Abstract
The electrocatalytical property of single-wall carbon nanotube (SWNT) modified electrode toward NADH detection was explored by cyclic voltammetry and amperometry techniques. The experimental results show that SWNT decrease the overvoltage required for oxidation of NADH (to +300 mV vs. Ag/AgCl) and this property make them suitable for dehydrogenases based biosensors. The behavior of the SWNT modified biosensor for L-malic acid was studied as an example for dehydrogenases biosensor. The amperometric measurements indicate that malate dehydrogenase (MDH) can be strongly adsorbed on the surface of the SWNT-modified electrode to form an approximate monolayer film. Enzyme immobilization in Nafion membrane can increase the biosensor stability. A linear calibration curve was obtained for L-malic acid concentrations between 0.2 and 1mM.
1. Introduction
The need for cheap, fast, and easy to use analytical tools during the last decades, resulted in biosensors progress as a dynamic technique for qualitative and quantitative determination of different analytes for environmental monitoring, clinical diagnosis, and food and process control. The development of electrochemical biosensors has recently gained increasing interest for biological applications since they have the advantages of sensitivity, selectivity, to operate in complex media and are amenable to miniaturization.
The most attractive feature of electrochemical techniques is the possibility to design a chemically modified electrode (CME) for sensitive and selective analytical applications. To prepare the CME, most often a thin film of selected chemical is either bound or coated onto the electrode surface to provide the electrode with chemical, electrochemical, electrical, and other desirable properties of the film. Electrocatalytic property is one of the noticeable features of CME to be utilized in electroanalytical chemistry [1].
Carbon nanotubes (CNT), a fast developing material having branches of single-wall (SWNT) and multi-wall (MWNT), are also used for modifying the electrode surface by simple casting from acetone, dimethylformamide (DMF), Nafion or diluted HNO3 sonicated solutions. Various chemical sensors and biosensors based on CNT have been developed to detect some important species that are related to human health or food monitoring, such as glucose, NADH, ascorbic acid, cytochrome C and DNA [2-11]. Researchers have demonstrated that CNT have a high electrocatalytic effect, a fast electron-transfer rate, and a large working surface area [12-14]. The electrochemical sensor application of the CNT was reviewed by Zhuang et al. [15] and later by Wang [16].
The electrochemical oxidation of NADH or NADPH is becoming more and more interesting, especially for the purpose of analysis, because many oxidoreductases, particularly dehydrogenases, need it as cofactor to catalyze redox reaction. The ability of CNT to promote the electron transfer reactions of NADH has been used for the development of dehydrogenase-biosensors [17-21]. In addition, electrochemical biosensors based on dehydrogenases have been developed through electrocatalytic oxidation of NAD(P)H cofactors onto the modified CNT or functionalized CNT [22, 23]. Antiochia et al. [24] prepared CNT paste electrodes modified with electrodeposited film derived from 3,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde and constructed glucose biosensors by successively coupling with glucose dehydrogenase. Zhang et al. [25] used chitosan to solubilize the CNT and to create a biocompatible environment for enzyme immobilization onto the surface of CNT.
Malic acid is widely distributed in small amounts in many natural food products. It is the predominant acid in many fruits, being known as “apple acid” because it is found in high concentration in apples, apricots, peaches, grapes as well as various citrus fruits, berries, figs, carrots, peas, beans and tomatoes [26]. There is a need to develop selective methods based on existing biosensor technology to determine malic acid, which is a taste determining constituent of fruits and fruit juices.
The enzymatic pathway exploited for the determination of malic acid is the reaction catalyzed by malate dehydrogenase:
This work proposes a low potential amperometric enzyme biosensor based on a carbon nanotubes-modified glassy carbon electrode for the determination of L-malic acid. Preliminary electrochemical characterization of the electrode was performed using NADH as intermediary analyte. This allowed the analytical performances of the electrode to be examined as well as to determine the oxidation peak potential of NADH.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Apparatus and reagents
All the chemical reagents were obtained from Sigma, of the highest grade available and used without further purification. Single-wall carbon nanotubes (SWNT) of 0.5-100 μm length were purchased from Aldrich. Malate dehydrogenase – MAD-211 (E.C.1.1.1.37) extracted from microorganism was delivered by Sorachim, France. Nafion 5% was purchased from Fluka.
Cyclic voltammetry and amperometry experiments were performed using an electrochemical analyzer μAutolab type III connected to a PC for collecting the data. The electrochemical cell was assembled with a conventional three-electrode system: the glassy carbon (GC) electrode as working electrode, an Ag/AgCl reference electrode and a Pt counter electrode.
2.2. Electrode assembly
Prior to the surface modification, the glassy carbon electrodes were polished with 1, 0.3 and 0.05μm alumina particles, washed with distilled water and finally were sonicated with distilled water for 5 min. The single wall carbon nanotubes (SWNT) were immobilized onto the GC electrodes by using dimethylformamide (DMF) as the dispersing agent. The casting solution was prepared by introducing 2 mg of SWNT into 1mL of DMF. These solutions were sonicated for 1h to promote the homogenous dispersion of the nanotubes. An aliquot of 2.5μL from each solution was placed directly onto the electrode surface and allowed for the solvent evaporation.
The enzyme electrodes have been prepared by simple physical adsorption of the enzyme on the SWNT layer. A 2.5μL of the MDH solution of different activity (1120UI/mL, 560UI/mL and 280UI/mL) have been deposited on the electrode surface and allowed to dry at room temperature. For the cross-linked enzyme electrode, 100μL solution of MDH (270U/mL) prepared in pyrophosphate buffer pH 9.3, was mixed with 4 mg BSA and 20μL of glutaraldehyde (5% or 2.5% v/v). For Nafion membrane, the MDH solution (420UI/mL) was mixed with Nafion 1% in a 2:1 ratio (v/v) followed by casting a small volume of the solution (2.5μL) onto the electrode surface and allowing the solvent to evaporate.
2.3. Procedure
All the measurements accomplished for the NADH sensor and for malic acid biosensor characterization were carried out in 0.1 M pyrophosphate buffer, pH 9.3, taking into account the fact that this enzyme exhibits the higher activity in this medium [27, 28]. Amperometric detection was performed under magnetic stirring, by applying the proper potential. The steady-state current was recorded prior (as a baseline) and after the addition of the analyte. Cyclic voltammetry experiments were accomplished at a scan rate of 100mV/s over the relevant potential range. All experiments were performed at room temperature.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Voltammetric behaviour of the SWNT-GC sensor toward NADH
Fig. 1 compares cyclic voltammograms for NADH, at unmodified and SWNT modified glassy carbon electrodes. The oxidation of NADH takes place at lower potential when GC electrode is modified with SWNT; the oxidation peak is negatively shifted from 700 mV to 300 mV vs. Ag/AgCl. The anodic peak current of the oxidation of NADH at bare GC electrode is much lower than that obtained on a SWNT-GC electrode, suggesting that CNT material is very effective in promoting the electrochemical oxidation of NADH.
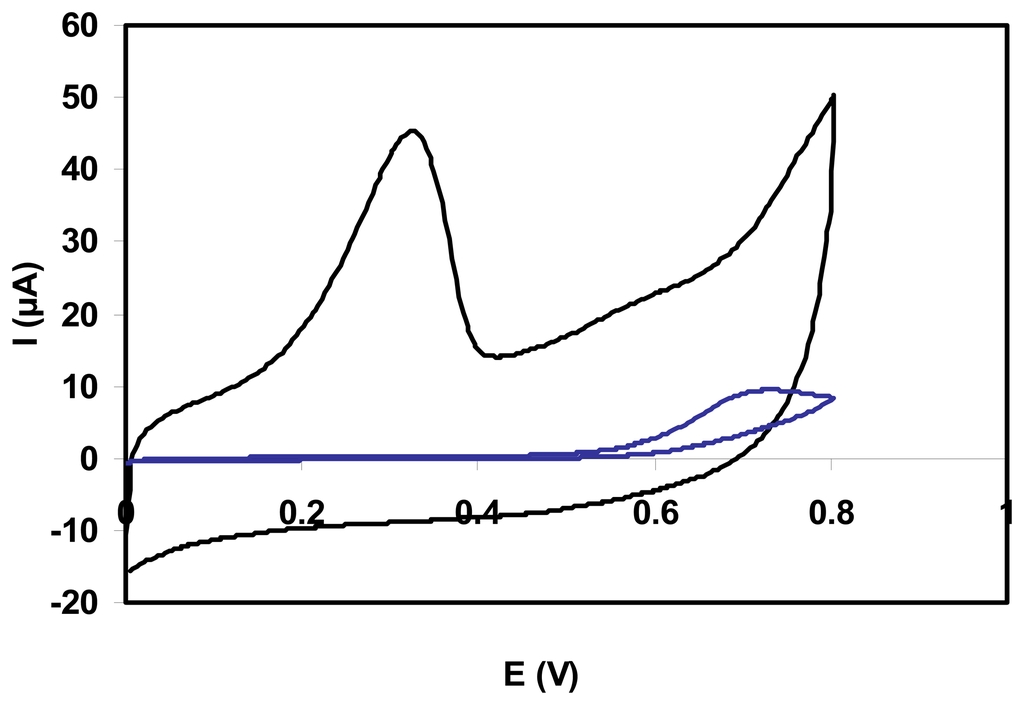
Figure 1.
Cyclic voltammograms for 1 mM NADH at unmodified GC (blue line) and SWNT-GC (black line) electrodes. Scan rate 100 mV/s; 0.1 M pyrophosphate buffer, pH 9.3.
Cyclic voltammetric experiments for NADH with SWNT-GC electrodes have indicated an improved electrochemical reactivity towards the oxidation of this compound compared to common glassy carbon electrodes.
3.2. Electroanalytical performance of the NADH sensor
Amperometric technique was used to determine NADH by applying a potential of 300 mV and the resulting calibration plots reflect the sensitivity of SWNT-GC electrodes for the range of concentration explored (Fig. 2).
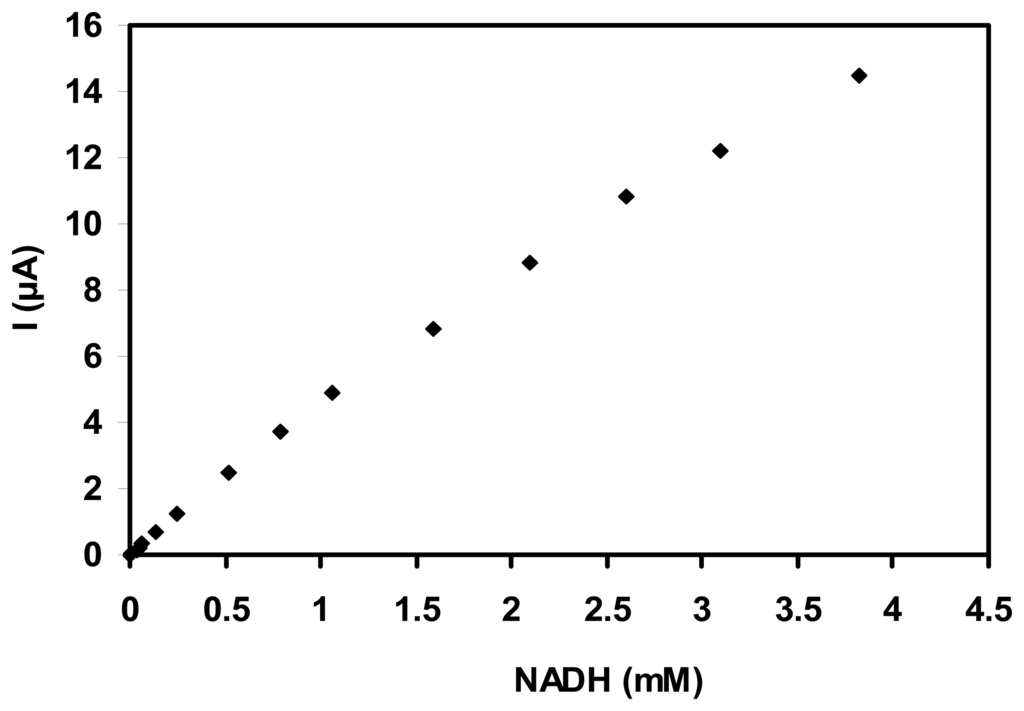
Figure 2.
Calibration curve of SWNT-GC electrode using successive addition of NADH (E = 300 mV vs. Ag/AgCl).
After each addition of NADH, the anodic current increased and reached a steady state within 4 s. The sensitivity is about 4.6 mA/M (with a SD of ±0.25, for n=3), a linear response range is observed up to 3 mM NADH and a detection limit of 0.5 μM (based on signal/noise = 3) was calculated.
The oxidation of NADH was shown to occur at lower potential at the SWNT modified electrodes compared to the bare electrodes. The stability of the sensors is a critical feature for their successful practical applications. The operational stability (Fig.3) of the SWNT modified electrodes was examined by amperometric detection of 0.05 mM NADH at an applied potential of +300 mV versus Ag/AgCl. SWNT-GC electrodes have maintained more than 100% of the initial activity during 10 repetitive measurements. Furthermore, a slowly increasing of the electrode response was noticed. When the SWNT-GC sensor was not in use, it was stored in the air at room temperature. A decrease of 5% was observed for amperometric response after 2 weeks.
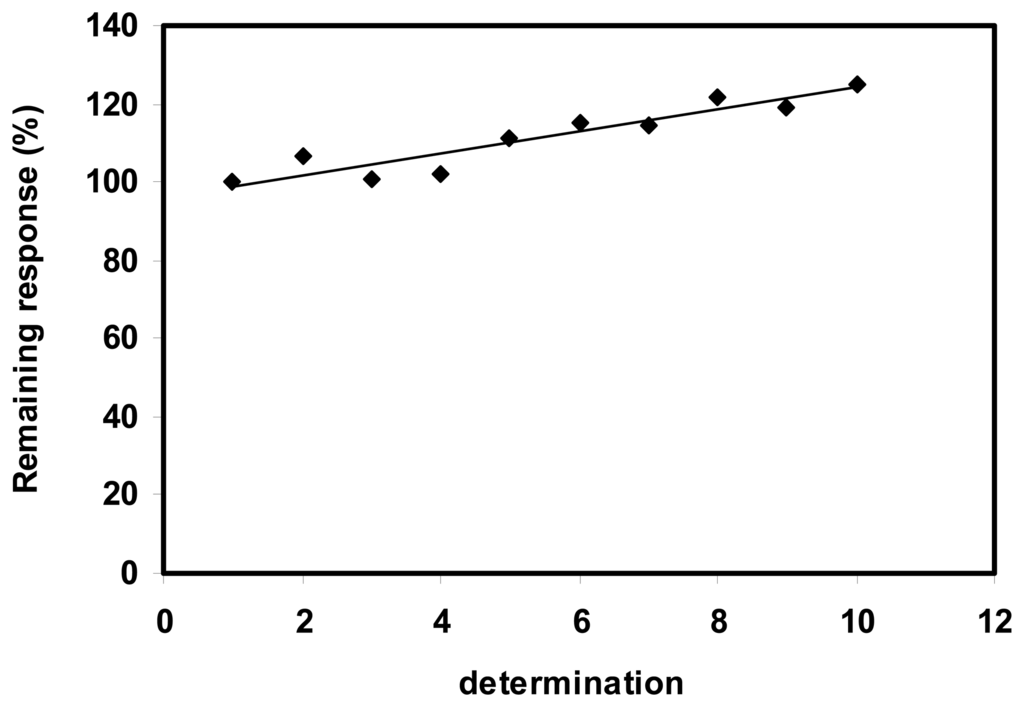
Figure 3.
Operational stability of the SWNT-GC electrode. (0.05mM NADH, E = 300mV).
Their highly stable amperometric response to NADH is an extremely attractive feature of the SWNT-modified electrodes making them suitable for dehydrogenase biosensor assembling.
3.3. Biosensor for L-malic acid
For developing a biosensor for L-malic acid, the enzyme has to be placed in the close vicinity of SWNT layer. For initials experiments, the enzyme was immobilized by physical adsorption. In order to improve the stability of biosensors and overcome the problems associated with leaching of enzyme, some membranes were used for immobilization.
3.3.1. Adsorbed enzyme
Initial tests were focused on determining the minimum enzyme loading required to generate a maximum current response from the system. For this purpose, the electrodes were prepared with 0.7, 1.4 and 2.8 UI MDH adsorbed on the SWNT layer. tests were performed until saturating levels of L-malic acid (up to 1 mM L-malic acid). The currents detected at enzyme modified electrode (MDH/SWNT-GC) are due to the oxidation of NADH produced by the enzymatic catalysed reaction of NAD+ with the L-malic acid substrate. Catalytic currents for NADH oxidation were observed with all three types of the electrodes but the higher response was obtained when the enzyme loading was smaller.
The experimental results are summarized in table 1. The LOD is calculated for a signal-to-noise ratio of 3.

Table 1.
Analytical characteristics of the L-malic acid biosensors.
The response of the MDH/SWNT-GC electrodes to malic acid addition was rather fast, and the response time was about 8 s for all three types of electrodes.
The stability of the MDH/SWNT-GC electrode was studied by repetitive amperometric measurements of a solution of L-malic acid 0.1 mM. Although the response of biosensor decreased from an assay to another due to the leakage of a part of enzyme, the electrode could still retain about 75% of the initial response after 5 determinations for all three cases of enzyme loading (Fig. 4).
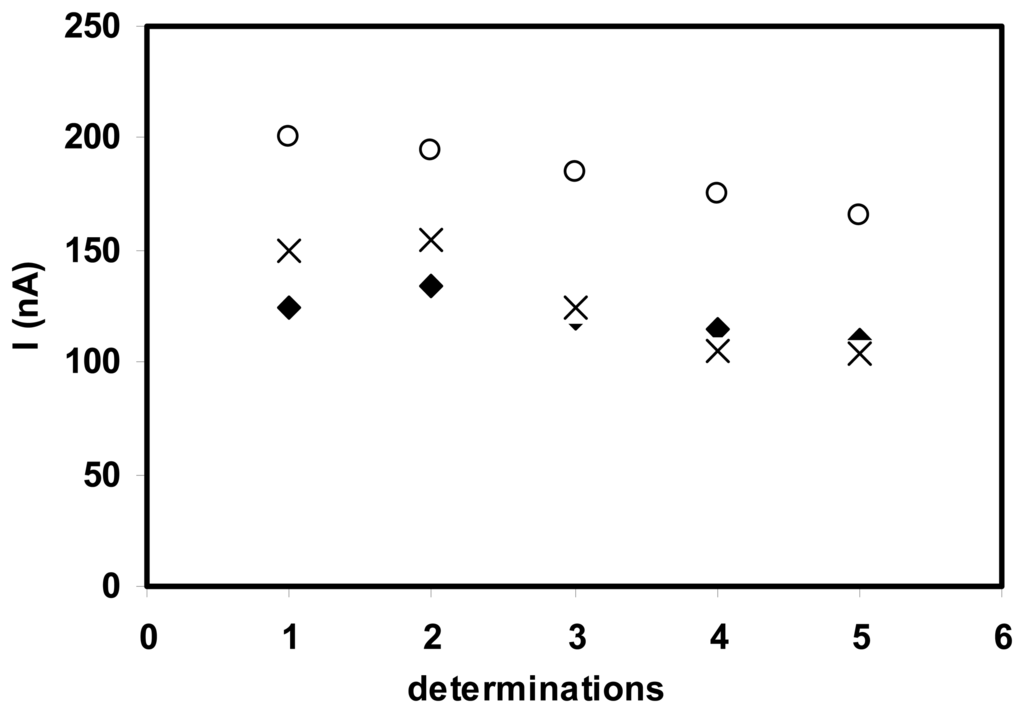
Figure 4.
Stability of L-malic acid biosensor with (◆) 2.8 UI, (×) 1.4 UI and (○) 0.7 UI MDH loading. (0.1 mM L-malic acid, 2 mM NAD+, E= 300 mV vs. Ag/AgCl).
The good stability of the MDH/SWNT-GC electrodes proves that the enzyme is strongly adsorbed on the nanotubes layer.
3.3.2. Cross-linked enzyme
MDH immobilized by glutaraldehyde cross-linking with BSA showed low activity, even for additional amount of cofactor supplied in solution. For a concentration of 0.1 mM L-malic acid the amperometric response of the biosensor with 0.7 UI enzyme is about 15±5nA. Glutaraldehyde appeared to significantly deactivate MDH and thus, alternative immobilization strategies were investigated.
3.3.3. Nafion membrane - enzyme
L-malic acid biosensor was prepared by casting the MDH-Nafion membranes over SWNT-modified glassy carbon electrodes to have a final 0.7 UI MDH loading on the surface. The biosensor can linearly detect L-malic acid from 0.2 up to the 1mM level (Fig. 5A), with a sensitivity of 200nA/mM, which is approximately 2 times lower than the sensitivity of biosensor with adsorbed enzyme.
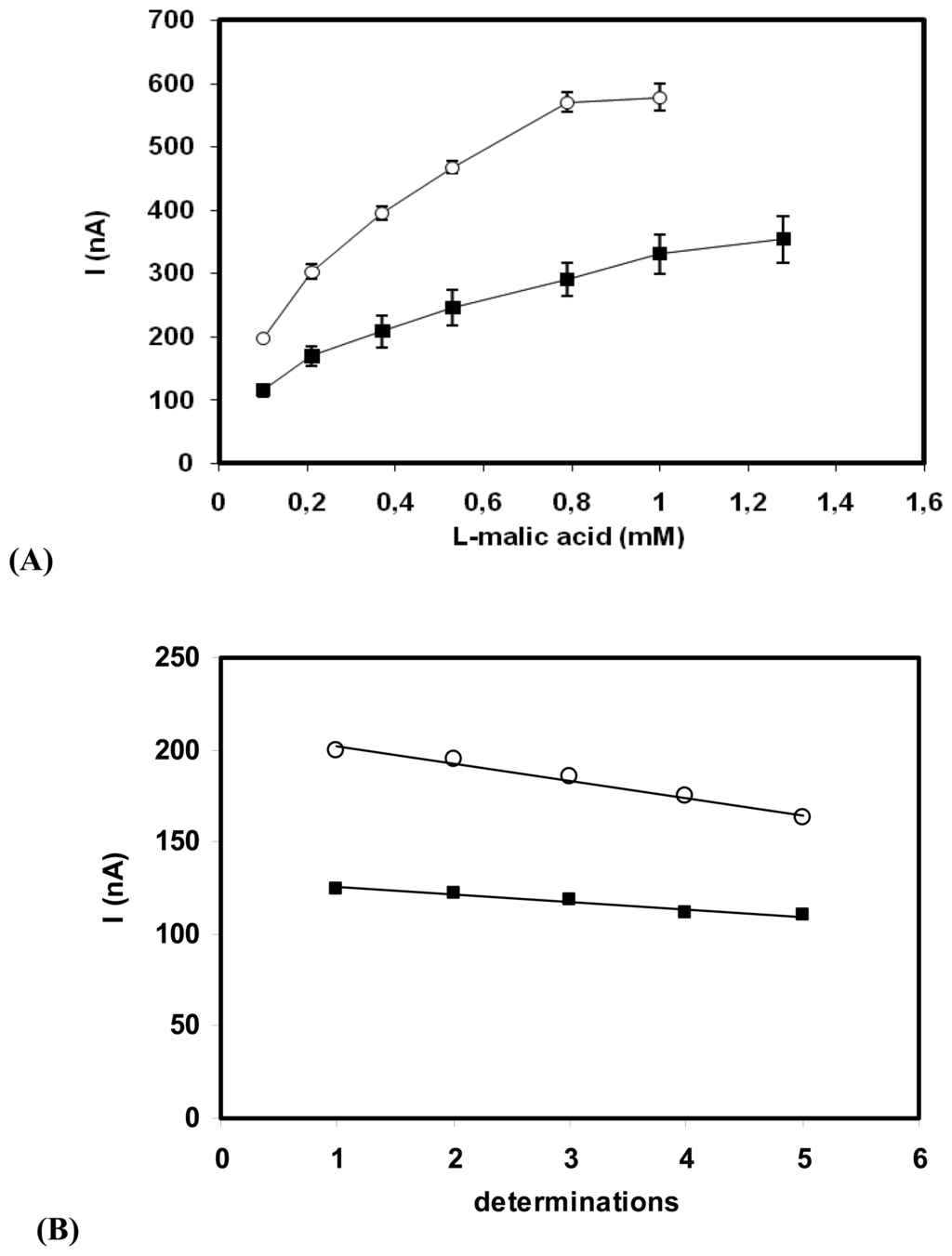
Figure 5.
(A) Calibration curves of MDH biosensors: (■) MDH-Nafion/SWNT-GC and (○) MDH/SWNT-GC electrodes. (0.7UI MDH/electrode; 2 mM NAD+; E= 300 mV vs. Ag/AgCl) (B) Operational stability of the MDH biosensors. (■) MDH-Nafion/SWNT-GC electrode and (○); MDH/SWNT-GC electrode. (0.1 mM L-malic acid, 2 mM NAD+; E= 300 mV vs. Ag/AgCl)
A comparison with the previously reported enzyme electrodes based on physical adsorption of MDH, shows that the proposed approach displays an improvement in operational stability of the resulting biosensor (Fig. 5B).
The biosensor based on enzyme immobilized in Nafion-membrane presented a relatively fast response to 0.1mM L-malic - less than 15 s.
3.4. Conclusions
The new application of carbon nanotubes, an attractive electrocatalytic nanomaterial, for preparation of an amperometric biosensor is proposed. Electrochemical techniques were employed to test the function and performance of the constructed biosensor. Characterization of the carbon nanotube modified electrode was performed using NADH as the analyte of interest. The resulting SWNT-modified electrode shows a very efficient electrocatalytic behavior toward the oxidation of NADH at a low potential, a good operational stability and presents a high sensitivity.
The new application of the catalyst described to biosensor development has been demonstrated by the construction of a very simple L-malic acid biosensor. The sensors for NADH and dehydrogenase substrate exhibit good analytical performance with low cost, convenient preparation, sensitive and rapid detection.
For initial tests, the biosensor for L-malic acid was realized by immobilizing the enzymes through physical adsorption. An improvement of the biosensor stability was obtained if the enzyme was immobilized onto the electrode surface through Nafion membrane. The methods for preparing the sensor and biosensor were simple and reproducible and the range of analytes could be extended to other dehydrogenases substrates.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to MECT-CNCSIS for financial support.
References and Notes
- Zen, J.-M.; Kumar, A. S.; Tsai, D.-M. Recent Updates of Chemically Modified Electrodes in Analytical Chemistry. Electroanalysis 2003, 15(13), 1073–1087. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Musameh, M.; Lin, Y. Solubilization of Carbon Nanotubes by Nafion Towards the Preparation of Amperometric Biosensors. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2003, 125, 2408–2409. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.-X.; Li, M.; Shi, Z.; Li, N.; Guo, Z. Direct electrochemistry of cytochrome c at a glassy carbon electrode modified with single-wall carbon nanotubes. Analytical Chemistry 2002, 74(9), 1993–1997. [Google Scholar]
- Musameh, M.; Wang, J.; Merkoci, A.; Lin, Y. Low potential stable NADH detection at carbon-nanotube-modified glassy carbon electrodes. Electrochemistry Communications 2002, 4, 743–746. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Li, M.; Shi, Z.; Li, N.; Guo, Z. Electrocatalytic oxidation of norepinephrine at a glassy carbon electrode modified with single wall carbon nanotubes. Electroanalysis 2002, 14(3), 225–230. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Liang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Luo, G. Carbon nanotube-modified electrodes for the simultaneous determination of dopamine and ascorbic acid. Analyst 2002, 127(5), 653–658. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Pomales, G.; Morales-Negron, Y.; Cabrera, C.R. Study of self-assembled monolayers of DNA and DNA-carbon nanotube hybrids. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2005, 10, 261–265. [Google Scholar]
- Shim, M.; Kam, N.W.S.; Chen, R.J.; Li, Y.; Dai, H. Functionalization of carbon nanotubes for biocompatibility and biomolecular recognition. Nano Letters 2002, 2(4), 285–288. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Liu, G.; Jan, M. Ultrasensitive Electrical Biosensing of Proteins and DNA: Carbon-Nanotube Derived Amplification of the Recognition and Transduction Events. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2004, 126, 3010–3011. [Google Scholar]
- Ferancová, A.; Ovádeková, R.; Vaníčková, M.; Šatka, A.; Viglaský, R.; Zima, J.; Barek, J.; Labuda, J. DNA-modified screen-printed electrodes with nanostructured films of multiwall carbon nanotubes, hydroxyapatite and montmorillonite. Electroanalysis 2006, 18(2), 163–168. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S. CNT Sensors for Detecting Gases with Low Adsorption Energy by Ionization. Sensors 2006, 6, 503–51. [Google Scholar]
- Banks, C.E.; Davies, T.J.; Wildgoose, G.G.; Compton, R.G. Electrocatalysis at graphite and carbon nanotube modified electrodes: edge-plane sites and tube ends are the reactive sites. Chemistry Communications 2005, 7, 829–841. [Google Scholar]
- Banks, C.E.; Compton, R.G. Exploring the electrocatalytic sites of carbon nanotubes for NADH detection: an edge plane pyrolytic graphite electrode study. Analyst 2005, 130(9), 1232–1239. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.; Lü, Y.; Wu, P.; Cai, C. Direct Electrochemistry of Redox Proteins and Enzymes Promoted by Carbon Nanotubes. Sensors 2005, 5, 220–234. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Gan, Z.; Zhuang, Q. Electrochemical sensors based on carbon nanotubes. Electroanalysis 2002, 14, 1609–1613. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J. Carbon-Nanotube Based Electrochemical Biosensors: A Review. Electroanalysis 2005, 17, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Tangkuaram, T.; Wang, J.; Rodríguez, M. C.; Laocharoensuk, R.; Veerasai, W. Highly Stable Amplified Low-Potential Electrocatalytic Detection of NAD+ at Azure-Chitosan Modified Carbon Electrodes. Sensors and Actuators B 2007, 121, 277–281. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Musameh, M. Carbon Nanotube/Teflon Composite Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors. Analytical Chemistry 2003, 75(9), 2075–2079. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Musameh, M. A Reagentless Amperometric Alcohol Biosensor Based on Carbon-Nanotube/Teflon Composite Electrodes. Analytical Letters 2003, 36(9), 2041–2048. [Google Scholar]
- Valentini, F.; Amine, A.; Orlanducci, S.; Terranova, M. L.; Palleschi, G. Carbon Nanotube Purification: Preparation and Characterization of Carbon Nanotube Paste Electrodes. Analytical Chemistry 2003, 75, 5413–5421. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, R. R.; Banks, C. E.; Compton, R. G. Basal plane pyrolytic graphite modified electrodes: comparison of carbon nanotubes and graphite powder as electrocatalysts. Analytical Chemistry 2004, 76(10), 2677–2682. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, A.S.; Pereira, A.C.; Durán, N.; Kubota, L.T. Amperometric biosensor for ethanol based on co-immobilization of alcohol dehydrogenase and Meldola's Blue on multi-wall carbon nanotube. Electrochimica Acta 2006, 52(1), 215–220. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, A.C.; Aguiar, M.R.; Kisner, A.; Macedo, D.V.; Kubota, L.T. Amperometric biosensor for lactate based on lactate dehydrogenase and Meldola Blue coimmobilized on multi-wall carbon-nanotube. Sensors and Actuators B 2007, 124(1), 269–276. [Google Scholar]
- Antiochia, R.; Lavagnini, I.; Pastore, P. A comparison between the use of a redox mediator in solution and of surface modified electrodes in the electrocatalytic oxidation of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. Bioelectrochemistry 2004, 64, 157–163. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Smith, A.; Gorski, W. Carbon nanotube-chitosan system for electrochemical sensing based on dehydrogenase enzymes. Analytical Chemistry 2004, 76, 5045–5050. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, W.H. Handbook of Food Additives, 2nd ed.; Furia, T.E., Ed.; CRC Press: Cleveland, OH, 1973; p. 239. [Google Scholar]
- Segundo, M. A.; Rangel, A. O. S. S. Kinetic determination of L(-)malic acid in wines using sequential injection analysis. Analytica Chimica Acta 2003, 499, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Gallarta, F.; Sáinz, F. J.; Sáenz, C. Fluorescent sensing layer for the determination of L -malic acid in wine. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry 2007, 387(6), 2297–2305. [Google Scholar]
© 2008 by MDPI Reproduction is permitted for noncommercial purposes.