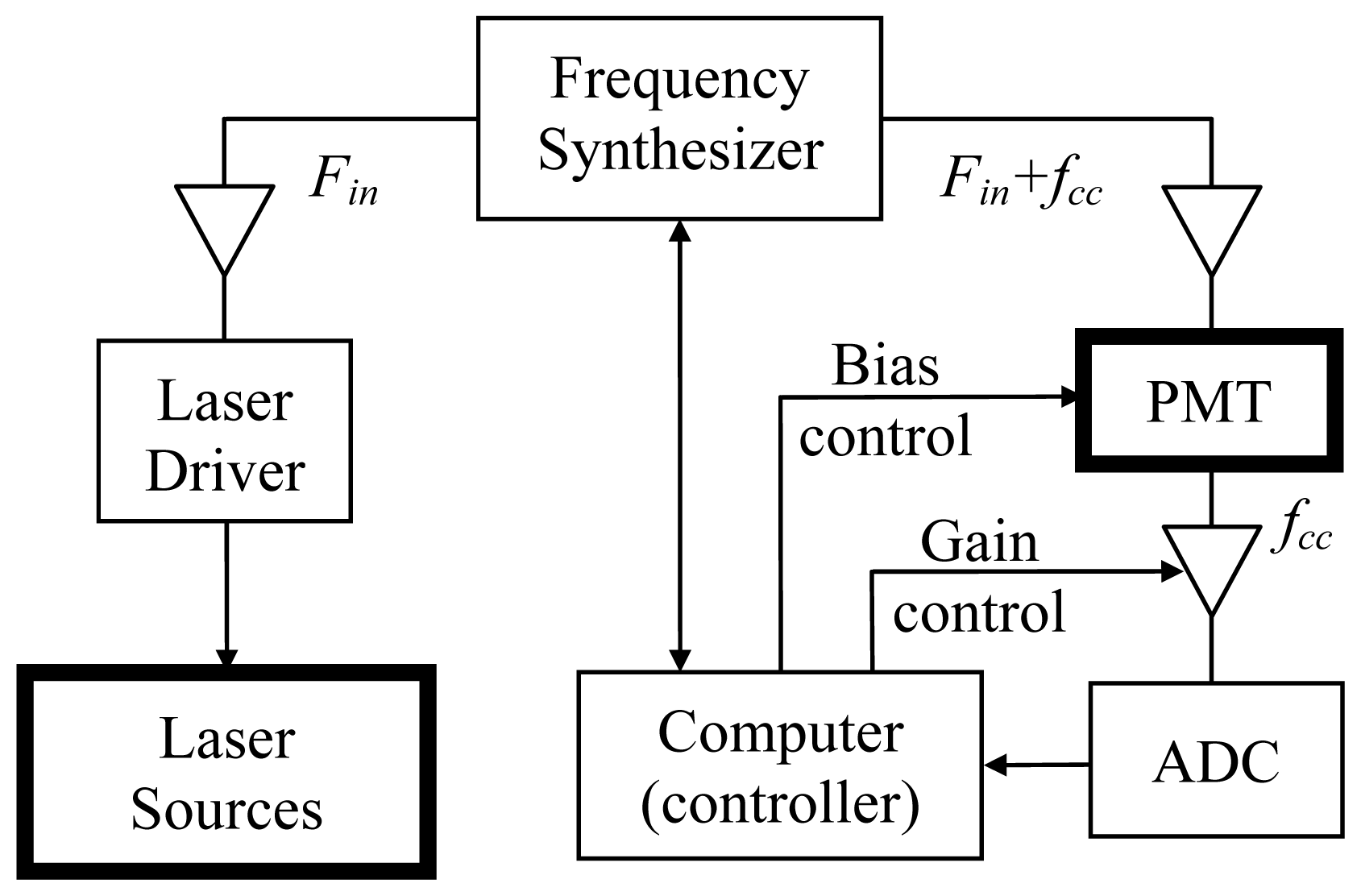
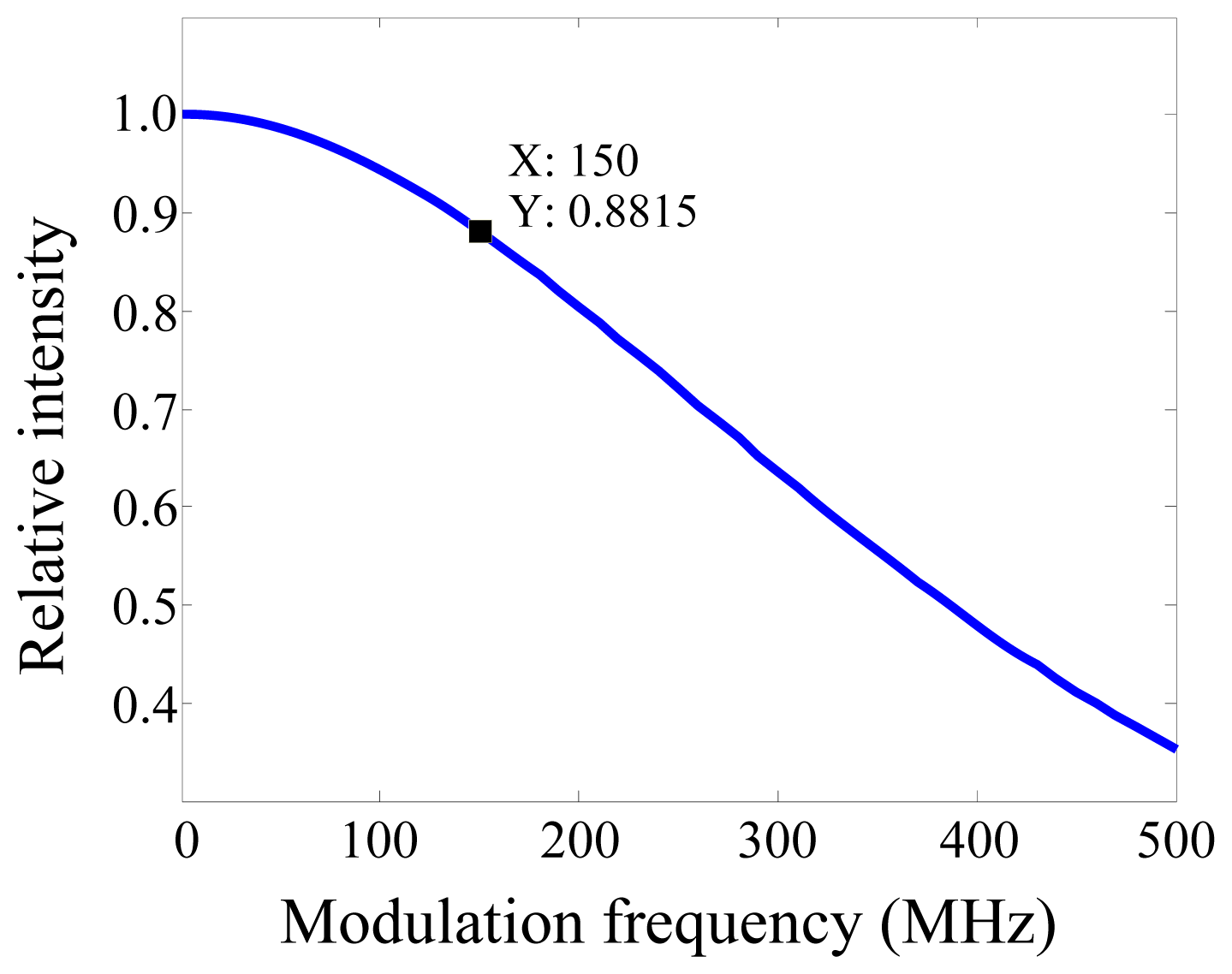
2. Experimental Section
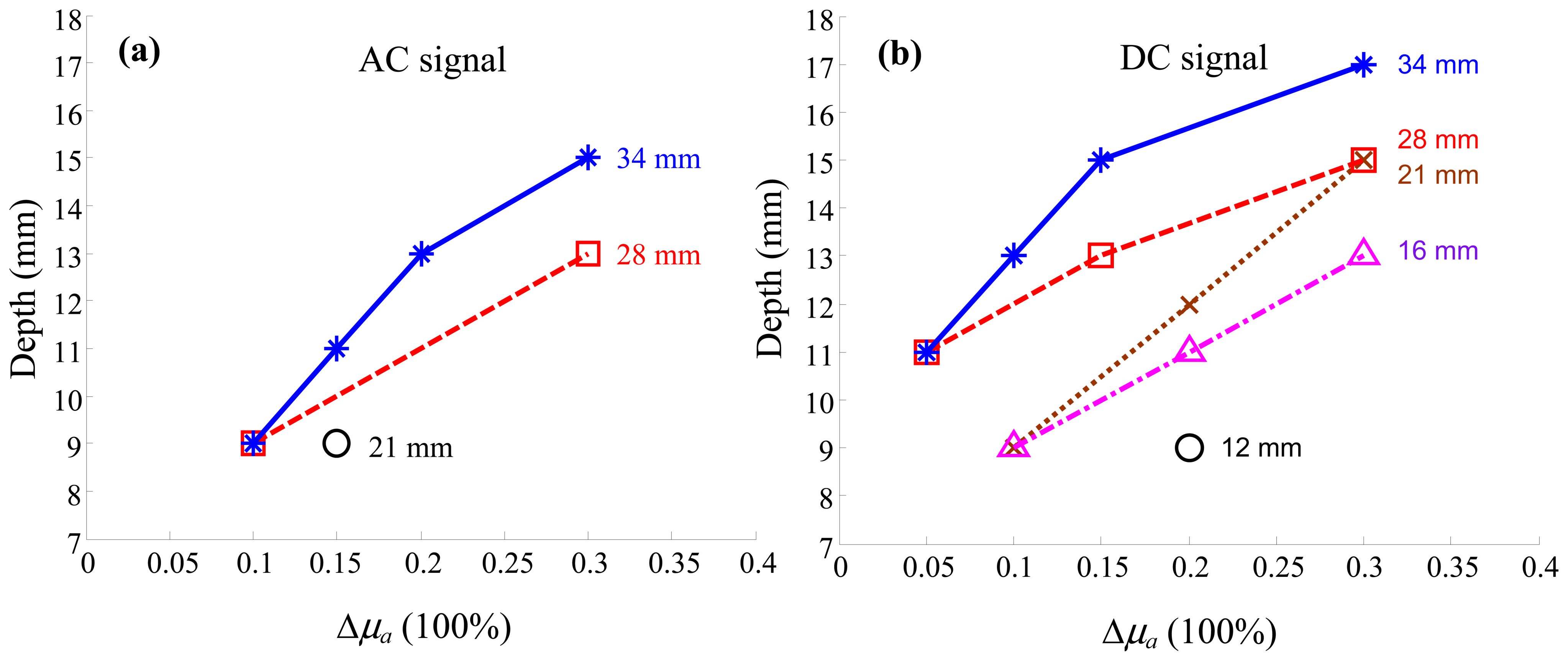
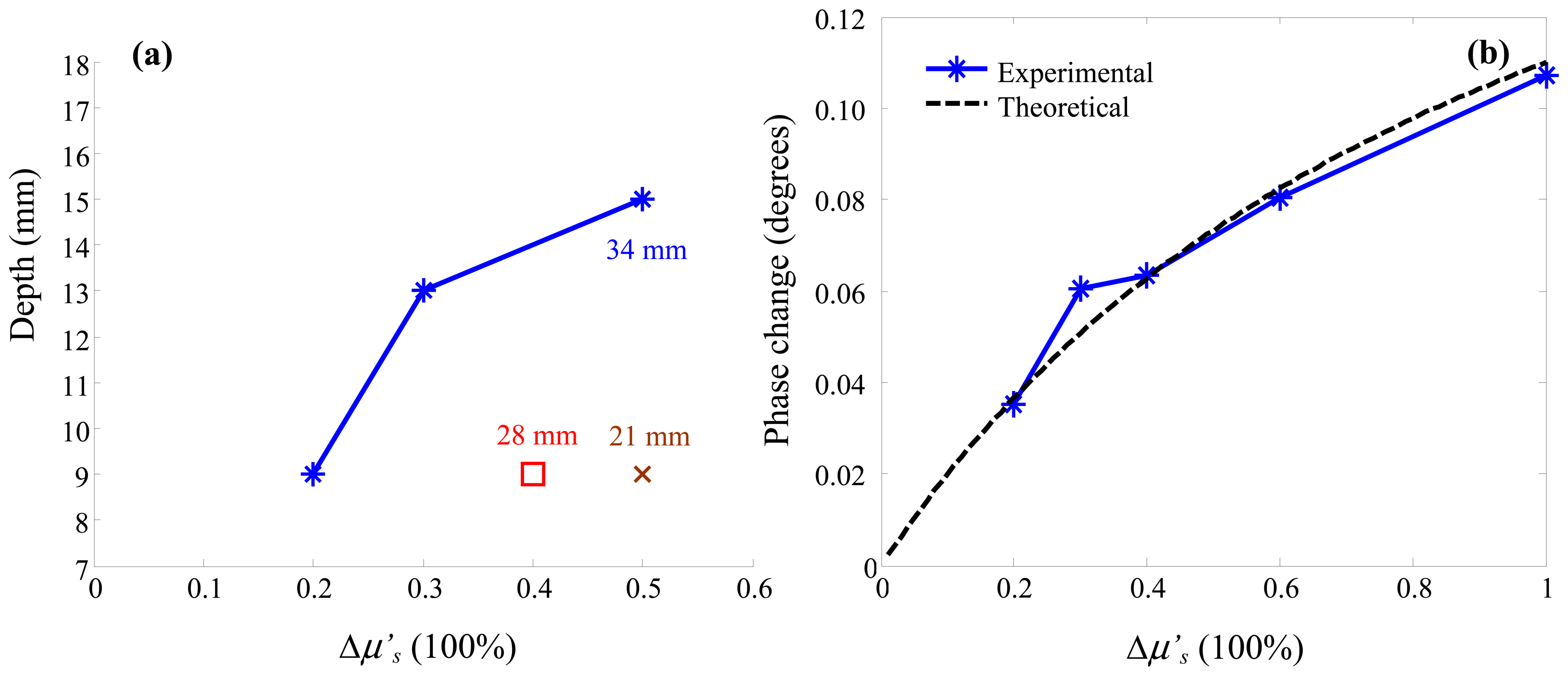
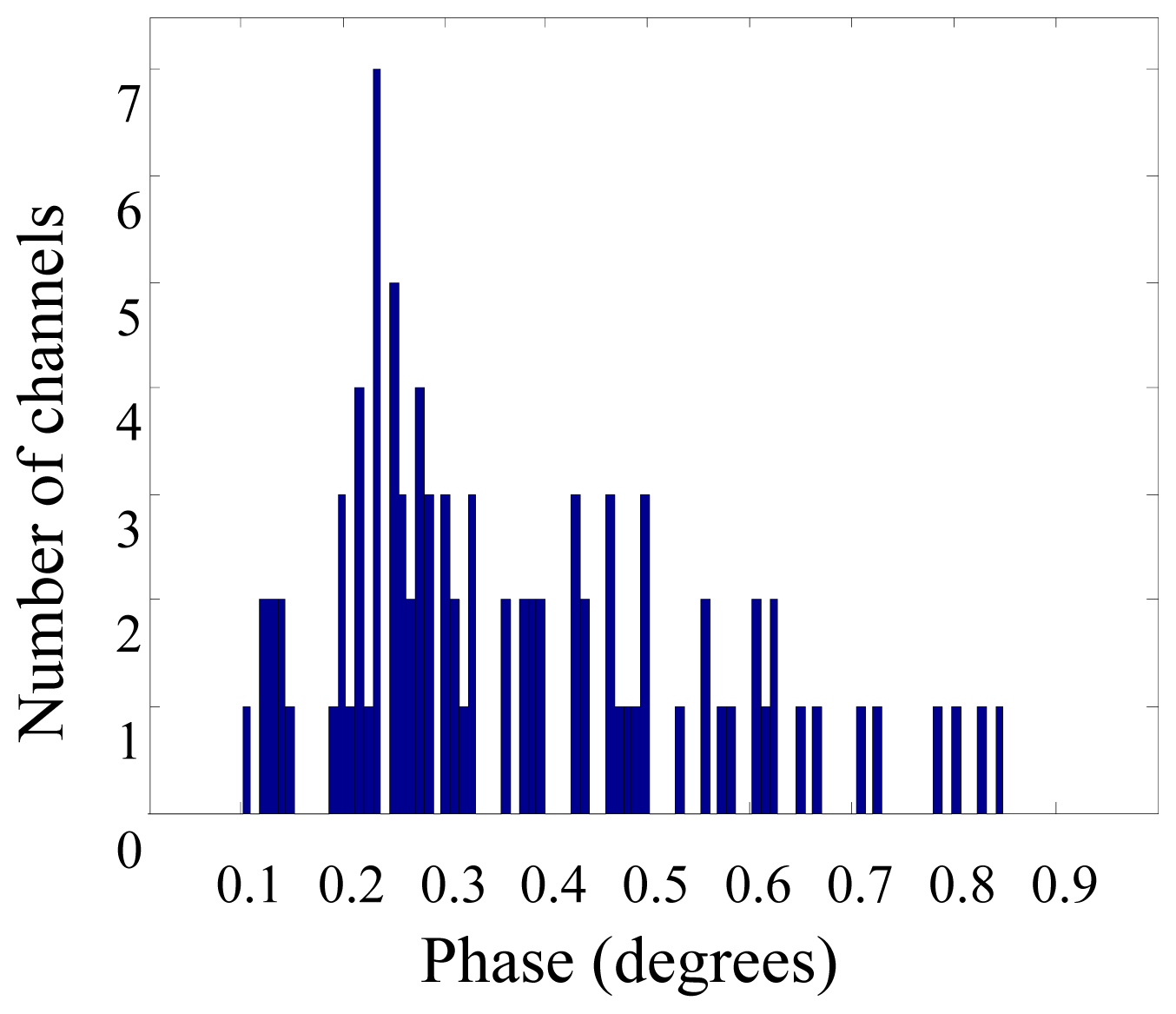
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Chance, B.; Luo, Q.; Nioka, S.; Alsop, D.C.; Detre, J.A. Optical investigations of physiology: A study of intrinsic and extrinsic biomedical contrast. Philos. Trans. Roy. Soc. Lond B Biol. Sci. 1997, 352, 707–716. [Google Scholar]
- Obrig, H.; Villringer, A. Beyond the visible—Imaging the human brain with light. J. Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2003, 23, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Toronov, V.; Walker, S.; Gupta, R.; Choi, J.H.; Gratton, E.; Hueber, D.; Webb, A. The roles of changes in deoxyhemoglobin concentration and regional cerebral blood volume in the fMRI BOLD signal. Neuroimage 2003, 19, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar]
- Gratton, E.; Toronov, V.; Wolf, U.; Wolf, M.; Webb, A. Measurement of brain activity by near-infrared light. J. Biomed. Opt. 2005, 10, 11008. [Google Scholar]
- Franceschini, M.A.; Joseph, D.K.; Huppert, T.J.; Diamond, S.G.; Boas, D.A. Diffuse optical imaging of the whole head. J. Biomed. Opt. 2006, 11, 054007. [Google Scholar]
- Sassaroli, A.; deB. Frederick, B.; Tong, Y.; Renshaw, P.F.; Fantini, S. Spatially weighted BOLD signal for comparison of functional magnetic resonance imaging and near-infrared imaging of the brain. Neuroimage 2006, 33, 505–514. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, J.Q.; Wilke, L.G.; Geradts, J.; Kennedy, S.A.; Palmer, G.M.; Ramanujam, N. Quantitative optical spectroscopy: A robust tool for direct measurement of breast cancer vascular oxygenation and total hemoglobin content in vivo. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 2919–2926. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, H.L.; Yu, B.; Lo, J.Y.; Palmer, G.M.; Kuech, T.F.; Ramanujam, N. A low-cost, portable, and quantitative spectral imaging system for application to biological tissues. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 12630–12645. [Google Scholar]
- Arridge, S.R. Methods in diffuse optical imaging. Philos. Trans. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2011, 369, 4558–4576. [Google Scholar]
- Gurley, K.; Shang, Y.; Yu, G. Noninvasive optical quantification of absolute blood flow, blood oxygenation, and oxygen consumption rate in exercising skeletal muscle. J. Biomed. Opt. 2012, 17, 075010. [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschmidt, A.; Obrig, H.; Requardt, M.; Merboldt, K.D.; Dirnagl, U.; Villringer, A.; Frahm, J. Simultaneous recording of cerebral blood oxygenation changes during human brain activation by magnetic resonance imaging and near-infrared spectroscopy. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1996, 16, 817–826. [Google Scholar]
- Mehagnoul-Schipper, D.J.; van der Kallen, B.F.; Colier, W.N.; van der Sluijs, M.C.; van Erning, L.J.; Thijssen, H.O.; Oeseburg, B.; Hoefnagels, W.H.; Jansen, R.W. Simultaneous measurements of cerebral oxygenation changes during brain activation by near-infrared spectroscopy and functional magnetic resonance imaging in healthy young and elderly subjects. Human Brain Map. 2002, 16, 14–23. [Google Scholar]
- Strangman, G.; Culver, J.P.; Thompson, J.H.; Boas, D.A. A quantitative comparison of simultaneous BOLD fMRI and NIRS recordings during functional brain activation. Neuroimage 2002, 17, 719–731. [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto, M.; Dan, H.; Shimizu, K.; Takeo, K.; Amita, T.; Oda, I.; Konishi, I.; Sakamoto, K.; Isobe, S.; Suzuki, T.; Kohyama, K.; Dan, I. Multimodal assessment of cortical activation during apple peeling by NIRS and fMRI. Neuroimage 2004, 21, 1275–1288. [Google Scholar]
- Gulsen, G.; Birgul, O.; Unlu, M.B.; Shafiiha, R.; Nalcioglu, O. Combined diffuse optical tomography (DOT) and MRI system for cancer imaging in small animals. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2006, 5, 351–363. [Google Scholar]
- Schroeter, M.L.; Kupka, T.; Mildner, T.; Uludag, K.; von Cramon, D.Y. Investigating the post-stimulus undershoot of the BOLD signal—A simultaneous fMRI and fNIRS study. Neuroimage 2006, 30, 349–358. [Google Scholar]
- Toronov, V.Y.; Zhang, X.; Webb, A.G. A spatial and temporal comparison of hemodynamic signals measured using optical and functional magnetic resonance imaging during activation in the human primary visual cortex. Neuroimage 2007, 34, 1136–1148. [Google Scholar]
- Gratton, G.; Fabiani, M. The event-related optical signal (EROS) in visual cortex: Replicability, consistency, localization, and resolution. Psychophysiology 2003, 40, 561–571. [Google Scholar]
- Medvedev, A.V.; Kainerstorfer, J.M.; Borisov, S.V.; Gandjbakhche, A.H.; Vanmeter, J. “Seeing” electroencephalogram through the skull: Imaging prefrontal cortex with fast optical signal. J. Biomed. Opt. 2010, 15, 061702. [Google Scholar]
- Steinbrink, J.; Kohl, M.; Obrig, H.; Curio, G.; Syre, F.; Thomas, F.; Wabnitz, H.; Rinneberg, H.; Villringer, A. Somatosensory evoked fast optical intensity changes detected non-invasively in the adult human head. Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 291, 105–108. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, M.; Wolf, U.; Choi, J.H.; Gupta, R.; Safonova, L.P.; Paunescu, L.A.; Michalos, A.; Gratton, E. Functional frequency-domain near-infrared spectroscopy detects fast neuronal signal in the motor cortex. Neuroimage 2002, 17, 1868–1875. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, Y.; Martin, J.M.; Sassaroli, A.; Clervil, P.R.; Bergethon, P.R.; Fantini, S. Fast optical signals in the peripheral nervous system. J. Biomed. Opt. 2006, 11, 044014. [Google Scholar]
- Tse, C.Y.; Tien, K.R.; Penney, T.B. Event-related optical imaging reveals the temporal dynamics of right temporal and frontal cortex activation in pre-attentive change detection. Neuroimage 2006, 29, 314–320. [Google Scholar]
- Rector, D.M.; Poe, G.R.; Kristensen, M.P.; Harper, R.M. Light scattering changes follow evoked potentials from hippocampal Schaeffer collateral stimulation. J. Neurophysiol. 1997, 78, 1707–1713. [Google Scholar]
- Rector, D.M.; Carter, K.M.; Volegov, P.L.; George, J.S. Spatio-temporal mapping of rat whisker barrels with fast scattered light signals. Neuroimage 2005, 26, 619–627. [Google Scholar]
- Suh, M.; Bahar, S.; Mehta, A.D.; Schwartz, T.H. Blood volume and hemoglobin oxygenation response following electrical stimulation of human cortex. Neuroimage 2006, 31, 66–75. [Google Scholar]
- Steinbrink, J.; Kempf, F.C.; Villringer, A.; Obrig, H. The fast optical signal—Robust or elusive when non-invasively measured in the human adult? Neuroimage 2005, 26, 996–1008. [Google Scholar]
- Pogue, B.W.; Davis, S.C.; Song, X.; Brooksby, B.A.; Dehghani, H.; Paulsen, K.D. Image analysis methods for diffuse optical tomography. J. Biomed. Opt. 2006, 11, 33001. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, A.; Yusof, R.M.; Dehghani, H.; Riley, J.; Everdell, N.; Richards, R.; Hebden, J.C.; Schweiger, M.; Arridge, S.R.; Delpy, D.T. Optical tomography of a realistic neonatal head phantom. Appl. Opt. 2003, 42, 3109–3116. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.; Sassaroli, A.; Fantini, S. Two-dimensional phased arrays of sources and detectors for depth discrimination in diffuse optical imaging. J. Biomed. Opt. 2005, 10, 051801. [Google Scholar]
- Passos, D.; Hebden, J.C.; Pinto, P.N.; Guerra, R. Tissue phantom for optical diagnostics based on a suspension of microspheres with a fractal size distribution. J. Biomed. Opt. 2005, 10, 064036. [Google Scholar]
- Pogue, B.W.; Patterson, M.S. Review of tissue simulating phantoms for optical spectroscopy, imaging and dosimetry. J. Biomed. Opt. 2006, 11, 041102. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, K.P.; Radhakrishnan, S.; Reddy, M.R. Brain tissue phantoms for optical near infrared imaging. Exper. Brain Res. Exper. Hirnforsch. Exper. Cereb. 2006, 170, 433–437. [Google Scholar]
- Hebden, J.C.; Price, B.D.; Gibson, A.P.; Royle, G. A soft deformable tissue-equivalent phantom for diffuse optical tomography. Phys. Med. Biol. 2006, 51, 5581–5590. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, A.P.; Hebden, J.C.; Riley, J.; Everdell, N.; Schweiger, M.; Arridge, S.R.; Delpy, D.T. Linear and nonlinear reconstruction for optical tomography of phantoms with nonscattering regions. Appl. Opt. 2005, 44, 3925–3936. [Google Scholar]
- Kienle, A.; Patterson, M.S.; Dognitz, N.; Bays, R.; Wagninures, G.; van den Bergh, H. Noninvasive determination of the optical properties of two-layered turbid media. Appl. Opt. 1998, 37, 779–791. [Google Scholar]
- Fantini, S.; Franceschini, M.A.; Fishkin, J.B.; Barbieri, B.; Gratton, E. Quantitative determination of the absorption spectra of chromophores in strongly scattering media: A light-emitting-diode based technique. Appl. Opt. 1994, 33, 5204–5213. [Google Scholar]
- Bandettini, P.A.; Jesmanowicz, A.; Wong, E.C.; Hyde, J.S. Processing strategies for time-course data sets in functional MRI of the human brain. Magn. Resona. Med. 1993, 30, 161–173. [Google Scholar]
- Franceschini, M.A.; Toronov, V.; Filiaci, M.; Gratton, E.; Fantini, S. On-line optical imaging of the human brain with 160-ms temporal resolution. Opt. Express 2000, 6, 49–57. [Google Scholar]
- Toronov, V.; Franceschini, M.A.; Filiaci, M.; Fantini, S.; Wolf, M.; Michalos, A.; Gratton, E. Near-infrared study of fluctuations in cerebral hemodynamics during rest and motor stimulation: temporal analysis and spatial mapping. Med. Phys. 2000, 27, 801–815. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, K.; Ogata, S.; Atsumi, Y.; Yamamoto, R.; Shiotsuka, S.; Maki, A.; Yamashita, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Koizumi, H.; Hirasawa, H.; Igawa, M. Activation of the visual cortex imaged by 24-channel near-infrared spectroscopy. J. Biomed. Opt. 2000, 5, 93–96. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.P.; Duong, T.Q.; Yang, G.; Iadecola, C.; Kim, S.G. Relative changes of cerebral arterial and venous blood volumes during increased cerebral blood flow: Implications for BOLD fMRI. Magn. Resona. Med. 2001, 45, 791–800. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, M.; Wolf, U.; Choi, J.H.; Toronov, V.; Paunescu, L.A.; Michalos, A.; Gratton, E. Fast cerebral functional signal in the 100-ms range detected in the visual cortex by frequency-domain near-infrared spectrophotometry. Psychophysiology 2003, 40, 521–528. [Google Scholar]
- Buxton, R.B.; Uludag, K.; Dubowitz, D.J.; Liu, T.T. Modeling the hemodynamic response to brain activation. Neuroimage 2004, 23 (Suppl 1), S220–S233. [Google Scholar]
- Hoge, R.D.; Franceschini, M.A.; Covolan, R.J.; Huppert, T.; Mandeville, J.B.; Boas, D.A. Simultaneous recording of task-induced changes in blood oxygenation, volume, and flow using diffuse optical imaging and arterial spin-labeling MRI. Neuroimage 2005, 25, 701–707. [Google Scholar]
- Selb, J.; Stott, J.J.; Franceschini, M.A.; Sorensen, A.G.; Boas, D.A. Improved sensitivity to cerebral hemodynamics during brain activation with a time-gated optical system: analytical model and experimental validation. J. Biomed. Opt. 2005, 10, 11013. [Google Scholar]
- Gatto, R.; Hoffman, W.; Mueller, M.; Flores, A.; Valyi-Nagy, T.; Charbel, F.T. Frequency domain near-infrared spectroscopy technique in the assessment of brain oxygenation: A validation study in live subjects and cadavers. J. Neurosci. Methods 2006, 157, 274–277. [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi, H.; Hayashi, T.; Kato, T.; Okada, E. Theoretical evaluation of accuracy in position and size of brain activity obtained by near-infrared topography. Phys. Med. Biol. 2004, 49, 2753–2765. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan, S.; Pogue, B.W.; Dehghani, H.; Jiang, S.; Song, X.; Paulsen, K.D. Improved quantification of small objects in near-infrared diffuse optical tomography. J. Biomed. Opt. 2004, 9, 1161–1171. [Google Scholar]
- Intes, X.; Maloux, C.; Guven, M.; Yazici, B.; Chance, B. Diffuse optical tomography with physiological and spatial a priori constraints. Phys. Med. Biol. 2004, 49, N155–N163. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Brooks, D.H.; Boas, D.A. A haemodynamic response function model in spatio-temporal diffuse optical tomography. Phys. Med. Biol. 2005, 50, 4625–4644. [Google Scholar]
- Corlu, A.; Choe, R.; Durduran, T.; Lee, K.; Schweiger, M.; Arridge, S.R.; Hillman, E.M.; Yodh, A.G. Diffuse optical tomography with spectral constraints and wavelength optimization. Appl. Opt. 2005, 44, 2082–2093. [Google Scholar]
- Arridge, S.R.; Cope, M.; Delpy, D.T. The theoretical basis for the determination of optical pathlengths in tissue: Temporal and frequency analysis. Phys. Med. Biol. 1992, 37, 1531–1560. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Toronov, V.Y.; Webb, A.G. An integrated measurement system for simultaneous functional magnetic resonance imaging and diffuse optical tomography in human brain mapping. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2006, 77, 114301–1143018. [Google Scholar]
- Fantini, S.; Franceschini, M.A.; Gratton, E. Semi-infinite-geometry boundary problem for light migration in highly scattering media: A frequency-domain study in the diffusion approximation. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1994, 11, 2128–2138. [Google Scholar]
- Arridge, S.R.; Lionheart, W.R.B. Nonuniqueness in diffusion-based optical tomography. Opt. Lett. 1998, 23, 882–884. [Google Scholar]

© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Webb, A. Detectability of Absorption and Reduced Scattering Coefficients in Frequency-Domain Measurements Using a Realistic Head Phantom. Sensors 2013, 13, 152-164. https://doi.org/10.3390/s130100152
Zhang X, Webb A. Detectability of Absorption and Reduced Scattering Coefficients in Frequency-Domain Measurements Using a Realistic Head Phantom. Sensors. 2013; 13(1):152-164. https://doi.org/10.3390/s130100152
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaofeng, and Andrew Webb. 2013. "Detectability of Absorption and Reduced Scattering Coefficients in Frequency-Domain Measurements Using a Realistic Head Phantom" Sensors 13, no. 1: 152-164. https://doi.org/10.3390/s130100152
APA StyleZhang, X., & Webb, A. (2013). Detectability of Absorption and Reduced Scattering Coefficients in Frequency-Domain Measurements Using a Realistic Head Phantom. Sensors, 13(1), 152-164. https://doi.org/10.3390/s130100152



