Isolation, Characterization and Biological Evaluation of Jellyfish Collagen for Use in Biomedical Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Jellyfish Collagen Purification
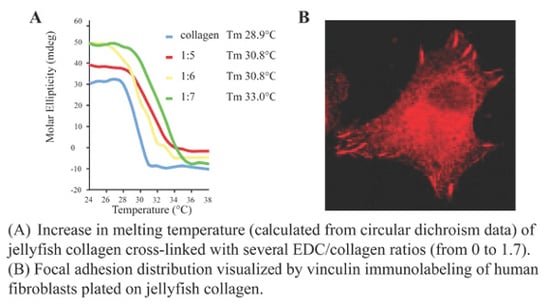
2.2. R. pulmo Collagen Stability
2.3. Biochemical Characterization of R. pulmo Fibrillar Collagen
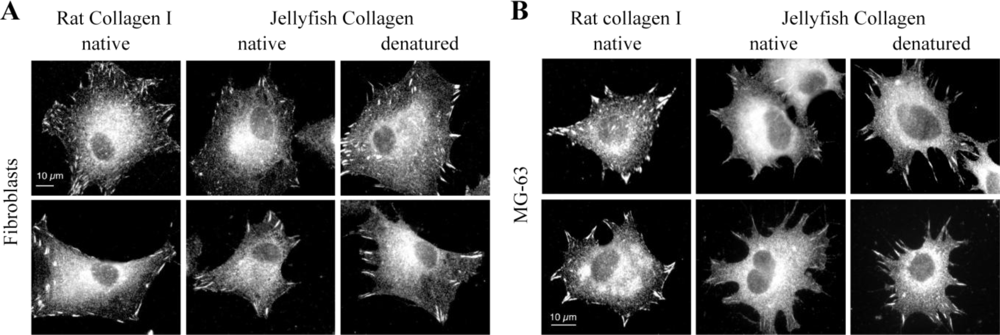
2.4. Biological Properties of R. pulmo Fibrillar Collagen
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Jellyfish Collagen Purification
3.2. Ion-Exchange Chromatography
3.3. Solid-Phase Binding Assay for Heparin Binding
3.4. Heparin-Affinity Chromatography
3.5. Cross-Linking of Jellyfish Collagen
3.6. Circular Dichroism
3.7. Cell Culture
3.8. Cell Cytotoxicity
3.9. Cell Adhesion Assay
3.10. Immunofluorescence
3.11. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
- Samples Availability: Available from the authors.
References
- Exposito, JY; Cluzel, C; Garrone, R; Lethias, C. Evolution of collagens. Anat Rec 2002, 268, 302–316. [Google Scholar]
- Ricard-Blum, S; Ruggiero, F; van der Rest, M. The collagen superfamily. Top Curr Chem 2005, 247, 35–84. [Google Scholar]
- Aouacheria, A; Geourjon, C; Aghajari, N; Navratil, V; Deléage, G; Lethias, C; Exposito, JY. Insights into early extracellular matrix evolution: Spongin short chain collagen-related proteins are homologous to basement membrane type IV collagens and form a novel family widely distributed in invertebrates. Mol Biol Evol 2006, 23, 2288–2302. [Google Scholar]
- Exposito, JY; van der Rest, M; Garrone, R. The complete intron/exon structure of Ephydatia mülleri fibrillar collagen gene suggests a mechanism for the evolution of an ancestral gene module. J Mol Evol 1993, 37, 254–259. [Google Scholar]
- Ramshaw, JAM; Peng, YY; Glattauer, V; Werkmeister, JA. Collagens as biomaterials. J Mater Sci Mater Med 2009, 20(Suppl. 1), S3–S8. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, I; Salerno, AJ; Patterson, T; Williams, JI. Cloning and expression of a collagen-analog-encoding synthetic gene in Escherichia coli. Gene 1989, 80, 305–314. [Google Scholar]
- John, DC; Watson, R; Kind, AJ; Scott, AR; Kadler, KE; Bulleid, NJ. Expression of an engineered form of recombinant procollagen in mouse milk. Nat Biotechnol 1999, 17, 385–389. [Google Scholar]
- Ruggiero, F; Exposito, JY; Bournat, P; Gruber, V; Perret, S; Comte, J; Olagnier, B; Garrone, R; Theisen, M. Triple helix assembly and processing of human collagen produced in transgenic tobacco plants. FEBS Lett 2000, 469, 132–136. [Google Scholar]
- Vuorela, A; Myllyharju, J; Nissi, R; Pihlajaniemi, T; Kivirikko, KI. Assembly of human prolyl 4-hydroxylase and type III collagen in the yeast pichia pastoris: Formation of a stable enzyme tetramer requires coexpression with collagen and assembly of a stable collagen requires coexpression with prolyl 4-hydroxylase. EMBO J 1997, 16, 6702–6712. [Google Scholar]
- Kittiphattanabawon, P; Benjakul, S; Visessanguan, W; Nagai, T; Tanaka, M. Caracterisation of acid-soluble collagen from skin and bone of bigeye snapper (Priacanthus tayenus). Food Chem 2005, 89, 363–372. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, S; Miyauchi, Y; Uchida, N. Scale and bone type I collagens of carp (Cyprinus carpio). Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 1991, 99, 473–476. [Google Scholar]
- Exposito, JY; Valcourt, U; Cluzel, C; Lethias, C. The fibrillar collagen family. Int J Mol Sci 2010, 11, 407–426. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, AJ; Bakun, A; Hays, GC; Gibbons, MJ. The jellyfish joyride: Causes, consequences and management responses to a more gelatinous future. Trends Ecol Evol 2009, 24, 312–322. [Google Scholar]
- Mariottini, GL; Pane, L. Mediterranean jellyfish venoms: A review on scyphomedusae. Mar Drugs 2010, 8, 1122–1152. [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi, T; Nagai, Y. The anomalous behavior of collagen peptides on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis is due to the low content of hydrophobic acid residues. J Biochem 1980, 87, 803–808. [Google Scholar]
- Deyl, Z; Miksik, I. Advanced separation methods for collagen parent α-chains, their polymers and fragments. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 2000, 739, 3–31. [Google Scholar]
- Calejo, MT; Morais, ZB; Fernandes, AI. Isolation and biochemical characterisation of a novel collagen from Catostylus tagi. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 2009, 20, 2073–2087. [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno, K; Hayashi, T; Bächinger, HP. Hydroxylation-induced stabilization of the collagen triple helix. Further characterization of peptides with 4(R)-hydroxyproline in the Xaa position. J Biol Chem 2003, 278, 32373–32379. [Google Scholar]
- Miura, S; Kimura, S. Jellyfish mesogloea collagen. Characterization of molecules as α1α2α3 heterotrimers. J Biol Chem 1985, 260, 15352–15356. [Google Scholar]
- Nagai, T; Ogawa, T; Nakamura, T; Ito, T; Nakagawa, H; Fujiki, K; Nakao, M; Yano, T. Collagen of edible jellyfish exumbrella. J Sci Food Agric 1999, 79, 855–858. [Google Scholar]
- Privalov, PL. Stability of proteins. Proteins which do not present a single cooperative system. Adv Protein Chem 1982, 35, 1–104. [Google Scholar]
- Exposito, JY; Larroux, C; Cluzel, C; Valcourt, U; Lethias, C; Degnan, BM. Demosponge and sea anemone fibrillar collagen diversity reveals the early emergence of A/C clades and the maintenance of the modular structure of type V/XI collagens from sponge to human. J Biol Chem 2008, 283, 28226–28235. [Google Scholar]
- Everaerts, F; Torrianni, M; Hendriks, M; Feijen, J. Biomechanical properties of carbodiimide crosslinked collagen: Influence of the formation of ester crosslinks. J Biomed Mater Res A 2008, 85, 547–555. [Google Scholar]
- Song, E; Kim, SY; Chun, T; Byun, H-J; Lee, YM. Collagen scaffolds derived from a marine source and their biocompatibility. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 2951–2961. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W; Itoh, S; Aizawa, T; Okawa, A; Sakai, K; Ohkuma, T; Demura, M. Development of an injectable chitosan/marine collagen composite gel. Biomed Mater 2010, 5, 065009. [Google Scholar]
- Sweeney, SM; Guy, CA; Fields, GB; San Antonio, JD. Defining the domains of type I collagen involved in heparin-binding and endothelial tube formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998, 95, 7275–7280. [Google Scholar]
- Leitinger, B; Hohenester, E. Mammalian collagen receptors. Matrix Biol 2007, 26, 146–155. [Google Scholar]
- Nordwig, A; Nowack, H; Hieber-Rogall, E. Sea anemone collagen: Further evidence for the existence of only one α-chain type. J Mol Evol 1973, 2, 175–180. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, KM; Keller, JM; Kühn, K. The C-terminus of type I collagen is a major binding site for heparin. Biochim Biophys Acta 1986, 882, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Gullberg, D; Gehlsen, KR; Turner, DC; Ahlén, K; Zijenah, LS; Barnes, MJ; Rubin, K. Analysis of α1β1, α2β1 and α3β1 integrins in cell—collagen interactions: Identification of conformation dependent α1β1 binding sites in collagen type I. EMBO J 1992, 11, 3865–3873. [Google Scholar]
- Cardarelli, PM; Yamagata, S; Taguchi, I; Gorcsan, F; Chiang, SL; Lobl, T. The collagen receptor α2β1, from MG-63 and HT1080 cells, interacts with a cyclic RGD peptide. J Biol Chem 1992, 267, 23159–23164. [Google Scholar]
- Heino, J. The collagen family members as cell adhesion proteins. BioEssays 2007, 29, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, GE. Affinity of integrins for damaged extracellular matrix: αVβ3 binds to denatured collagen type I through RGD sites. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1992, 182, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar]
- Lethias, C; Elefteriou, F; Parsiegla, G; Exposito, JY; Garrone, R. Identification and characterization of a conformational heparin-binding site involving two fibronectin type III modules of bovine tenascin-X. J Biol Chem 2001, 276, 16432–16438. [Google Scholar]
- Faye, C; Moreau, C; Chautard, E; Jetne, R; Fukai, N; Ruggiero, F; Humphries, MJ; Olsen, BR; Ricard-Blum, S. Molecular interplay between endostatin, integrins, and heparan sulfate. J Biol Chem 2009, 284, 22029–22040. [Google Scholar]
- Berrier, AL; Yamada, KM. Cell-matrix adhesion. J Cell Physiol 2007, 213, 565–573. [Google Scholar]
- Owen, GR; Meredith, DO; ap Gwynn, I; Richards, RG. Focal adhesion quantification—a new assay of material biocompatibility? Review. Eur Cell Mater 2005, 9, 85–96. [Google Scholar]
- Echtermeyer, F; Baciu, PC; Saoncella, S; Ge, Y; Goetinck, PF. Syndecan-4 core protein is sufficient for the assembly of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers. J Cell Sci 1999, 112, 3433–3441. [Google Scholar]
- Geiger, B; Spatz, JP; Bershadsky, AD. Environmental sensing through focal adhesions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2009, 10, 21–33. [Google Scholar]
- Margaron, Y; Bostan, L; Exposito, JY; Malbouyres, M; Trunfio-Sfarghiu, A-M; Berthier, Y; Lethias, C. Tenascin-X increases the stiffness of collagen gels without affecting fibrillogenesis. Biophys Chem 2010, 147, 87–91. [Google Scholar]
- Deyl, Z; Miksík, I. Comparison of different electrokinetic separation modes applicable to a model peptide mixture (collagen type I and III CNBr fragments). J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 2000, 745, 251–260. [Google Scholar]
- Olde Damink, LH; Dijkstra, PJ; van Luyn, MJ; van Wachem, PB; Nieuwenhuis, P; Feijen, J. Cross-linking of dermal sheep collagen using a water-soluble carbodiimide. Biomaterials 1996, 17, 765–773. [Google Scholar]
- Elefteriou, F; Exposito, JY; Garrone, R; Lethias, C. Cell adhesion to tenascin-X mapping of cell adhesion sites and identification of integrin receptors. Eur J Biochem 1999, 263, 840–848. [Google Scholar]








| Species, organ | Collagen (mg/g) |
|---|---|
| Rhizostoma pulmo, umbrella | 0.83 to 3.15 (3 animals) |
| Rhizostoma pulmo, oral arms | 2.61 to 10.3 (5 animals) |
| Cotylorhiza tuberculata, umbrella | 0.453 (1 animal) |
| Cotylorhiza tuberculata, oral arms | 1.94 (1 animal) |
| Pelagia noctiluca, whole body | 0.074 (1 animal) |
| Aurelia aurita, whole body | 0.0079 (1 animal) |
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Addad, S.; Exposito, J.-Y.; Faye, C.; Ricard-Blum, S.; Lethias, C. Isolation, Characterization and Biological Evaluation of Jellyfish Collagen for Use in Biomedical Applications. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 967-983. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9060967
Addad S, Exposito J-Y, Faye C, Ricard-Blum S, Lethias C. Isolation, Characterization and Biological Evaluation of Jellyfish Collagen for Use in Biomedical Applications. Marine Drugs. 2011; 9(6):967-983. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9060967
Chicago/Turabian StyleAddad, Sourour, Jean-Yves Exposito, Clément Faye, Sylvie Ricard-Blum, and Claire Lethias. 2011. "Isolation, Characterization and Biological Evaluation of Jellyfish Collagen for Use in Biomedical Applications" Marine Drugs 9, no. 6: 967-983. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9060967
APA StyleAddad, S., Exposito, J.-Y., Faye, C., Ricard-Blum, S., & Lethias, C. (2011). Isolation, Characterization and Biological Evaluation of Jellyfish Collagen for Use in Biomedical Applications. Marine Drugs, 9(6), 967-983. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9060967