Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential of Gabapentin with a Focus on Topical Formulations to Treat Ocular Surface Diseases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Pharmacology of GBP Action
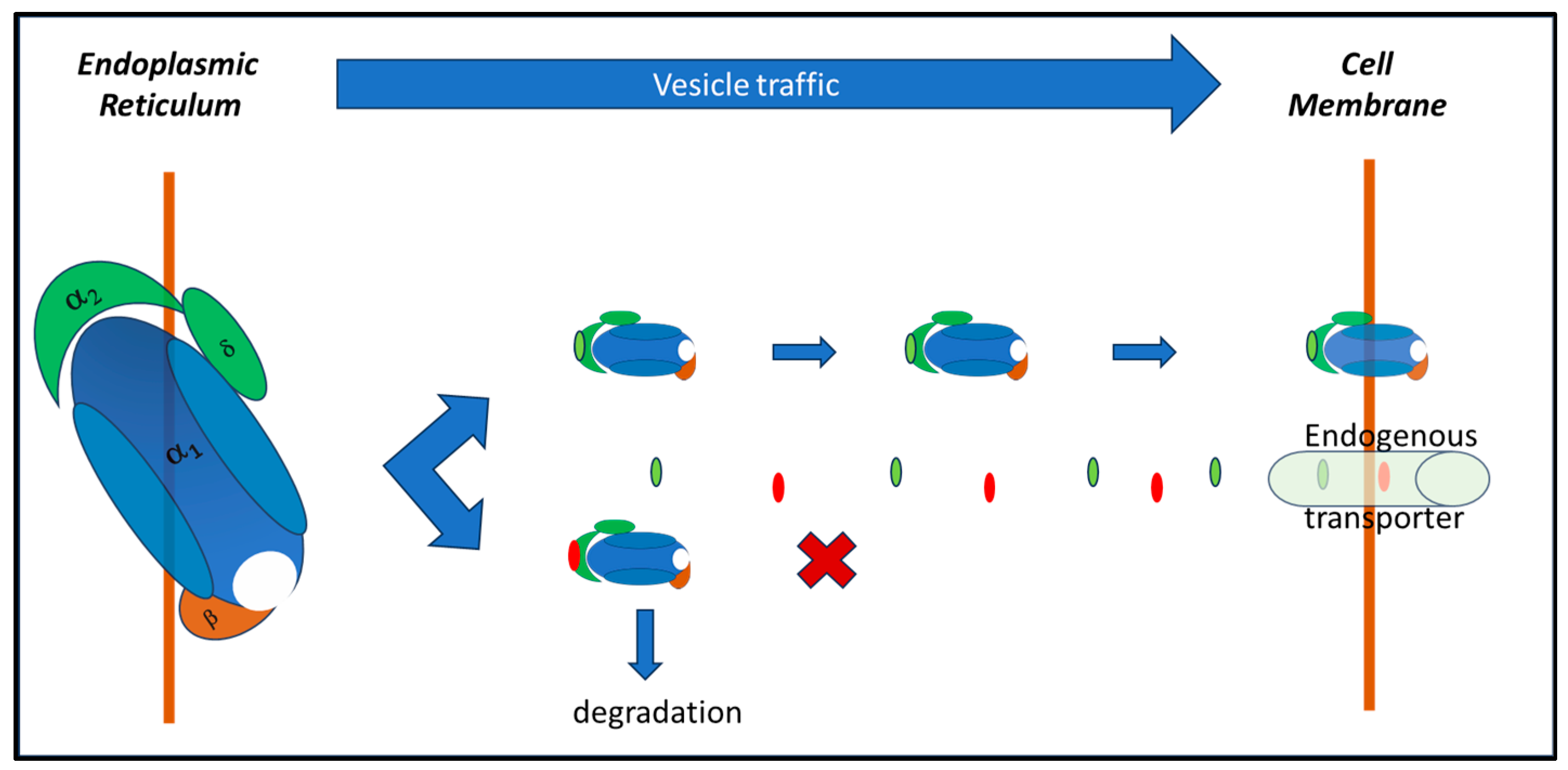
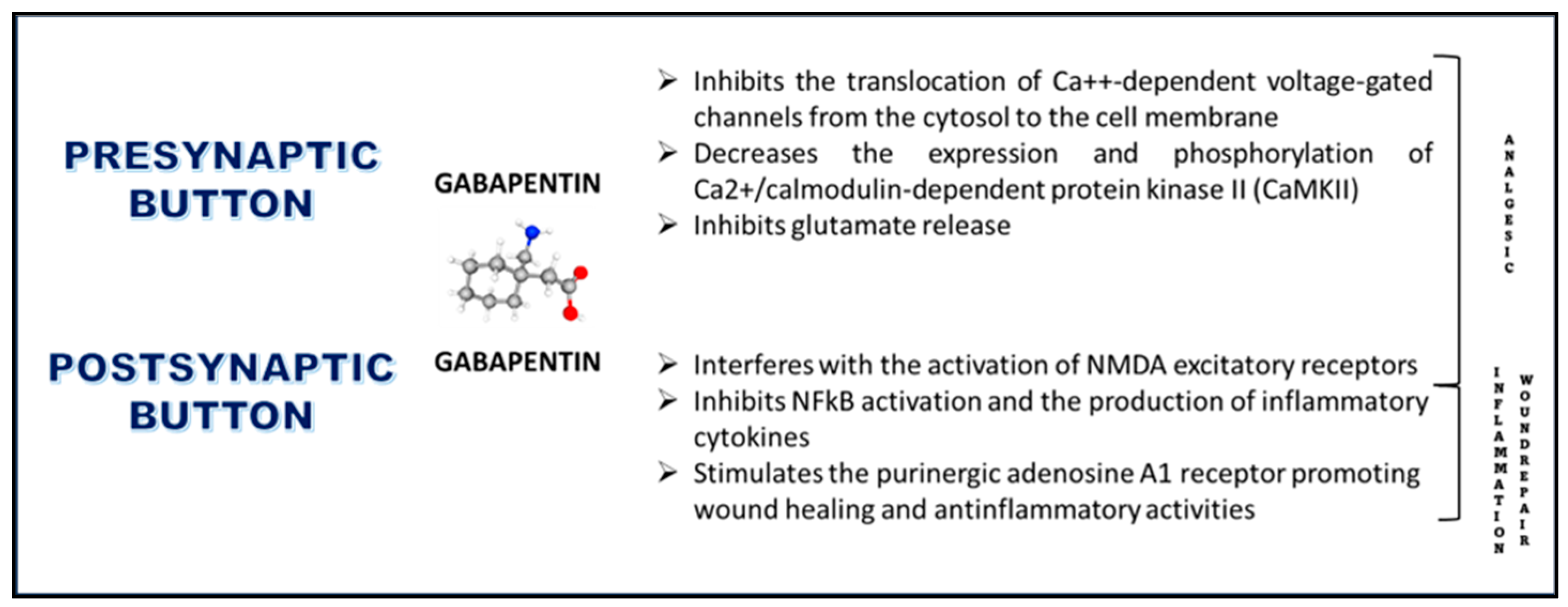
2.1. Effects on Voltage-Gated Calcium Channels
2.2. Effects on CaMKII
2.3. Effects on Glutamate Receptors
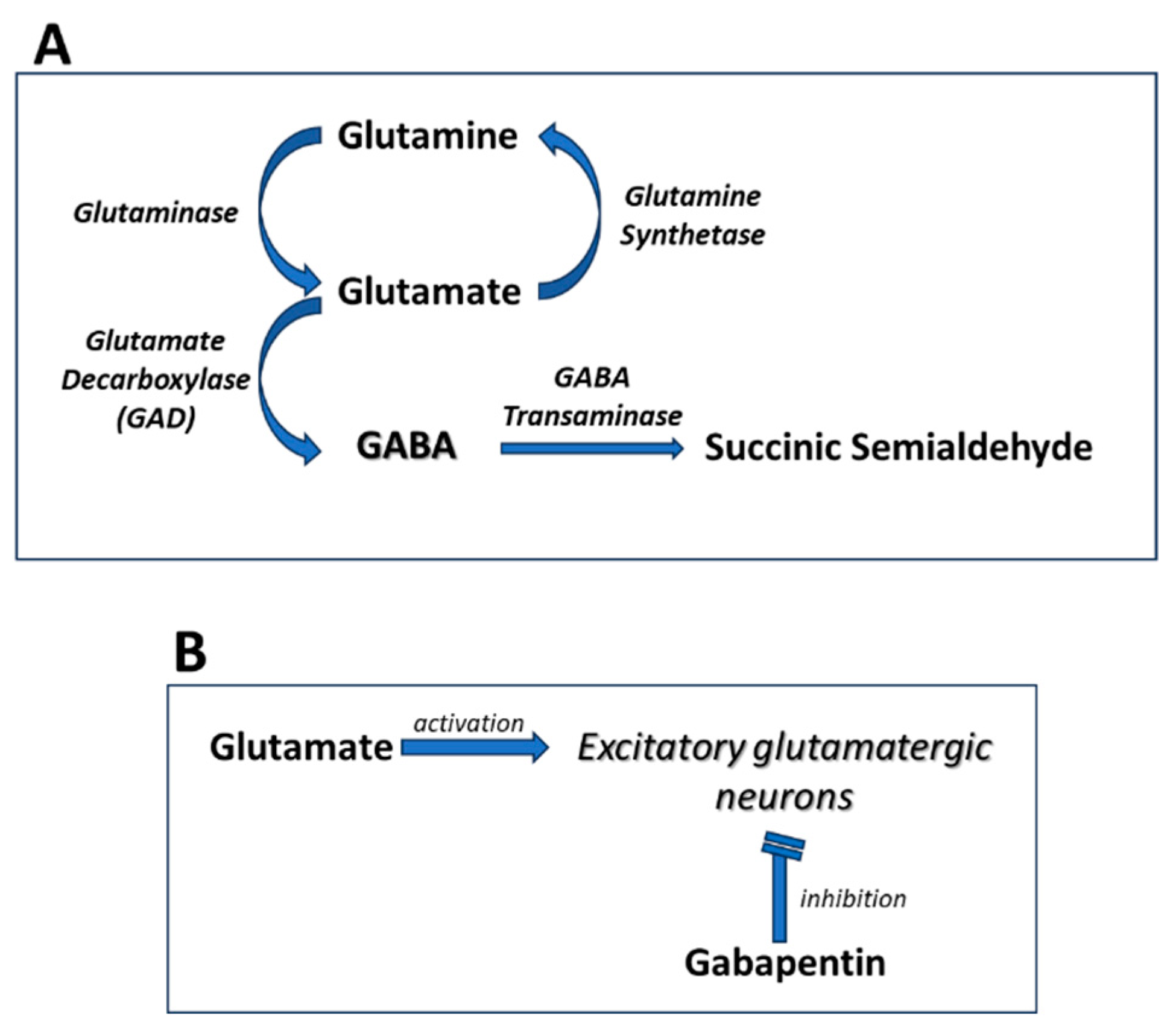
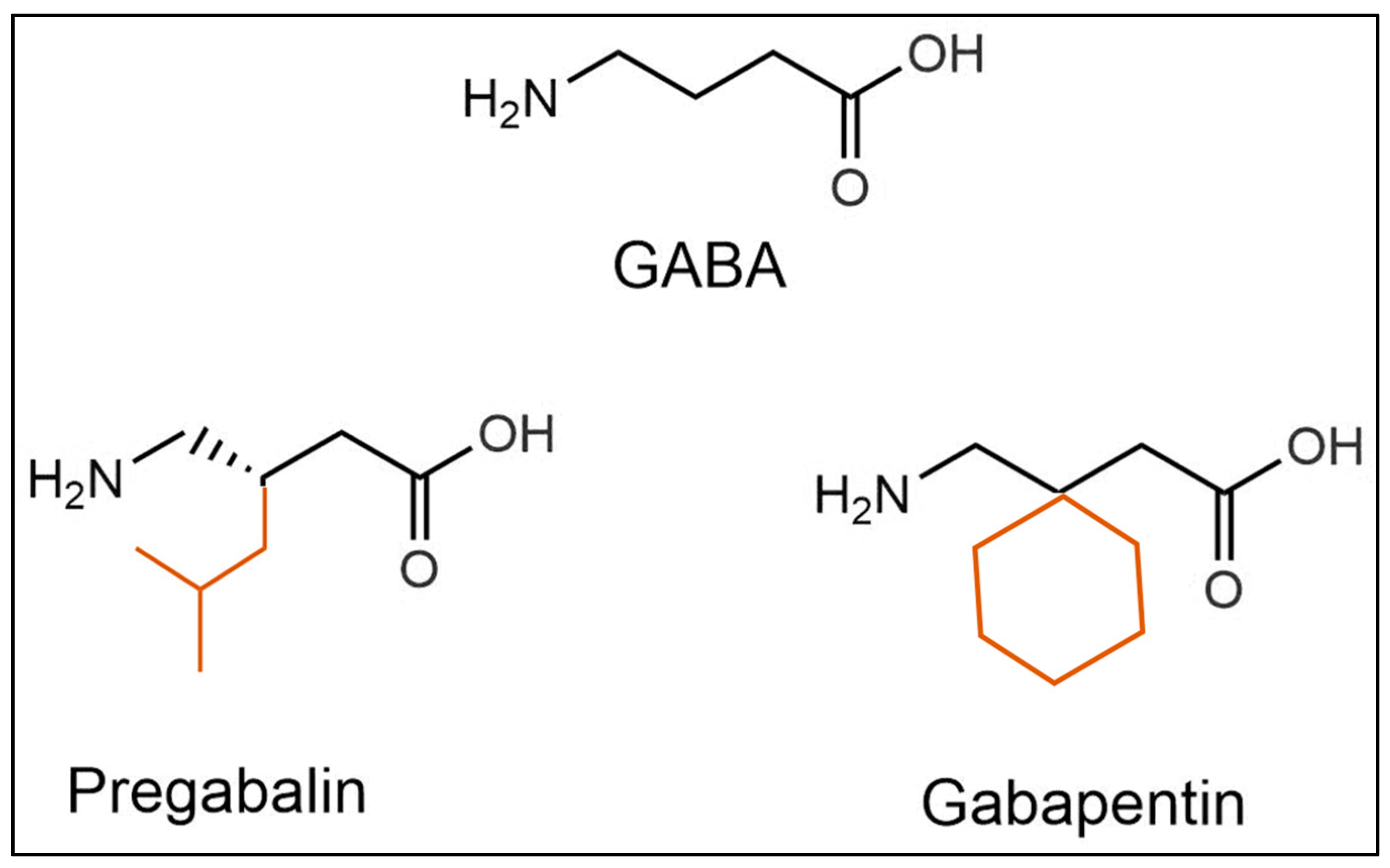
2.4. Effects on GABA Synthesis
2.5. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
2.6. Effects on Adenosine A1 Receptors
2.7. Effects on Wound-Healing
3. Current Therapeutic Applications of Systemic GBP
3.1. Psychiatric Disorders
3.2. Anxiety Disorders
3.3. Substance Use Disorders
3.4. Bipolar Disorder
3.5. Insomnia
3.6. Pain Management
4. Experimental Evidence of Ophthalmic Use of GBP
4.1. Inflammation and Neuropathic Ocular Pain
4.2. Topical Formulation and Treatment with GBP Eye Drops
5. Final Considerations
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goudet, C.; Magnaghi, V.; Landry, M.; Nagy, F.; Gereau, R.W., 4th; Pin, J.P. Metabotropic receptors for glutamate and GABA in pain. Brain Res. Rev. 2009, 60, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas, R.A. The GABAergic System: An Overview of Physiology, Physiopathology and Therapeutics. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Pharmacother. 2018, 3, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osikowicz, M.; Mika, J.; Przewlocka, B. The glutamatergic system as a target for neuropathic pain relief. Exp. Physiol. 2013, 98, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honarmand, A.; Safavi, M.; Zare, M. Gabapentin: An update of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic use in epilepsy. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2011, 16, 1062–1069. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Edelsberg, J.S.; Lord, C.; Oster, G. Systematic review and meta-analysis of efficacy, safety, and tolerability data from randomized controlled trials of drugs used to treat postherpetic neuralgia. Ann. Pharmacother. 2011, 45, 1483–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satzinger, G. Antiepileptics from gamma-aminobutyric acid. Arzneimittelforschung 1994, 44, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taylor, C.P. Mechanisms of action of gabapentin. Rev. Neuro 1997, 153 (Suppl. S1), S39–S45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hendrich, J.; Van Minh, A.T.; Heblich, F.; Nieto-Rostro, M.; Watschinger, K.; Striessnig, J.; Wratten, J.; Davies, A.; Dolphin, A.C. Pharmacological disruption of calcium channel trafficking by the alpha2delta ligand gabapentin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 3628–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tzellos, T.G.; Papazisis, G.; Amaniti, E.; Kouvelas, D. Efficacy of pregabalin and gabapentin for neuropathic pain in spinal-cord injury: An evidence-based evaluation of the literature. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2008, 64, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heblich, F.; Tran Van Minh, A.; Hendrich, J.; Watschinger, K.; Dolphin, A.C. Time course and specificity of the pharmacological disruption of the trafficking of voltage-gated calcium channels by gabapentin. Channels 2008, 2, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.L.; Liu, W.; Huang, Y.G.; Yang, N.; Zuo, P.P. Analgesic effect of gabapentin in a rat model for chronic constrictive injury. Chin. Med. J. 2011, 124, 4304–4309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Coderre, T.J.; Kumar, N.; Lefebvre, C.D.; Yu, J.S. Evidence that gabapentin reduces neuropathic pain by inhibiting the spinal release of glutamate. J. Neurochem. 2005, 94, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, K.; Sata, T. Inhibitory effect of gabapentin on N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2007, 51, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; Chang, H.K.; Lee, J.W.; Sung, Y.H.; Kim, S.E.; Shin, M.S.; Yi, J.W.; Park, J.H.; Kim, H.; Kim, C.J. Protective effect of gabapentin on N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced excitotoxicity in rat hippocampal CA1 neurons. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 109, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, L.; Chen, S.R.; Chen, H.; Xie, J.D.; Sirrieh, R.E.; MacLean, D.M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, M.H.; Jayaraman, V.; et al. The α2δ-1-NMDA Receptor Complex Is Critically Involved in Neuropathic Pain Development and Gabapentin Therapeutic Actions. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 2307–2321, Erratum in Cell Rep. 2022, 38, 110308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, C.P.; Gee, N.S.; Su, T.Z.; Kocsis, J.D.; Welty, D.F.; Brown, J.P.; Dooley, D.J.; Boden, P.; Singh, L. A summary of mechanistic hypotheses of gabapentin pharmacology. Epilepsy Res. 1998, 29, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Wang, D.S.; Bonin, R.P.; Penna, A.; Alavian-Ghavanini, A.; Zurek, A.A.; Rauw, G.; Baker, G.B.; Orser, B.A. Gabapentin increases expression of δ subunit-containing GABAA receptors. EBioMedicine 2019, 42, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Errante, L.D.; Petroff, O.A. Acute effects of gabapentin and pregabalin on rat forebrain cellular GABA, glutamate, and glutamine concentrations. Seizure 2003, 12, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Ahn, E.S.; Han, D.W.; Lee, J.H.; Min, K.T.; Kim, H.; Hong, Y.W. Pregabalin and gabapentin inhibit substance P-induced NF-kappaB activation in neuroblastoma and glioma cells. J. Cell Biochem. 2008, 105, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.S.; Jun, I.G.; Kim, S.H.; Park, J.Y. Intrathecal gabapentin increases interleukin-10 expression and inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokine in a rat model of neuropathic pain. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2013, 28, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dias, J.M.; de Brito, T.V.; de Aguiar Magalhães, D.; da Silva Santos, P.W.; Batista, J.A.; do Nascimento Dias, E.G.; de Barros Fernandes, H.; Damasceno, S.R.; Silva, R.O.; Aragão, K.S.; et al. Gabapentin, a synthetic analog of gamma-aminobutyric acid, reverses systemic acute inflammation and oxidative stress in mice. Inflammation 2014, 37, 1826–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Qin, Y.; Yang, B.; Wang, C.; Lu, T.; Xu, J.; Zhu, L.; Yuan, C.; Han, W. Gabapentin attenuates cardiac remodeling after myocardial infarction by inhibiting M1 macrophage polarization through the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 967, 176398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuchora, B.; Wielosz, M.; Urbańska, E.M. Adenosine A1 receptors and the anticonvulsant potential of drugs effective in the model of 3-nitropropionic acid-induced seizures in mice. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2005, 15, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.Y.; Jun, I.G. The interaction of gabapentin and N6-(2-phenylisopropyl)-adenosine R-(-)isomer (R-PIA) on mechanical allodynia in rats with a spinal nerve ligation. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2008, 23, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Martins, D.F.; Prado, M.R.; Daruge-Neto, E.; Batisti, A.P.; Emer, A.A.; Mazzardo-Martins, L.; Santos, A.R.; Piovezan, A.P. Caffeine prevents antihyperalgesic effect of gabapentin in an animal model of CRPS-I: Evidence for the involvement of spinal adenosine A1 receptor. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2015, 20, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chincholkar, M. Analgesic mechanisms of gabapentinoids and effects in experimental pain models: A narrative review. Br. J. Anaesth. 2018, 120, 1315–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarıtaş, T.B.; Korkmaz, M.; Sevimli, A.; Sarıtaş, Z.K. Comparison of the effects of gabapentin and pregabalin on wound healing in rats. Int. Wound J. 2016, 13, 748–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Asfour, H.Z.; Alhakamy, N.A.; Ahmed, O.A.A.; Fahmy, U.A.; Md, S.; El-Moselhy, M.A.; Rizg, W.Y.; Alghaith, A.F.; Eid, B.G.; Abdel-Naim, A.B. Enhanced healing efficacy of an optimized gabapentin-melittin nanoconjugate gel-loaded formulation in excised wounds of diabetic rats. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 1892–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Costales, B.; Goodin, A.J. Outpatient Off-Label Gabapentin Use for Psychiatric Indications Among U.S. Adults, 2011–2016. Psychiatr. Serv. 2021, 72, 1246–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berlin, R.K.; Butler, P.M.; Perloff, M.D. Gabapentin Therapy in Psychiatric Disorders: A Systematic Review. Prim. Care Companion CNS Disord. 2015, 17, 27293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Martin, J.C.; Gainer, D. Psychiatric Uses of Gabapentin. Innov. Clin. Neurosci. 2022, 19, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Garakani, A.; Murrough, J.W.; Freire, R.C.; Thom, R.P.; Larkin, K.; Buono, F.D.; Iosifescu, D.V. Pharmacotherapy of Anxiety Disorders: Current and Emerging Treatment Options. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 595584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gaba, A.; Shah, K.; Olson, C.; Munjal, S. Treatment of Acute Intermittent Porphyria-Associated Anxiety Disorder With Gabapentin: Case Report and Review of Literature. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2024, 44, 58–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felsted, J.A.; Meng, A.; Ameroso, D.; Rios, M. Sex-specific Effects of α2δ-1 in the Ventromedial Hypothalamus of Female Mice Controlling Glucose and Lipid Balance. Endocrinology 2020, 161, bqaa068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- İspir, G.Z.; Danışman, M.; Katar, K.S. A Hidden Pandemic? Abuse of Gabapentinoids: A Brief Review of Recent Studies. Curr. Drug Res. Rev. 2023. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modesto-Lowe, V.; Barron, G.C.; Aronow, B.; Chaplin, M. Gabapentin for alcohol use disorder: A good option, or cause for concern? Cleve. Clin. J. Med. 2019, 86, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buttram, M.E.; Kurtz, S.P.; Ellis, M.S.; Cicero, T.J. Gabapentin prescribed during substance abuse treatment: The perspective of treatment providers. J. Subst. Abuse Treat. 2019, 105, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ng, Q.X.; Han, M.X.; Teoh, S.E.; Yaow, C.Y.L.; Lim, Y.L.; Chee, K.T. A Systematic Review of the Clinical Use of Gabapentin and Pregabalin in Bipolar Disorder. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hong, J.S.W.; Atkinson, L.Z.; Al-Juffali, N.; Awad, A.; Geddes, J.R.; Tunbridge, E.M.; Harrison, P.J.; Cipriani, A. Gabapentin and pregabalin in bipolar disorder, anxiety states, and insomnia: Systematic review, meta-analysis, and rationale. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 1339–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Goodman, C.W.; Brett, A.S. A Clinical Overview of Off-label Use of Gabapentinoid Drugs. JAMA Intern. Med. 2019, 179, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellitteri, G.; Versace, S.; Merlino, G.; Nilo, A.; Gigli, G.L.; Valente, M. A comprehensive update on the ADMET considerations for α2δ calcium channel ligand medications for treating restless legs syndrome. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2024, 20, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Li, W.; Ma, M.; Jiang, W. Efficacy and Safety of Gabapentin in Improving Sleep Quality of Patients with Sensory Nervous System Diseases: A Meta-Analysis. Altern. Ther. Health Med. 2023, 29, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saul, H.; Gursul, D.; Cassidy, S.; Harrison, P. Little evidence supports gabapentinoid use in bipolar disorder or insomnia. BMJ 2022, 379, o2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, Q.Z.; Robinson, C.L.; Simopoulos, T.T.; Burns, J.C.; Madabhushi, S.V.; Gill, J.S. Comparative Descriptive Analysis of Physician Versus Patient-Directed Gabapentin Usage In Chronic Pain—A Preliminary Report. Pain Physician 2023, 26, E687–E693. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bragg, S.; Marrison, S.T.; Haley, S. Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: Prevention and Treatment. Am. Fam. Physician 2024, 109, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Albrecht, P.J.; Liu, Y.; Houk, G.; Ruggiero, B.; Banov, D.; Dockum, M.; Day, A.J.; Rice, F.L.; Bassani, G. Cutaneous targets for topical pain medications in patients with neuropathic pain: Individual differential expression of biomarkers supports the need for personalized medicine. Pain Rep. 2024, 9, e1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- De Stefano, G.; Di Pietro, G.; Truini, A.; Cruccu, G.; Di Stefano, G. Considerations When Using Gabapentinoids to Treat Trigeminal Neuralgia: A Review. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2023, 19, 2007–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Patel, P.; Rajput, H.S.; Chavda, K.; Mistry, S.; Bhagat, S.; Hadia, R.; Saiyed, M.; Khadela, A. Assessing the effectiveness of gabapentin in paclitaxel-induced arthralgia, myalgia, and neuropathic pain: An observational, cohort study. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2024, 5, 10781552231225148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerfas, I.; McGinn, R.; Smith, M.A. Pharmacologic Management of Cancer-Related Pain in Pregnant Patients. Drugs 2023, 83, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drake, R.; Prael, G.; Phyo, Y.; Chang, S.; Hunt, J.; Herbert, A.; Mott, C.; Hynson, J.; Phillips, M.; Cossich, M.; et al. Gabapentin for Pain in Pediatric Palliative Care. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2024, 67, 212–222.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleser, L.; Tibbetts, E.; Hanson, A.; Chu, E.C.; Gura, K.; Tom, C.; Williams, K.; Levy, P. Evaluating Gabapentin Dosing, Efficacy and Safety in Infants. J. Pediatr. Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 29, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Anfuso, C.D.; Olivieri, M.; Fidilio, A.; Lupo, G.; Rusciano, D.; Pezzino, S.; Gagliano, C.; Drago, F.; Bucolo, C. Gabapentin Attenuates Ocular Inflammation: In vitro and In vivo Studies. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yoon, H.J.; Kim, J.; Yoon, K.C. Treatment Response to Gabapentin in Neuropathic Ocular Pain Associated with Dry Eye. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ongun, N.; Ongun, G.T. Is gabapentin effective in dry eye disease and neuropathic ocular pain? Acta Neurol. Belg. 2021, 121, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissman, S.A.; Tractenberg, R.E.; Babbar-Goel, A.; Pasternak, J.F. Oral gabapentin for the treatment of postoperative pain after photorefractive keratectomy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2008, 145, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtinger, A.; Purcell, T.L.; Schanzlin, D.J.; Chayet, A.S. Gabapentin for postoperative pain after photorefractive keratectomy: A prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Refract. Surg. 2011, 27, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakravan, M.; Roshani, M.; Yazdani, S.; Faramazi, A.; Yaseri, M. Pregabalin and gabapentin for post-photorefractive keratectomy pain: A randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 22 (Suppl. S7), S106–S113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serna-Ojeda, J.C.; Santana-Cruz, O.; Quiroz-Casian, N.; González-Mendoza, E.; Mercado-Orozco, J.L.; Navas, A.; Lichtinger, A.; Graue-Hernandez, E.O. Pain Management in Corneal Collagen Crosslinking for Keratoconus: A Comparative Case Series. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 35, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavalieratos, C.S.; Dimou, T. Gabapentin therapy for painful, blind glaucomatous eye: Case report. Pain Med. 2008, 9, 377–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, R.; Jeffers, J.V.; Messenger, W.; Aref, A.A. Gabapentin for presumed neuropathic ocular pain. Am. J. Ophthalmol. Case Rep. 2020, 19, 100836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jehle, T.; Lagrèze, W.A.; Blauth, E.; Knörle, R.; Schnierle, P.; Lücking, C.H.; Feuerstein, T.J. Gabapentin-lactam (8-aza-spiro[5,4]decan-9-on; GBP-L) inhibits oxygen glucose deprivation-induced [3H]glutmate release and is a neuroprotective agent in amodel of acute retinal ischemia. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2000, 362, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagrèze, W.A.; Müller-Velten, R.; Feuerstein, T.J. The neuroprotective properties of gabapentin-lactam. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2001, 239, 845–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pielen, A.; Kirsch, M.; Hofmann, H.D.; Feuerstein, T.J.; Lagrèze, W.A. Retinal ganglion cell survival is enhanced by gabapentin-lactam in vitro: Evidence for involvement of mitochondrial KATP channels. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2004, 242, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cammalleri, M.; Amato, R.; Olivieri, M.; Pezzino, S.; Bagnoli, P.; Dal Monte, M.; Rusciano, D. Effects of Topical Gabapentin on Ocular Pain and Tear Secretion. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 671238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cristaldi, M.; Olivieri, M.; Spampinato, G.; Anfuso, C.D.; Scalia, M.; Lupo, G.; Rusciano, D. Isolation and Characterization of a New Human Corneal Epithelial Cell Line: HCE-F. Cornea 2020, 39, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.J.; Anand, A.; Huang, C.C.; Lai, J.Y. Unveiling the Power of Gabapentin-Loaded Nanoceria with Multiple Therapeutic Capabilities for the Treatment of Dry Eye Disease. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 25118–25135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kargozar, S.; Baino, F.; Hoseini, S.J.; Hamzehlou, S.; Darroudi, M.; Verdi, J.; Hasanzadeh, L.; Kim, H.W.; Mozafari, M. Biomedical applications of nanoceria: New roles for an old player. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 3051–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maccarone, R.; Tisi, A.; Passacantando, M.; Ciancaglini, M. Ophthalmic Applications of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 36, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yılmaz, B.; Yaşar, E.; Köroğlu Omaç, Ö.; Göktepe, A.S.; Tan, A.K. Gabapentin vs. Pregabalin for the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain in Patients with Spinal Cord Injury: A Crossover Study. Turk. J. Phys. Med. Rehab. 2015, 61, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davari, M.; Amani, B.; Amani, B.; Khanijahani, A.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Shabestan, R. Pregabalin and gabapentin in neuropathic pain management after spinal cord injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Korean J. Pain 2020, 33, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kelly, A.; Bradley, M.; Sana, S.; Ashley, S. Is pregabalin more effective than gabapentin for chronic neuropathic pain? Evid. Based Pract. 2021, 24, 38–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Shen, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Liu, W.; Jiang, G. A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials Comparing the Efficacy and Safety of Pregabalin and Gabapentin in the Treatment of Postherpetic Neuralgia. Pain Ther. 2023, 12, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Small, L.R.; Galor, A.; Felix, E.R.; Horn, D.B.; Levitt, R.C.; Sarantopoulos, C.D. Oral Gabapentinoids and Nerve Blocks for the Treatment of Chronic Ocular Pain. Eye Contact Lens. 2020, 46, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faktorovich, E.G.; Melwani, K. Efficacy and safety of pain relief medications after photorefractive keratectomy: Review of prospective randomized trials. J. Cataract Refract Surg. 2014, 40, 1716–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rusciano, D. Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential of Gabapentin with a Focus on Topical Formulations to Treat Ocular Surface Diseases. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17050623
Rusciano D. Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential of Gabapentin with a Focus on Topical Formulations to Treat Ocular Surface Diseases. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(5):623. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17050623
Chicago/Turabian StyleRusciano, Dario. 2024. "Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential of Gabapentin with a Focus on Topical Formulations to Treat Ocular Surface Diseases" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 5: 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17050623
APA StyleRusciano, D. (2024). Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential of Gabapentin with a Focus on Topical Formulations to Treat Ocular Surface Diseases. Pharmaceuticals, 17(5), 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17050623





