Adaptively Constrained Stochastic Model Predictive Control for the Optimal Dispatch of Microgrid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- An adaptively constrained stochastic MPC approach is proposed to coordinate the energy storage unit and uncertain RESs/electric loads in MGs, in which there is no any requirement for a priori information about the probability distribution of the uncertainties.
- (2)
- A novel online adaption strategy is developed, in which the current change rate of constraint violation frequency is considered in order to improve the dynamic performance of the MG dispatch method.
- (3)
- In cases of uncertain RESs generation and electricity load, the proposed adaptively constrained stochastic MPC method can improve the dispatch performance compared with the scenarios-based robust MPC and adaptively constrained stochastic MPC with other adaption strategies.
2. Modeling of Adaptively Constrained Stochastic MPC for MG Dispatch
2.1. Problem Description of the Chance-Constrained MPC in MG Dispatch
2.2. Mathematical Formulation of Adaptively Constrained Stochastic MPC for MG Dispatch
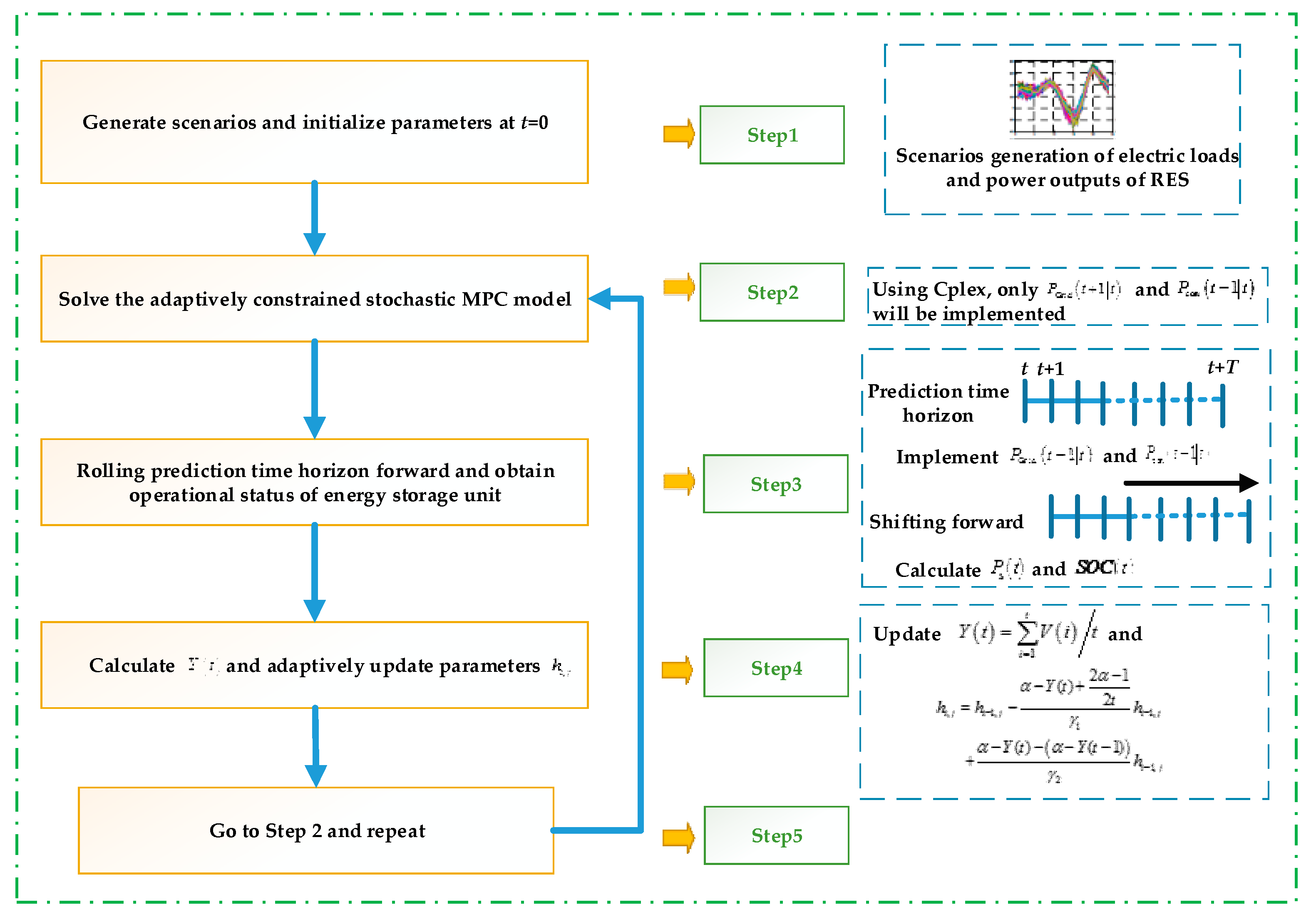
3. Solving of Adaptively Constrained Stochastic MPC for MG Dispatch
- Step (1)
- When t = 0, generate scenarios of electric loads and power outputs of RES over the prediction time horizon T, and initialize the parameters .
- Step (2)
- Solve the adaptively constrained stochastic MPC optimization model, i.e., the objective (2) and the constraints (3)–(12) and (17)–(20), with respect to time t via Cplex, and only the dispatch results and for the next time step (t + 1) in control sequence will be implemented.
- Step (3)
- The prediction time horizon is shifted forward (i.e., the time instant moves to t = t + 1), and with the actual values of electricity load and RES power output at time t and the dispatching results derived in Step (2), calculate the actual power output of energy storage unit at time t according to the supply and demand balance of the electricity power, and then derive of energy storage unit.
- Step (4)
- Calculate via (21), and adaptively update parameters via (22).
- Step (5)
- Go to Step (2) and repeat.
4. Simulation Results and Discussions
4.1. Comparison between the Proposed Method and the Robust MPC via Scenarios Optimization
4.2. Comparison among Different Adaptive Constraint Update Strategies
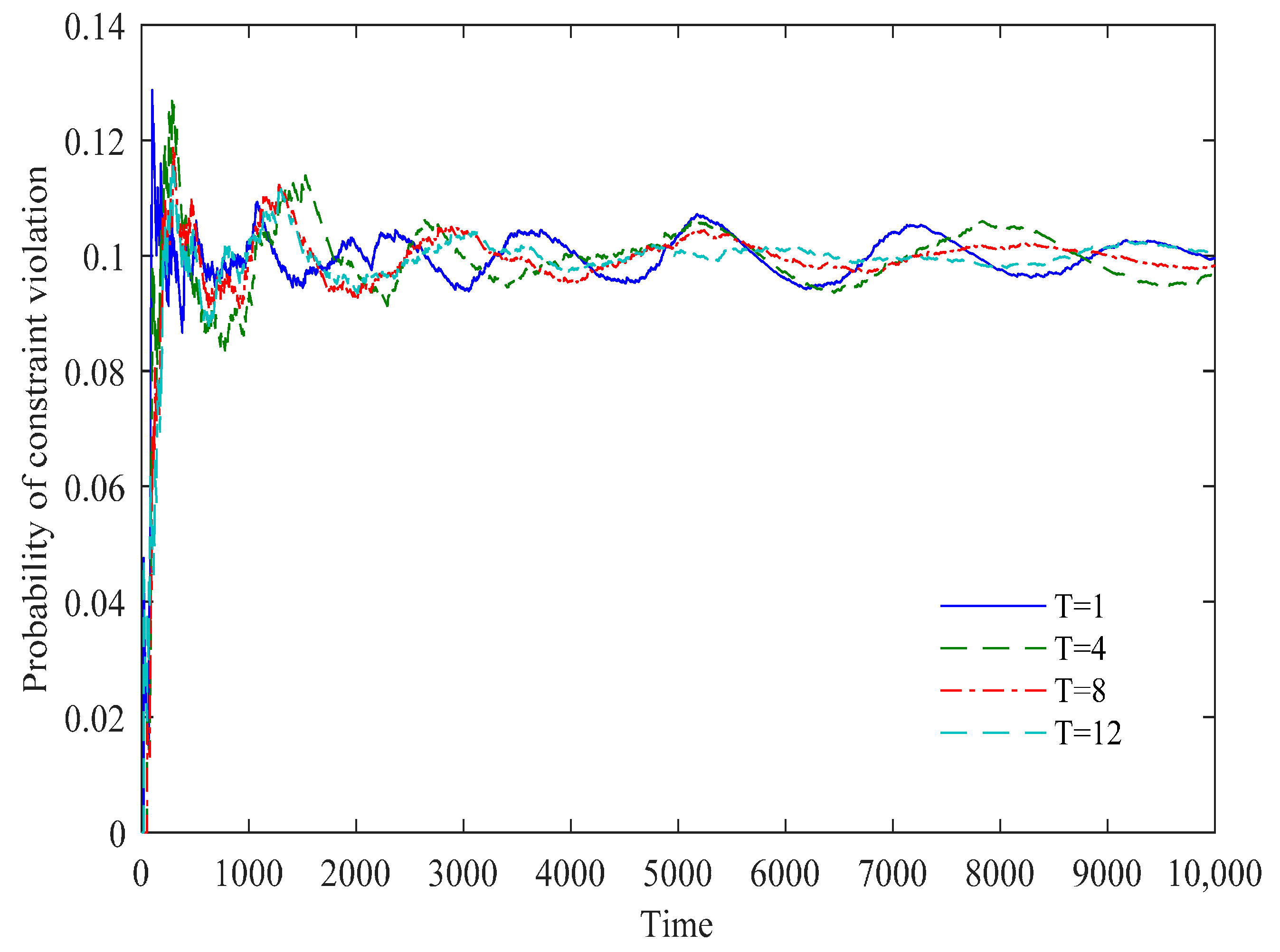
4.3. Influence of Prediction Horizon on Control Performance
4.4. Influence of Constraint Update Parameters on Performance
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Subscripts | |
| con | Controllable generator in MG |
| Grid | Electricity purchase from the distribution grid |
| s | Energy storage unit |
| L | Electric loads |
| RES | Renewable energy source |
| ch | Charging of energy storage unit |
| disch | Discharging of energy storage unit |
| max | Suggested maximum value |
| min | Suggested minimum value |
| Parameters | |
| RD | Ramping down limit |
| RU | Ramping up limit |
| Cost coefficient of controllable generator operation | |
| Price of purchasing electricity from the distribution grid | |
| Charging/discharging efficiency of energy storage unit | |
| T | Prediction time horizon |
| Desired constraint violation level | |
| C | Capacity of energy storage unit |
| Variables | |
| P | Electric power |
| SOC | State-of-charge of energy storage unit |
| I | Charging/discharging status of energy storage unit |
| X | Percentage of maximum charging or discharging power |
| V | Indicator representing the constraint violation status |
| Y | Cumulative probability of constraint violation |
References
- Hatziargyriou, N.; Asona, H.; Iravani, R.; Marnay, C. Microgrids. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 2007, 5, 78–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katiraei, F.; Iravani, R.; Hatziargyriou, N.; Dimeas, A. Microgrids management: Controls and operation aspects of microgrids. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 2008, 6, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, Z.; Yang, Q.; Xu, L.; Wu, T. A multi time-scale and multi energy-type coordinated microgrid scheduling solution-part I: Model and methodology. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2015, 30, 2257–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, Z.; Yang, Q.; Xu, L.; Wu, T. A multi time-scale and multi energy-type coordinated microgrid scheduling solution-part II: Optimization algorithm and case studies. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2015, 30, 2267–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Cheng, M. Intelligent control battery equalization for series connected lithium-ion battery strings. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2005, 52, 1297–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, P.; Liang, D.; Gao, L.; Gao, F. Stochastic coordination of plug-in electric vehicles and wind turbines in microgrid: A model predictive control approach. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2016, 7, 1537–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Jia, Q.; Guan, X. Multi-timescale optimization between distributed wind generators and electric vehicles in microgrid. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering (CASE), Gothenburg, Sweden, 24–28 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cominesi, S.R.; Farina, M.; Giulioni, L.; Picasso, B.; Scattolini, R. Two-layer predictive control of a micro-grid including stochastic energy sources. In Proceedings of the 2015 American Control Conference, Chicago, IL, USA, 1–3 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Otomega, B.; Marinakis, A.; Glavic, M.; Cutsem, T. Model predictive control to alleviate thermal overloads. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2007, 22, 1384–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meibom, P.; Barth, R.; Hasche, B.; Brand, H.; Weber, C.; O’Malley, M. Stochastic optimization model to study the operational impacts of high wind penetrations in Ireland. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2011, 26, 1367–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Zhang, J.; Elaiw, A. A model predictive control approach to dynamic economic dispatch problem. In Proceedings of the IEEE Bucharest Power Tech Conference, Bucharest, Romania, 28 June–2 July 2009; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Biyik, E.; Chandra, R. Optimal control of microgrids-algorithms and field implementation. In Proceedings of the 2014 American Control Conference, Portland, OR, USA, 4–6 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Olivares, D.E.; Mehrizi-Sani, A.; Etemadi, A.H.; Hatziargyriou, N.D. Trends in microgrid control. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2014, 5, 1905–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares, D.E.; Canizares, C.A.; Kazerani, M. A centralized energy management system for isolated microgrids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2014, 5, 1864–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisio, A.; Rikos, E.; Glielmo, L. A model predictive control approach to microgrid operation optimization. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2014, 22, 1813–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Torres, F.; Valverde, L.; Bordons, C. Optimal load sharing of hydrogen-based microgrids with hybrid storage using model predictive control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 4919–4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilj, J.; Gros, S.; Jakus, D.; Zanon, M. Day-ahead scheduling and real-time economic MPC of CHP unit in Microgrid with smart buildings. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.G.; Wu, J.; Li, S.Y.; Long, C.N.; Paschalidis, I. Distributed MPC for coordinated energy efficiency utilization in Microgrid systems. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisio, A.; Wiezorek, C.; Kyntaja, T.; Elo, J.; Strunz, K.; Johansson, K.H. Cooperative MPC-based energy management for networked Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 8, 3066–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares, D.E.; Lara, J.D.; Canizares, C.A.; Kazerani, M. Stochastic predictive energy management system for isolated Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2015, 6, 2681–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Huang, X.L.; Xu, C.F.; Sun, H.T. Accelerated model predictive control for electric vehicle integrated Microgrid energy management: A hybrid robust and stochastic approach. Energies 2016, 9, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.S.; Kim, M.K. A dynamic economic dispatch model for uncertain power demands in an interconnected Microgrid. Energies 2017, 10, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Chae, S.; Neely, J.; Baek, J.; Cook, M. Efficient model predictive control strategies for resource management in an islanded Microgrid. Energies 2017, 10, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldewurtel, F.; Sturzenegger, D.; Esfahani, P.; Andersson, G.; Morari, M.; Lygeros, J. Adaptively constrained stochastic model predictive control for closed-loop constraint satisfaction. In Proceedings of the 2013 American Control Conference, Washingtong, DC, USA, 17–19 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Oldewurtel, F.; Roald, L.; Andersson, G.; Tomlin, C. Adaptively constrained stochastic model predictive control applied to security constrained optimal power flow. In Proceedings of the 2015 American Control Conference, Palmer House Hilton, Chicago, IL, USA, 1–3 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Calafiore, G.; Fagiano, L. Robust model predictive control via scenario optimization. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2013, 58, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejowski, J. Predictive Control with Constraints; Prentice-Hall: Harlow, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Rawlings, J.; Mayne, D. Model Predictive Control: Theory and Design; Nob Hill Publishing: Madison, WI, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]









| Index | Parameters |
|---|---|
| Exchanged power | , , |
| Controllable generator | , , |
| Energy storage unit | , , , , , , , , , |
| Index | Robust MPC via Scenarios Optimization | The Proposed Method |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum SOC | 0.770 | 0.811 |
| Minimum SOC | 0.104 | 0.084 |
| 0 | 0.0143 | |
| Maximum power (kW) | 103.41 | 126.68 |
| Minimum power (kW) | −103.98 | −123.43 |
| 0.0005 | 0.0510 | |
| 0.0006 | 0.0387 |
| Methods | T = 1 | T = 2 | T = 4 | T = 8 | T = 12 | T = 16 | T = 24 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The proposed method | 0.01 s | 0.01 s | 0.01 s | 0.01 s | 0.01 s | 0.02 s | 0.03 s |
| Robust MPC via Scenarios optimization | 0.02 s | 0.04 s | 0.20 s | 1.76 s | 6.98 s | 18.31 s | Out of memory |
| Type | Maximum Violation | Settling Time (±5%) |
|---|---|---|
| Strategy (a) | 0.1156 at t = 294 | 1438 |
| Strategy (b) | 0.1218 at t = 1281 | 8528 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, X.; Bao, Z.; Li, Z.; Yan, W. Adaptively Constrained Stochastic Model Predictive Control for the Optimal Dispatch of Microgrid. Energies 2018, 11, 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11010243
Guo X, Bao Z, Li Z, Yan W. Adaptively Constrained Stochastic Model Predictive Control for the Optimal Dispatch of Microgrid. Energies. 2018; 11(1):243. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11010243
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Xiaogang, Zhejing Bao, Zhijie Li, and Wenjun Yan. 2018. "Adaptively Constrained Stochastic Model Predictive Control for the Optimal Dispatch of Microgrid" Energies 11, no. 1: 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11010243
APA StyleGuo, X., Bao, Z., Li, Z., & Yan, W. (2018). Adaptively Constrained Stochastic Model Predictive Control for the Optimal Dispatch of Microgrid. Energies, 11(1), 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11010243






