Observational Studies and a Statistical Early Warning of Surface Ozone Pollution in Tangshan, the Largest Heavy Industry City of North China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
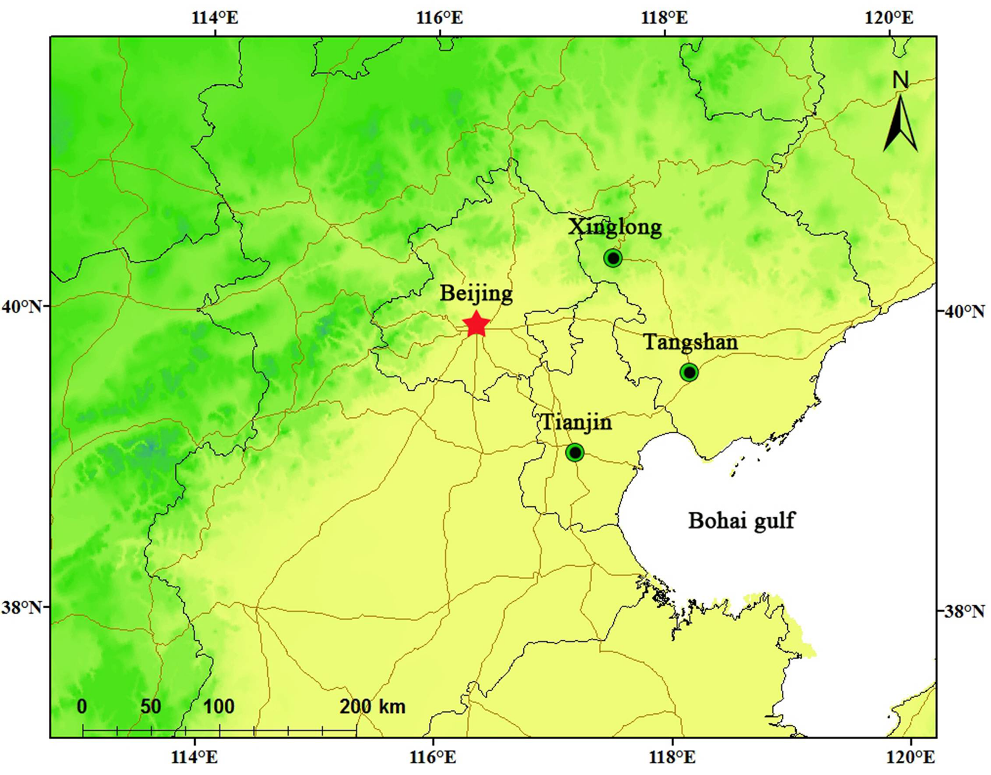
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Variation of O3 in Tangshan during the Summertime
| Period | O3 | NO | NO2 | NOX | OX | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O3_mean | O3_1-h max | O3_8-h max | |||||
| 2008: 06/01–09/30 | 75 ± 25 | 157 ± 55 | 129 ± 46 | 5 ± 4 | 41 ± 10 | 46 ± 13 | 116 ± 27 |
| 2009: 07/13–09/30 | 69 ± 29 | 161 ± 54 | 126 ± 52 | 7 ± 5 | 43 ± 10 | 50 ± 13 | 113 ± 28 |
| 2010: 06/01–09/30 | 53 ± 22 | 120 ± 50 | 97 ± 42 | 6 ± 5 | 47 ± 13 | 54 ± 14 | 100 ± 32 |
| 2011: 06/01–08/10 | 79 ± 35 | 178 ± 75 | 143 ± 64 | 4 ± 4 | 39 ± 10 | 44 ± 12 | 118 ± 36 |
| Mean | 69 ± 28 | 154 ± 61 | 124 ± 51 | 5 ± 5 | 43 ± 11 | 49 ± 13 | 112 ± 31 |

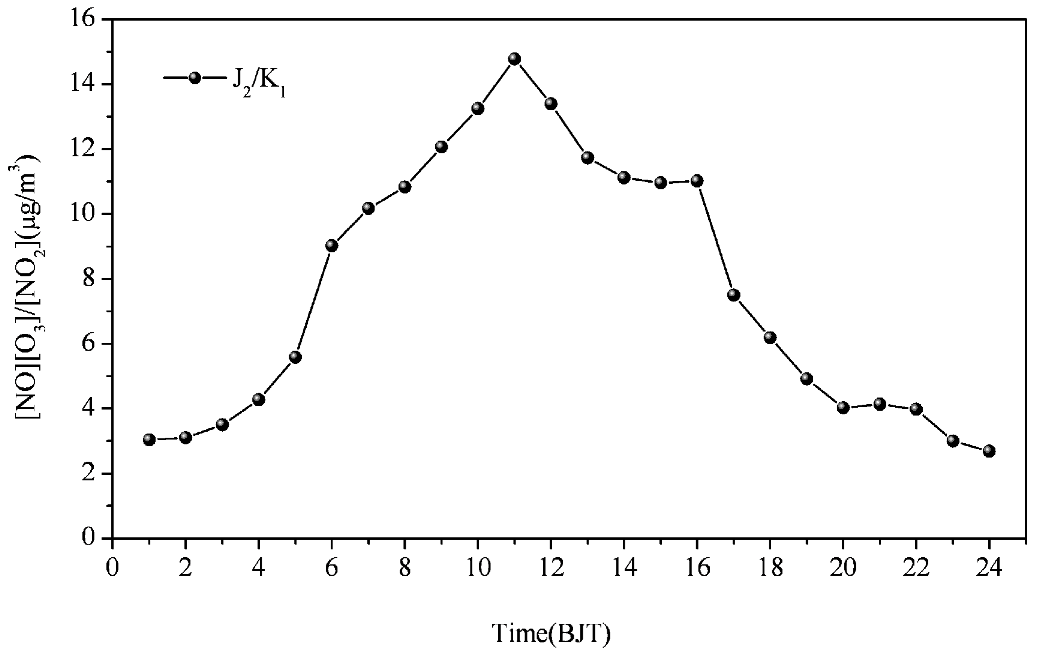
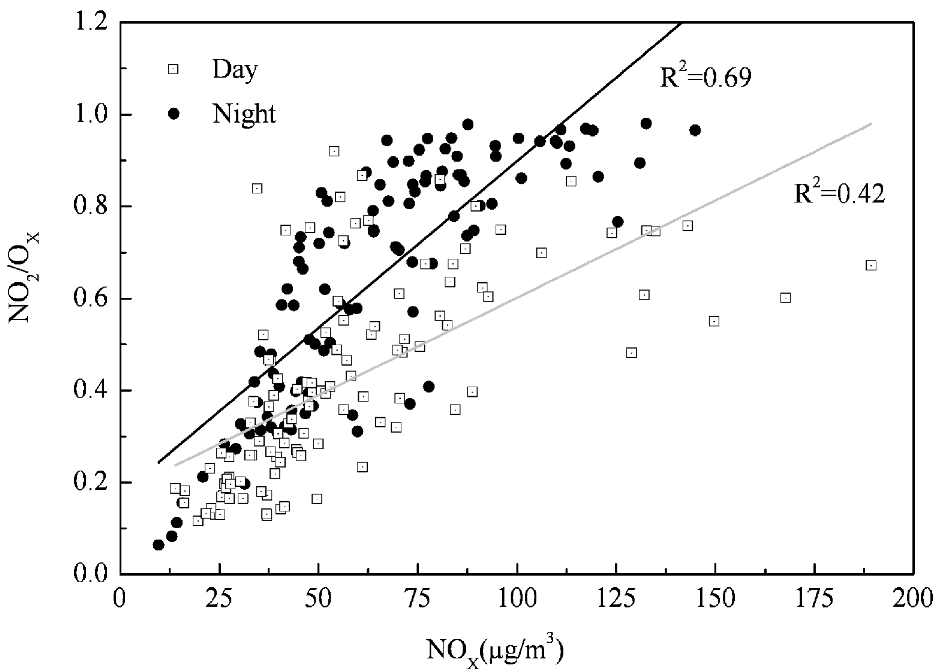
3.2. Chemical Coupling of O3, NO and NO2



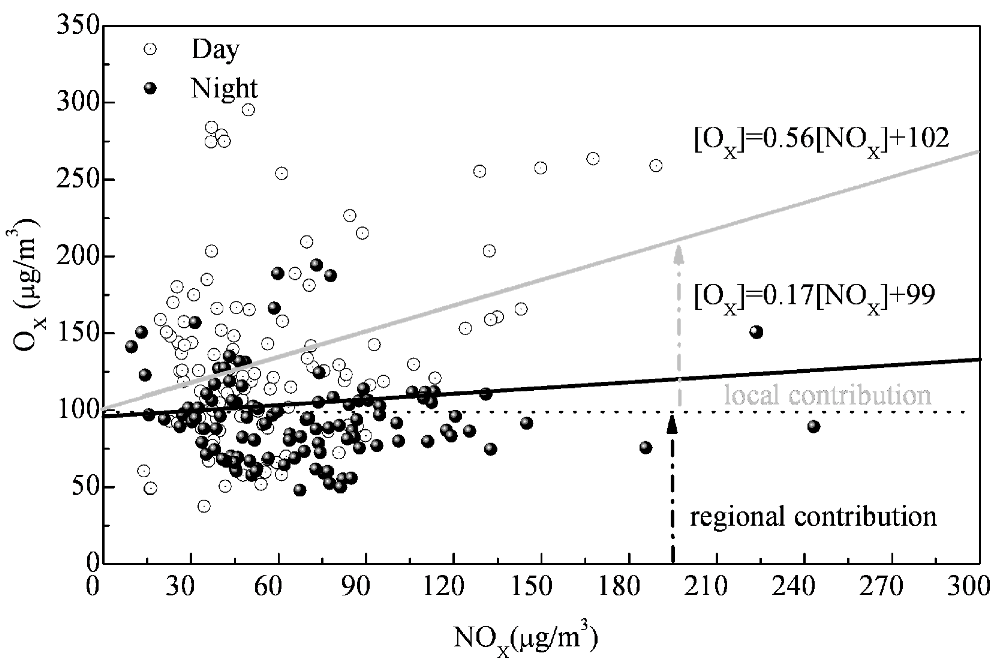
3.3. Local and Regional Contributions to Oxidant
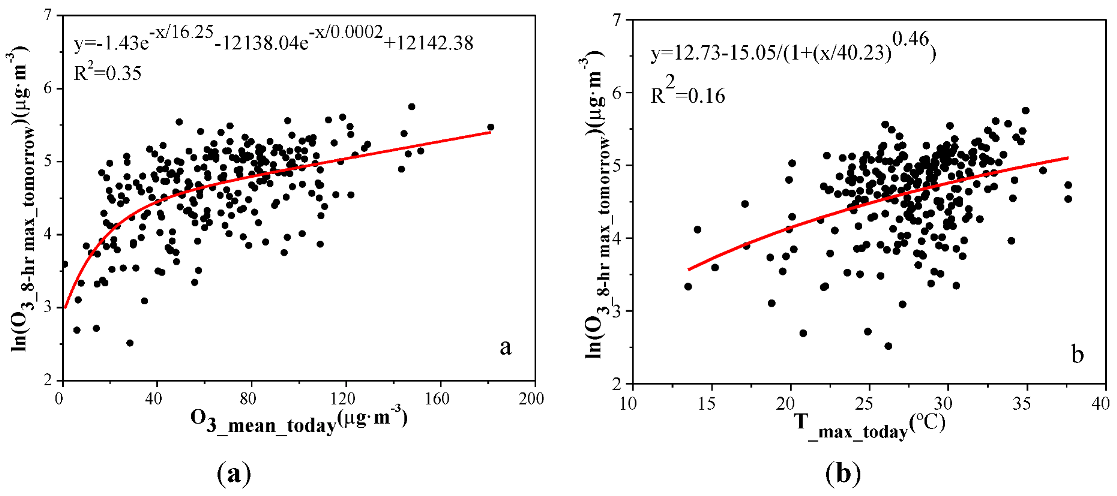
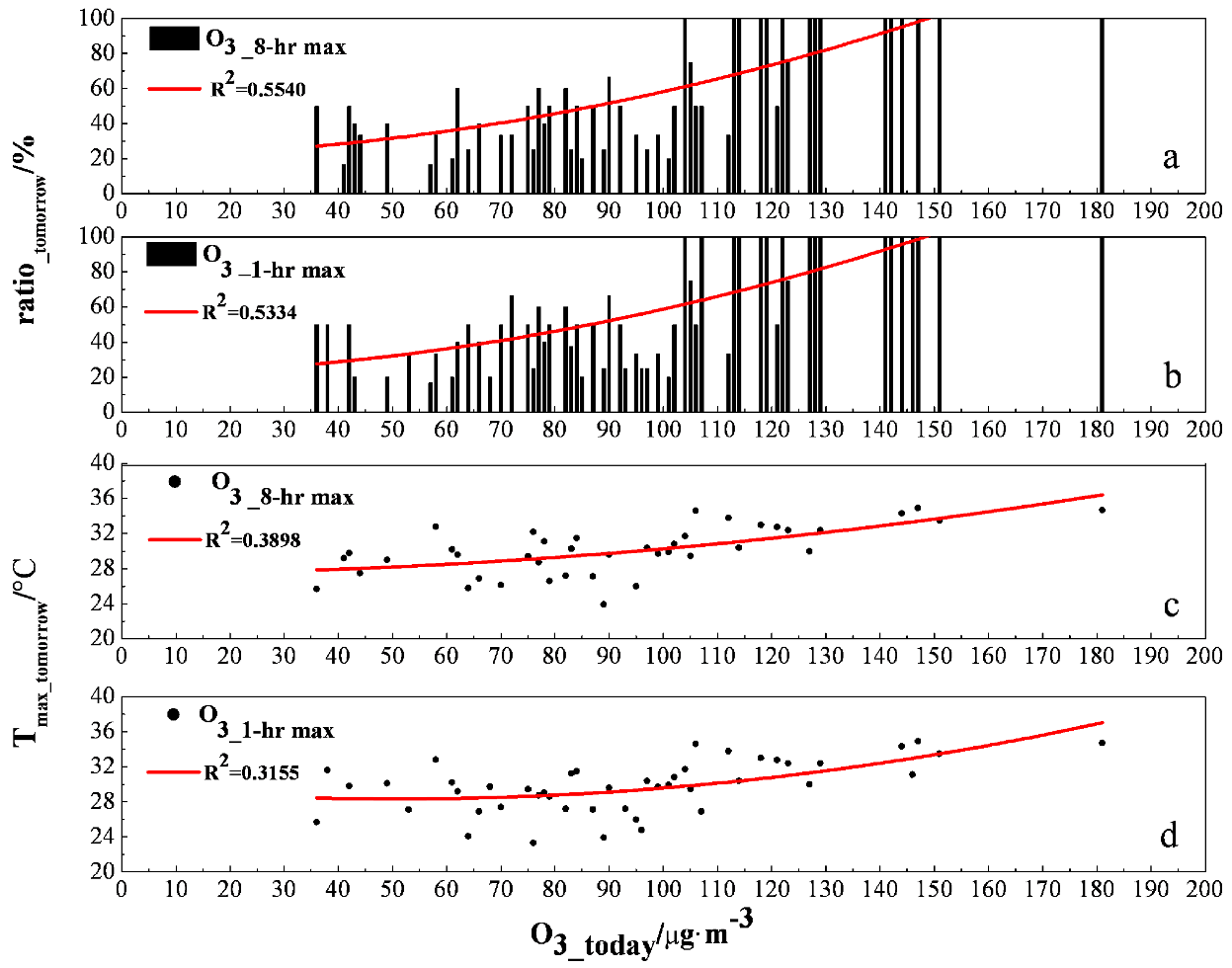
3.4. Ozone Assessment and Early Warning
| 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | Mean | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Rates | No. | Rates | No. | Rates | No. | Rates | No. | Rates | |
| 1-h average | 25 | 21% | 21 | 27% | 10 | 10% | 27 | 40% | 83 | 23% |
| 8-h average | 29 | 24% | 23 | 29% | 10 | 10% | 29 | 43% | 91 | 25% |
| Mean | 54 | 22% | 44 | 28% | 20 | 10% | 56 | 41% | 174 | 24% |
| Factor | O3_1-h max | O3_8-h max | Factor | O3_1-h max | O3_8-h max | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | T_mean | 0.38 ** | 0.39 ** | 9 | △T24 | −0.01 | −0.01 |
| 2 | T_max | 0.45 ** | 0.46 ** | 10 | OX_mean | 0.45 ** | 0.45 ** |
| 3 | Td_mean | 0.28 ** | 0.24 ** | 11 | O3_mean | 0.54 ** | 0.57 ** |
| 4 | Ttd_mean | 0.11 | 0.13 | 12 | NO_mean | −0.24 ** | −0.24 ** |
| 5 | RH_mean | −0.12 * | −0.14 * | 13 | NO2_mean | −0.19 * | −0.22 * |
| 6 | WS_mean | −0.17 * | −0.14 * | 14 | NOx_mean | −0.27 * | −0.27 * |
| 7 | Vis_mean | 0.03 | 0.09 | 15 | [NO/NO2]_mean | −0.15 * | −0.19 * |
| 8 | △P24 | 0.08 | 0.09 |
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Ramzi, M.K.; James, K. Ozone enhances Diesel Exhaust Particles (DEP)-induced interleukin-8 (IL-8) gene expression in human airway epithelial cells through activation of nuclear factors-kappaB (NF-kappaB) and IL-6 (NF-IL6). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2005, 2, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Air Quality Guidelines for Particulate Matter, Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide and Sulfur Dioxide-Global Update, 2005. Available online: http://whqlibdoc.who.int/hq/2006/WHO_SDE_PHE_OEH_06.02_eng.pdf (accessed on 18 December 2012).
- Lee, D.S.; Holland, M.K.; Falla, N. The potential impact of ozone on materials in the UK. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 30, 1053–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duanjun, L.; Remata, S.R.; Rosa, F.; William, R.S.; Quinton, L.W.; Paul, B.T. Sensitivity odeling study for an ozone occurrence during the 1996 Paso Del Norte ozone campaign. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2008, 5, 181–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roselle, S.J.; Pierce, T.E.; Schere, K.L. The sensitivity of regional ozone modeling to biogenic hydrocarbons. J. Geophys. Res. 1991, 96, 7371–7394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Shao, M. Chemistry of the Atmospheric Environment(in Chinese), 2nd ed; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Logan, J.A.; Prather, M.J.; Wofsy, S.C. Troposphere chemistry: A global perspective. J. Geophys. Res. 1981, 86, 7210–7254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, F.H.; Tie, X.X.; Xu, J.M.; Zhou, G.Q.; Peng, L.; Gao, W.; Tang, X.; Zhao, C.S. Characterizations of ozone, NOX, and VOCs measured in Shanghai, China. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 6873–6883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynette, J.C.; Michael, E.J. Analysis of the relationship between ambient levels of O3, NO2 and NO as a function of NOX in the UK. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 6391–6405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzeo, N.A.; Venegasa, L.E.; Choren, H. Analysis of NO, NO2, O3 and NOX concentrations measured at a green area of Buenos Aires City during wintertime. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 3055–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.G.; Zhang, L.; Chen, C.H.; Yuan, J.Y. Retrospect and prospect for the studies of atmospheric environment in the Lanzhou area (in Chinese). J. Lanzhou Univ. 1999, 35, 189–204. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, W.Z.; Wang, X.K.; Wang, W.J.; Leung, A.Y.T.; Yuen, K.K. A preliminary study of ozone trend and its impact on environment in Hong Kong. Environ. Int. 2002, 28, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.S.; Li, J.L.; Zhang, Y.H.; Xie, S.D.; Tang, X.Y. Ozone source attribution during a severe photochemical smog episode in Beijing, China. Sci. Chin. B Chem. 2009, 39, 548–559. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.C.; Calori, G.; Hills, P.; Carmichael, G.R. Ozone episodes in urban Hong Kong 1994–1999. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 1957–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.D.; Ding, G.A.; Yu, H.Q.; Liu, Y.; Xu, X.D. Vertical distribution of ozone in the planetary boundary layer at the Ming Tombs, Beijing. Sci. Chin. Ser. D Sci. 2005, 35, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ji, D.; Ren, S.; Gao, X. Surface ozone trend details and interpretations in Beijing, 2001-2006. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 8813–8823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Xin, J.Y.; Wang, Y.S.; Feng, X.X.; Zhang, Y.P. Observation and analysis of air pollution in Tangshan during summer and autumn time. Environ. Sci. 2010, 31, 878–885. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, J.Y.; Wang, Y.S.; Tang, G.Q.; Wang, L.L.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.H.; Hu, B.; Song, T.; Ji, D.S.; Wang, W.F.; et al. Variability and reduction of atmospheric pollutants in Beijing and its surrounding area during the Beijing 2008 Olympic Games. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2010, 55, 1937–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ji, D.; Gao, X. Spatial-temporal variations in surface ozone in Northern China as observed during 2009–2010 and possible implications for future air quality control strategies. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 2757–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangshan Environmental Protection Agency. Tangshan Environment Bulletin. Available online: www.tshbj.net/portal/manage/manage.action?column=e253b3528d2c467b8c9e362a9b5c6280&article=3358424b72dd4b12afa1f16613e9c5f7 (accessed on 18 December 2012).
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. Atmospheric chemistry and physics. In Air Pollution to Climate Changes; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Leighton, P.A. Photochemistry of Air Pollution; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, K.D.; Zhang, Y.H.; Su, H.; Shao, M.; Zeng, L.M.; Zhong, L.J.; Xiang, Y.R.; Chang, C.C.; Chou, C.K.C.; Andreas, W. Regional ozone pollution and key controlling factors of photochemical ozone production in Pearl River Delta during summer time. Sci. Chin. 2010, 53, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapp, L.J.; Jenkin, M.E. Analysis of the relationship between ambient levels of O3, NO2 and NO as a function of NOx in UK. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 6391–6405. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, W.Z.; He, H.D.; Dong, L.Y. Performance assessment of air quality monitoring networks using principal component analysis and cluster analysis. Build. Environ. 2011, 46, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamantaras, K.I.; Kung, S.Y. Principal Component Neural Networks: Theory and Applications; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Cangelosi, R.; Goriely, A. Component retention in principal component analysis with application to cDNA microarray data. Biol. Direct 2007, 2, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Schuurmans, D. Efficient Global Optimization for Exponential Family PCA and Low-Rank Matrix Factorization. In Proceedings of Allerton Conference on Communication Control, and Computing, Urbana, IL, USA, 23–26 September 2008.
- Olawale, F.; Garwe, D. Obstacles to the growth of new SMEs in South Africa: A principal component analysis approach. Afr. J. Bus. Manag. 2010, 4, 729–738. [Google Scholar]
- Corani, G. Air quality prediction in Milan: Feed-forward neural networks, pruned neural networks and lazy learning. Ecol. Model. 2005, 185, 513–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Sanchis, J.; Martin-Guerrero, J.D.; Soria-Olivas, E.; Vila-Frances, J.; Carrasco, J.L.; Valle-Tascon, S.D. Neural networks for analysing the relevance of input variables in the prediction of tropospheric ozone concentration. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 6173–6180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.S.; Kim, D.S. A new method of ozone forecasting using fuzzy expert and neural network systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 325, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, M.W.; Dorling, S.R. Neural network modelling and prediction of hourly NOX and NO2 concentrations in urban air in London. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 709–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Lee, Y.; Wahba, G. Support Vector Machines for Classification in Nonstandard Situations; Technical Report 1016 for Department of Statistics, University of Wisconsin: Madison, WI, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Rish, I.; Grabarnilk, G.; Cecchi, G.; Pereira, F.; Gordon, G. Closed-Form Supervised Dimensionality Reduction with Generalized Linear Models. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Helsinki, Finland, 5–9 July 2008.
- Lu, W.Z.; Wang, D. Ground-level ozone prediction by support vector machine approach with a cost-sensitive classification scheme. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 395, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.D.; Shi, X.H.; Xie, L.A.; Ding, G.A.; Miao, Q.J.; Ma, J.Z.; Zheng, X.D. Spatial character of the gaseous and particulate state compound correction of urban atmospheric pollution in winter and summer. Sci. Chin. Ser. DSci. 2005, 35, 53–65. [Google Scholar]
- Jacob, D.J. Introduction to Atmospheric Chemistry; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.C.; Kong, Q.X.; Chen, H.B.; Xuan, Y.J.; Wan, X.W. Characteristics of ozone vertical distribution in the atmospheric over Beijing. Adv. Earth Sci. 2004, 19, 743–748. [Google Scholar]
- An, J.L.; Wang, Y.S.; Li, X.; Sun, Y.; Shen, S.H.; Shi, L.Q. Analysis of the relationship between NO, NO2 and O3 concentrations in Beijing. Environ. Sci. 2010, 28, 706–711. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, P.; Xin, J.; Bai, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, S.; Feng, X. Observational Studies and a Statistical Early Warning of Surface Ozone Pollution in Tangshan, the Largest Heavy Industry City of North China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 1048-1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10031048
Li P, Xin J, Bai X, Wang Y, Wang S, Liu S, Feng X. Observational Studies and a Statistical Early Warning of Surface Ozone Pollution in Tangshan, the Largest Heavy Industry City of North China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2013; 10(3):1048-1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10031048
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Pei, Jinyuan Xin, Xiaoping Bai, Yuesi Wang, Shigong Wang, Shixi Liu, and Xiaoxin Feng. 2013. "Observational Studies and a Statistical Early Warning of Surface Ozone Pollution in Tangshan, the Largest Heavy Industry City of North China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 10, no. 3: 1048-1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10031048
APA StyleLi, P., Xin, J., Bai, X., Wang, Y., Wang, S., Liu, S., & Feng, X. (2013). Observational Studies and a Statistical Early Warning of Surface Ozone Pollution in Tangshan, the Largest Heavy Industry City of North China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 10(3), 1048-1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10031048





