Fucoxanthin Attenuates Rifampin-Induced Cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) and Multiple Drug Resistance 1 (MDR1) Gene Expression Through Pregnane X Receptor (PXR)-Mediated Pathways in Human Hepatoma HepG2 and Colon Adenocarcinoma LS174T Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Fucoxanthin Inhibits the Basal and Attenuated Rifampin-Induced CYP3A4 Enzyme Activity in HepG2 Cells
2.2. Fucoxanthin Inhibits the Basal and Attenuated Rifampin-Induced CYP3A4 mRNA Expression in HepG2 and LS174T Cells

2.3. Fucoxanthin Inhibits the Basal and Attenuated Rifampin-Induced CYP3A4 Protein Expression in HepG2 Cells
2.4. Fucoxanthin Inhibits PXR-Mediated CYP3A4 Promoter Activity in HepG2 Cells

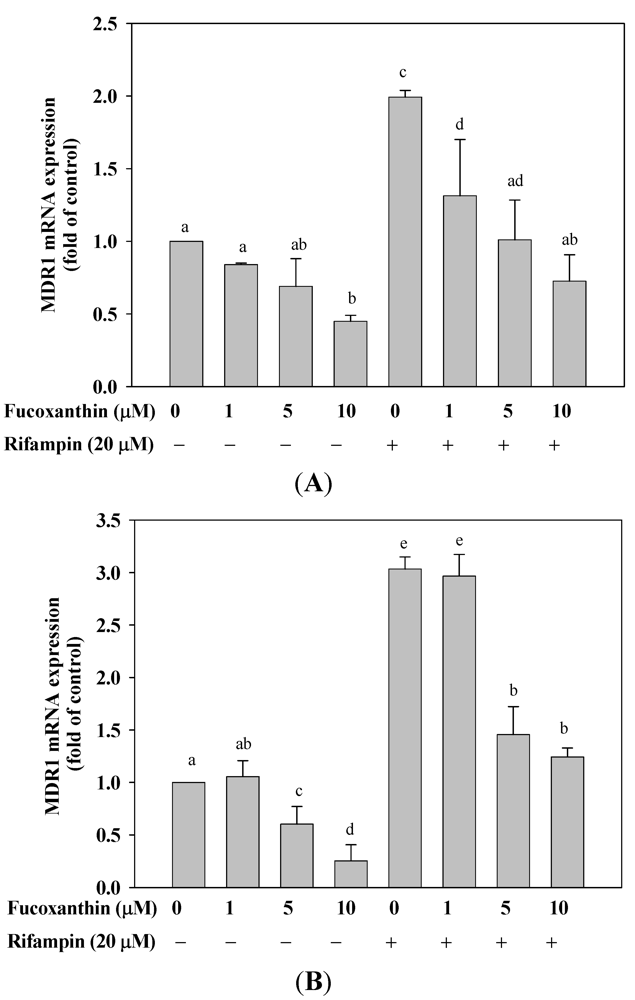
2.5. Fucoxanthin Inhibits the Basal and Attenuated Rifampin-Induced MDR1 mRNA Expression in HepG2 and LS174T Cells
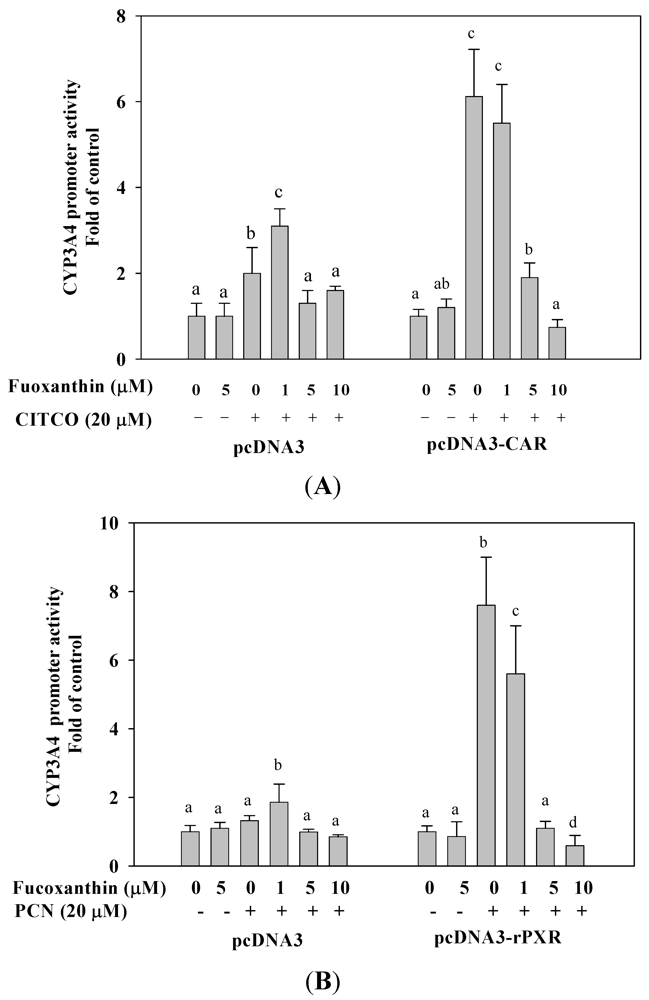
2.6. Fucoxanthin Inhibits hCAR- and rPXR-Mediated CYP3A4 Promoter Transactivation in HepG2 Cells
2.7. Fucoxanthin Disrupt the Interaction of PXR and Coactivator Interactions in HepG2 Cells

3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Plasmids Construction
4.4. Determination of CYP3A4 Enzymatic Activities Using P450-Glo™ Assay
4.5. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction of CYP3A4 and MDR1
| Gene | 5′-3′ sequence | PCR condition (45 cycles) |
|---|---|---|
| CYP3A4 | ||
| Forward | 5′-GGGAAGCAGAGACAGGCAAG-3′ | Denaturation |
| Reverse | 5′-GAGCGTTTCATTCACCACCA-3′ | (30 s at 95 °C) |
| MDR1 | ||
| Forward | 5′-AAAAAGATCAACTCGTAGGAGTA-3′ | Annealing |
| Reverse | 5′-GCACAAAATACACCAACAA-3′ | (30 s at 60 °C) |
| β-actin | ||
| Forward | 5′-GTGGGGCGCCCCAGGCACCA-3′ | Extension |
| Reverse | 5′-CACCCCGCGGGGTCCGTGGT-3′ | (30 s at 72 °C) |
4.6. Western Blotting
4.7. Transient Transfection, CYP3A4 Reporter Assay, and Mammalian Two-Hybrid Assay
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
- Samples Availability: Available from the authors.
References
- Maeda, H.; Hosokawa, M.; Sashima, T.; Takahashi, N.; Kawada, T.; Miyashita, K. Fucoxanthin and its metabolite, fucoxanthinol, suppress adipocyte differentiation in 3T3-L1 cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2006, 18, 147–152. [Google Scholar]
- Nishino, H.; Tokuda, H.; Murakoshi, M.; Satomi, Y.; Masuda, M.; Onozuka, M.; Yamaguchi, S.; Takayasu, J.; Tsuruta, J.; Okuda, M.; Khachik, F.; Narisawa, T.; Takasuka, N.; Yano, M. Cancer prevention by natural carotenoids. Biofactors 2000, 13, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Shiratori, K.; Ohgami, K.; Ilieva, I.; Jin, X.H.; Koyama, Y.; Miyashita, K.; Yoshida, K.; Kase, S.; Ohno, S. Effects of fucoxanthin on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in vitro and in vivo. Exp. Eye Res. 2005, 81, 422–428. [Google Scholar]
- Kotake-Nara, E.; Kushiro, M.; Zhang, H.; Sugawara, T.; Miyashita, K.; Nagao, A. Carotenoids affect proliferation of human prostate cancer cells. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 3303–3306. [Google Scholar]
- Kotake-Nara, E.; Terasaki, M.; Nagao, A. Characterization of apoptosis induced by fucoxanthin in human promyelocytic leukemia cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2005, 69, 224–227. [Google Scholar]
- Hosokawa, M.; Kudo, M.; Maeda, H.; Kohno, H.; Tanaka, T.; Miyashita, K. Fucoxanthin induces apoptosis and enhances the antiproliferative effect of the PPARgamma ligand, troglitazone, on colon cancer cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1675, 113–119. [Google Scholar]
- Sugawara, T.; Baskaran, V.; Tsuzuki, W.; Nagao, A. Brown algae fucoxanthin is hydrolyzed to fucoxanthinol during absorption by caco-2 human intestinal cells and mice. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 946–951. [Google Scholar]
- Asai, A.; Sugawara, T.; Ono, H.; Nagao, A. Biotransformation of fucoxanthinol into amarouciaxanthin a in mice and HepG2 cells: Formation and cytotoxicity of fucoxanthin metabolites. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2004, 32, 205–211. [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto, T.; Ozaki, Y.; Mizuno, M.; Yoshida, M.; Nishitani, Y.; Azuma, T.; Komoto, A.; Maoka, T.; Tanino, Y.; Kanazawa, K. Pharmacokinetics of fucoxanthinol in human plasma after the oral administration of kombu extract. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 16, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, B.H.; Kim, C.G.; Lim, Y.; Shin, S.Y.; Lee, Y.H. Curcumin down-regulates the multidrug-resistance mdr1b gene by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/NF kappa B pathway. Cancer Lett. 2008, 259, 111–118. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, M.M.; Soprano, K.J.; Weinstein, K.; Fong, D. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate delivers hydrogen peroxide to induce death of ovarian cancer cells and enhances their cisplatin susceptibility. J. Cell. Physiol. 2006, 207, 389–396. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, J.T.; Kwak, D.W.; Lin, S.K.; Kim, H.M.; Kim, Y.M.; Park, O.J. Resveratrol induces apoptosis in chemoresistant cancer cells via modulation of AMPK signaling pathway. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1095, 441–448. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, M.H.; Gao, J.H.; Lai, C.S.; Wang, Y.J.; Chen, W.M.; Lo, C.Y.; Wang, M.; Dushenkov, S.; Ho, C.T. Antitumor activity of 3,5,4′-trimethoxystilbene in COLO 205 cells and xenografts in SCID mice. Mol. Carcinog. 2008, 47, 184–196. [Google Scholar]
- Molnar, J.; Gyemant, N.; Mucsi, I.; Molnar, A.; Szabo, M.; Kortvelyesi, T.; Varga, A.; Molnár, P.; Tóth, G. Modulation of multidrug resistance and apoptosis of cancer cells by selected carotenoids. In Vivo 2004, 18, 237–244. [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich, F.P. Cytochrome P-450 3A4: Regulation and role in drug metabolism. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1999, 39, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, L.B.; Goodwin, B.; Jones, S.A.; Wisely, G.B.; Serabjit-Singh, C.J.; Willson, T.M.; Collins, J.L.; Kliewer, S.A. St. John’s wort induces hepatic drug metabolism through activation of the pregnane X receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 7500–7502. [Google Scholar]
- Ambudkar, S.V.; Kimchi-Sarfaty, C.; Sauna, Z.E.; Gottesman, M.M. P-glycoprotein: From genomics to mechanism. Oncogene 2003, 22, 7468–7485. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, S.P.; Bhardwaj, G.; Gerlach, J.H.; Mackie, J.E.; Grant, C.E.; Almquist, K.C.; Stewart, A.J.; Kurz, E.U.; Duncan, A.M.; Deeley, R.G. Overexpression of a transporter gene in a multidrug-resistant human lung cancer cell line. Science 1992, 258, 1650–1654. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, R.C.; Inoue, S.; Roitelman, J.; Schimke, R.T.; Simoni, R.D. Peptide transport by the multidrug resistance pump. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 5731–5734. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuruo, T.; Naito, M.; Tomida, A.; Fujita, N.; Mashima, T.; Sakamoto, H.; Haga, N. Molecular targeting therapy of cancer: Drug resistance, apoptosis and survival signal. Cancer Sci. 2003, 94, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, A.; Mani, S.; Redinbo, M.R.; Krasowski, M.D.; Li, H.; Ekins, S. Elucidating the “Jekyl and Hyde” nature of PXR: The case for discovering antagonists or Allosteric antagonists. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 1807–1815. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, S.; Mani, S. Orphan nuclear receptors as targets for drug development. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 1439–1468. [Google Scholar]
- Kliewer, S.A.; Moore, J.T.; Wade, L.; Staudinger, J.L.; Watson, M.A.; Jones, S.A.; McKee, D.D.; Oliver, B.B.; Willson, T.M.; Zetterström, R.H.; Perlmann, T.; Lehmann, J.M. An orphan nuclear receptor activated by pregnanes defines a novel steroid signaling pathway. Cell 1998, 92, 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Kliewer, S.A.; Goodwin, B.; Willson, T.M. The nuclear pregnane X receptor: A key regulator of xenobiotic metabolism. Endocr. Rev. 2002, 23, 687–702. [Google Scholar]
- Gollamudi, R.; Gupta, D.; Goel, S.; Mani, S. Novel orphan nuclear receptors-coregulator interactions controlling anti-cancer drug metabolism. Curr. Drug Metab. 2008, 9, 611–613. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Venkatesh, M.; Li, H.; Goetz, R.; Mukherjee, S.; Biswas, A.; Zhu, L.; Kaubisch, A.; Wang, L.; Pullman, J.; Whitney, K.; Kuro, M.; Roig, A.I.; Shay, J.W.; Mohammadi, M.; Mani, S. Pregnane X receptor activation induces FGF19-dependent tumor aggressiveness in humans and mice. J. Clin. Invest. 2011, 121, 3220–3232. [Google Scholar]
- Miki, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Kitada, K.; Yabuki, N.; Shibuya, R.; Moriya, T.; Takanori, I.; Noriaki, O.; Bruce, B.; Hironobu, S. Expression of the steroid and xenobiotic receptor and its possible target gene, organic anion transporting polypeptide-A, in human breast carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 535–542. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Nie, D. Pregnane X receptor and its potential role in drug resistance in cancer treatment. Recent Pat. Anticancer Drug Discov. 2009, 4, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg, B.; Sabbagh, W., Jr.; Juguilon, H.; Bolado, J., Jr.; van Meter, C.M.; Ong, E.S.; Evans, R.M. SXR, a novel steroid and xenobiotic-sensing nuclear receptor. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 3195–3205. [Google Scholar]
- Dussault, I.; Forman, B.M. The nuclear receptor PXR: A master regulator of “homeland” defense. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2002, 12, 53–64. [Google Scholar]
- Synold, T.W.; Dussault, I.; Forman, B.M. The orphan nuclear receptor SXR coordinately regulates drug metabolism and efflux. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 584–590. [Google Scholar]
- Glass, C.K.; Rosenfeld, M.G. The coregulator exchange in transcriptional functions of nuclear receptors. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 121–141. [Google Scholar]
- Bertilsson, G.; Heidrich, J.; Svensson, K.; Asman, M.; Jendeberg, L.; Sydow-Backman, M.; Ohlsson, R.; Postlind, H.; Blomquist, P.; Berkenstam, A. Identification of a human nuclear receptor defines a new signaling pathway for CYP3A induction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 12208–12213. [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin, B.; Hodgson, E.; Liddle, C. The orphan human pregnane X receptor mediates the transcriptional activation of CYP3A4 by rifampicin through a distal enhancer module. Mol. Pharmacol. 1999, 56, 1329–1339. [Google Scholar]
- Pavek, P.; Dvorak, Z. Xenobiotic-induced transcriptional regulation of xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes of the cytochrome P450 superfamily in human extrahepatic tissues. Curr. Drug Metab. 2008, 9, 129–143. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, L.B.; Parks, D.J.; Jones, S.A.; Bledsoe, R.K.; Consler, T.G.; Stimmel, J.B.; Goodwin, B.; Liddle, C.; Blanchard, S.G.; Willson, T.M.; Collins, J.L.; Kliewer, S.A. Orphan nuclear receptors constitutive androstane receptor and pregnane X receptor share xenobiotic and steroid ligands. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 15122–15127. [Google Scholar]
- Kliewer, S.A.; Willson, T.M. Regulation of xenobiotic and bile acid metabolism by the nuclear pregnane X receptor. J. Lipid Res. 2002, 43, 359–364. [Google Scholar]
- Auerbach, S.S.; Stoner, M.A.; Su, S.; Omiecinski, C.J. Retinoid X receptor-alpha-dependent transactivation by a naturally occurring structural variant of human constitutive androstane receptor (NR1I3). Mol. Pharmacol. 2005, 68, 1239–1253. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yao, X. Induction of CYP3A4 and MDR1 gene expression by baicalin, baicalein, chlorogenic acid, and ginsenoside Rf through constitutive androstane receptor- and pregnane X receptor-mediated pathways. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 640, 46–54. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Wang, H.; Sinz, M.; Zoeckler, M.; Staudinger, J.; Redinbo, M.R.; Teotico, D.G.; Locker, J.; Kalpana, G.V.; Mani, S. Inhibition of drug metabolism by blocking the activation of nuclear receptors by ketoconazole. Oncogene 2007, 26, 258–268. [Google Scholar]
- Healan-Greenberg, C.; Waring, J.F.; Kempf, D.J.; Blomme, E.A.; Tirona, R.G.; Kim, R.B. A human immunodeficiency virus protease inhibitor is a novel functional inhibitor of human pregnane X receptor. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2007, 36, 500–507. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Li, H.; Moore, L.B.; Johnson, M.D.; Maglich, J.M.; Goodwin, B.; Parks, D.J.; Collins, J.L.; Willson, T.M.; Kalpana, G.V.; Venkatesh, M.; Xie, W.; Cho, S.Y.; Roboz, J.; Redinbo, M.; Moore, J.T.; Mani, S. The phytoestrogen coumestrol is a naturally occurring antagonist of the human pregnane X receptor. Mol. Endocrinol. 2008, 22, 838–857. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Tang, Y.; Robbins, G.T.; Nie, D. Camptothecin attenuates cytochrome P450 3A4 induction by blocking the activation of human pregnane X receptor. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 334, 999–1008. [Google Scholar]
- Krausova, L.; Stejskalova, L.; Wang, H.; Vrzal, R.; Dvorak, Z.; Mani, S.; Pavek, P. Metformin suppresses pregnane X receptor (PXR)-regulated transactivation of CYP3A4 gene. Biochem. Pharmcol. 2011, 82, 1771–1780. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.; Poulton, E.J.; Grun, F.; Bammler, T.K.; Blumberg, B.; Thummel, K.E.; Eaton, D.L. The dietary isothiocyanate sulforaphane is an antagonist of the human steroid and xenobiotic nuclear receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 71, 220–229. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.L.; Huang, Y.S.; Hosokawa, M.; Miyashita, K.; Hu, M.L. Inhibition of proliferation of a hepatoma cell line by fucoxanthin in relation to cell cycle arrest and enhanced gap junctional intercellular communication. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2009, 182, 165–172. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.Y.; Huang, C.S.; Hu, M.L. The use of fetal bovine serum as delivery vehicle to improve the uptake and stability of lycopene in cell culture studies. Br. J. Nutr. 2007, 98, 226–232. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, Y.P.; Liu, C.H.; Shyu, L.J.; Huang, J.D. Functional characterization of a novel polymorphism of pregnane X receptor, Q158K, in Chinese subjects. Pharmacogenet. Genomics 2005, 15, 337–441. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, Y.P.; Huang, J.D. Pregnane X receptor polymorphism affects CYP3A4 induction via a ligand-dependent interaction with steroid receptor coactivator-1. Pharmacogenet. Genomics 2007, 17, 369–382. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.-L.; Lim, Y.-P.; Hu, M.-L. Fucoxanthin Attenuates Rifampin-Induced Cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) and Multiple Drug Resistance 1 (MDR1) Gene Expression Through Pregnane X Receptor (PXR)-Mediated Pathways in Human Hepatoma HepG2 and Colon Adenocarcinoma LS174T Cells. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 242-257. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10010242
Liu C-L, Lim Y-P, Hu M-L. Fucoxanthin Attenuates Rifampin-Induced Cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) and Multiple Drug Resistance 1 (MDR1) Gene Expression Through Pregnane X Receptor (PXR)-Mediated Pathways in Human Hepatoma HepG2 and Colon Adenocarcinoma LS174T Cells. Marine Drugs. 2012; 10(1):242-257. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10010242
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Cheng-Ling, Yun-Ping Lim, and Miao-Lin Hu. 2012. "Fucoxanthin Attenuates Rifampin-Induced Cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) and Multiple Drug Resistance 1 (MDR1) Gene Expression Through Pregnane X Receptor (PXR)-Mediated Pathways in Human Hepatoma HepG2 and Colon Adenocarcinoma LS174T Cells" Marine Drugs 10, no. 1: 242-257. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10010242
APA StyleLiu, C.-L., Lim, Y.-P., & Hu, M.-L. (2012). Fucoxanthin Attenuates Rifampin-Induced Cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) and Multiple Drug Resistance 1 (MDR1) Gene Expression Through Pregnane X Receptor (PXR)-Mediated Pathways in Human Hepatoma HepG2 and Colon Adenocarcinoma LS174T Cells. Marine Drugs, 10(1), 242-257. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10010242




