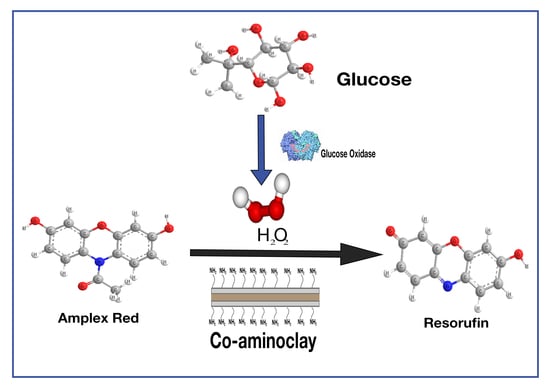
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Eight Types of Aminoclays
2.2. Characterizations of As-Prepared Aminoclays
2.3. Screening of Catalytic Activities of As-Prepared Aminoclays
2.4. Fluorometric Detection for H2O2 Using Co-Aminoclay
2.5. Fluorescent Determination of Glucose Using Co-Aminoclay and Glucose Oxidase
2.6. Glucose Detection in Human Serum
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. TEM Observation of Eight Types of Aminoclays
3.2. XRD Patterns and FT-IR Spectra of Eight Types of Aminoclays
3.3. Screening of Peroxidase or Oxidase-Like Activity of Diverse Aminoclays
3.4. Investigation for Peroxidase-Like Activity of Co-Aminoclay for the Determination of H2O2
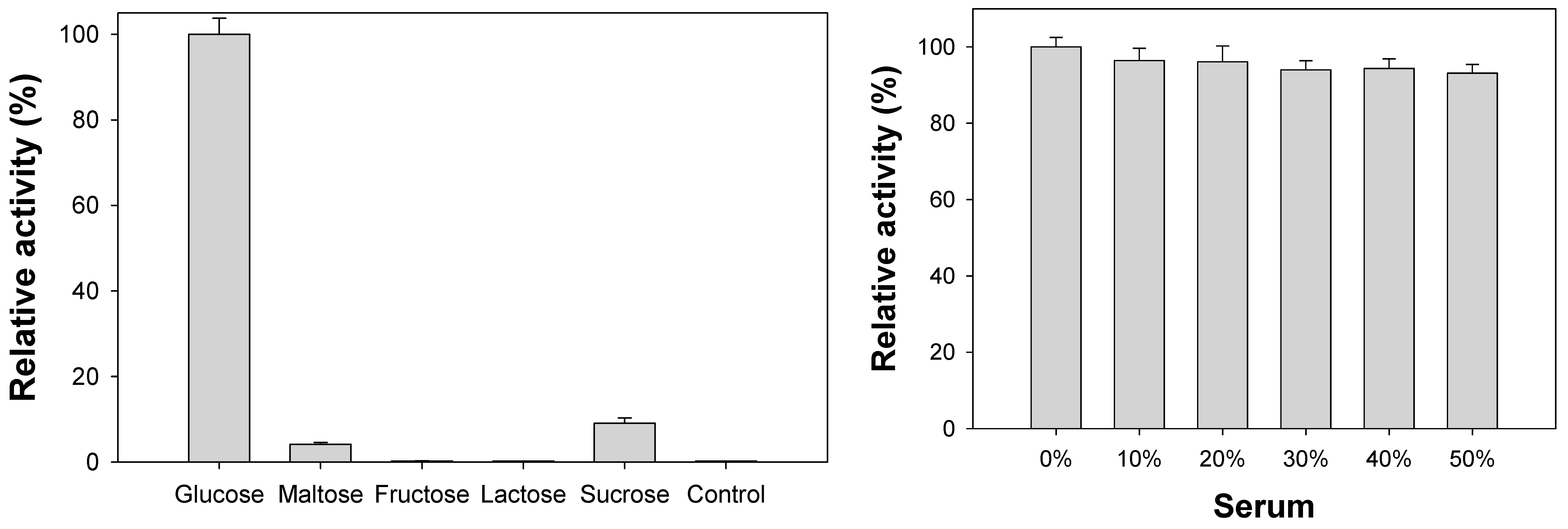
3.5. Analytical Capabilities of Co-Aminoclay for the Detection of Glucose
3.6. Diagnosis of High Level of Glucose (Hyperglycemia) Using Blood Serum Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nicolas, J.; Mura, S.; Brambilia, D.; Mackiewicz, N.; Couvreur, P. Design, functionalization strageties and biomedical applications of targeted biodegradable/biocompatible polymer-based nanocarriers for drug delivery. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 1147–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liong, M.; Lu, J.; Kovochich, M.; Xia, T.; Ruehm, S.G.; Nel, A.E.; Tamanoi, F.; Zink, J.I. Multifunctional inorganic nanoparticles for imaging, targeting, and drug delivery. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, C.; Belleville, P.; Popall, M.; Nicole, L. Applications of advanced hybrid organic-inorganic nanomaterials: From laboratory to market. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 696–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanh, N.T.K.; Green, L.A.W. Functionalisation of nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Nano Today 2010, 5, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avvakumova, S.; Colombo, M.; Tortora, P.; Prosperi, D. Biotechnological approaches toward nanoparticle biofunctionalization. Trends Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, S.; Burkett, S.L.; Davis, S.A.; Fowler, C.E.; Mendelson, N.H.; Sims, S.D.; Walsh, D.; Whilton, N.T. Sol-gel synthesis of organized matter. Chem. Mater. 1997, 9, 2300–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkett, S.L.; Press, A.; Mann, S. Synthesis, characterication and reactivity of layer inorganic-organic nanocomposites based on 2:1 trioctanhedral phyllosilicates. Chem. Mater. 1997, 9, 1071–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, S. Self-assembly and transformation of hybrid nano-objects and nanostructures under equilibrium and non-equilibrium conditions. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmstrom, S.C.; Patil, A.J.; Butler, M.; Mann, S. Influence of polymer co-intercalation on guest release from aminopropyl-functionalized magnesium phyllosilicate mesolamellar nanocomposites. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 3894–3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-C.; Park, W.-K.; Yang, J.-W. Removal of anionic metals by amino-organoclay for water treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, K.K.R.; Achari, A.; Eswaramoorthy, M. Aminoclay: A functional layered material with multifaceted applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 6707–6718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-C.; Kim, E.J.; Ko, D.A.; Yang, J.-W. Water-soluble organo-building blocks of aminoclay as a soil-flushing agent for heavy metal contaminated soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 196, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-C.; Jin, E.; Jung, S.W.; Kim, Y.-M.; Chang, K.S.; Yang, J.-W.; Kim, S.-W.; Kim, Y.-O.; Shin, H.-J. Utilizing the algicidal activity of aminoclay as a practical treatment for toxic red tides. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.-K.; Lee, Y.-C.; Lee, M.-Y.; Patil, A.J.; Shin, H.-J. Magnesium and calcium organophyllosilicates: Synthesis and in vitro cytotoxicity study. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 2564–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaturbedy, P.; Jagadeesan, D.; Eswaramoorthy, M. Ph-sensitive breathing of clay within polyelectrolyte matrix. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 5921–5929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Lee, Y.-C.; Kim, M.I.; Park, H.G.; Huh, Y.S.; Shao, Y.; Han, H.-K. Biodistribution and clearance of aminoclay nanoparticles: Implication for in vivo applicability as a tailor-made drug delivery carrier. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 7567–7574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-C.; Kim, M.-I.; Woo, M.-A.; Park, H.G.; Han, J.-I. Effective peroxidase-like activity of a water-solubilized fe-aminoclay for use in immunoassay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 42, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, A.J.; Mann, S. Self-assembly of bio-inorganic nanohybrids using organoclay building blocks. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 4605–4615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-C.; Huh, Y.S.; Farooq, W.; Han, J.-I.; Oh, Y.-K.; Park, J.Y. Oil extraction by aminoparticle-based H2O2 activation via wet microalgae harvesting. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 12802–12809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-C.; Kim, B.; Farooq, W.; Chung, J.; Han, J.-I.; Shin, H.-J.; Jeong, S.H.; Park, J.-Y.; Lee, J.-S.; Oh, Y.-K. Harvesting of oleaginous chlorella sp. By organoclays. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 132, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, M.A.M., Jr.; Alroldi, C. Energetic features of copper and lead sorption by innovative aminoalcohol-functionalized cobalt phyllosilicates. Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 10217–10227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.-M.; Lee, H.U.; Kim, E.J.; Seo, S.; Kim, B.; Lee, G.-W.; Oh, Y.-K.; Kim, J.Y.; Huh, Y.S.; Song, H.A.; et al. Efficient harvesting of wet blue-green microalgal biomass by two-aminoclay [AC]-mixture systems. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 15, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alencar, J.M.; Oliveira, F.J.V.E.; Alroldi, C.; Filho, E.C.S. Organophilic nickel phyllosilicate for reactive blue dye removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 236, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, H.-S.; Park, D.; Lim, S.E.; Jeong, K.-H.; Park, J.-S.; Park, H.-J.; Kang, S.; Kang, K.S.; Park, H.G.; An, H.-R.; et al. Two zinc-aminoclays’ in vitro cytotoxicity assessment in hela cells and in vivo embryotoxicity assay in zebrafish. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 137, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.-H.; Hwang, Y.; Lee, H.U.; Kim, B.; Lee, G.-W.; Oh, Y.-K.; Andersen, H.R.; Lee, Y.-C.; Huh, Y.S. Aquatic ecotoxicity effect of engineered aminoclay nanoparticles. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 102, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-C.; Chang, S.-J.; Choi, M.-H.; Jeon, T.-J.; Ryu, T.; Huh, Y.S. Self-assembled graphene oxide with organo-building blocks of fe-aminoclay for heterogeneous fenton-like reactin at near-neutral ph: A batch experiment. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2013, 142–143, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, L. Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of CO3O4 nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 2540–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valekar, A.H.; Batule, B.S.; Kim, M.I.; Cho, K.-H.; Hong, D.-Y.; Lee, U.H.; Chang, J.-S.; Park, H.G.; Hwang, Y.K. Novel amine-functionalized iron trimesates with enhanced peroxidase-like activity and their applications for the fluorescent assay of choline and acetylcholine. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.I.; Shim, J.; Li, T.; Lee, J.; Park, H.G. Fabrication of nanoporous nanocomposites entrapping Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles and oxidases for colorimetric biosensing. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 10700–10707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Wang, E. Nanomaterials with enzyme-like characteristics (nanozymes): Next-generation artifical enzymes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6060–6093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.Y.; Park, T.J.; Kim, M.I. Recent research trends and future prospects in nanozymes. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, D.R.; Sharifi, M.; Al-Rasadi, K. Familial hypercholesterolaemia. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2002, 29, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Original Amount (mM) | Added (mM) | Expected (mM) | (mM) | SD | CV (%) | Recovery (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 1.46 | 2.5 | 3.96 | 3.95 | 0.05 | 1.27 | 99.75 |
| Boundary | 5 | 6.46 | 6.52 | 0.33 | 5.06 | 100.93 | |
| High | 10 | 11.46 | 11.96 | 0.55 | 4.60 | 104.44 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, H.P.; Lee, Y.; Bui, V.K.H.; Oh, Y.-K.; Park, H.G.; Kim, M.I.; Lee, Y.-C. Effective Peroxidase-Like Activity of Co-Aminoclay [CoAC] and Its Application for Glucose Detection. Sensors 2018, 18, 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18020457
Song HP, Lee Y, Bui VKH, Oh Y-K, Park HG, Kim MI, Lee Y-C. Effective Peroxidase-Like Activity of Co-Aminoclay [CoAC] and Its Application for Glucose Detection. Sensors. 2018; 18(2):457. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18020457
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Han Pill, Yongil Lee, Vu Khac Hoang Bui, You-Kwon Oh, Hyun Gyu Park, Moon Il Kim, and Young-Chul Lee. 2018. "Effective Peroxidase-Like Activity of Co-Aminoclay [CoAC] and Its Application for Glucose Detection" Sensors 18, no. 2: 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18020457
APA StyleSong, H. P., Lee, Y., Bui, V. K. H., Oh, Y.-K., Park, H. G., Kim, M. I., & Lee, Y.-C. (2018). Effective Peroxidase-Like Activity of Co-Aminoclay [CoAC] and Its Application for Glucose Detection. Sensors, 18(2), 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18020457