Bridging the Gap: Harnessing Plant Bioactive Molecules to Target Gut Microbiome Dysfunctions in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Microbiome and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
2.1. The Healthy Microbiome
2.2. Microbiome Alterations in ALS
3. Essential Oils and ALS
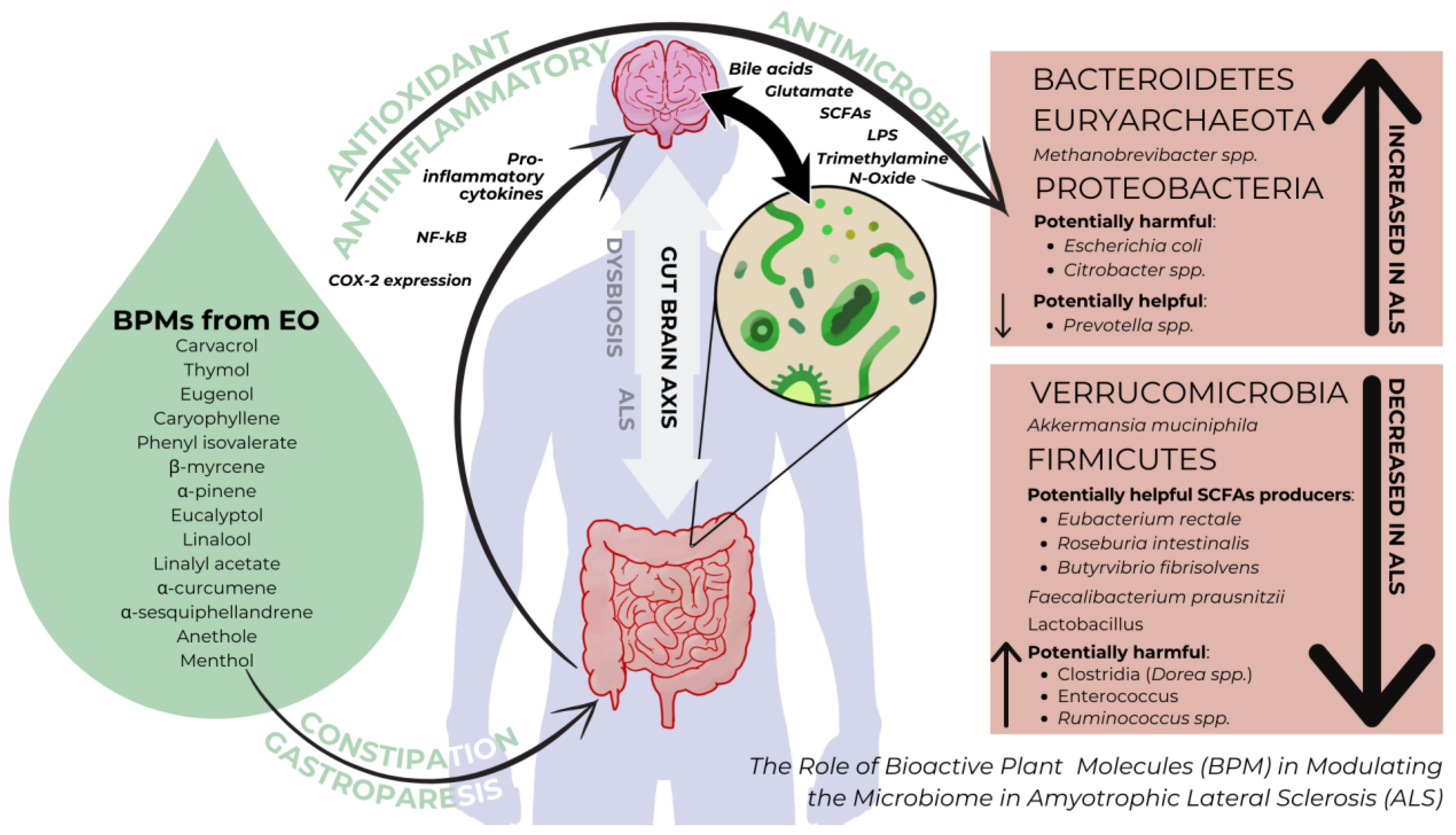
3.1. General Overview of Bioactive Plant Molecules from Essential Oils
3.2. The Interplay of Bioactive Plant Molecules and the Microbiome in ALS
3.3. Microbiome-Associated Dysfunctions in ALS
4. The Potential of Bioactive Plant Molecules to Regulate Microbiome-Derived Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in ALS
4.1. Oxidative Stress
4.2. Inflammation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, R.H.; Al-Chalabi, A. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdmanis, P.N.; Daoud, H.; Dion, P.A.; Rouleau, G.A. Recent advances in the genetics of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2009, 9, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, K.C.; Calvo, A.; Price, T.R.; Geiger, J.T.; Chiò, A.; Traynor, B.J. Projected increase in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis from 2015 to 2040. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, S.; Orrell, R.W. Pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Br. Med. Bull. 2016, 119, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.; Logroscino, G.; Jick, S.S.; Hernán, M.A. Incidence and lifetime risk of motor neuron disease in the United Kingdom: A population-based study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2009, 16, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, I.; Di Curzio, D.; Civetta, A.; Douville, R.N. Drosophila as a Model for Human Viral Neuroinfections. Cells 2022, 11, 2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Curzio, D.; Gurm, M.; Turnbull, M.; Nadeau, M.J.; Meek, B.; Rempel, J.D.; Fineblit, S.; Jonasson, M.; Hebert, S.; Ferguson-Parry, J.; et al. Pro-Inflammatory Signaling Upregulates a Neurotoxic Conotoxin-Like Protein Encrypted Within Human Endogenous Retrovirus K. Cells 2020, 9, 1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obrador, E.; Salvador, R.; López-Blanch, R.; Jihad-Jebbar, A.; Vallés, S.L.; Estrela, J.M. Oxidative Stress, Neuroinflammation and Mitochondria in the Pathophysiology of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa-Wagner, A.; Mitran, S.; Sivanesan, S.; Chang, E.; Buga, A.-M. ROS and Brain Diseases: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 963520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motataianu, A.; Serban, G.; Barcutean, L.; Balasa, R. Oxidative Stress in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Synergy of Genetic and Environmental Factors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacquard, S.; Garrido-Oter, R.; González, A.; Spaepen, S.; Ackermann, G.; Lebeis, S.; McHardy, A.C.; Dangl, J.L.; Knight, R.; Ley, R.; et al. Microbiota and Host Nutrition across Plant and Animal Kingdoms. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sender, R.; Fuchs, S.; Milo, R. Are We Really Vastly Outnumbered? Revisiting the Ratio of Bacterial to Host Cells in Humans. Cell 2016, 164, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, E.A.; Nance, K.; Chen, S. The Gut–Brain Axis. Annu. Rev. Med. 2022, 73, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Ludvigsson, J.F.; Roelstraete, B.; Pawitan, Y.; Fang, F. Gastrointestinal biopsies and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis—Results from a cohort study of 1.1 million individuals. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2021, 22, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Bander, Z.; Nitert, M.D.; Mousa, A.; Naderpoor, N. The Gut Microbiota and Inflammation: An Overview. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.R.; Osadchiy, V.; Kalani, A.; Mayer, E.A. The Brain-Gut-Microbiome Axis. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 6, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Haq, R.; Schlachetzki, J.C.M.; Glass, C.K.; Mazmanian, S.K. Microbiome-microglia connections via the gut-brain axis. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glebov, K.; Löchner, M.; Jabs, R.; Lau, T.; Merkel, O.; Schloss, P.; Steinhäuser, C.; Walter, J. Serotonin stimulates secretion of exosomes from microglia cells. Glia 2015, 63, 624–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, M.; Ibáñez, F.; Guerri, C. Exosomes as mediators of neuron-glia communication in neuroinflammation. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, M.K. Riluzole and edaravone: A tale of two amyotrophic lateral sclerosis drugs. Med. Res. Rev. 2019, 39, 733–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boddy, S.L.; Giovannelli, I.; Sassani, M.; Cooper-Knock, J.; Snyder, M.P.; Segal, E.; Elinav, E.; Barker, L.A.; Shaw, P.J.; McDermott, C.J. The gut microbiome: A key player in the complexity of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). BMC Med. 2021, 19, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, D.; Zhang, C.; Wu, W.; Lu, X.; Zhang, L. Modulation of the gut–brain axis via the gut microbiota: A new era in treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1133546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Hong, Y.; Xu, D.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, L.; Ruan, K.; Yang, X. A Review of Experimental Research on Herbal Compounds in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Phytother. Res. 2014, 28, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Zhang, L.; Feng, L.; Yao, L. The anxiolytic effect of essential oil of Cananga odorata exposure on mice and determination of its major active constituents. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 1727–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.-J.; Heinbockel, T. Essential Oils and Their Constituents Targeting the GABAergic System and Sodium Channels as Treatment of Neurological Diseases. Molecules 2018, 23, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lizarraga-Valderrama, L.R. Effects of essential oils on central nervous system: Focus on mental health. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 657–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Hong, S.; Ahn, M.; Kim, J.; Moon, C.; Matsuda, H.; Tanaka, A.; Nomura, Y.; Jung, K.; Shin, T. Eugenol alleviates the symptoms of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice by suppressing inflammatory responses. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 128, 111479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wu, H.; Guo, L.; Huang, W. Microcapsule of sweet orange essential oil changes gut microbiota in diet-induced obese rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 505, 991–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fu, X.; Ma, X.; Geng, S.; Jiang, X.; Huang, Q.; Hu, C.; Han, X. Intestinal Microbiome-Metabolome Responses to Essential Oils in Piglets. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illiano, P.; Brambilla, R.; Parolini, C. The mutual interplay of gut microbiota, diet and human disease. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 833–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grice, E.A.; Segre, J.A. The Human Microbiome: Our Second Genome. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2012, 13, 151–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morais, L.H.; Schreiber, H.L.; Mazmanian, S.K. The gut microbiota–brain axis in behaviour and brain disorders. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinninella, E.; Raoul, P.; Cintoni, M.; Franceschi, F.; Miggiano, G.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M. What is the Healthy Gut Microbiota Composition? A Changing Ecosystem across Age, Environment, Diet, and Diseases. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chidambaram, S.B.; Essa, M.M.; Rathipriya, A.G.; Bishir, M.; Ray, B.; Mahalakshmi, A.M.; Tousif, A.H.; Sakharkar, M.K.; Kashyap, R.S.; Friedland, R.P.; et al. Gut dysbiosis, defective autophagy and altered immune responses in neurodegenerative diseases: Tales of a vicious cycle. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 231, 107988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccioni, A.; Rosa, F.; Manca, F.; Pignataro, G.; Zanza, C.; Savioli, G.; Covino, M.; Ojetti, V.; Gasbarrini, A.; Franceschi, F.; et al. Gut Microbiota and Clostridium difficile: What We Know and the New Frontiers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thursby, E.; Juge, N. Introduction to the human gut microbiota. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 1823–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsimmerman, I.S. Eubiosis and dysbiosis of gastrointestinal tract: Myths and reality. Klin. Meditsina 2013, 91, 4–11. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, K.; Wu, Z.-X.; Chen, X.-Y.; Wang, J.-Q.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, C.; Zhu, D.; Koya, J.B.; Wei, L.; Li, J.; et al. Microbiota in health and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doifode, T.; Giridharan, V.V.; Generoso, J.S.; Bhatti, G.; Collodel, A.; Schulz, P.E.; Forlenza, O.V.; Barichello, T. The impact of the microbiota-gut-brain axis on Alzheimer’s disease pathophysiology. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 164, 105314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saji, N.; Murotani, K.; Hisada, T.; Tsuduki, T.; Sugimoto, T.; Kimura, A.; Niida, S.; Toba, K.; Sakurai, T. The relationship between the gut microbiome and mild cognitive impairment in patients without dementia: A cross-sectional study conducted in Japan. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indiani, C.M.D.S.P.; Rizzardi, K.F.; Castelo, P.M.; Ferraz, L.F.C.; Darrieux, M.; Parisotto, T.M. Childhood Obesity and Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio in the Gut Microbiota: A Systematic Review. Child. Obes. 2018, 14, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, S.; Nie, Q.; He, H.; Tan, H.; Geng, F.; Ji, H.; Hu, J.; Nie, S. Gut firmicutes: Relationship with dietary fiber and role in host homeostasis. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 12073–12088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Lukiw, W.J. Bacteroidetes Neurotoxins and Inflammatory Neurodegeneration. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 9100–9107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Cong, L.; Lukiw, W.J. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) Accumulates in Neocortical Neurons of Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Brain and Impairs Transcription in Human Neuronal-Glial Primary Co-cultures. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuziel, G.A.; Rakoff-Nahoum, S. The gut microbiome. Curr. Biol. 2022, 32, R257–R264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Cai, X.; Lao, L.; Wang, Y.; Su, H.; Sun, H. Brain-Gut-Microbiota Axis in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Historical Overview and Future Directions. Aging Dis. 2024, 15, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, S.T.; Restuadi, R.; McCrae, A.F.; Van Eijk, R.P.; Garton, F.; Henderson, R.D.; Wray, N.R.; McCombe, P.A.; Steyn, F.J. Progression and survival of patients with motor neuron disease relative to their fecal microbiota. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2020, 21, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, D.; Hiergeist, A.; Adis, C.; Mayer, B.; Gessner, A.; Ludolph, A.C.; Weishaupt, J.H. The fecal microbiome of ALS patients. Neurobiol. Aging 2018, 61, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burberry, A.; Wells, M.F.; Limone, F.; Couto, A.; Smith, K.S.; Keaney, J.; Gillet, G.; Van Gastel, N.; Wang, J.; Pietilainen, O.; et al. C9orf72 suppresses systemic and neural inflammation induced by gut bacteria. Nature 2020, 582, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gioia, D.; Bozzi Cionci, N.; Baffoni, L.; Amoruso, A.; Pane, M.; Mogna, L.; Gaggìa, F.; Lucenti, M.A.; Bersano, E.; Cantello, R.; et al. A prospective longitudinal study on themicrobiota composition in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, K.; Bjornevik, K.; Abu-Ali, G.; Chan, J.; Cortese, M.; Dedi, B.; Jeon, M.; Xavier, R.; Huttenhower, C.; Ascherio, A.; et al. The human gut microbiota in people with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2021, 22, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowin, J.; Xia, Y.; Jung, B.; Sun, J. Gut inflammation and dysbiosis in human motor neuron disease. Physiol. Rep. 2017, 5, e13443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blacher, E.; Bashiardes, S.; Shapiro, H.; Rothschild, D.; Mor, U.; Dori-Bachash, M.; Kleimeyer, C.; Moresi, C.; Harnik, Y.; Zur, M.; et al. Potential roles of gut microbiome and metabolites in modulating ALS in mice. Nature 2019, 572, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Reau, A.J.; Suen, G. The Ruminococci: Key symbionts of the gut ecosystem. J. Microbiol. 2018, 56, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longstreth, W.T.; Meschke, J.S.; Davidson, S.K.; Smoot, L.M.; Smoot, J.C.; Koepsell, T.D. Hypothesis: A motor neuron toxin produced by a clostridial species residing in gut causes ALS. Med. Hypotheses 2005, 64, 1153–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhifi, W.; Bellili, S.; Jazi, S.; Bahloul, N.; Mnif, W. Essential Oils’ Chemical Characterization and Investigation of Some Biological Activities: A Critical Review. Medicines 2016, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukhatem, M.N.; Boumaiza, A.; Nada, H.G.; Rajabi, M.; Mousa, S.A. Eucalyptus globulus Essential Oil as a Natural Food Preservative: Antioxidant, Antibacterial and Antifungal Properties In Vitro and in a Real Food Matrix (Orangina Fruit Juice). Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, A.; Przychodna, M.; Sopata, S.; Bodalska, A.; Fecka, I. Thymol and Thyme Essential Oil—New Insights into Selected Therapeutic Applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh Behbahani, B.; Falah, F.; Lavi Arab, F.; Vasiee, M.; Tabatabaee Yazdi, F. Chemical Composition and Antioxidant, Antimicrobial, and Antiproliferative Activities of Cinnamomum zeylanicum Bark Essential Oil. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 5190603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkali, F.; Averbeck, S.; Averbeck, D.; Idaomar, M. Biological effects of essential oils—A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 446–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coșeriu, R.L.; Vintilă, C.; Pribac, M.; Mare, A.D.; Ciurea, C.N.; Togănel, R.O.; Cighir, A.; Simion, A.; Man, A. Antibacterial Effect of 16 Essential Oils and Modulation of mex Efflux Pumps Gene Expression on Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Clinical Isolates: Is Cinnamon a Good Fighter? Antibiotics 2023, 12, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, A.; Mare, A.-D.; Mares, M.; Ruta, F.; Pribac, M.; Maier, A.-C.; Cighir, A.; Ciurea, C.N. Antifungal and anti-virulence activity of six essential oils against important Candida species—A preliminary study. Future Microbiol. 2022, 17, 737–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez, L.A.; Stashenko, E.; Ocazionez, R.E. Comparative Study on In Vitro Activities of Citral, Limonene and Essential Oils from Lippia citriodora and L. alba on Yellow Fever Virus. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2013, 8, 1934578X1300800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahani, N.; Sangtarash, M.H.; Alipour Eskandani, M.; Houshmand, M. Zataria multiflora Boiss. Essential Oil Induce Apoptosis in Two Human Colon Cancer Cell Lines (HCT116 & SW48). Iran. J. Public Health 2020, 49, 753–762. [Google Scholar]
- Agassi, S.F.T.; Yeh, T.-M.; Chang, C.-D.; Hsu, J.-L.; Shih, W.-L. Potentiation of Differentiation and Apoptosis in a Human Promyelocytic Leukemia Cell Line by Garlic Essential Oil and Its Organosulfur Compounds. Anticancer Res. 2020, 40, 6345–6354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seal, S.; Chatterjee, P.; Bhattacharya, S.; Pal, D.; Dasgupta, S.; Kundu, R.; Mukherjee, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Bhuytan, M.; Bhattacharyya, P.R.; et al. Vapor of Volatile Oils from Litsea cubeba Seed Induces Apoptosis and Causes Cell Cycle Arrest in Lung Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruberto, G.; Baratta, M.T. Antioxidant activity of selected essential oil components in two lipid model systems. Food Chem. 2000, 69, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, D.P.; Damasceno, R.O.S.; Amorati, R.; Elshabrawy, H.A.; De Castro, R.D.; Bezerra, D.P.; Nunes, V.R.V.; Gomes, R.C.; Lima, T.C. Essential Oils: Chemistry and Pharmacological Activities. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva-López, N.; Gutiérrez-Grijalva, E.; Vazquez-Olivo, G.; Heredia, J. Essential Oils of Oregano: Biological Activity beyond Their Antimicrobial Properties. Molecules 2017, 22, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Shen, J.; Chen, K.; Zhou, J.; Liao, Q.; Lu, K.; Yuan, J.; Bi, F. The alteration of gut microbiome and metabolism in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Ba, L.; Tang, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, M.; Yang, C.; Ding, F.; Zhang, M. Gut microbiota links with cognitive impairment in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A multi-omics study. J. Biomed. Res. 2023, 37, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.; Battistini, C.; Sun, J. A Gut Feeling in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Microbiome of Mice and Men. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 839526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, S.; Meng, F.; Wang, X.; Wei, H.; Chen, T. Evaluation of the Microbial Diversity in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Using High-Throughput Sequencing. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crost, E.H.; Coletto, E.; Bell, A.; Juge, N. Ruminococcus gnavus: Friend or foe for human health. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2023, 47, fuad014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziółkowska-Klinkosz, M.; Kedzia, A.; Meissner, H.O.; Kedzia, A.W. Evaluation of the tea tree oil activity to anaerobic bacteria—In Vitro study. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2016, 73, 389–394. [Google Scholar]
- Thapa, D.; Louis, P.; Losa, R.; Zweifel, B.; Wallace, R.J. Essential oils have different effects on human pathogenic and commensal bacteria in mixed faecal fermentations compared with pure cultures. Microbiology 2015, 161, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, D.; Losa, R.; Zweifel, B.; Wallace, R.J. Sensitivity of pathogenic and commensal bacteria from the human colon to essential oils. Microbiology 2012, 158, 2870–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzini, L.; Mogna, L.; De Marchi, F.; Amoruso, A.; Pane, M.; Aloisio, I.; Cionci, N.B.; Gaggìa, F.; Lucenti, A.; Bersano, E.; et al. Potential Role of Gut Microbiota in ALS Pathogenesis and Possible Novel Therapeutic Strategies. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2018, 52 (Suppl. S1), S68–S70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helander, I.M.; Alakomi, H.-L.; Latva-Kala, K.; Mattila-Sandholm, T.; Pol, I.; Smid, E.J.; Gorris, L.G.M.; Von Wright, A. Characterization of the Action of Selected Essential Oil Components on Gram-Negative Bacteria. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 3590–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñalver, P.; Huerta, B.; Borge, C.; Astorga, R.; Romero, R.; Perea, A. Antimicrobial activity of five essential oils against origin strains of the Enterobacteriaceae family. APMIS 2005, 113, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahlou, Y.; Moujabbir, S.; Aboukhalaf, A.; El Amraoui, B.; Bamhaoud, T. Antibacterial activity of essential oils of Salvia Officinalis growing in Morocco. Rocz. Państwowego Zakładu Hig. 2023, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Chen, T. Engineered Akkermansia muciniphila: A promising agent against diseases. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotkine, M.; Kviatcovsky, D.; Elinav, E. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and intestinal microbiota—Toward establishing cause and effect. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 1833–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, C.-D.; Zheng, J.-J.; An, B.-C.; Huang, H.-F.; Tan, Z.-C. Intestinal microbiota composition in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Establishment of bacterial and archaeal communities analyses. Chin. Med. J. 2019, 132, 1815–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miquel, S.; Martín, R.; Rossi, O.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.; Chatel, J.; Sokol, H.; Thomas, M.; Wells, J.; Langella, P. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and human intestinal health. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2013, 16, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Siles, M.; Enrich-Capó, N.; Aldeguer, X.; Sabat-Mir, M.; Duncan, S.H.; Garcia-Gil, L.J.; Martinez-Medina, M. Alterations in the Abundance and Co-occurrence of Akkermansia muciniphila and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii in the Colonic Mucosa of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Subjects. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertzberg, V.S.; Singh, H.; Fournier, C.N.; Moustafa, A.; Polak, M.; Kuelbs, C.A.; Torralba, M.G.; Tansey, M.G.; Nelson, K.E.; Glass, J.D. Gut microbiome differences between amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients and spouse controls. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2022, 23, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Cao, H.; Zhang, S.; Guo, P.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, S. Effects of the Supplementation of Essential Oil Mixtures on Growth Performance, Nutrient Digestibility, Immune Status and Microbial Community in Weaned Piglets. Animals 2023, 13, 3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dighe, A.S.; Jangid, K.; González, J.M.; Pidiyar, V.J.; Patole, M.S.; Ranade, D.R.; Shouche, Y.S. Comparison of 16S rRNA gene sequences of genus Methanobrevibacter. BMC Microbiol. 2004, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attaluri, A.; Jackson, M.; Valestin, J.; Rao, S.S. Methanogenic Flora Is Associated with Altered Colonic Transit but Not Stool Characteristics in Constipation without IBS. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 1407–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kala, A.; Kamra, D.N.; Agarwal, N.; Chaudhary, L.C.; Joshi, C.G. Insights into Metatranscriptome, and CAZymes of Buffalo Rumen Supplemented with Blend of Essential Oils. Indian J. Microbiol. 2020, 60, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, K.; Banerjee, S. Microbiome and motor neuron diseases. In Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 176, pp. 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kačániová, M.; Vukovič, N.; Horská, E.; Šalamon, I.; Bobková, A.; Hleba, L.; Mellen, M.; Vatľák, A.; Petrová, J.; Bobko, M. Antibacterial activity against Clostridium genus and antiradical activity of the essential oils from different origin. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2014, 49, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Yi, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Sun, J. Leaky intestine and impaired microbiome in an amyotrophic lateral sclerosis mouse model. Physiol. Rep. 2015, 3, e12356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkawara, S.; Furuya, H.; Nagashima, K.; Asanuma, N.; Hino, T. Effect of Oral Administration of Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens MDT-1 on Experimental Enterocolitis in Mice. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2006, 13, 1231–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Jung, E.; Lee, H.G.; Kim, B.; Cho, S.; Lee, S.; Kwon, I.; Seo, J. Essential oil mixture on rumen fermentation and microbial community—An in vitro study. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 32, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moțățăianu, A.; Șerban, G.; Andone, S. The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Microbiota-Gut-Brain Cross-Talk with a Focus on Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Systematic Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2023, 24, 15094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toepfer, C.; Folwaczny, A.; Klauser, R.M. Gastrointestinal dysfunction in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Other Mot. Neuron Disord. 2000, 1, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pupillo, E.; Bianchi, E.; Chiò, A.; Casale, F.; Zecca, C.; Tortelli, R.; Beghi, E. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and food intake. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2018, 19, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, T.; Aida, S.; Suemasu, S.; Mizushima, T. Anethole restores delayed gastric emptying and impaired gastric accommodation in rodents. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 472, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inamori, M.; Akiyama, T.; Akimoto, K.; Fujita, K.; Takahashi, H.; Yoneda, M.; Abe, Y.; Kubota, K.; Saito, S.; Ueno, N.; et al. Early effects of peppermint oil on gastric emptying: A crossover study using a continuous real-time 13C breath test (BreathID system). J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 42, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Sowndhararajan, K.; Kim, S. The Chemical Composition and Biological Activities of Essential Oil from Korean Native Thyme Bak-Ri-Hyang (Thymus quinquecostatus Celak.). Molecules 2022, 27, 4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Pizzol, R.; Gabbanini, S.; Baschieri, A.; Amorati, R.; Valgimigli, L. Absolute Antioxidant Activity of Five Phenol-Rich Essential Oils. Molecules 2021, 26, 5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postu, P.A.; Sadiki, F.Z.; El Idrissi, M.; Cioanca, O.; Trifan, A.; Hancianu, M.; Hritcu, L. Pinus halepensis essential oil attenuates the toxic Alzheimer’s amyloid beta (1-42)-induced memory impairment and oxidative stress in the rat hippocampus. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 112, 108673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Che, Y.; Wang, H. Bergamot essential oil attenuate aluminum-induced anxiety-like behavior through antioxidation, anti-inflammatory and GABA regulation in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 145, 111766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Che, Y.; Wang, H. Nono-titanium dioxide exposure during the adolescent period induces neurotoxicities in rats: Ameliorative potential of bergamot essential oil. Brain Behav. 2021, 11, e02099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.; Yeom, M.; Shim, I.; Lee, H.; Hahm, D. Inhibitory effect of carvacrol on lipopolysaccharide-induced memory impairment in rats. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2020, 24, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Guo, J.; Sun, C. Eucalyptol ameliorates early brain injury after subarachnoid haemorrhage via antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects in a rat model. Pharm. Biol. 2021, 59, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, V.; Nielsen, B.; Solas, M.; Ramírez, M.J.; Jäger, A.K. Exploring Pharmacological Mechanisms of Lavender (Lavandula angustifolia) Essential Oil on Central Nervous System Targets. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Zhou, X.; Hong, X.; Wang, S.; Wei, J.; Huang, J.; Ji, L.; Yang, Y.; Efferth, T.; Hong, C.; et al. Essential oil of Acorus tatarinowii Schott inhibits neuroinflammation by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activation in 3 × Tg-AD transgenic mice. Phytomedicine 2023, 112, 154695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeena, K.; Liju, V.B.; Kuttan, R. Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive activities of essential oil from ginger. Indian J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2013, 57, 51–62. [Google Scholar]
- Hakansson, A.; Molin, G. Gut Microbiota and Inflammation. Nutrients 2011, 3, 637–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandsma, E.; Kloosterhuis, N.J.; Koster, M.; Dekker, D.C.; Gijbels, M.J.J.; Van Der Velden, S.; Ríos-Morales, M.; Van Faassen, M.J.R.; Loreti, M.G.; De Bruin, A.; et al. A Proinflammatory Gut Microbiota Increases Systemic Inflammation and Accelerates Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, A.W.F.; Kersten, S. Potential mediators linking gut bacteria to metabolic health: A critical view. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, C.D. The Gut Microbiome and Its Role in Obesity. Nutr. Today 2016, 51, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Yin, J.; Zhang, J.; Ward, R.E.; Martin, R.J.; Lefevre, M.; Cefalu, W.T.; Ye, J. Butyrate Improves Insulin Sensitivity and Increases Energy Expenditure in Mice. Diabetes 2009, 58, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Just, S.; Mondot, S.; Ecker, J.; Wegner, K.; Rath, E.; Gau, L.; Streidl, T.; Hery-Arnaud, G.; Schmidt, S.; Lesker, T.R.; et al. The gut microbiota drives the impact of bile acids and fat source in diet on mouse metabolism. Microbiome 2018, 6, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.; Patel, V.H. Inflammation and Metabolic Syndrome: An Overview. Curr. Res. Nutr. Food Sci. J. 2015, 3, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, Q.; Xu, W.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Q.; Eatman, D.; You, S.; Zou, J.; Champion, J.; Zhao, L.; et al. C-Reactive Protein Causes Adult-Onset Obesity Through Chronic Inflammatory Mechanism. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tedelind, S.; Westberg, F.; Kjerrulf, M.; Vidal, A. Anti-inflammatory properties of the short-chain fatty acids acetate and propionate: A study with relevance to inflammatory bowel disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 2826–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Guo, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Ou, Z.; Peng, Y. Phascolarctobacterium faecium abundant colonization in human gastrointestinal tract. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 3122–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furet, J.-P.; Kong, L.-C.; Tap, J.; Poitou, C.; Basdevant, A.; Bouillot, J.-L.; Mariat, D.; Corthier, G.; Doré, J.; Henegar, C.; et al. Differential Adaptation of Human Gut Microbiota to Bariatric Surgery–Induced Weight Loss. Diabetes 2010, 59, 3049–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, H.; Mahmood, N.; Kumar, M.; Varikuti, S.R.; Challa, H.R.; Myakala, S.P. Effect of Probiotic (VSL#3) and Omega-3 on Lipid Profile, Insulin Sensitivity, Inflammatory Markers, and Gut Colonization in Overweight Adults: A Randomized, Controlled Trial. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 348959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, T. The Nuclear Factor NF-κB Pathway in Inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a001651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisberg, S.P.; McCann, D.; Desai, M.; Rosenbaum, M.; Leibel, R.L.; Ferrante, A.W. Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1796–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirmer, M.; Smeekens, S.P.; Vlamakis, H.; Jaeger, M.; Oosting, M.; Franzosa, E.A.; Ter Horst, R.; Jansen, T.; Jacobs, L.; Bonder, M.J.; et al. Linking the Human Gut Microbiome to Inflammatory Cytokine Production Capacity. Cell 2016, 167, 1125–1136.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.-Y.; Yang, L.; Jiang, J.-G.; Zheng, C.-Y.; Zhu, W. Immune enhancement effects and extraction optimization of polysaccharides from Citrus aurantium L. var. amara Engl. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 796–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastaki, S.M.; Adeghate, E.; Amir, N.; Ojha, S.; Oz, M. Menthol inhibits oxidative stress and inflammation in acetic acid-induced colitis in rat colonic mucosa. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 4210–4222. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shahid, M.; Lee, M.Y.; Yeon, A.; Cho, E.; Sairam, V.; Valdiviez, L.; You, S.; Kim, J. Menthol, a unique urinary volatile compound, is associated with chronic inflammation in interstitial cystitis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.S.; Suk, K.D. Anti-nociceptive, Anti-inflammatory, Mental Effects of Essential Oil from Thymus magnus. Yakhak Hoeji 2007, 51, 508–516. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, J.; Zhu, L.; Li, T.; Jiang, W.; Zhou, J.; Peng, W.; Wu, C. Zanthoxylum bungeanum Maxim. (Rutaceae): A Systematic Review of Its Traditional Uses, Botany, Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics, and Toxicology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omonijo, F.A.; Liu, S.; Hui, Q.; Zhang, H.; Lahaye, L.; Bodin, J.-C.; Gong, J.; Nyachoti, M.; Yang, C. Thymol Improves Barrier Function and Attenuates Inflammatory Responses in Porcine Intestinal Epithelial Cells during Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Inflammation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pribac, M.; Motataianu, A.; Andone, S.; Mardale, E.; Nemeth, S. Bridging the Gap: Harnessing Plant Bioactive Molecules to Target Gut Microbiome Dysfunctions in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 4471-4488. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46050271
Pribac M, Motataianu A, Andone S, Mardale E, Nemeth S. Bridging the Gap: Harnessing Plant Bioactive Molecules to Target Gut Microbiome Dysfunctions in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2024; 46(5):4471-4488. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46050271
Chicago/Turabian StylePribac, Mirela, Anca Motataianu, Sebastian Andone, Elena Mardale, and Sebastian Nemeth. 2024. "Bridging the Gap: Harnessing Plant Bioactive Molecules to Target Gut Microbiome Dysfunctions in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 46, no. 5: 4471-4488. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46050271




