The Effect of Distributed Parameters on Conducted EMI from DC-Fed Motor Drive Systems in Electric Vehicles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Literature Review
1.2. Motivation and Innovation
1.3. Organization of the Paper
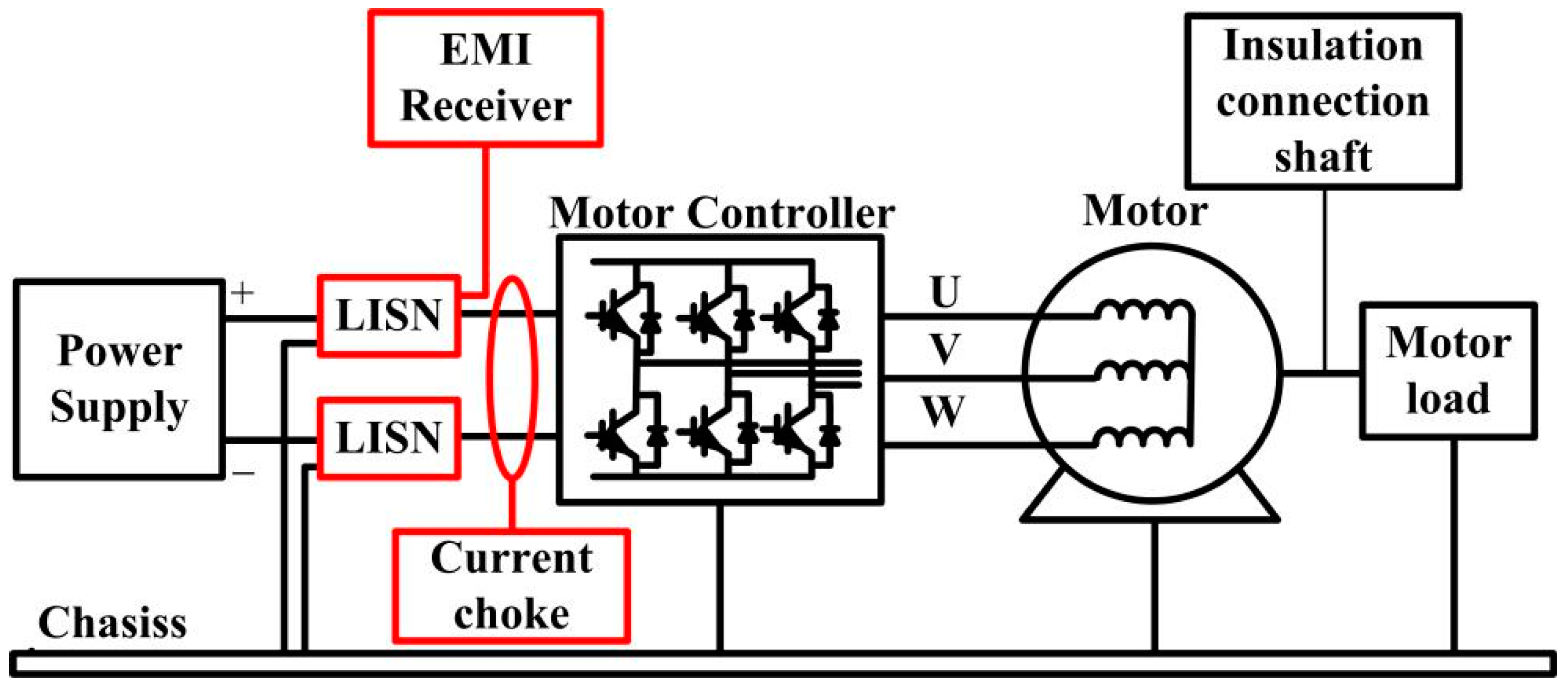
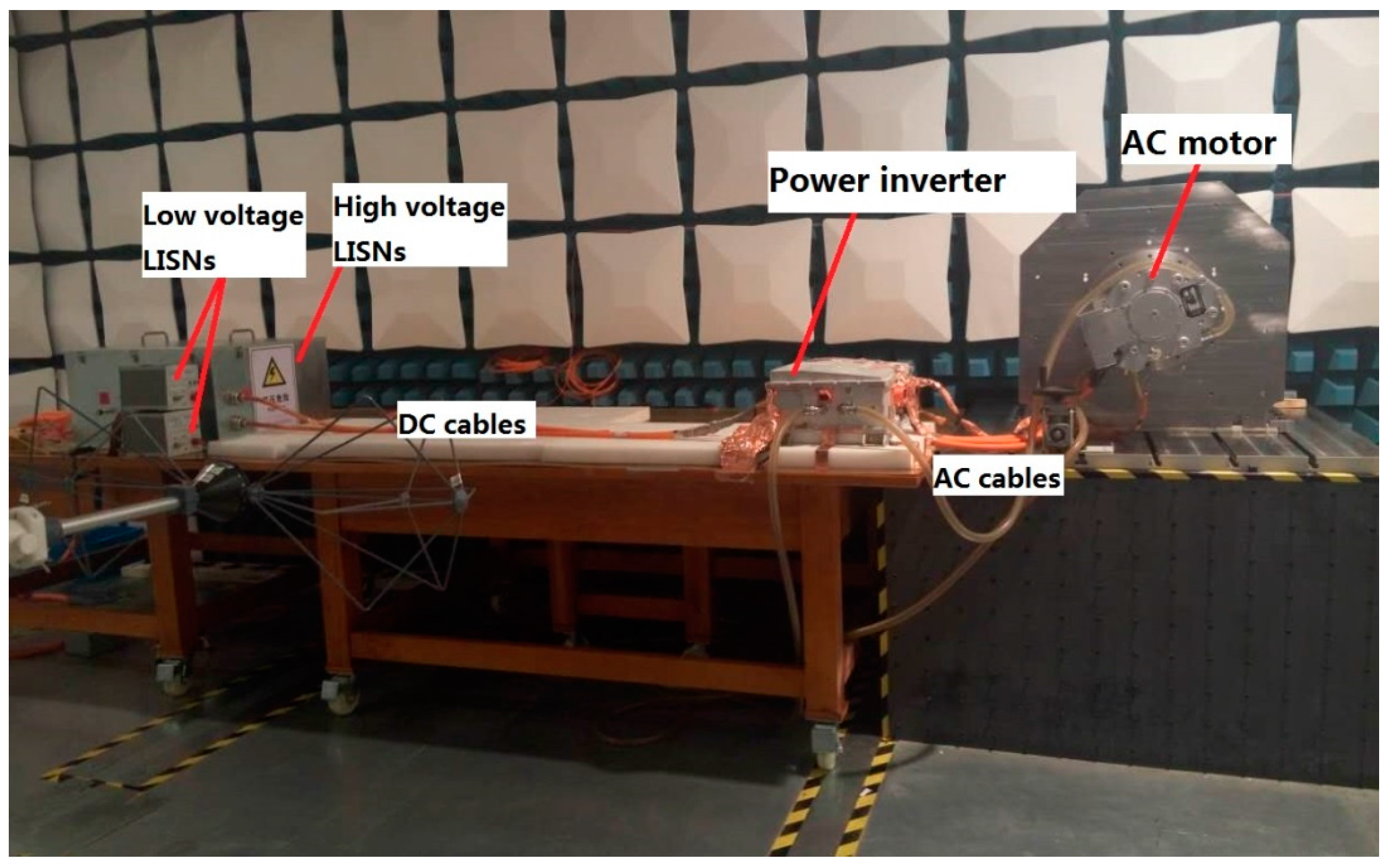
2. System Conducted Emission Measurement
2.1. Conducted EMI Emission Setup
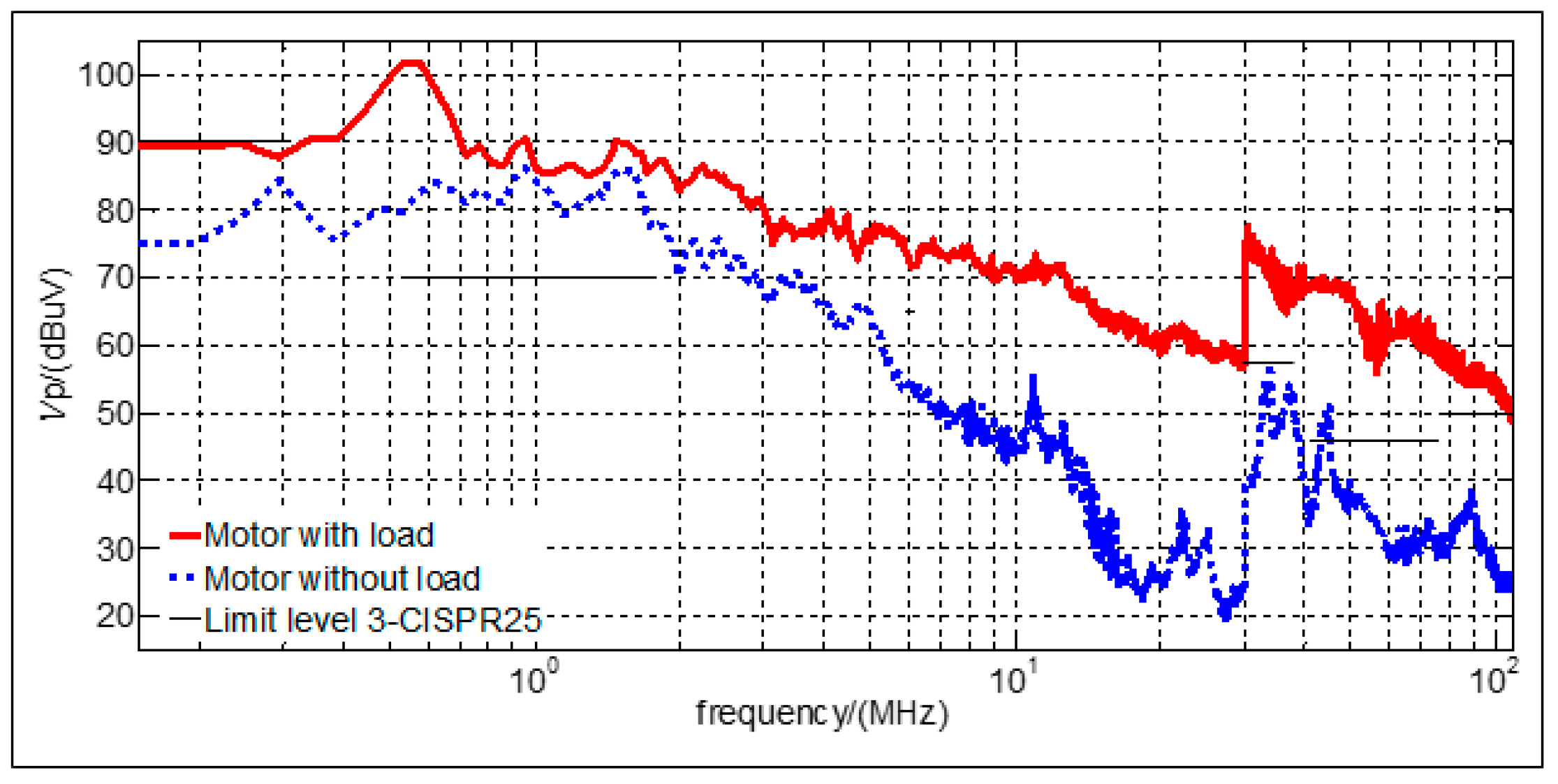
2.2. Conducted EMI Experiment Results
3. System Conducted Emission Analysis
3.1. Noise Source
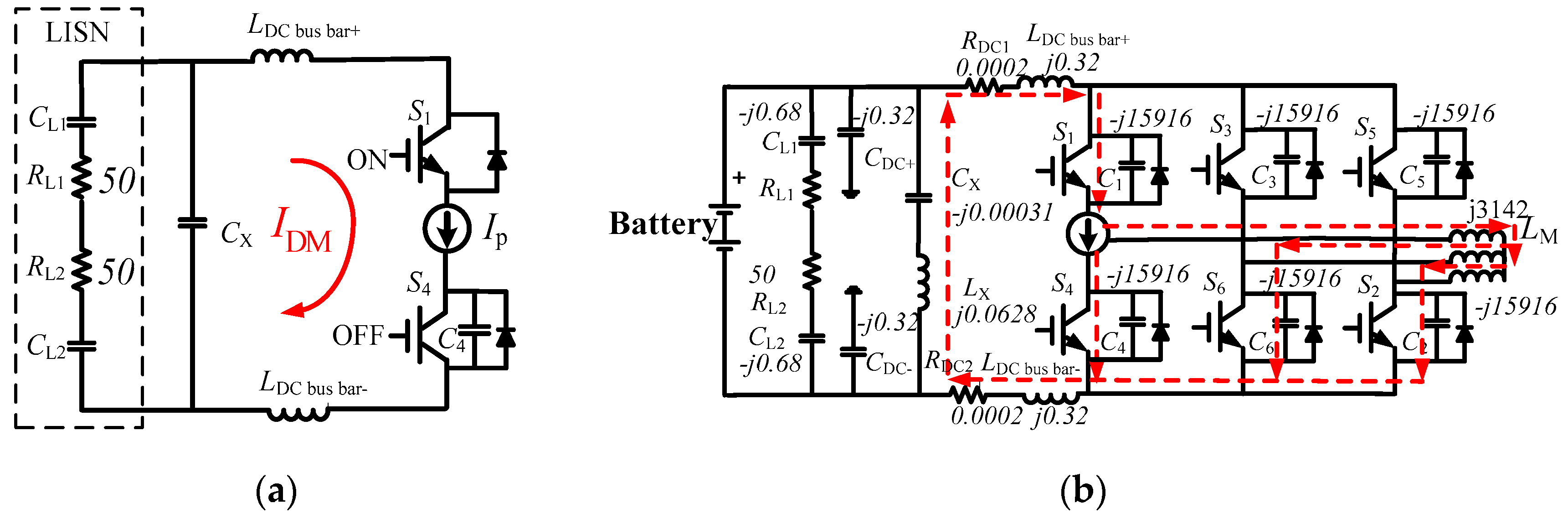
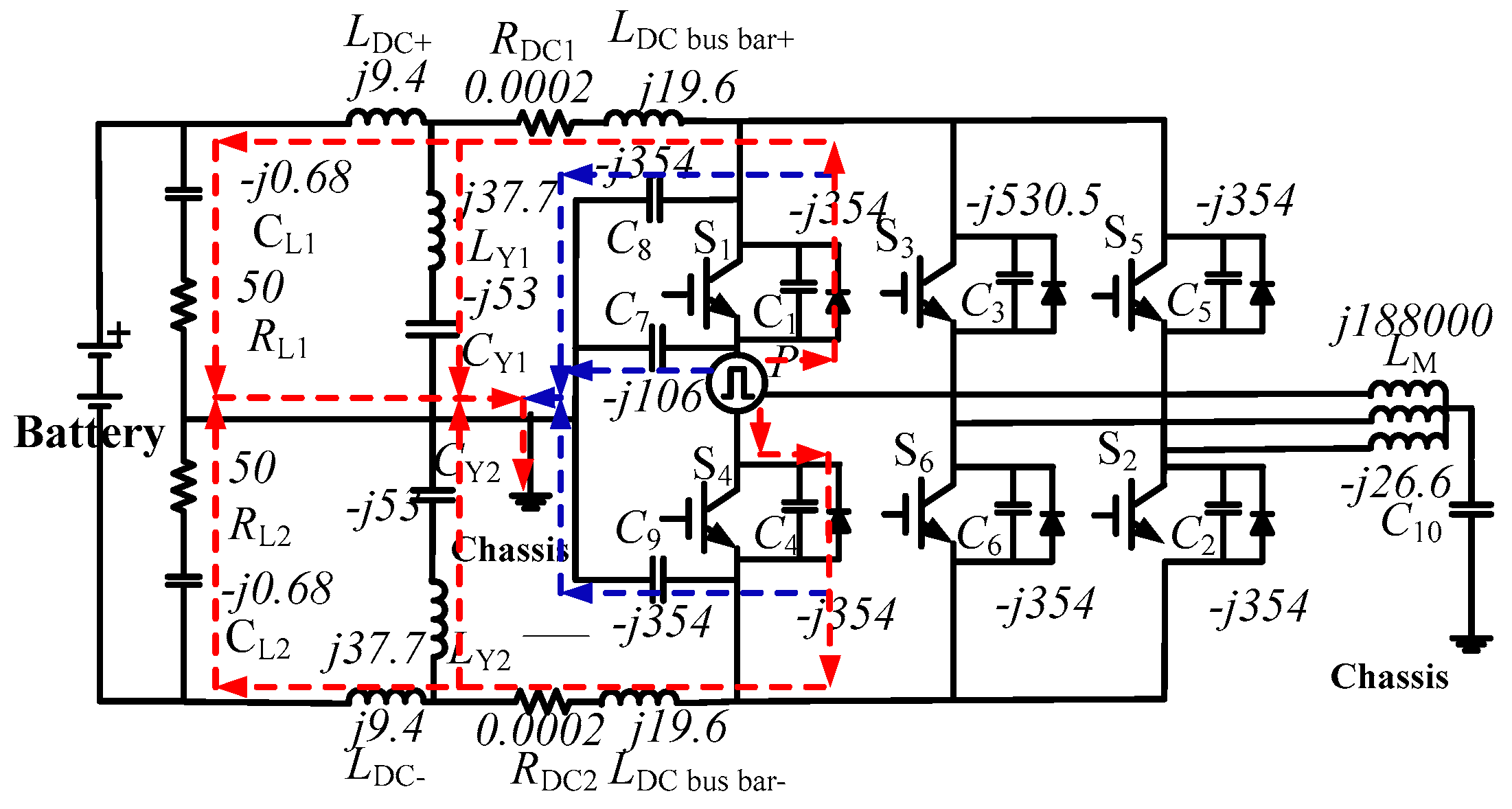
3.2. Analysis of the Current Path of Conducted Emissions
3.2.1. Analysis of the DM Current Path for 500 kHz
- current loop I: IDM→C4→LDC bus bar−→RDC2→LX→CX→RDC1→LDC bus bar+→C1→IDM
- current loop II: IDM→LM→C6→LDC bus bar−→RDC2→LX→CX→RDC1→LDC bus bar+→C1→IDM
- current loop III: IDM→LM→C2→LDC bus bar−→RDC2→LX→CX→RDC1→LDC bus bar+→C1→IDM
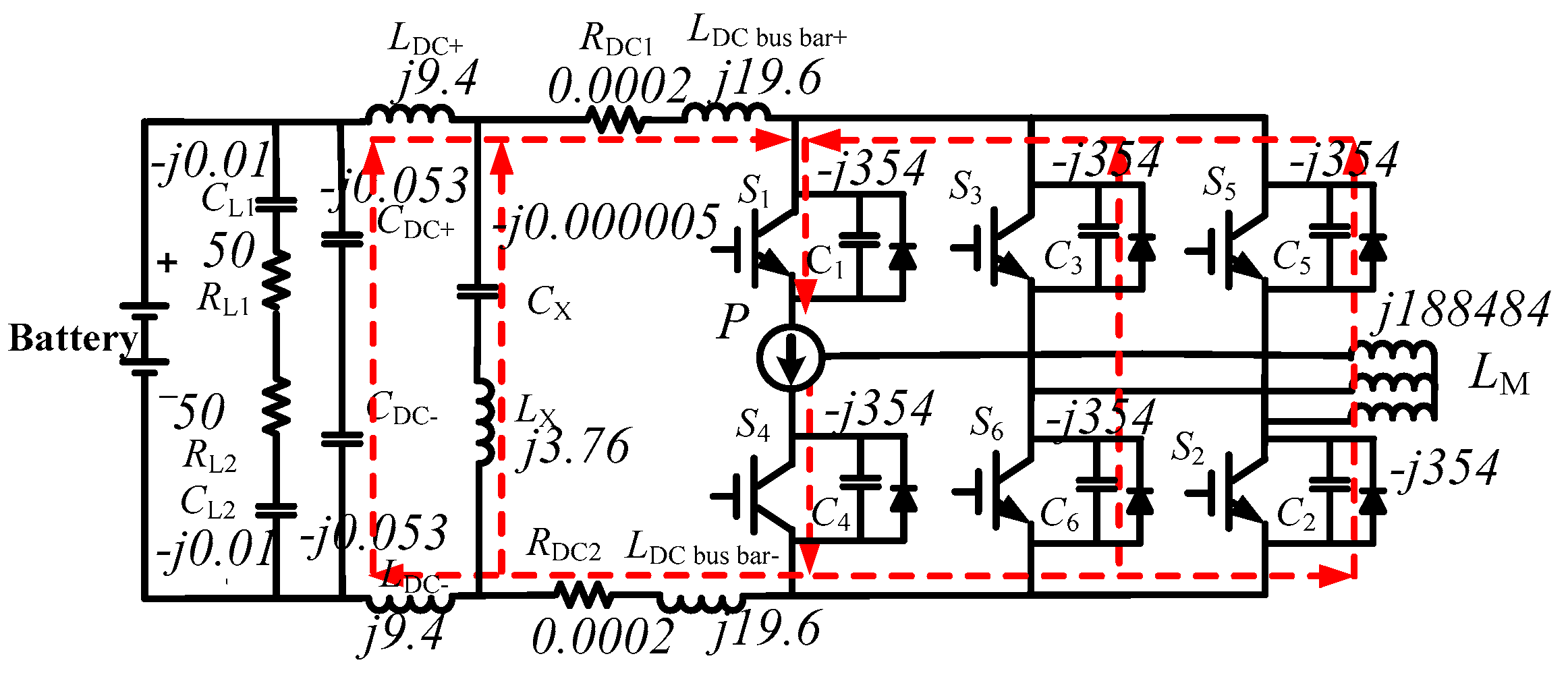
3.2.2. Analysis of DM Current Path for 30 MHz
- current loop I: IDM→C4→LDC bus bar−→RDC2→LX→CX→RDC1→LDC bus bar+→C1→IDM
- current loop II: IDM→C4→C6→C3→C1→IDM
- current loop III: IDM→C4→C2→C5→C1→IDM
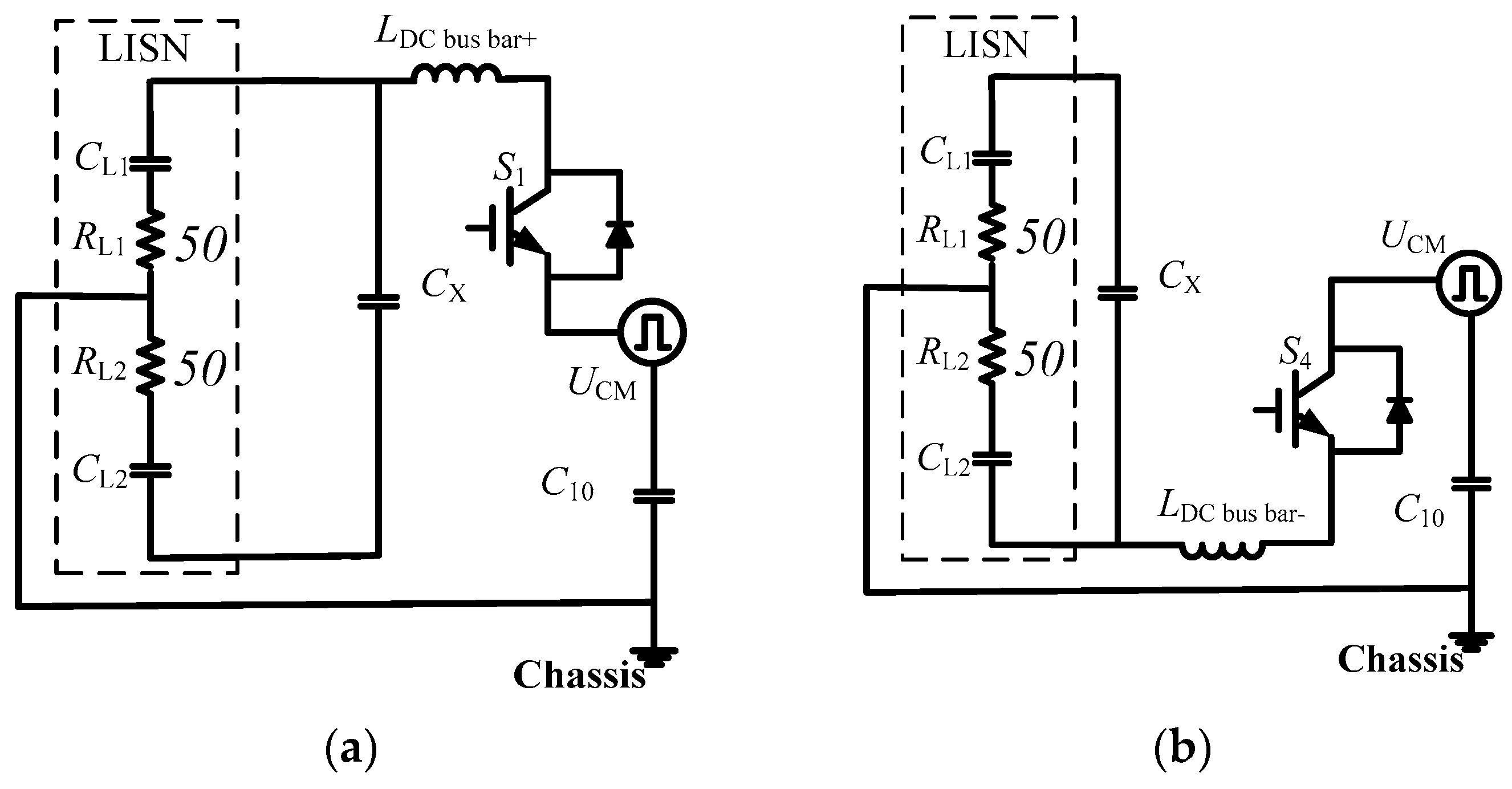
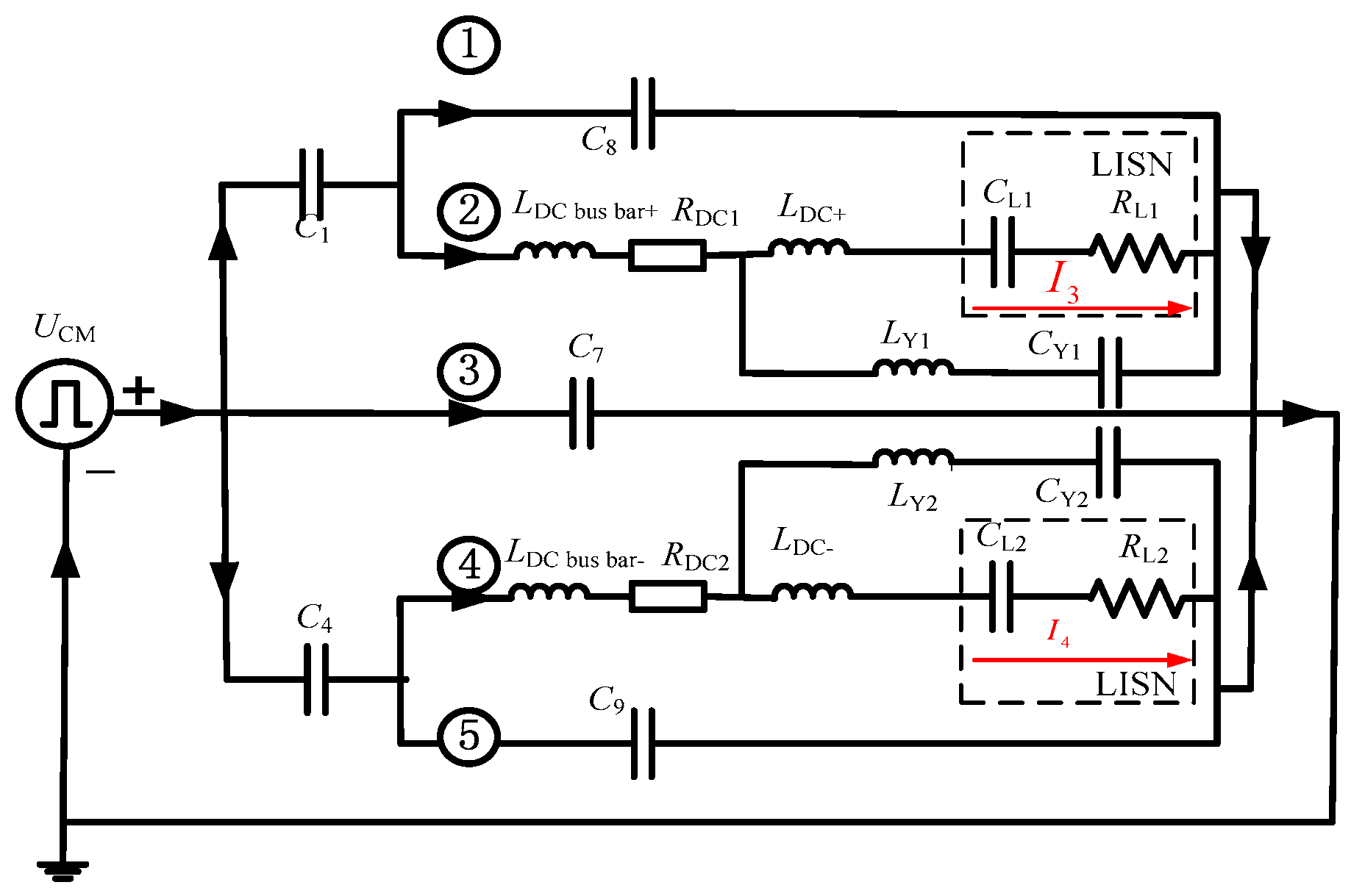
3.2.3. Analysis of CM Current Path for 500 kHz
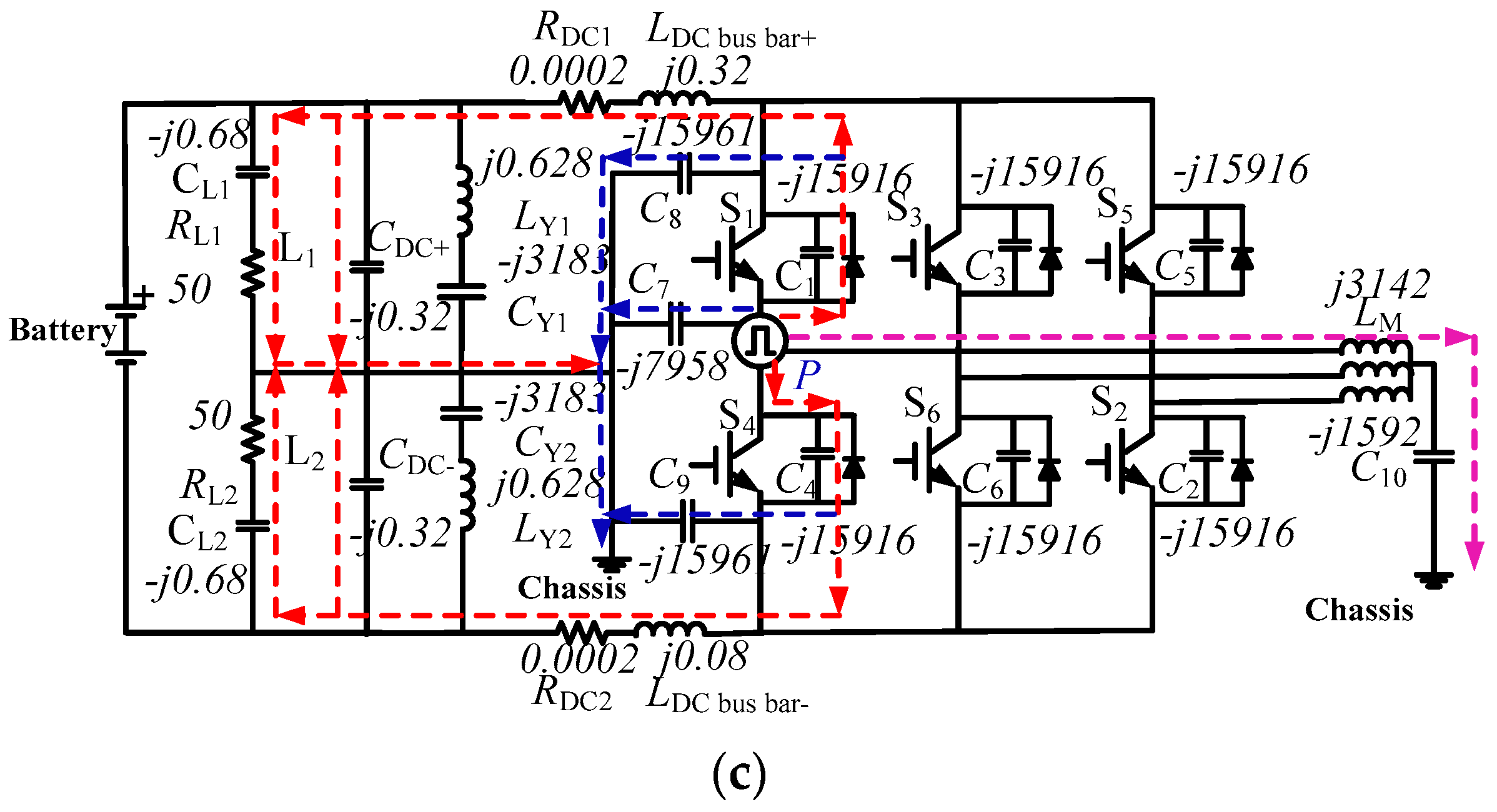
3.2.4. Analysis of CM Current Path for 30 MHz
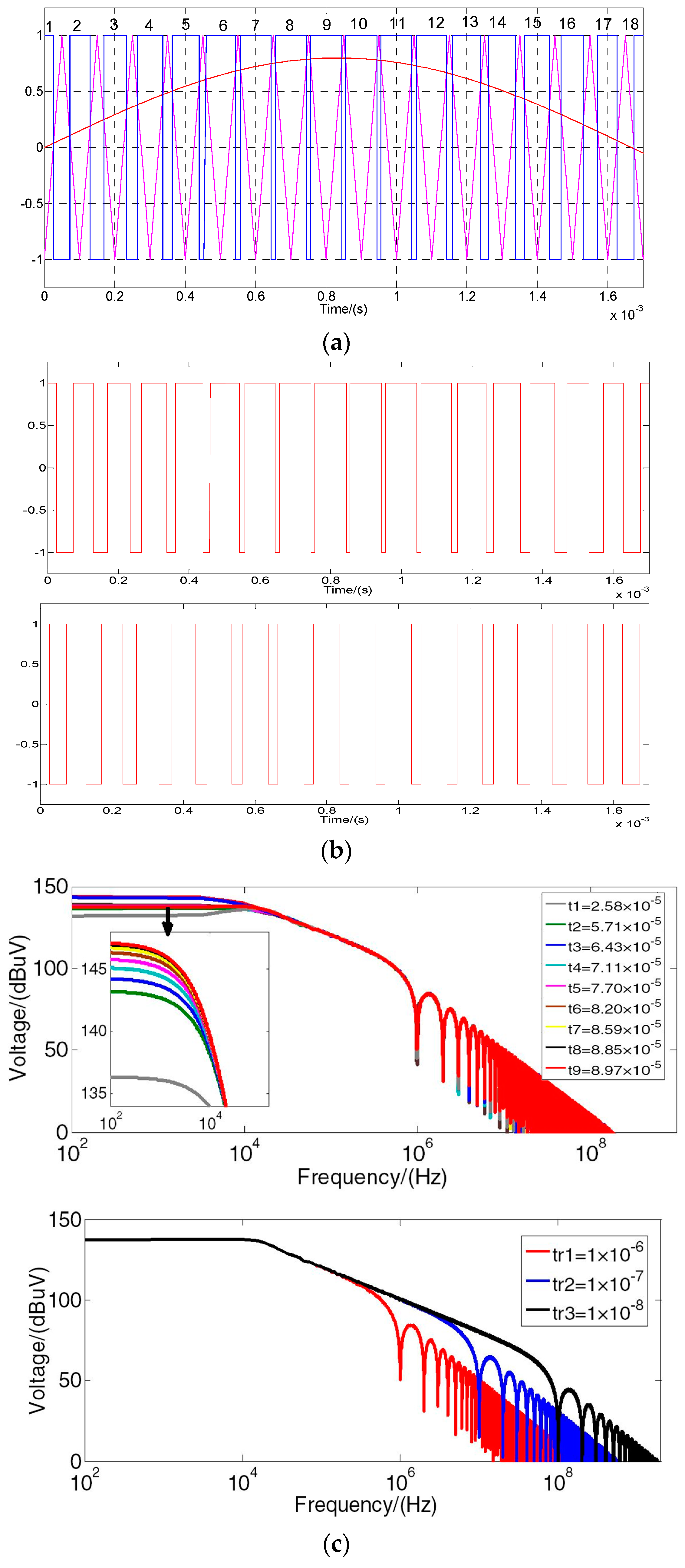
4. Simulation of the Effect of Distributed Parameters
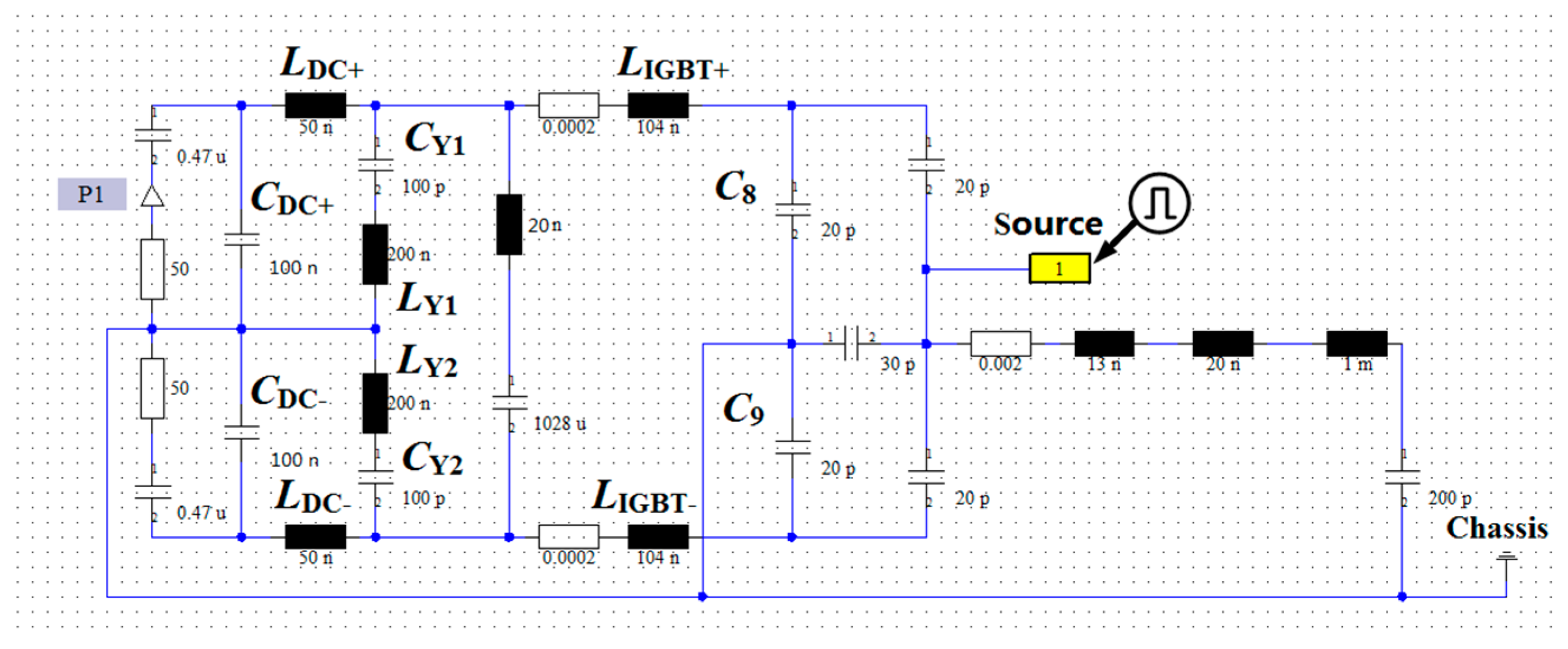
4.1. System Conducted EMI Modeling
4.2. The Effect of Distributed Parameters
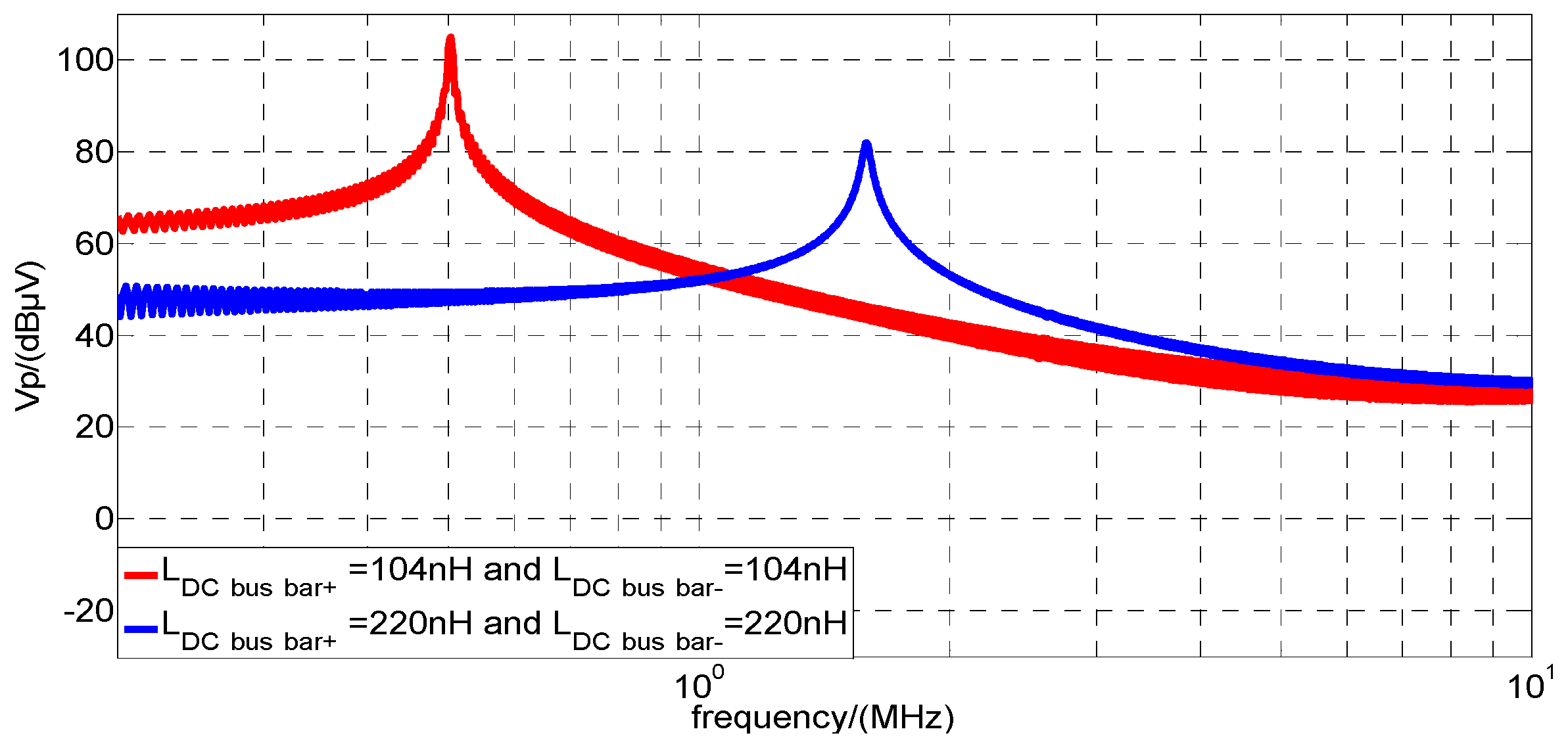
4.2.1. The Effect of LDC bus bar+ and LDC bus bar−
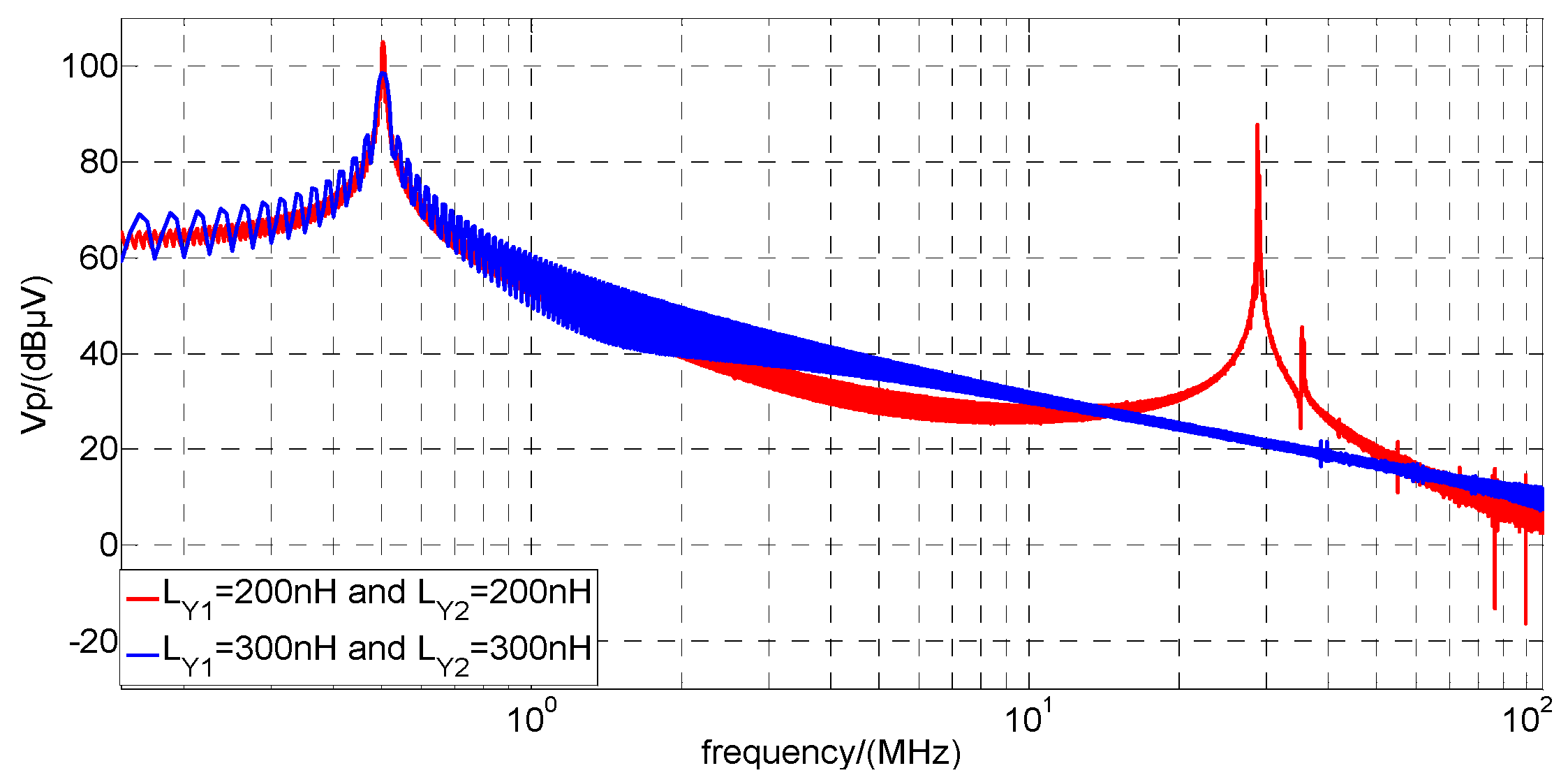
4.2.2. The Effect of LY1 and LY2
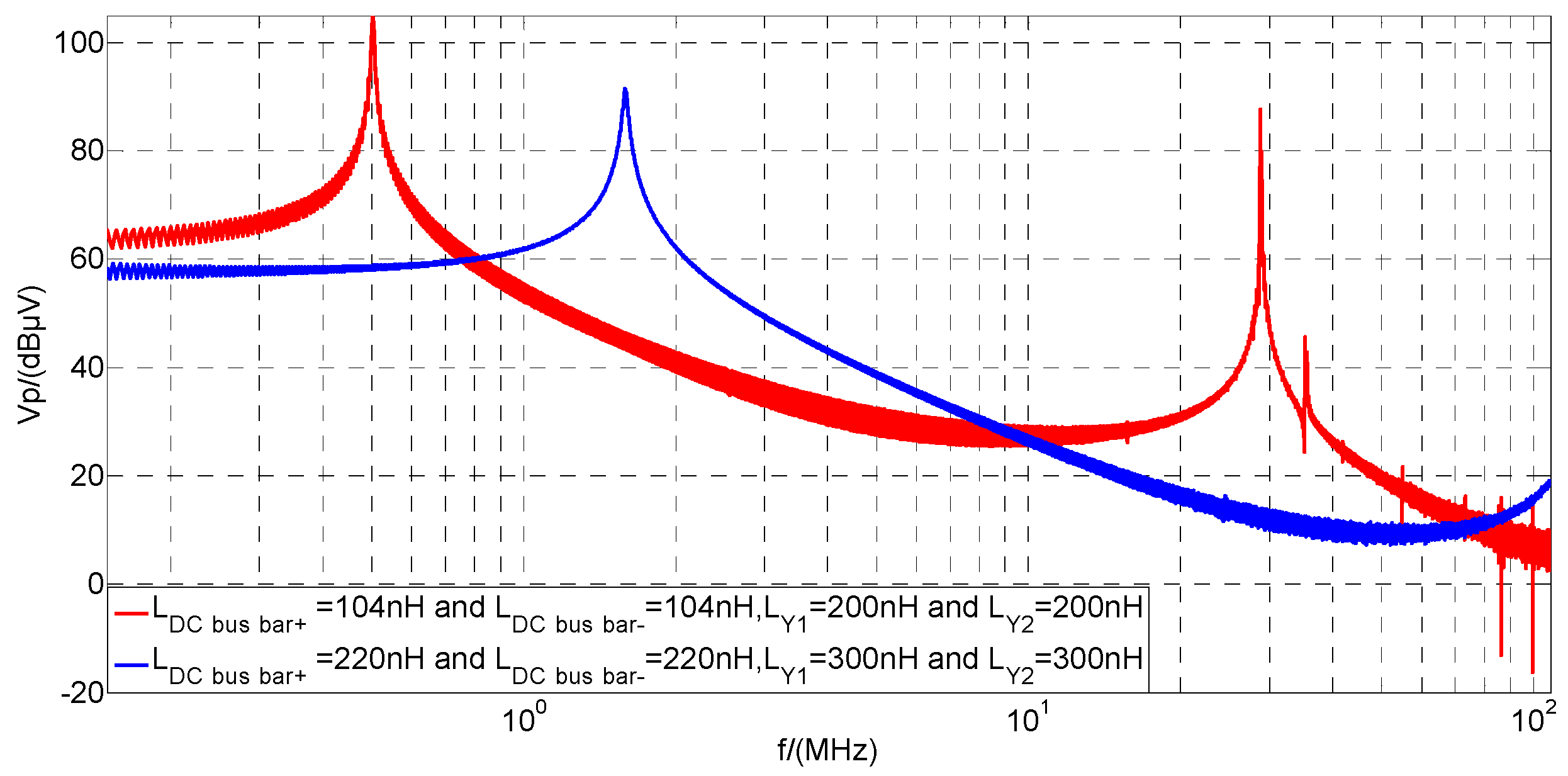
4.2.3. The Effect of Combination of LDC bus bar+, LDC bus bar−, LY1 and LY2
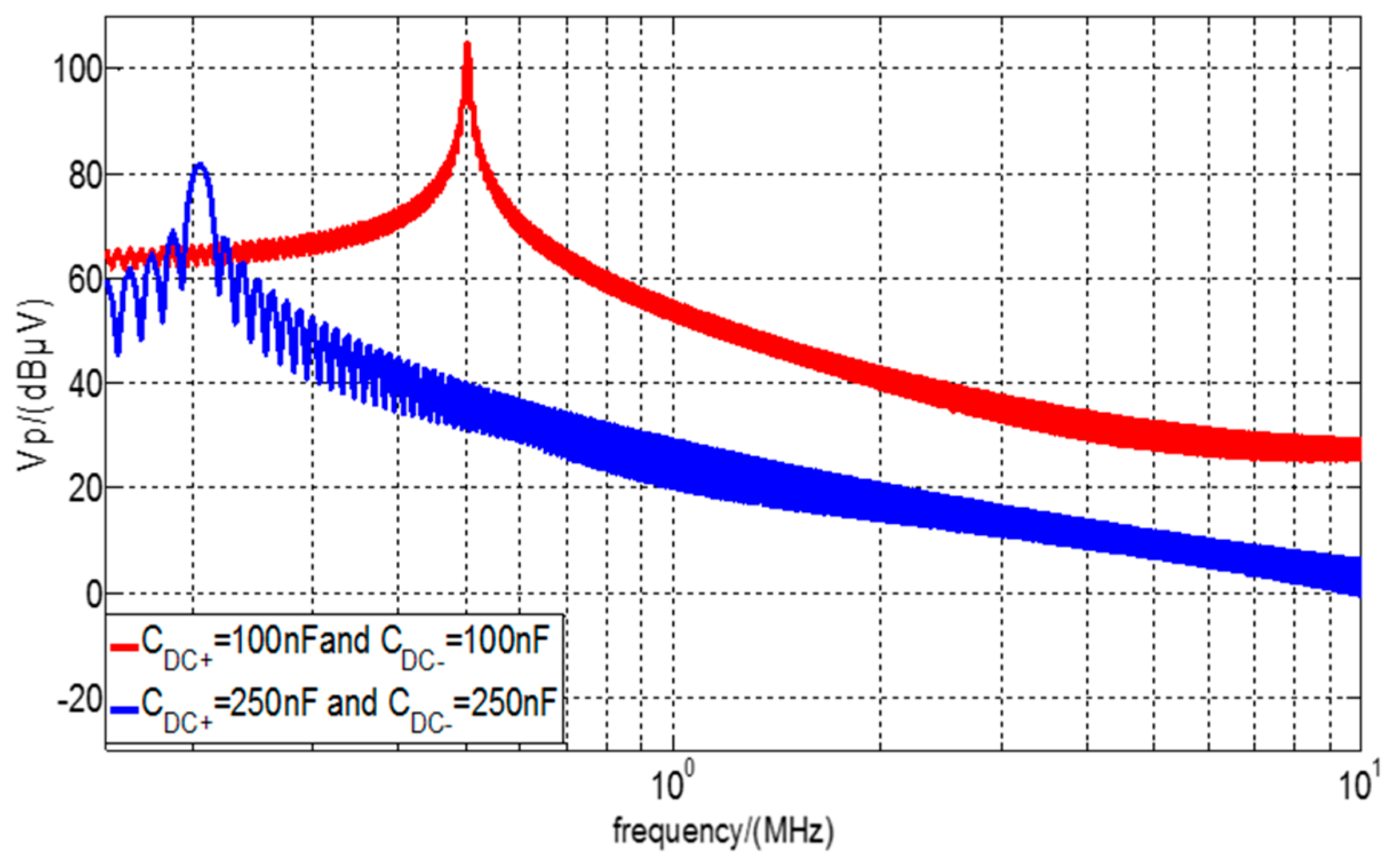
4.2.4. The Effect of CDC+ and CDC−
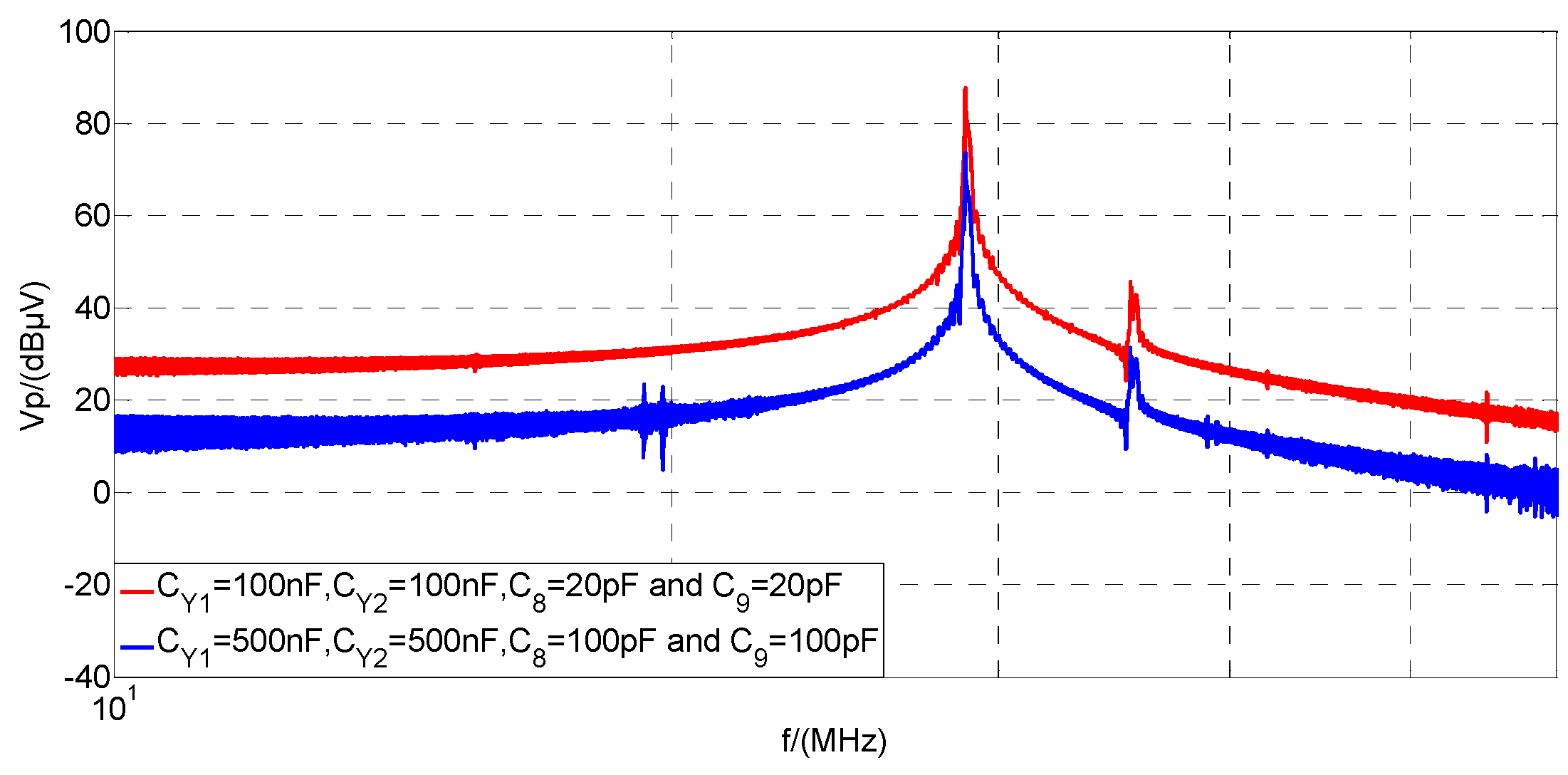
4.2.5. The Effect of the Combination of CY1, CY2, C8 and C9
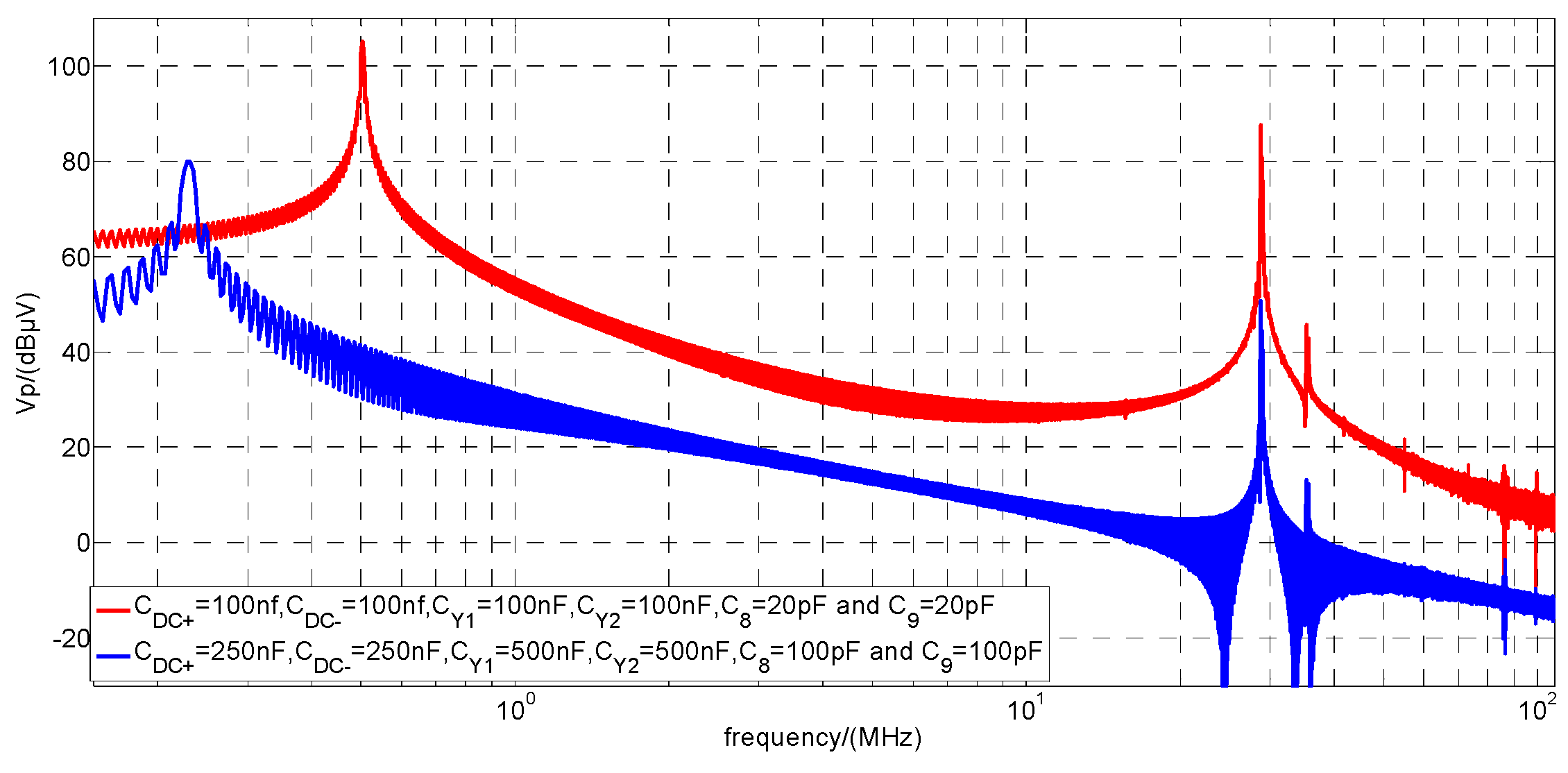
4.2.6. The Effect of the Combination of CDC+, CDC−, CY1, CY2, C8 and C9
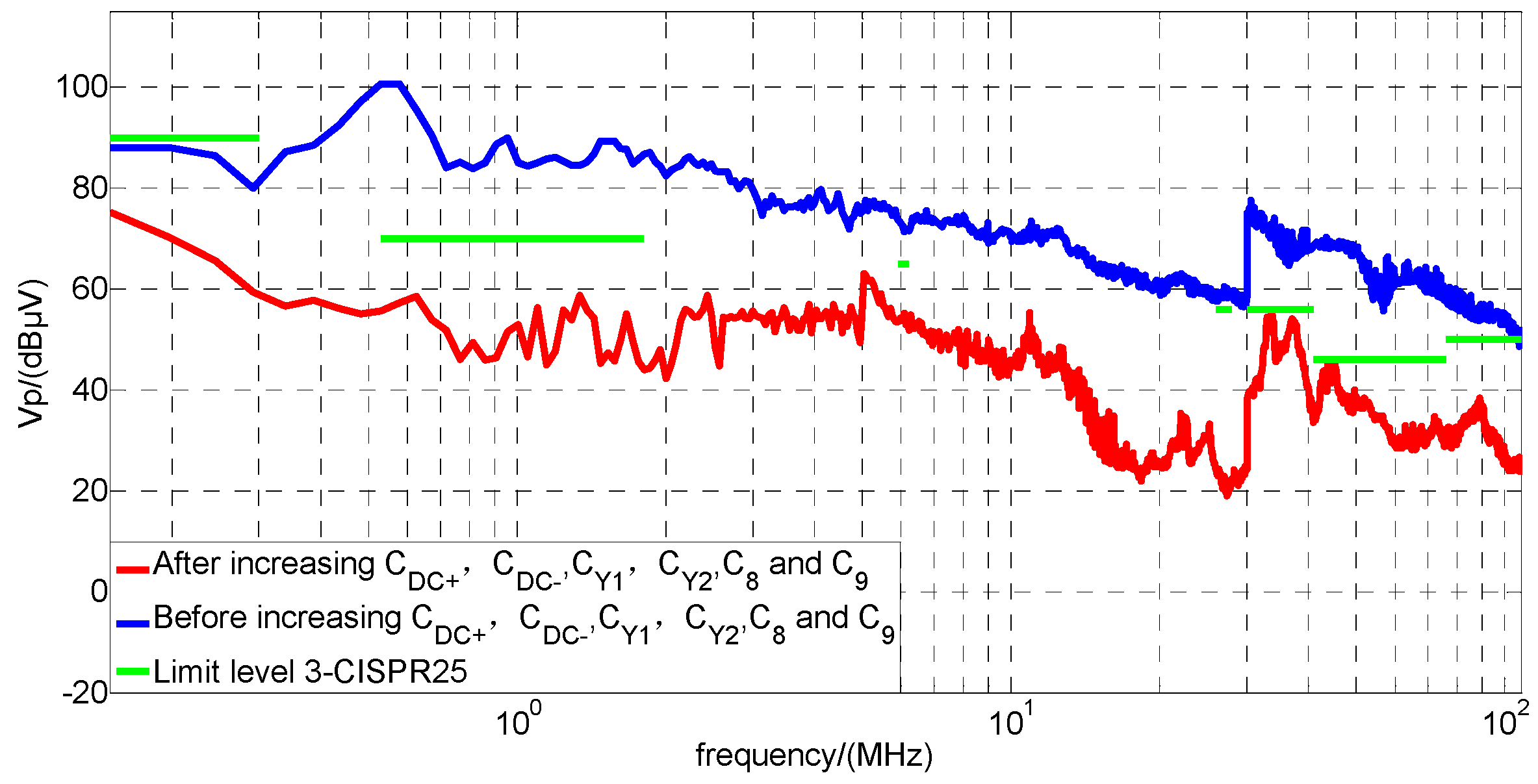
5. Experimental Verification
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, F.; Xiong, R.; He, H. A systematic state-of-charge estimation framework for multi-cell battery pack in electric vehicles using bias correction technique. Appl. Energy 2016, 162, 1399–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, E.; Alessandrini, S.; Balanzino, A.; Yan, J. Impact of the electric vehicles on the air pollution from a highway. Appl. Energy 2016, 169, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Murgovski, N.; Johannesson, L.; Bo, E. Energy efficiency analysis of a series plug-in hybrid electric bus with different energy management strategies and battery sizes. Appl. Energy 2013, 111, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xiong, R.; Wang, C.; Cao, J. An on-line predictive energy management strategy for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles to counter the uncertain prediction of the driving cycle. Appl. Energy 2016, 185, 1663–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torresa, J.L.; Gonzalezb, R.; Gimeneza, A.; Lopeza, J. Energy management strategy for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. A comparative study. Appl. Energy 2014, 113, 816–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.; Zhang, X.; Bondarenko, N.; Loken, D.; Doren, T.V.; Beetner, D.G. Mitigation emission strategy based on resonances from a power inverter system in electric vehicles. Energies 2016, 9, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsani, M.; Gao, Y.; Emadi, A. Modern Electric, Hybrid Electric, and Fuel Cell Vehicles: Fundamentals, Theory, and Design; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ardon, V.; Aime, J.; Chadebec, O.; Clavel, E. EMC modeling of an industrial variable speed drive with an adapted PEEC method. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2010, 46, 2892–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.S.; Huang, X.; Chen, S.; Nehl, T.W. EMI characterization and simulation with parasitic models for a low-Voltage high-current AC motor drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2004, 40, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jettanasen, C.; Costa, F.; Vollaire, C. Common-mode emissions measurements and simulation in variable-speed drive systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2009, 24, 2456–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tommasini, R.; Spertino, F. Electric power distribution and environment: Interference of power installation magnetic fields on computer systems. Appl. Energy 1999, 64, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toure, B.; Schanen, J.-L.; Gerbaud, L.; Meynard, T.; Roudet, J.; Ruelland, R. EMC modeling of drives for aircraft applications: Modeling process, EMI filter optimization and technological choice. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 28, 1145–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.S. Resonant snubber-based soft-switching inverters for electric propulsion drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1997, 44, 71–80. [Google Scholar]
- Mutoh, N.; Ogata, M. New methods to control EMI noises generated in motor drive systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2004, 40, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebholz, H.M.; Tenbohlen, S.; Kohler, W. Time-domain characterization of RF sources for the design of noise suppression filters. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2009, 51, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, M.; Friedl, T.; Tenbohlen, S.; Köhler, W. Emulation of conducted emissions of an automotive inverter for filter development in HV networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC), Denver, CO, USA, 5–9 August 2013; pp. 236–241.
- Trzynadlowski, A.M.; Wang, Z.; Nagashima, J.; Stancu, C. Comparative investigation of PWM techniques for general motor’s new drive for electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the IEEE Industry Applications Conference, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 13–18 October 2002; pp. 2010–2015.
- Piazza, M.C.D.; Ragusa, A.; Tine, G.; Vitale, G. A model of electromagnetic radiated emissions for dual Voltage automotive electrical systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, Ajaccio, France, 4–7 May 2004; pp. 317–322.
- Akagi, H.; Shimizu, T. Attenuation of conducted EMI emissions from an inverter-driven motor. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2008, 23, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Maillet, Y.Y.; Wang, F.; Lai, R.; Luo, F.; Boroyevich, D. Parasitic effects of grounding paths on common-mode EMI filter’s performance in power electronics systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 3050–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishnoi, H.; Baisden, A.C.; Mattavelli, P.; Boroyevich, D. Analysis of EMI terminal modeling of switched power converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 3924–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Ferreira, A.J. Comparison and reduction of conducted EMI in SiC JFET and Si IGBT-based motor drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 1757–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revol, B.; Roudet, J.; Schanen, J.L.; Loizelet, P. EMI study of three-phase inverter-fed motor drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2011, 47, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevanovic, I.; Skibin, S.; Masti, M.; Laitinen, M. Behavioral modeling of chokes for EMI simulations in power electronics. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 28, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutoh, N.; Ogata, M.; Gulez, K.; Harashima, F. New methods to suppress EMI noises in motor drive systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2002, 49, 474–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishnoi, H.; Mattavelli, P.; Burgos, R.; Boroyevich, D. EMI behavioral models of DC-fed three-phase motor drive systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 4633–4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondarenko, N.; Zhai, L.; Xu, B.; Li, G.; Makharashvili, T.; Loken, D.; Berger, P.; Doren, T.P.V.; Beetner, D.G. A measurement-based model of the electromagnetic emissions from a power inverter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 5522–5531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Australia, S. Vehicle, Boats and Internal Combustion Engines—Limits and Methods of Measurement for the Protection of on-Board Receivers; CISPR25; International Special Committee on Radio Interference: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mihalic, F.; Kos, D. Reduced conductive EMI in switched-mode DC–DC power converters without EMI filters: PWM versus randomized PWM. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2006, 21, 1783–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Nehl, T.W.; Lai, J.-S.; Huang, X.; Pepa, E.; de Doncker, R.; Voss, I. Towards EMI prediction of a PM motor drive for automotive applications. In Proceedings of the Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition, Miami Beach, FL, USA, 9–13 February 2003; pp. 14–22.
- Paul, C.R. Introduction to EMC; Wiley & Sons. Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 466–474. [Google Scholar]
- Mugur, P.R.; Roudet, J.; Crebier, J.C. Power electronic converter EMC analysis through state variable approach techniques. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2001, 43, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Service Band | Frequency/MHz | Limit/dB (µv) |
|---|---|---|
| Broadcast | 0.15–0.30 | 90 |
| 0.53–1.80 | 70 | |
| 5.9–6.2 | 65 | |
| 41–88 | 46 | |
| 76–108 | 50 | |
| Mobile services | 26–28 | 56 |
| 30–54 | 56 | |
| 68–87 | 50 |
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| LY1, LY2 | 200 nH | CX | 1028 µF |
| C7 | 30 pF | LX | 20 nH |
| C8 | 20 pF | C1–C6 | 20 pF |
| C9 | 20 pF | RL1, RL2 | 50 Ω |
| C10 | 200 pF | CL1, CL2 | 0.47 µF |
| CY1, CY2 | 100 pF | LM | 1 mH |
| LDC+, LDC− | 50 nH | CDC+, CDC− | 100 nF |
| RDC+, RDC− | 0.0002 Ω | LDC bus bar+, LDC bus bar− | 104 nH |
| Changing of Parameters | Current | Voltage |
|---|---|---|
| LDC bus bar+ ↑ or ↓ | I1 ↓ | UR ↓ |
| LDC bus bar− ↑ or ↓ | I1 ↓ | UR ↓ |
| CDC+ ↑ or ↓ | I1 ↓ | UR ↓ |
| CDC−↑ or ↓ | I1 ↓ | UR ↓ |
| C8 ↑ | I2 ↓ | UR ↓ |
| C9 ↑ | I2 ↓ | UR ↓ |
| LY1 ↑ | I2 ↓ | UR ↓ |
| LY2 ↑ | I2 ↓ | UR ↓ |
| CY1 ↑ | I2 ↓ | UR ↓ |
| CY2 ↑ | I2 ↓ | UR ↓ |
| LDC bus bar+ ↑ | I2 ↓ | UR ↓ |
| LDC bus bar− ↑ | I2 ↓ | UR ↓ |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhai, L.; Lin, L.; Zhang, X.; Song, C. The Effect of Distributed Parameters on Conducted EMI from DC-Fed Motor Drive Systems in Electric Vehicles. Energies 2017, 10, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10010001
Zhai L, Lin L, Zhang X, Song C. The Effect of Distributed Parameters on Conducted EMI from DC-Fed Motor Drive Systems in Electric Vehicles. Energies. 2017; 10(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhai, Li, Liwen Lin, Xinyu Zhang, and Chao Song. 2017. "The Effect of Distributed Parameters on Conducted EMI from DC-Fed Motor Drive Systems in Electric Vehicles" Energies 10, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10010001
APA StyleZhai, L., Lin, L., Zhang, X., & Song, C. (2017). The Effect of Distributed Parameters on Conducted EMI from DC-Fed Motor Drive Systems in Electric Vehicles. Energies, 10(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10010001






