The Effect of 17α-Ethynylestradiol on Steroidogenesis and Gonadal Cytokine Gene Expression Is Related to the Reproductive Stage in Marine Hermaphrodite Fish
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. EE2 Reduces the Stripped Volume of Seminal Fluid and Sperm Motility in Specimens in the Spermatogenesis Stage
| Sperm volume (mL) | Sperm concentration (cell/mL) | Sperm motility index | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment (EE2) | 7 days | 28 days | 7 days | 28 days | 7 days | 28 days |
| 0 μg/g food | 0.63 ± 0.19 | 1.80 ± 0.38 | (3.28 ± 0.76) × 109 | (6.46 ± 1.22) × 109 | 2.08 ± 0.48 | 2.43 ± 0.23 |
| 5 μg/g food | 0.25 ± 0.09 | 1.30 ± 0.79 * | (1.58 ± 0.97) × 109 | (2.57 ± 1.45) × 109 | 1.46 ± 0.70 | 0.95 ± 0.48 * |
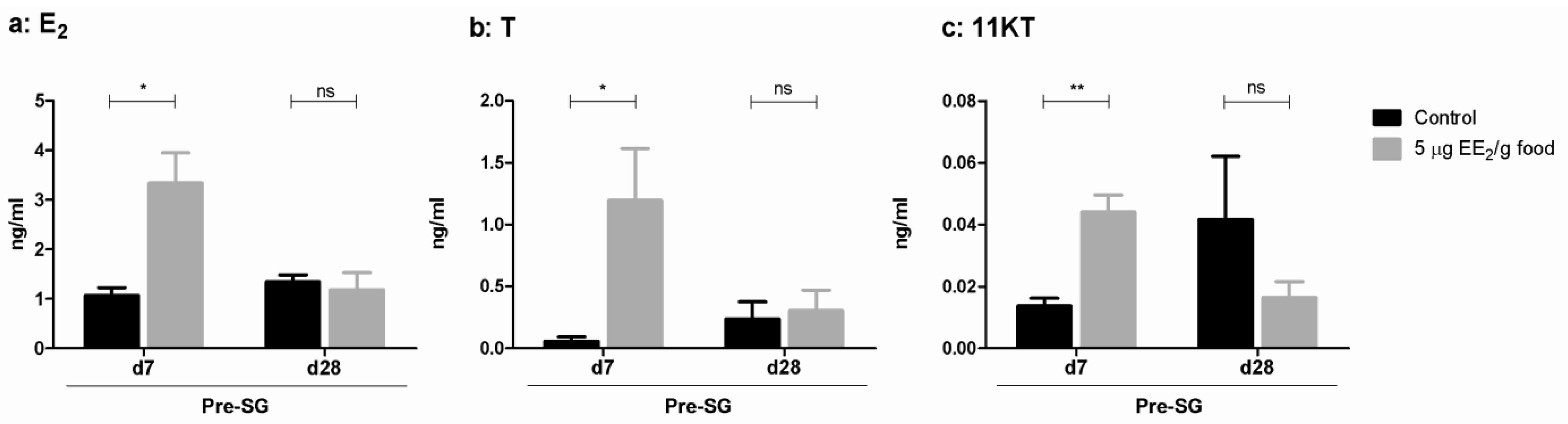
2.2. EE2 Modifies Serum Sex Steroid Levels and Modulates the Gene Expression Profile of Some Steroidogenic Enzymes

2.3. EE2 Increases the Expression Profile of the Hepatic vtg Gene

2.4. EE2 Modulates the Expression of Testicular Specific Protein, Dmrt1, and Some Hormone Receptor Genes in the Gonad
2.5. EE2 Modifies the Gene Expression of Molecules Relevant in the Immune Response in the Gonad


3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Animals and Experimental Design
4.2. Measurement of the Volume of Seminal Fluid and Sperm Concentration and Motility
4.3. Analytical Techniques
4.4. Analysis of Gene Expression
| Gene | Accession Number | Name | Nucleotide sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| star | AM905934 | F1 R1 | ACATCGGGAAGGTGTTCAAG TCTCTGCAGACACCTCATGG |
| cyp11a1 | FM159974.1 | F R | CGCTGCTGTGGACATTGTAT CATCATGTCTCCCTGGCTTT |
| hsd3b | HS985587 | F R | GGAGGACAAACTGGTGGAGG ACATTCTCCGTTCCGGTGAC |
| cyp19a1a | AF399824 | F2 R2 | CAATGGAGAGGAAACCCTCA ATGCAGCTGAGTCCCTGTCT |
| cyp11b1 | FP332145 | F R | GCTATCTTTGGACCCCATCA CTTGACTGTGCCTTTCAGCA |
| srd5a | AM958800 | F R | TGCACTTTCGTGACTCTGCT TTTCGCACAAGACGTCCAGA |
| hsd11b | AM973598 | F R | AGACATGGGCAACGAGTCAG TCCACATCTCCCTCCCACAT |
| vtg | AF210428 | F1 R1 | CTGCTGAAGAGGGACCAGAC TTGCCTGCAGGATGATGATA |
| dmrt1 | AM493678 | F R | GATGGACAATCCCTGACACC GGGTAGCGTGAAGGTTGGTA |
| era | AF136979 | F R | GCTTGCCGTCTTAGGAAGTG TGCTGCTGATGTGTTTCCTC |
| fshr | AY587262 | F2 R2 | TCCCACTACGGATCCTCATC AACGGGAACAGTCAGTTTG |
| lhr | AY587261 | F2 R2 | ATACACGACCACGCATTCAA CGCCGGTAACTTCTTGAGAG |
| il1b | AJ277166 | F2 R3 | GGGCTGAACAACAGCACTCTC TTAACACTCTCCACCCTCCA |
| tnfa | AJ413189 | FE1 RE3 | TCGTTCAGAGTCTCCTGCAG CATGGACTCTGAGTAGCGCGA |
| tgfb1 | AF424703 | F R | AGAGACGGGCAGTAAAGAA GCCTGAGGAGACTCTGTTGG |
| mmp9 | AM905938 | F1 R1 | GGGGTACCCTCTGTCGATTT CCTCCCCAGCAATATTCAGA |
| mmp13 | AM905935 | F R | CGGTGATTCCTACCCATTTG TGAGCGGAAAGTGAAGGTCT |
| tlr9 | AY751798 | F2 R2 | GGAGGAGAGGGACTGGAT GATCACACCGTCACTGTCTC |
| mhc1a | AY292461 | F R | CCAGAGCTTCCCTCAGTGTC CATCTGGAAGGTTCCATCGT |
| ccl4 | AM765840 | F1 R1 | GCTGTGTTTGTGCTGATGCT GCTGGCTGGTCTTTTGGTAG |
| il8 | AM765841 | F2 R2 | GCCACTCTGAAGAGGACAGG TTTGGTTGTCTTTGGTCGAA |
| sele | AM749963 | F1 R1 | GACAGTGAGCAGGCGTACAA ATCGCTTCATGATCCACACA |
| ighm | AM493677 | F1 R1 | CAGCCTCGAGAAGTGGAAAC GAGGTTGACCAGGTTGGTGT |
| ight | FM145138 | F1 R1 | TGGCAAATTGATGGACAAAA CCATCTCCCTTGTGGACAGT |
| rps18 | AM490061 | F R | AGGGTGTTGGCAGACGTTAC CTTCTGCCTGTTGAGGAACC |
4.5. Calculation and Statistics
5. Conclusions
Declaration
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jones, O.A.; Voulvoulis, N.; Lester, J.N. Potential ecological and human health risks associated with the presence of pharmaceutically active compounds in the aquatic environment. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2004, 34, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, K.A.; Blanchfield, P.J.; Mills, K.H.; Palace, V.P.; Evans, R.E.; Lazorchak, J.M.; Flick, R.W. Collapse of a fish population after exposure to a synthetic estrogen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 8897–8901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, J.; Winter, M.J.; Tyler, C.R. Pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment: A critical review of the evidence for health effects in fish. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2010, 40, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthiessen, P.; Allen, Y.; Bamber, S.; Craft, J.; Hurst, M.; Hutchinson, T.; Feist, S.; Katsiadaki, I.; Kirby, M.; Robinson, C.; et al. The impact of oestrogenic and androgenic contamination on marine organisms in the United Kingdom—Summary of the EDMAR programme. Endocrine Disruption in the Marine Environment. Mar. Environ. Res. 2002, 54, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribecco, C.; Baker, M.E.; Sasik, R.; Zuo, Y.; Hardiman, G.; Carnevali, O. Biological effects of marine contaminated sediments on Sparus aurata juveniles. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 104, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilton, S.C.; Foran, C.M.; Benson, W.H. Relationship between ethinylestradiol-mediated changes in endocrine function and reproductive impairment in Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2005, 24, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ternes, T.A.; Stumpf, M.; Mueller, J.; Haberer, K.; Wilken, R.D.; Servos, M. Behavior and occurrence of estrogens in municipal sewage treatment plants—I. Investigations in Germany, Canada and Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 225, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinteman, T.; Schneider, C.; Scholer, H.F.; Schneider, R.J. Field study using two immunoassays for the determination of estradiol and ethinylestradiol in the aquatic environment. Water Res. 2006, 40, 2287–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.C.; Aerni, H.R.; Gerritsen, A.; Gibert, M.; Giger, W.; Hylland, K.; Jurgens, M.; Nakari, T.; Pickering, A.; Suter, M.J.; et al. Comparing steroid estrogen, and nonylphenol content across a range of European sewage plants with different treatment and management practices. Water Res. 2005, 39, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soffker, M.; Tyler, C.R. Endocrine disrupting chemicals and sexual behaviors in fish—A critical review on effects and possible consequences. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2012, 42, 653–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.M.; Scrimshaw, M.D.; Lester, J.N. Prediction of the bioaccumulation factors and body burden of natural and synthetic estrogens in aquatic organisms in the river systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 289, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fostier, A.; Jalabert, B.; Billard, R.; Breton, B.; Zohar, Y. The gonadal steroids. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 1983, 9A, 227–372. [Google Scholar]
- Kime, D.E. Classical and non classical reproductive steroids in fish. Rev. Fish Biol. 1993, 3, 160–180. [Google Scholar]
- George, F.W.; Wilson, J.D. Sex Determination and Differentiation. In The Physiology of Reproduction; Knobil, E., Neill, J.D., Eds.; Raven Press: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 3–28. [Google Scholar]
- Borg, B. Androgens in teleost fishes. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1994, 109C, 219–245. [Google Scholar]
- Amer, M.A.; Miura, T.; Miura, C.; Yamauchi, K. Involvement of sex steroid hormones in the early stages of spermatogenesis in Japanese huchen (Hucho perryi). Biol. Reprod. 2001, 65, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, R.A. Estrogen in the adult male reproductive tract: A review. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2003, 1, 1–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, T.; Miura, C.; Ohta, T.; Nader, M.R.; Todo, T.; Yamauchi, K. Estradiol-17beta stimulates the renewal of spermatogonial stem cells in males. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 264, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves-Pozo, E.; Liarte, S.; Fernández-Alacid, L.; Abellán, E.; Meseguer, J.; Mulero, V.; García-Ayala, A. Pattern of expression of immune-relevant genes in the gonad of a teleost, the gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L.). Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 2998–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves-Pozo, E.; Mulero, V.; Meseguer, J.; García-Ayala, A. An overview of cell renewal in the testis throughout the reproductive cycle of a seasonal breeding teleost, the gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L). Biol. Reprod. 2005, 72, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liarte, S.; Chaves-Pozo, E.; García-Alcázar, A.; Mulero, V.; Meseguer, J.; García-Ayala, A. Testicular involution prior to sex change in gilthead seabream is characterized by a decrease in DMRT1 gene expression and by massive leukocyte infiltration. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2007, 5, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Departamento de Pesca y Acuicultura de la FAO. Programa de Información de Especies Acuáticas. Sparus aurata. Available online: http://www.fao.org/fishery/culturedspecies/Sparus_aurata/es (accessed on 3 December 2013).
- De Benito, F.; Maicas, F.; Jauralde, I.; Martínez, S.; Marín, M.; Jover, M. Evaluación de la rentabilidad económica de la producción de dorada (Sparus aurata) en jaulas marinas. Rev. Aquat. 2012, 37, 123–138. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilar, A.; Borrell, A.; Reijnders, P.J. Geographical and temporal variation in levels of organochlorine contaminants in marine mammals. Mar. Environ. Res. 2002, 53, 425–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossi, M.C.; Casini, S.; Marsili, L. Potential toxicological hazard due to endocrine-disrupting chemicals on Mediterranean top predators: State of art, gender differences and methodological tools. Environ. Res. 2007, 104, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, R.W.; Menting, S.; Bogerd, J.; Franca, L.R.; Vilela, D.A.; Godinho, H.P. Sertoli cell proliferation in the adult testis—Evidence from two fish species belonging to different orders. Biol. Reprod. 2005, 73, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, R.W.; de Franca, L.R.; Lareyre, J.J.; Le Gac, F.; Chiarini-Garcia, H.; Nobrega, R.H.; Miura, T. Spermatogenesis in fish. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2010, 165, 390–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves-Pozo, E.; Arjona, F.J.; García-López, A.; García-Alcázar, A.; Meseguer, J.; García-Ayala, A. Sex steroids and metabolic parameter levels in a seasonal breeding fish (Sparus aurata L.). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2008, 156, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves-Pozo, E.; Liarte, S.; García-Ayala, A. Immune and Reproductive Interaction: An Essential Clue for Understanding Gonad Functions in Gilthead Seabream. In Recent Advances in Fish Reproductive Biology; García-Ayala, A., Meseguer, J., Chaves-Pozo, E., Eds.; Research Signpost: Kerala, India, 2010; pp. 127–139. [Google Scholar]
- Sepulcre, M.P.; López-Castejón, G.; Meseguer, J.; Mulero, V. The activation of gilthead seabream professional phagocytes by different PAMPs underlines the behavioural diversity of the main innate immune cells of bony fish. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 2009–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepulcre, M.P.; Pelegrín, P.; Mulero, V.; Meseguer, J. Characterisation of gilthead seabream acidophilic granulocytes by a monoclonal antibody unequivocally points to their involvement in fish phagocytic response. Cell Tissue Res. 2002, 308, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liarte, S.; Chaves-Pozo, E.; Abellán, E.; Meseguer, J.; Mulero, V.; García-Ayala, A. 17beta-Estradiol regulates gilthead seabream professional phagocyte responses through macrophage activation. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves-Pozo, E.; Liarte, S.; Mulero, I.; Abellán, E.; Meseguer, J.; García-Ayala, A. Early presence of immune cells in the developing gonad of the gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata Linnaeus, 1758). J. Reprod. Dev. 2009, 55, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabas, I.; Chaves-Pozo, E.; García-Alcázar, A.; Meseguer, J.; Mulero, V.; García-Ayala, A. Dietary intake of 17alpha-ethinylestradiol promotes leukocytes infiltration in the gonad of the hermaphrodite gilthead seabream. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 48, 2079–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabas, I.; Liarte, S.; Garcia-Alcazar, A.; Meseguer, J.; Mulero, V.; Garcia-Ayala, A. 17alpha-Ethynylestradiol alters the immune response of the teleost gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L.) both in vivo and in vitro. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2012, 36, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, R.W.; Liemburg, M.; Garcia-Lopez, A.; Dijk, W.; Bogerd, J. Androgens modulate testicular androgen production in African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) depending on the stage of maturity and type of androgen. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2008, 156, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumpter, J.P.; Jobling, S. Vitellogenesis as a biomarker for estrogenic contamination of the aquatic environment. Environ. Health Perspect. 1995, 103, 173–178. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, J.; Bontrop, R.E.; Dawkins, R.L.; Erlich, H.A.; Gyllensten, U.B.; Heise, E.R.; Jones, P.P.; Parham, P.; Wakeland, E.K.; Watkins, D.I. Nomenclature for the major histocompatibility complexes of different species: A proposal. Immunogenetics 1990, 31, 217–219. [Google Scholar]
- Lange, A.; Katsu, Y.; Ichikawa, R.; Paull, G.C.; Chidgey, L.L.; Coe, T.S.; Iguchi, T.; Tyler, C.R. Altered sexual development in roach (Rutilus rutilus) exposed to environmental concentrations of the pharmaceutical 17alpha-ethinylestradiol and associated expression dynamics of aromatases and estrogen receptors. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 106, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Chen, H.; Song, H. Exposure to 17alpha-ethynylestradiol impairs reproductive functions of both male and female zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 2008, 88, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, N.S.; Currie, S.; LeBlanc, S.; Hewitt, L.M.; MacLatchy, D.L. Modulation of steroidogenesis and estrogen signalling in the estuarine killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus) exposed to ethinylestradiol. Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 98, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves-Pozo, E.; Liarte, S.; Vargas-Chacoff, L.; García-López, A.; Mulero, V.; Meseguer, J.; Mancera, J.M.; García-Ayala, A. 17Beta-estradiol triggers postspawning in spermatogenically active gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L.) males. Biol. Reprod. 2007, 76, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.F.; Lau, E.L.; Lin, B.Y. Stimulation of spermatogenesis or of sex reversal according to the dose of exogenous estradiol-17 beta in juvenile males of protandrous black porgy, Acanthopagrus schlegeli. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1995, 100, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arukwe, A. Steroidogenic acute regulatory (StAR) protein and cholesterol sidechain cleavage (P450scc)-regulated steroidogenesis as an organ-specific molecular and cellular target for endocrine disrupting chemicals in fish. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2008, 24, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condeca, J.B.; Canario, A.V. The effect of estrogen on the gonads and on in vitro conversion of androstenedione to testosterone, 11-ketotestosterone, and estradiol-17beta in Sparus aurata (Teleostei, Sparidae). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1999, 116, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Don, J.; Nir, U.; Breitbart, H. DMRT1 at the border between mitosis and meiosis. Asian J. Androl. 2011, 13, 189–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akingbemi, B.T. Estrogen regulation of testicular function. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2005, 3, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liarte, S.; Cabas, I.; Chaves-Pozo, E.; Arizcun, M.; Meseguer, J.; Mulero, V.; García-Ayala, A. Natural and synthetic estrogens modulate the inflammatory response in the gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L.) through the activation of endothelial cells. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 48, 1917–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnevali, O.; Tosti, L.; Speciale, C.; Peng, C.; Zhu, Y.; Maradonna, F. DEHP impairs zebrafish reproduction by affecting critical factors in oogenesis. PLoS One 2011, 5, e10201. [Google Scholar]
- O’Bryan, M.K.; Hedger, M.P. Inflammatory Networks in the Control of Spermatogenesis: Chronic Inflammation in an Immunologically Privileged Tissue? In Molecular Mechanisms in Spermatogenesis; Cheng, C.Y., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Volume 636, pp. 92–114. [Google Scholar]
- Chaves-Pozo, E.; Pelegrín, P.; Mulero, V.; Meseguer, J.; García-Ayala, A. A role for acidophilic granulocytes in the testis of the gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L., Teleostei). J. Endocrinol. 2003, 179, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves-Pozo, E.; Mulero, V.; Meseguer, J.; García-Ayala, A. Professional phagocytic granulocytes of the bony fish gilthead seabream display functional adaptation to testicular microenvironment. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2005, 78, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lui, W.Y.; Lee, W.M.; Cheng, C.Y. TGF-betas: Their role in testicular function and Sertoli cell tight junction dynamics. Int. J. Androl. 2003, 26, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, A.; van der Kraak, G. Modulation of goldfish testicular testosterone production in vitro by tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin-1beta, and macrophage conditioned media. J. Exp. Zool. 2002, 292, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves-Pozo, E.; Castillo-Briceño, P.; García-Alcázar, A.; Meseguer, J.; Mulero, V.; García-Ayala, A. A role for matrix metalloproteinases in granulocyte infiltration and testicular remodelation in a seasonal breeding teleost. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 2820–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palladino, M.A.; Johnson, T.A.; Gupta, R.; Chapman, J.L.; Ojha, P. Members of the Toll-like receptor family of innate immunity pattern-recognition receptors are abundant in the male rat reproductive tract. Biol. Reprod. 2007, 76, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves-Pozo, E.; Montero, J.; Cuesta, A.; Tafalla, C. Viral hemorrhagic septicemia and infectious pancreatic necrosis viruses replicate differently in rainbow trout gonad and induce different chemokine transcription profiles. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 648–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, F.J.; Mulero, I.; López-Muñoz, A.; Sepulcre, M.P.; Renshaw, S.A.; Meseguer, J.; Mulero, V. Evolution of the inflammatory response in vertebrates: Fish TNF-alpha is a powerful activator of endothelial cells but hardly activates phagocytes. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 5071–5081. [Google Scholar]
- Shved, N.; Berishvili, G.; D’Cotta, H.; Baroiller, J.F.; Segner, H.; Eppler, E.; Reinecke, M. Ethinylestradiol differentially interferes with IGF-I in liver and extrahepatic sites during development of male and female bony fish. J. Endocrinol. 2007, 195, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chereguini, O.; Cal, R.M.; Dreanno, C.; Ogier de Baulny, B.; Suquet, M.; Maisse, G. Short-term storage and cryopreservation of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) sperm. Aquat. Living Resour. 1997, 10, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Rodríguez, M. Contribution à l’Étude de l’Insemination Artificielle de la Truite (Salmo Gairdneri): Les Possibilités de Manipulation des GamÈtes et de Conservation du Sperme; Universidad París VI: Paris, France, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, L.; Begtashi, I.; Zanuy, S.; Carrillo, M. Development and validation of an enzyme inmunoassay for testosterone: Effects of photoperiod on plasma testosterone levels and gonadal development in male sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax, L.) at puberty. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2000, 23, 141–150. [Google Scholar]
- ZFIN Zebrafish Nomenclature Guidelines. Available online: https://wiki.zfin.org/display/general/ZFIN+Zebrafish+Nomenclature+Guidelines (accessed on 4 December 2013).
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Cabas, I.; Chaves-Pozo, E.; García-Alcázar, A.; Meseguer, J.; Mulero, V.; García-Ayala, A. The Effect of 17α-Ethynylestradiol on Steroidogenesis and Gonadal Cytokine Gene Expression Is Related to the Reproductive Stage in Marine Hermaphrodite Fish. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 4973-4992. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11124973
Cabas I, Chaves-Pozo E, García-Alcázar A, Meseguer J, Mulero V, García-Ayala A. The Effect of 17α-Ethynylestradiol on Steroidogenesis and Gonadal Cytokine Gene Expression Is Related to the Reproductive Stage in Marine Hermaphrodite Fish. Marine Drugs. 2013; 11(12):4973-4992. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11124973
Chicago/Turabian StyleCabas, Isabel, Elena Chaves-Pozo, Alicia García-Alcázar, José Meseguer, Victoriano Mulero, and Alfonsa García-Ayala. 2013. "The Effect of 17α-Ethynylestradiol on Steroidogenesis and Gonadal Cytokine Gene Expression Is Related to the Reproductive Stage in Marine Hermaphrodite Fish" Marine Drugs 11, no. 12: 4973-4992. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11124973
APA StyleCabas, I., Chaves-Pozo, E., García-Alcázar, A., Meseguer, J., Mulero, V., & García-Ayala, A. (2013). The Effect of 17α-Ethynylestradiol on Steroidogenesis and Gonadal Cytokine Gene Expression Is Related to the Reproductive Stage in Marine Hermaphrodite Fish. Marine Drugs, 11(12), 4973-4992. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11124973