Soil Water Measurement Using Actively Heated Fiber Optics at Field Scale
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Distributed Temperature Sensing System
2.3. Fiber Optic Cable Installation
2.4. Fiber Optic Cable Heating
2.5. Calibration Relationship and Validation
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Temperature Calibration
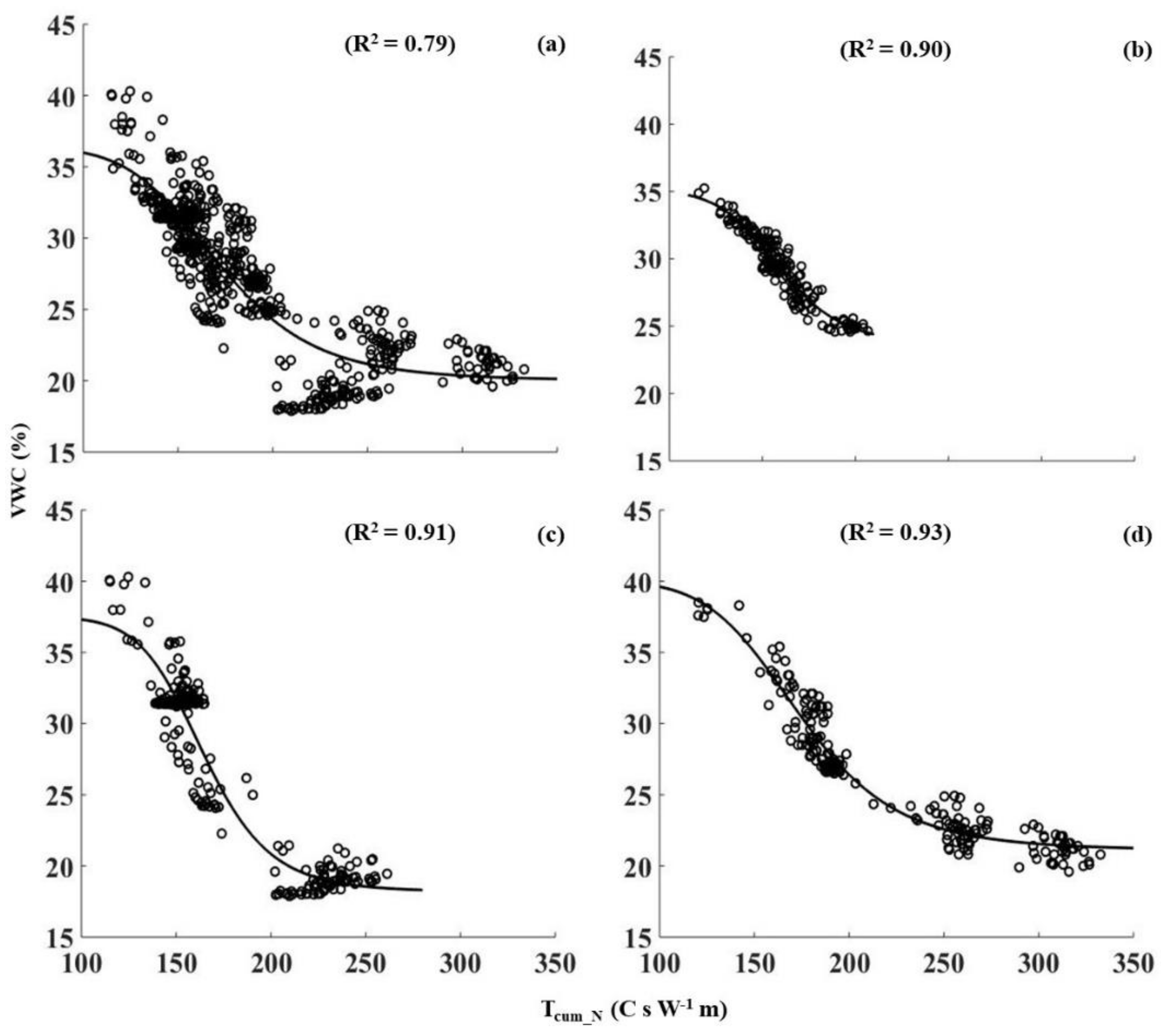
3.2. Calibration and Validation
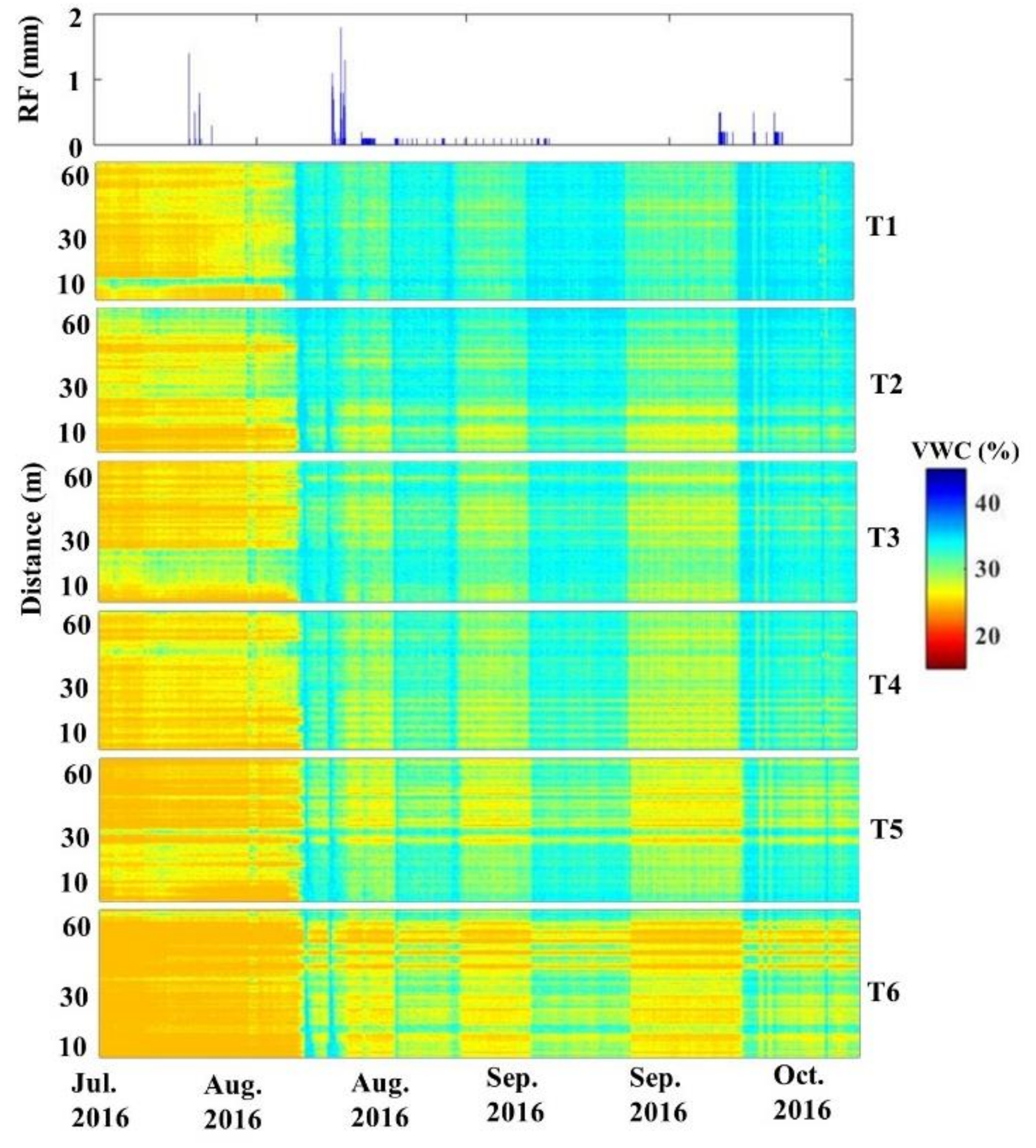
3.3. Monitoring Variability of Soil Water Using AHFO Technique
3.4. Challenge of Field Calibration
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grillakis, M.G.; Koutroulis, A.G.; Komma, J.; Tsanis, I.K.; Wagner, W.; Blöschl, G. Initial soil moisture effects on flash flood generation—A comparison between basins of contrasting hydro-climatic conditions. J. Hydrol. 2016, 541, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattivelli, L.; Rizza, F.; Badeck, F.-W.; Mazzucotelli, E.; Mastrangelo, A.M.; Francia, E.; Marè, C.; Tondelli, A.; Stanca, A.M. Drought tolerance improvement in crop plants: An integrated view from breeding to genomics. Field Crops Res. 2008, 105, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, M.; Orth, R.; Seneviratne, S.I. Investigating soil moisture–climate interactions with prescribed soil moisture experiments: An assessment with the community earth system model (Version 1.2). Geosci. Model Dev. 2017, 10, 1665–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, D.L.; Knapp, A.K.; Smith, M.D. Resistance and resilience of a grassland ecosystem to climate extremes. Ecology 2014, 95, 2646–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entin, J.K.; Robock, A.; Vinnikov, K.Y.; Hollinger, S.E.; Liu, S.; Namkhai, A. Temporal and spatial scales of observed soil moisture variations in the extratropics. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 11865–11877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, K.R.; Blanchard, B.J.; Schmugge, T.J.; Witczak, M.W. Analysis of surface moisture variations within large-field sites. Water Resour. Res. 1980, 16, 796–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Western, A.W.; Grayson, R.B.; Blöschl, G.; Willgoose, G.R.; McMahon, T.A. Observed spatial organization of soil moisture and its relation to terrain indices. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A. Landscape characteristics influence the spatial pattern of soil water storage: Similarity over times and at depths. CATENA 2014, 116, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.; Si, B.C. Identifying effects of local and nonlocal factors of soil water storage using cyclical correlation analysis. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 3669–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.; Si, B.C. Scales and locations of time stability of soil water storage in a hummocky landscape. J. Hydrol. 2011, 408, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.A.; Campbell, C.S.; Hopmans, J.W.; Hornbuckle, B.K.; Jones, S.B.; Knight, R.; Ogden, F.; Selker, J.; Wendroth, O. Soil moisture measurement for ecological and hydrological watershed-scale observatories: A review. Vadose Zone J. 2008, 7, 358–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topp, G.C. State of the art of measuring soil water content. Hydrol. Process. 2003, 17, 2993–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teuling, A.J.; Uijlenhoet, R.; Hupet, F.; van Loon, E.E.; Troch, P.A. Estimating spatial mean root-zone soil moisture from point-scale observations. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2006, 10, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampf, S.K.; Burges, S.J. Parameter estimation for a physics-based distributed hydrologic model using measured outflow fluxes and internal moisture states. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43, W12414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zreda, M.; Desilets, D.; Ferré, T.P.A.; Scott, R.L. Measuring soil moisture content non-invasively at intermediate spatial scale using cosmic-ray neutrons. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L21402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragab, R.; Evans, J.G.; Battilani, A.; Solimando, D. The cosmic-ray soil moisture observation system (cosmos) for estimating the crop water requirement: New approach. Irrig. Drain. 2017, 66, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadas, D.; Jadoon, K.Z.; McCabe, M.F. Spatiotemporal monitoring of soil water content profiles in an irrigated field using probabilistic inversion of time-lapse EMI data. Adv. Water Resour. 2017, 110, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdu, H.; Robinson, D.A.; Seyfried, M.; Jones, S.B. Geophysical imaging of watershed subsurface patterns and prediction of soil texture and water holding capacity. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W00D18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, K.M.; Small, E.E.; Gutmann, E.D.; Bilich, A.L.; Braun, J.J.; Zavorotny, V.U. Use of gps receivers as a soil moisture network for water cycle studies. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L24405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Rodríguez, M.; Rodríguez-Sinobas, L.; Benítez-Buelga, J.; Sánchez-Calvo, R. Application of active heat pulse method with fiber optic temperature sensing for estimation of wetting bulbs and water distribution in drip emitters. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 120, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayde, C.; Gregory, C.; Gil-Rodriguez, M.; Tufillaro, N.; Tyler, S.; van de Giesen, N.; English, M.; Cuenca, R.; Selker, J.S. Feasibility of soil moisture monitoring with heated fiber optics. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, W06201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciocca, F.; Lunati, I.; Van de Giesen, N.; Parlange, M.B. Heated optical fiber for distributed soil-moisture measurements: A lysimeter experiment. Vadose Zone J. 2012, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayde, C.; Benitez Buelga, J.; Rodriguez-Sinobas, L.; El Khoury, L.; English, M.; van de Giesen, N.; Selker, J.S. Mapping variability of soil water content and flux across 1–1000 m scales using the actively heated fiber optic method. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 7302–7317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele-Dunne, S.; Rutten, M.; Krzeminska, D.; Hausner, M.; Tyler, S.; Selker, J.; Bogaard, T.; Van de Giesen, N. Feasibility of soil moisture estimation using passive distributed temperature sensing. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, W03534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Striegl, A.M.; Loheide, I.; Steven, P. Heated distributed temperature sensing for field scale soil moisture monitoring. Groundwater 2012, 50, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Agliata, R.; Steele-Dunne, S.; Hoes, O.; Bogaard, T.; Greco, R.; van de Giesen, N. The impacts of heating strategy on soil moisture estimation using actively heated fiber optics. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland) 2017, 17, 2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan-Esfahani, L.; Torres-Rua, A.; Jensen, A.; McKee, M. Spatial root zone soil water content estimation in agricultural lands using bayesian-based artificial neural networks and high- resolution visual, nir, and thermal imagery. Irrig. Drain. 2017, 66, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajoie, P.G.; Stobbe, P.C. Soils Study of Soulanges and Vaudreuil Counties in the Province of Quebec; Edmond Cloutier: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1951; p. 73. [Google Scholar]
- Kaluli, J.W.; Madramootoo, C.A.; Zhou, X.; MacKenzie, A.F.; Smith, D.L. Subirrigation systems to minimize nitrate leaching. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1999, 125, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurashima, T.; Horiguchi, T.; Tateda, M. Distributed-temperature sensing using stimulated brillouin scattering in optical silica fibers. Opt. Lett. 1990, 15, 1038–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selker, J.; van de Giesen, N.; Westhoff, M.; Luxemburg, W.; Parlange, M.B. Fiber optics opens window on stream dynamics. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L24401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selker, J.S.; Thevenaz, L.; Huwald, H.; Mallet, A.; Luxemburg, W.; de Giesen, N.V.; Stejskal, M.; Zeman, J.; Westhoff, M.; Parlange, M.B. Distributed fiber-optic temperature sensing for hydrologic systems. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42, W12202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausner, M.B.; Suarez, F.; Glander, K.E.; van de Giesen, N.; Selker, J.S.; Tyler, S.W. Calibrating single-ended fiber-optic raman spectra distributed temperature sensing data. Sensors 2011, 11, 10859–10879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidana Gamage, D.N.; Biswas, A. Comparison of Power and Heating Time in Fiber Optic Distributed Temperature Sensing to Measure Soil Water. In Proceedings of the 2016 CSSS/PRSSS Annual Meeting, Kamloops, BC, Canada, 14–19 May 2016; Thompson Rivers University: Kamloops, BC, Canada, 2016; p. 83. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; McConkey, B.; Wang, H.; Janzen, H. Root distribution by depth for temperate agricultural crops. Field Crops Res. 2016, 189, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sourbeer, J.J.; Loheide, S.P. Obstacles to long-term soil moisture monitoring with heated distributed temperature sensing. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 1017–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, W.T.; Berg, A.A.; Cosh, M.H.; Loew, A.; Mohanty, B.P.; Panciera, R.; Rosnay, P.; Ryu, D.; Walker, J.P. Upscaling sparse ground-based soil moisture observations for the validation of coarse-resolution satellite soil moisture products. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vachaud, G.; Passerat De Silans, A.; Balabanis, P.; Vauclin, M. Temporal stability of spatially measured soil water probability density function. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1985, 49, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, D.; Zhang, W.; Hopmans, J.W.; Timm, L.C. Area representative soil water content estimations from limited measurements at time-stable locations or depths. J. Hydrol. 2015, 530, 580–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Si, B.C. Can soil water measurements at a certain depth be used to estimate mean soil water content of a soil profile at a point or at a hillslope scale? J. Hydrol. 2014, 516, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, H.; Rientjes, T.; Verhoef, W.; Yaseen, M. Assessing temporal stability for coarse scale satellite moisture validation in the maqu area, tibet. Sensors 2013, 13, 10725–10748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Li, P.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X. Effects of tillage and plastic mulch on soil water, growth and yield of spring-sown maize. Soil Tillage Res. 2011, 112, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, F.; Yang, S.; Chen, X. Soil water dynamics and water use efficiency in spring maize (Zea Mays L.) fields subjected to different water management practices on the loess plateau, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Western, A.W.; Grayson, R.B.; Blöschl, G. Scaling of soil moisture: A hydrologic perspective. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2002, 30, 149–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaki, T.; Limsuwat, A.; Smits, K.M.; Illangasekare, T.H. Empirical two-point α-mixing model for calibrating the ech2o ec-5 soil moisture sensor in sands. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W00D08. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usowicz, B.; Kossowski, J.; Baranowski, P. Spatial variability of soil thermal properties in cultivated fields. Soil Tillage Res. 1996, 39, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Hamdeh, N.H.; Reeder, R.C. Soil thermal conductivity effects of density, moisture, salt concentration, and organic matter. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 1285–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirksen, C.; Dasberg, S. Improved calibration of time domain reflectometry soil water content measurements. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1993, 57, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Calibration Routine | DTS Inbuilt | User Defined | DTS Inbuilt | User Defined |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time period | RMSE (°C) Mean ± SD | RMSE (°C) Mean ± SD | DE (°C) Mean ± SD | DE (°C) Mean ± SD |
| August | 0.65 ± 0.07 | 0.17 ± 0.04 | 0.21 ± 0.06 | 0.10 ± 0.04 |
| September | 0.59 ± 0.09 | 0.11 ± 0.08 | 0.17 ± 0.08 | 0.07 ± 0.02 |
| October | 0.62 ± 0.05 | 0.15 ± 0.03 | 0.19 ± 0.04 | 0.08 ± 0.03 |
| Soil Property | 0.05 m | 0.10 m | 0.20 m |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clay (%) | 9.52 ± 1.51 * | 10.70 ± 0.01 * | 10.09 ± 0.02 * |
| Silt (%) | 41.52 ± 24 * | 40.13 ± 2.68 * | 39.53 ± 1.38 * |
| Sand (%) | 48.96 ± 1.57 * | 49.18 ± 2.68 * | 50.38 ± 1.36 * |
| Textural class | Loam | Loam | Loam |
| Bulk density (Mg−3) | 1.44 ± 0.21 * | 1.41 ± 0.15 * | 1.37 ± 0.12 * |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vidana Gamage, D.N.; Biswas, A.; Strachan, I.B.; Adamchuk, V.I. Soil Water Measurement Using Actively Heated Fiber Optics at Field Scale. Sensors 2018, 18, 1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18041116
Vidana Gamage DN, Biswas A, Strachan IB, Adamchuk VI. Soil Water Measurement Using Actively Heated Fiber Optics at Field Scale. Sensors. 2018; 18(4):1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18041116
Chicago/Turabian StyleVidana Gamage, Duminda N., Asim Biswas, Ian B. Strachan, and Viacheslav I. Adamchuk. 2018. "Soil Water Measurement Using Actively Heated Fiber Optics at Field Scale" Sensors 18, no. 4: 1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18041116
APA StyleVidana Gamage, D. N., Biswas, A., Strachan, I. B., & Adamchuk, V. I. (2018). Soil Water Measurement Using Actively Heated Fiber Optics at Field Scale. Sensors, 18(4), 1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18041116






