Pollutant Removal from Synthetic Aqueous Solutions with a Combined Electrochemical Oxidation and Adsorption Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthetic Aqueous Solution Production
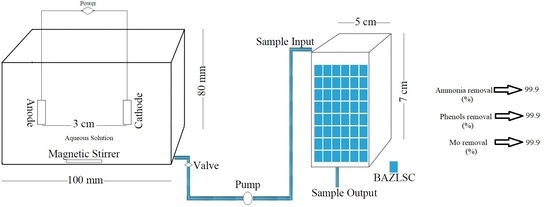
2.2. EO Reactor Characteristics
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Fixed-Bed Adsorption Column
2.4.1. Fixed-Bed Adsorption Column Preparation
2.4.2. Composite Adsorbent (BAZLSC) Preparation
2.4.3. Adsorption Isotherm
2.5. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Ammonia, Phenol, and Mo Removal Using EO
- (a)
- Electrochemical conversion, where the organic complexes are partly oxidized, according to the reaction (Equation (6)):R → RO + e−
- (b)
- Electrochemical combustion, where the organic complexes break down into CO2, water, and other inorganic complexes (Equation (7)):R → CO2 + H2O + Salt + e−
- (i)
- Direct oxidation, where metal cations (commonly heavy metals) are reduced at the cathode and organic contaminants are oxidized at the anode even without the connection of other chemical reagents [37].
- (ii)
- Indirect electrolysis, where the concentration of Na2S2O8 hastens the mineralization of organic compounds. In general, reasonable concentrations of Na2SO4 accelerate the mineralization of organic matter via indirect oxidation, as shown in the following reactions [38]; however, it should be mentioned that some researchers have applied heat or ultraviolet light + heat in order to improve the persulfate oxidation ability of phenols [39].
3.2. Energy Consumption (EC; kWh/kg N)
3.3. Ammonia, Phenol, and Mo Removal Using an Adsorption Column
3.4. Adsorption Isotherms of Pollutant Removal by the Composite Adsorbent
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barkhordar, B.; Ghiasseddin, M. Comparision of Langmuir and Freundlich Equilibriums in Cr, Cu and Ni Adsorption by Sargassum Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2004, 1, 58–64. [Google Scholar]
- Du, X. A review on the electrochemical treatment of the salty organic wastewater. IOP Conf. Ser. 2015, 87, 012037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bashir, M.J.K.; Isa, M.H.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Awang, Z.B.; Aziz, H.A.; Mohajeri, S.; Farooqi, I.H. Landfill leachate treatment by electrochemical oxidation. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 2534–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, S.Q.; Aziz, H.A.; Yusoff, M.S. Powdered activated carbon augmented double react-settle sequencing batch reactor process for treatment of landfill leachate. Desalination 2011, 277, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caetano, M.; Valderrama, C.; Farran, A.; Cortina, J.L. Phenol removal from aqueous solution by adsorption and ion exchange mechanisms onto polymeric resins. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 338, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, L.A.; Pintoda Silva, M.L.C.; Alvarez-Mendes, M.O.; dos Reis Coutinho, A.; Thim, G.P. Phenol removal from aqueous solution by activated carbon produced from avocado kernel seeds. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 174, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojiri, A.; Aziz, H.A.; Zaman, N.Q.; Aziz, S.; Zahed, M.A. Metals removal from municipal landfill leachate and wastewater using adsorbents combined with biological method. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 2819–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Huang, G.; Wang, J. Electrochemical Reduction/Oxidation in the Treatment of Heavy Metal Wastewater. J. Metall. Eng. 2013, 2, 161–164. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, F.; Li, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Crittenden, J.C.; Zhang, Y. Activated carbon electrodes: Electrochemical oxidation coupled with desalination for wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 2015, 125, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Q.; Liu, S.; Cao, Z.; Wang, Y. Ammonia removal from aqueous solution using natural Chinese clinoptilolite. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 44, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossu, R.; Polcaro, A.M.; Lavagnolo, M.C.; Mascia, M.; Palmas, S.; Renoldi, F. Electrochemical treatment of landfill leachate: Oxidation at Ti/PbO2 and Ti/SnO2 anodes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 3570–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojiri, A.; Ziyang, L.; Hui, W.; Ahmad, Z.; Tajuddin, R.M.; Abu Amr, S.S.; Kindaichi, T.; Aziz, H.; Farraji, H. Concentrated landfill leachate treatment with a combined system including electro-ozonation and composite adsorbent augmented sequencing batch reactor process. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 111, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, H.Y.; Hameed, B.H. An overview of landfill leachate treatment via activated carbon adsorption process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halim, A.A.; Aziz, H.A.; Johari, M.A.M.; Ariffin, K.S.; Bashir, M.J.K. Semi-Aerobic Landfill Leachate Treatment Using Carbon–Minerals Composite Adsorbent. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2012, 29, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risnawati, I.; Damanhuri, T.P. Faculty Civil and Environmental Engineering SW5-1 to SW5-11; Institute Technology Bandung: Kota Bandung, Indonesia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ashrafizadeh, S.N.; Khorasani, Z. Ammonia removal from aqueous solutions using hollow-fiber membrane contactors. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 162, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafpoor, A.A.; Dousti, S.; Jafari, A.J.; Hosseinzadeh, A. Efficiency in phenol removal from aqueous solutions of pomegranate peel ash as a natural adsorbent. Environ. Health Eng. Manag. 2016, 3, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Kafshgari, F.; Keshtkar, F.; Mousavian, M.A. Study of Mo (VI) removal from aqueous solution: Application of different mathematical models to continuous biosorption data. Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2013, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koppad, V.B. Performance Evaluation of Electrochemical Oxidation System to Treat Domestic Sewage. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2014, 3, 765–771. [Google Scholar]
- Kearney, D.; Dugauguez, O.; Bejan, D.; Bunce, N.J. Electrochemical Oxidation for Denitrification of Ammonia: A Conceptual Approach for Remediation of Ammonia in Poultry Barns. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, H.M.A.; Ahmad, T.; Hussain, S.N.; Sattar, H. Electrochemical Oxidation of Methylene Blue in Aqueous Solution. Int. J. Chem. Eng. Appl. 2015, 6, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Li, A.; Feng, L.; Cheng, X.; Ding, S. Destruction of Cyanide in Aqueous Solution by Electrochemical Oxidation Method. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 7516–7525. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Yao, J.; Fang, X.; Huang, Y.; Mu, Y. Electrolytic ammonia removal and current efficiency by a vermiculite-packed electrochemical reactor. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peings, V.; Frayret, J.; Pigot, T. Mechanism for the oxidation of phenol by sulfatoferrate (VI): Comparison with various oxidants. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 157, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, S.; Mishra, U. Continuous Fixed-Bed Column Study and Adsorption Modeling: Removal of Lead Ion from Aqueous Solution by Charcoal Originated from Chemical Carbonization of Rubber Wood Sawdust. J. Chem. 2015, 2015, 907379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dada, A.O.; Olalekan, A.P.; Olatunya, A.M.; Dada, O. Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin and Dubinin–Radushkevich Isotherms Studies of Equilibrium Sorption of Zn2+ Unto Phosphoric Acid Modified Rice Husk. IOSR J. App. Chem. 2012, 3, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Altig, J. The Langmuir Adsorption Isotherm; Revision 2.0; CHEM 331L; Physical Chemistry Laboratory: New Mexico, NM, USA, 2013; pp. 1–7. Available online: http://infohost.nmt.edu/~jaltig/Langmuir.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2018).
- Hamdaoui, O.; Naffrechoux, E. Modeling of adsorption isotherms of phenol and chlorophenols onto granular activated carbon Part, I. Two-parameter models and equations allowing determination of thermodynamic parameters. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 147, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association (APHA). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; APHA: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; p. 541. [Google Scholar]
- He, S.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Nie, Y. Investigation on Direct and Indirect Electrochemical Oxidation of Ammonia over Ru−Ir/TiO2 Anode. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 1447–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Zhao, Q.L.; Wei, L.L.; Chen, Y.; Shu, X. Ammonium nitrogen removal from wastewater with a three-dimensional electrochemical oxidation system. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 68, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saratale, R.S.; Hwang, K.J.; Song, J.Y. Electrochemical Oxidation of Phenol for Wastewater Treatment Using Ti/PbO2 Electrode. J. Environ. Eng. 2016, 142, 04015064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Huang, Z.H.; Lim, T.T. Enhanced electrochemical oxidation of phenol using a hydrophobic TiO2-NTs/SnO2-Sb-PTFE electrode prepared by pulse electrodeposition. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 32245–32255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasic, Z.; Gupta, V.K.; Antonijevic, M.M. The Mechanism and Kinetics of Degradation of Phenolics in Wastewaters Using Electrochemical Oxidation. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2014, 9, 3473–3490. [Google Scholar]
- Anglada, A.; Urtaga, A.; Ortiz, I. Contributions of electrochemical oxidation to waste-water treatment: Fundamentals and review of applications. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2009, 84, 1747–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.K.; Chiu, K.F.; Lin, C.Y.; Leu, H.J. Electrochemical treatment of wastewater: Selectivity of the heavy metals removal process. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 27741–27748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Englehardt, J.D. Electrochemical oxidation for landfill leachate treatment. Waste Manag. 2007, 27, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.H.; Tian, F.; Gan, F.X.; Zhang, X.J.; Peng, T.W. A study of electrochemical degradation of azo-dye AO7 on Na2SO4 medium. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2006, 15, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.; Yan, L.; Qu, R.; Wang, Z. Degradation of the UV-filter benzophenone-3 in aqueous solution using persulfate activated by heat, metal ions and light. Chemosphere 2018, 196, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.H.; Wei, L.; Hong, S.; Zhu, H.; Lin, A.; Gan, F.X. Enhanced electrochemical oxidation of phenol by introducing ferric ions and UV radiation. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 1386–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiaens, M.E.R.; Gildemyn, S.; Matassa, S.; Ysebaert, T.; de Varieze, J.; Rabaey, K. Electrochemical Ammonia Recovery from Source-Separated Urine for Microbial Protein Production. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2017, 51, 13143–13150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazloomi, F.; Jalali, M. Ammonium removal from aqueous solutions by natural Iranian zeolite in the presence of organic acids, cations and anions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1664–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haseena, P.V.; Padmavathy, K.S.; Rohit Krishnan, P.; Madhu, G. Adsorption of Ammonium Nitrogen from Aqueous Systems Using Chitosan-Bentonite Film Composite. Procedia Technol. 2016, 24, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leili, M.; Faradmal, J.; Kosravian, F.; Heydari, M. A Comparison Study on the Removal of Phenol from Aqueous Solution Using Organo-modified Bentonite and Commercial Activated Carbon. Avicenna J. Environ. Health Eng. 2015, 2, e2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglezakis, V.J.; Stylianou, M.; Loizidou, M. Ion exchange and adsorption equilibrium studies on clinoptilolite, bentonite and vermiculite. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2010, 71, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojiri, A.; Hui, W.; Arshad, A.K.; Ridzuan, A.R.M.; Hamid, N.H.M.; Farraji, H.; Gholami, A.; Vakili, A. Vanadium(V) removal from aqueous solutions using a new composite adsorbent (BAZLSC): Optimization by response surface methodology. Adv. Environ. Res. 2017, 6, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodbiba, G.; Wu, I.C.; Lee, Y.C.; Matsuo, S.; Fujita, T. Adsorption of Molybdenum Ion in Nitric Acid Solution by Using a Pb-Fe Based Adsorbent. Int. J. Soc. Mater. Eng. Resour. 2010, 17, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








| Level | Reaction Time (h) | Initial Pollutant Concentration (mg/L) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 1 | 10 | 3 |
| 0 | 2 | 30 | 4.5 |
| +1 | 3 | 50 | 6 |
| Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Surface area (m2/g) | 288.6 |
| External surface area (m2/g) | 246.7 |
| Micropore area (m2/g) | 61.9 |
| Micropore volume (cc/g) | 0.08 |
| Run | Contact Time (h) | Initial Concentration (mg/L) | pH | Ammonia Rem. * (%) | Phenols Rem. (%) | Mo Rem. (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13 | 0.8 | 30.0 | 4.5 | 74.17 | 45.17 | 49.64 |
| 6 | 1.0 | 10.0 | 3.0 | 72.11 | 51.95 | 49.87 |
| 8 | 1.0 | 10.0 | 6.0 | 82.62 | 35.12 | 40.13 |
| 4 | 1.0 | 50.0 | 3.0 | 69.53 | 35.11 | 44.00 |
| 11 | 1.0 | 50.0 | 6.0 | 81.11 | 28.71 | 34.18 |
| 17 | 2.0 | 6.0 | 4.5 | 74.31 | 44.11 | 46.11 |
| 2 | 2.0 | 30.0 | 4.5 | 77.00 | 50.86 | 58.95 |
| 3 | 2.0 | 30.0 | 6.3 | 90.11 | 33.00 | 38.00 |
| 5 | 2.0 | 30.0 | 2.7 | 71.17 | 43.84 | 47.11 |
| 9 | 2.0 | 54.0 | 4.5 | 72.00 | 42.92 | 47.11 |
| 10 | 2.0 | 30.0 | 4.5 | 76.92 | 49.97 | 58.74 |
| 12 | 2.0 | 30.0 | 4.5 | 77.11 | 50.81 | 59.49 |
| 15 | 2.0 | 30.0 | 4.5 | 77.12 | 50.57 | 58.00 |
| 16 | 2.0 | 30.0 | 4.5 | 77.00 | 50.89 | 58.76 |
| 18 | 2.0 | 30.0 | 4.5 | 76.93 | 51.18 | 59.00 |
| 20 | 2.0 | 30.0 | 4.5 | 76.93 | 51.11 | 59.40 |
| 22 | 2.0 | 30.0 | 4.5 | 77.71 | 50.35 | 59.10 |
| 7 | 3.0 | 10.0 | 6.0 | 84.13 | 37.19 | 43.45 |
| 21 | 3.0 | 10.0 | 3.0 | 73.46 | 52.17 | 48.69 |
| 14 | 3.0 | 50.0 | 3.0 | 71.64 | 41.50 | 50.13 |
| 1 | 3.0 | 50.0 | 6.0 | 90.95 | 29.97 | 37.64 |
| 19 | 3.2 | 30.0 | 4.5 | 73.18 | 46.18 | 53.90 |
| Response | Final Equation in Terms of Actual Factor a | R2 | Adj. R2 | Adec. P. | SD | CV | PRESS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammonia | 94.27 + 1.032A − 12.849C + 1.655C2 | 0.9422 | 0.8988 | 18.19 | 1.80 | 2.40 | 334.32 |
| Phenols | 3.532 − 0.039B + 21.99C − 0.008B2 − 3.003C2 | 0.9297 | 0.8769 | 11.68 | 2.72 | 6.93 | 668.22 |
| Mo(VI) | −22.835 + 30.369C − 0.013B2 − 3.634C2 | 0.9202 | 0.8604 | 11.98 | 3.06 | 6.65 | 712.52 |
| Parameter | Q (mg/g) | b (L/mg) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ammonia | 1.027 | 0.240 | 0.9333 |
| Phenols | 0.554 | 0.087 | 0.8696 |
| Mo | 0.874 | 0.45 | 0.8051 |
| Parameter | Kf (mg/g (L/mg)1/n) | 1/n | n | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammonia | 0.014 | 12.458 | 0.080 | 0.9795 |
| Phenols | 0.063 | 3.121 | 0.320 | 0.9641 |
| Mo | 0.028 | 6.368 | 0.157 | 0.9266 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mojiri, A.; Ohashi, A.; Ozaki, N.; Shoiful, A.; Kindaichi, T. Pollutant Removal from Synthetic Aqueous Solutions with a Combined Electrochemical Oxidation and Adsorption Method. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1443. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15071443
Mojiri A, Ohashi A, Ozaki N, Shoiful A, Kindaichi T. Pollutant Removal from Synthetic Aqueous Solutions with a Combined Electrochemical Oxidation and Adsorption Method. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2018; 15(7):1443. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15071443
Chicago/Turabian StyleMojiri, Amin, Akiyoshi Ohashi, Noriatsu Ozaki, Ahmad Shoiful, and Tomonori Kindaichi. 2018. "Pollutant Removal from Synthetic Aqueous Solutions with a Combined Electrochemical Oxidation and Adsorption Method" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15, no. 7: 1443. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15071443
APA StyleMojiri, A., Ohashi, A., Ozaki, N., Shoiful, A., & Kindaichi, T. (2018). Pollutant Removal from Synthetic Aqueous Solutions with a Combined Electrochemical Oxidation and Adsorption Method. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(7), 1443. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15071443