An All Fiber White Light Interferometric Absolute Temperature Measurement System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Previous Works
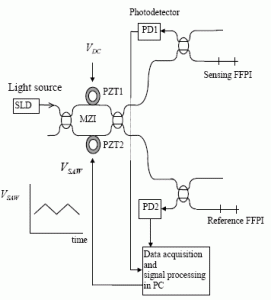
3. All fiber white light interferometry
4. Principle of absolute temperature measurement
5. Digital Signal Processing Algorithm
6. Experimental Results
6.1. Experimental arrangement
6.2. Stability test
6.3. Absolute temperature measurement
6.4. Hysteresis test
7. Robustness Test
7.1. Effect of laser diode temperature drift test
7.2. PZT non-linearity test
7.3. Effect of AFMZI temperature drift test
8. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- LeFerve, H.C. White-light interferometry in optical fibre sensors. Proceedings of 7th Optical Fibre Sensors Conference; 1990; p. 345. [Google Scholar]
- Grattan, K.T.V.; Meggitt, B.T. Optical Fiber Sensor Technology; Grattan, K.T.V.; Meggitt, B.T. Chapman & Hall: London, 1995; pp. 292–293. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Palmer, A.W.; Grattan, K.T.V.; Meggitt, B.T. Digital signal processing techniques for electronically scanned optical-fibre white light interferometry. Appl. Optics. 1992, 31, 6003–6010. [Google Scholar]
- Meggitt, B.T. Optical Fiber sensor technology; Grattan, K.T.V., Meggitt, B.T., Eds.; Chapman & Hall: London, 1995; p. 269. [Google Scholar]
- Jedrzejewska-Szczerska, M.; Bogdanowicz, R.; Gnyba, M.; Hypszer, R.; Kosmowski, B.B. Fiber-optic temperature sensor using low-coherence interferometry. Eur. Phys. J. Special Topics 2008, 154, 107–111. [Google Scholar]
- Bing, Y. Development of Tunable Optical Filters for Demodulation of White-Light Interferometric Sensors. Ph.D. dissertation, Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, Virginia, May 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, R.H.; Ning, Y.N.; Jiang, X.Q.; Palmer, A.W.; Meggitt, B.T.; Grattan, K.T.V. Novel white-light interferometer using an electronically scanned Mach-Zehnder interferometer. SPIE Proc. 1996, 2594, 159–167. [Google Scholar]
- Bosslemann, T. Multimode fibre coupled white-light interferometric position sensor. In Optical Fiber sensors, NATO ASI Series E; Chester, A.N., Martellucci, S., Verga Scheggi, A.M., Eds.; Springer, 1987; Volume 132, pp. 429–432. [Google Scholar]
- Dagenais, M.; Koo, K.; Bucholtz, F. Effects of parasitic fabry-perot cavities in fiber optic interferometric sensors. Opt. Lett. 1993, 18, 388–390. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.E.; Taylor, H.F. Fiber-optic Fabry-Pérot temperature sensor using a low-coherence source. J. Lightwave. Technol. 1991, 9, 129–134. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.C.; Taylor, H.F. Multiplexed fiber Fabry-Perot temperature sensor system using white light interferometry. Opt. Lett. 2002, 27, 903–905. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.E.; Taylor, H.F. Interferometric optical fiber sensors using internal mirrors. Electron. Lett. 1988, 24, 193–194. [Google Scholar]
- Udd, E. Fiber Optic Sensors; Wiley Interscience: New York, 1991; pp. 310–311. [Google Scholar]
- Hocker, G.B. Fiber-optic sensing of pressure and temperature. Appl. Opt. 1979, 18, 1445. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.E.; Atkins, R.A.; Taylor, H.F. Performance of a fiber-optic temperature sensor from -200 to 1050 C. Opt. Lett. 1988, 13, 1038–1040. [Google Scholar]
- Weir, K.; Gratten, K.T.V.; Palmer, A.W. White light interferometric fiber optic measurement systems. Proc SPIE 1994, 307, 2248. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J. H. A Novel Signal Processing Algorithm for FFPI and its sensor system application. Ph.D. dissertation, Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Kaddu, S.C.; Collins, S.F.; Booth, D.J. Multiplexed intrinsic optical fibre Fabry-Perot temperature and strain sensors addressed using white light interferometry. Meas. Sci. Technol. 1999, 10, 416–420. [Google Scholar]
- Meggitt, B.T.; Hall, C.J.; Weir, K. An all fibre white light interferometric strain measurement system. Sens. Actuat. A-Phys. 2000, 79, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Barlow, A.J.; Ramskov-Hanson, J.J.; Payne, D.N. Birefringence and polarization mode dispersion in spun single mode fibers. Appl. Opt. 1981, 20, 2962–2968. [Google Scholar]
- Kaminow, I.P. Polarization in optical fibers. IEEE J. Quantum Elect. 1981, 17, 15. [Google Scholar]
- http://socrates.berkeley.edu/∼budker/Physics208/Laser%20Gyroscope.ppt.
- Morey, W. Fiber optic grating technology. In Proc. SPIE-Pacific Northwest Fiber Optic Sensor Workshop; Troutdale, Oregon, 1995; Volume 2574, pp. 22–30. [Google Scholar]
- Donlagić, D.; Cibula, E. An all-fiber scanning interferometer with a large optical path length difference. Opt. Laser. Eng. 2005, vol. 43, 619–623. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Bock, W. J.; Urbanczyk, W. Error analysis of temperature-compensated white-light interferometric fiber-optic strain sensor. Sens. Actuat. A-Phys. 2004, 112, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann, L.; Müller, M.S.; Krämer, S.; Giebel, M.; Schwotzer, G.; Wieduwilt, T. Applications of fibre optic temperature measurement. Proc. Estonian Acad. Sci. Eng. 2007, 56, 363–378. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.Z.; Huang, Z.Y.; Shen, F.B.; Wang, A.B. Sapphire-fiber-based white-light interferometric sensor for high-temperature measurements. Opt. Lett. 2005, 30, 711–713. [Google Scholar]











| Fringe scan number | Phase delay [sample] | Statistics [sample] |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 54.10853 | |
| 2 | 54.14474 | |
| 3 | 54.10854 | |
| 4 | 54.07233 | |
| 5 | 54.03616 | |
| 6 | 53.89157 | |
| 7 | 53.78320 | |
| 8 | 55.18052 | |
| 9 | 53.56683 | |
| 10 | 53.56690 | Mean: |
| 11 | 53.53082 | 53.76878 |
| 12 | 53.46905 | Standard Dev.; |
| 13 | 53.36068 | 0.579 |
| 14 | 53.28855 | (0.015 fringe) |
| 15 | 53.18020 | |
| 16 | 53.14413 | |
| 17 | 53.14413 | |
| 18 | 54.71174 | |
| 19 | 54.60360 | |
| 20 | 53.14407 | |
| 21 | 53.10804 |
| Sensing FFPI Temp. [ K ] | Phase delay [sample] | Statistics [sample] |
|---|---|---|
| 297 | -7.223328 | Mean: |
| 297 | -7.248166 | -7.22836 |
| 297 | -7.223475 | Standard Dev.: |
| 297 | -7.223486 | 0.0110 |
| 297 | -7.223417 | (0.0004 fringe) |
| 298 | -11.47066 | Mean: |
| 298 | -11.47117 | -11.46902 |
| 298 | -11.47101 | Standard Dev.: |
| 298 | -11.47105 | 0.0043 |
| 298 | -11.46120 | (0.0001 fringe) |
| 299 | -15.70248 | Mean: |
| 299 | -15.70258 | -15.68762 |
| 299 | -15.67775 | Standard Dev.: |
| 299 | -15.67764 | 0.0136 |
| 299 | -15.67766 | (0.0005 fringe) |
| 300 | -19.80177 | Mean: |
| 300 | -19.80181 | -19.79668 |
| 300 | -19.77718 | Standard Dev.: |
| 300 | -19.80161 | 0.0109 |
| 300 | -19.80165 | (0.0004 fringe) |
| Heat-up | Cool-down | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temp. [ K ] | Zero-Order Fringe Peak Candidates [samples] | Zero-Order Fringe Peak Candidates [samples] | Temp. [ K ] | ||||
| H373 | p−1 -1130 | p0 -1109 | p+1 -1087 | p−2 -1179 | p−1 -1158 | p0 -1136 | C373 |
| H473 | p−2 -708 | p−1 -686 | p−0 -665 | p−1 -718 | p0 -696 | p+1 -675 | C473 |
| H573 | p−1 -237 | p0 -216 | p+1 -195 | p−1 -241 | p0 -220 | p+1 -189 | C573 |
| H673 | p−1 292 | p0 314 | p+1 335 | p−2 288 | p−1 310 | p0 331 | C673 |
| H773 | p0 817 | p+1 838 | p+2 860 | p−1 817 | p0 838 | p+1 859 | C773 |
| 873-1st | p−1 1366 | p0 1387 | p+1 1409 | p0 1366 | p+1 1387 | p+2 1409 | 873-3rd |
© 2008 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.H. An All Fiber White Light Interferometric Absolute Temperature Measurement System. Sensors 2008, 8, 6825-6845. https://doi.org/10.3390/s8116825
Kim JH. An All Fiber White Light Interferometric Absolute Temperature Measurement System. Sensors. 2008; 8(11):6825-6845. https://doi.org/10.3390/s8116825
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jeonggon Harrison. 2008. "An All Fiber White Light Interferometric Absolute Temperature Measurement System" Sensors 8, no. 11: 6825-6845. https://doi.org/10.3390/s8116825
APA StyleKim, J. H. (2008). An All Fiber White Light Interferometric Absolute Temperature Measurement System. Sensors, 8(11), 6825-6845. https://doi.org/10.3390/s8116825