Development of a New Bi-Arc Dynamic Numerical Model for Modeling AC Flashover Processes of EHV Ice-Covered Insulators
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. A Background of Ice-Covered Insulator Mathematical Flashover Models
2.1. The Obenaus/Rizk Single Arc Flashover Model
2.2. The Principle of the Static Mathematical Multi-Arcs Model
2.3. The Principle of Dynamic Mathematical Multi-Arcs Models
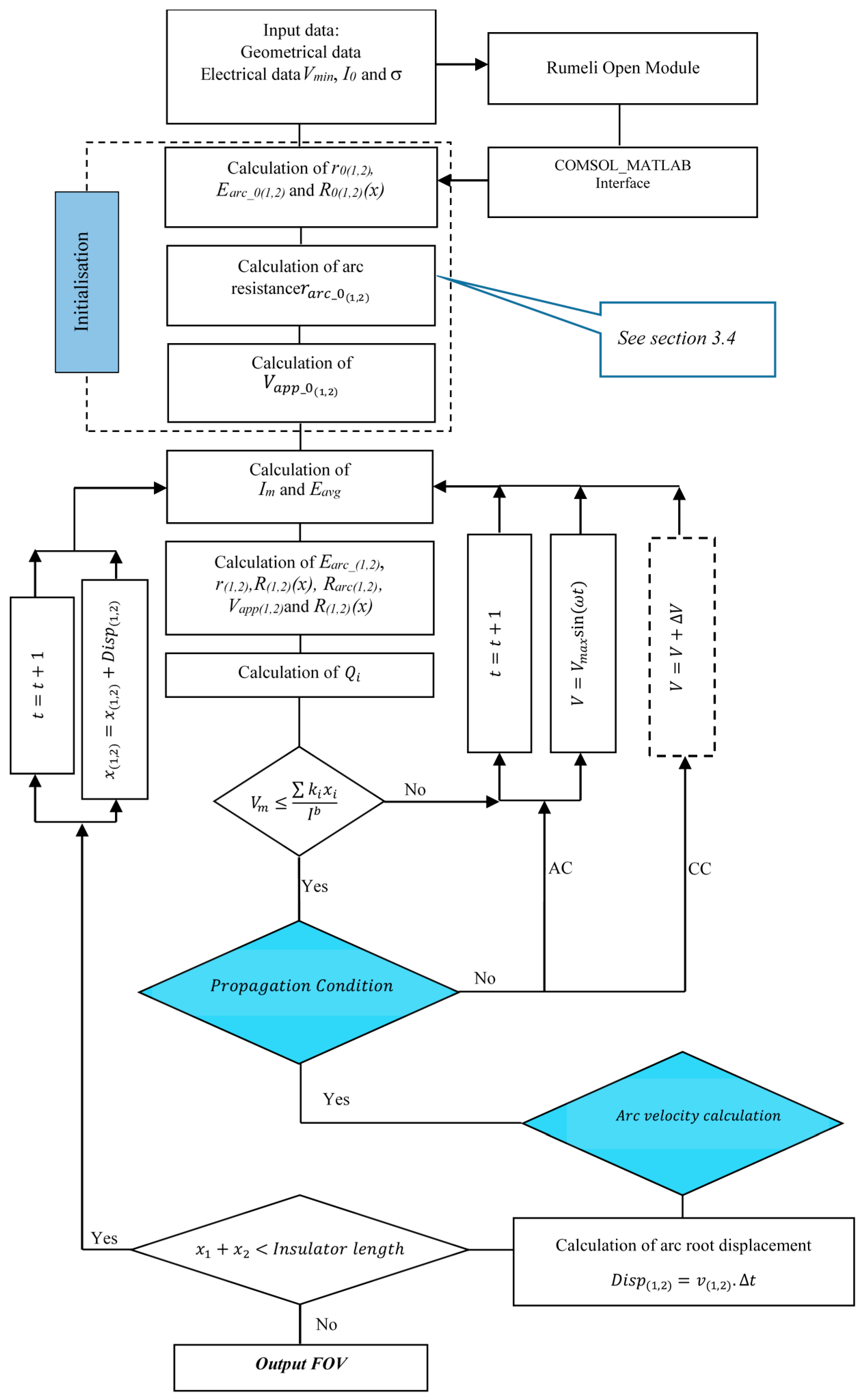
3. Numerical Implementation of the Bi-Arc Flashover Model
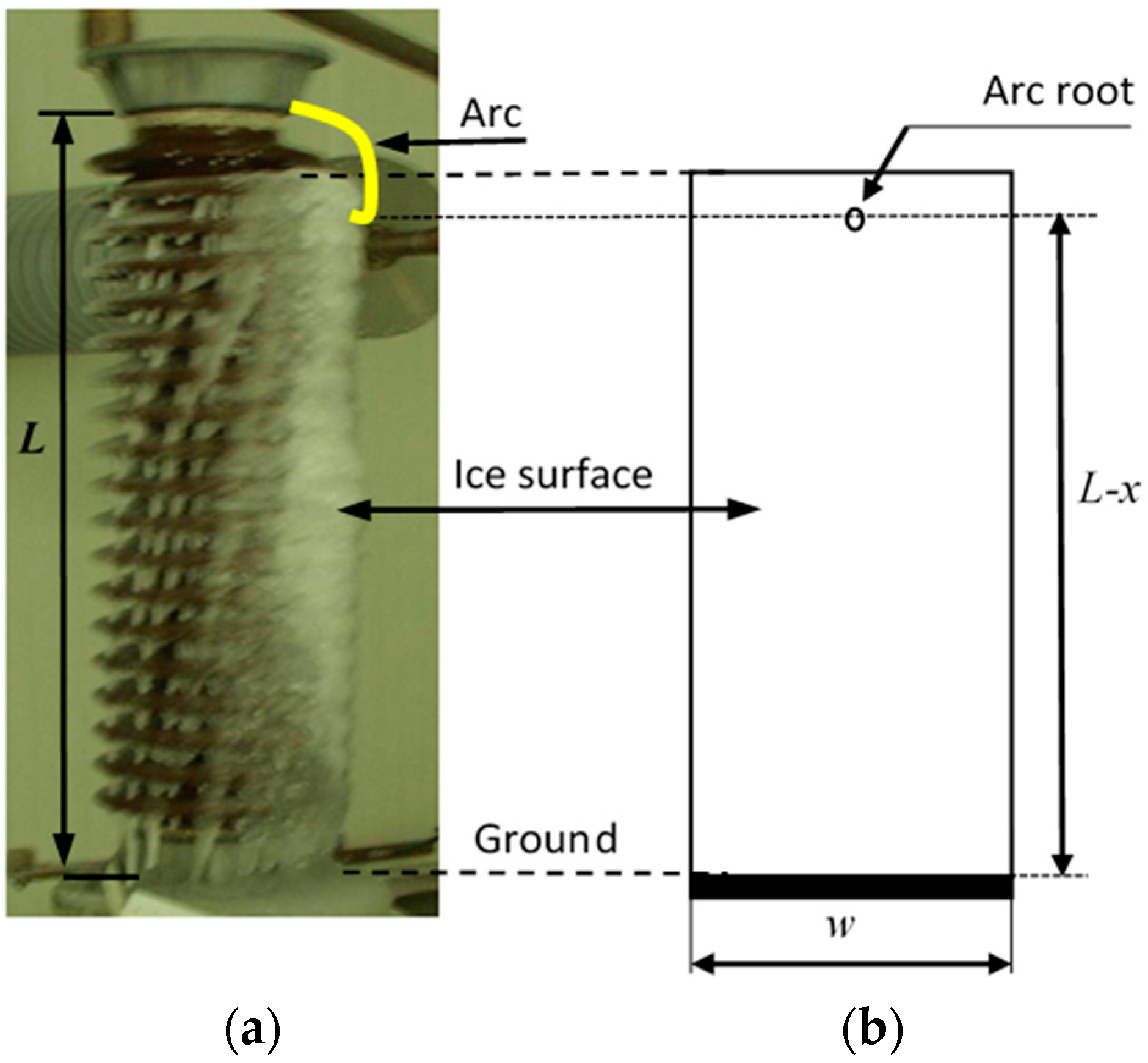
3.1. The Single Arc Dynamic Numerical Model
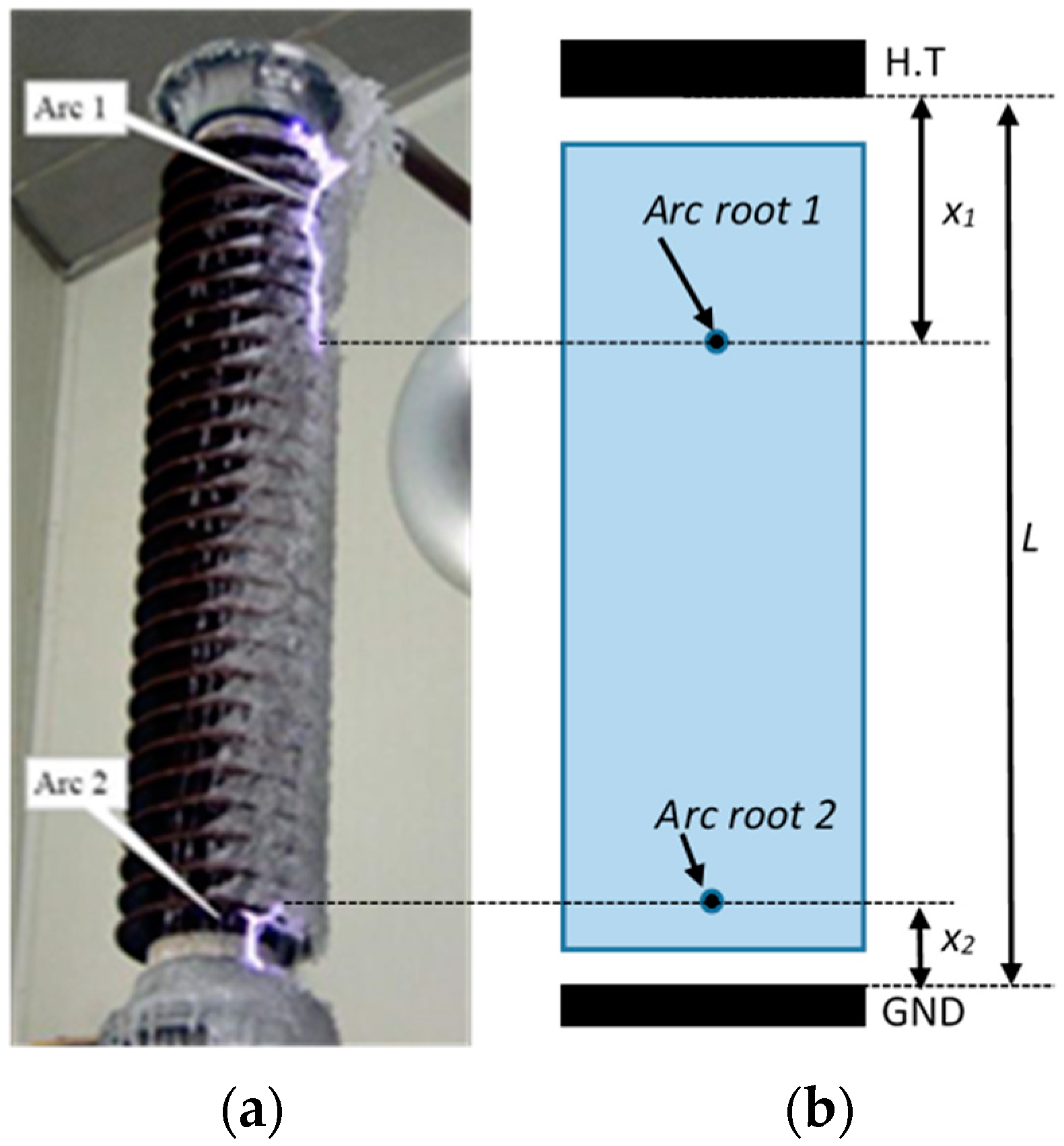
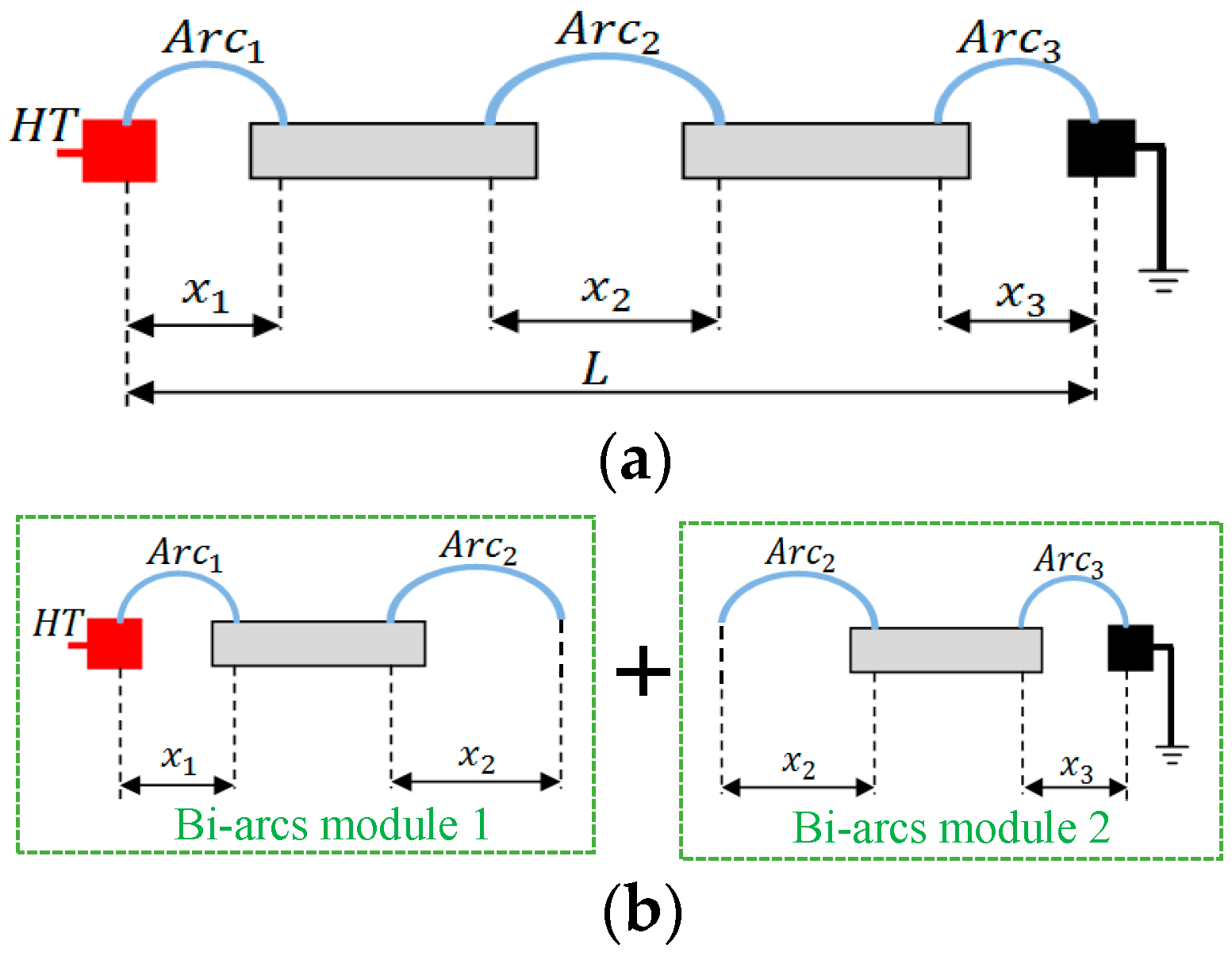
3.2. The Principle of the Bi-Arc Dynamic Numerical Model
3.3. The Validation of the Bi-Arc Dynamic Numerical Model
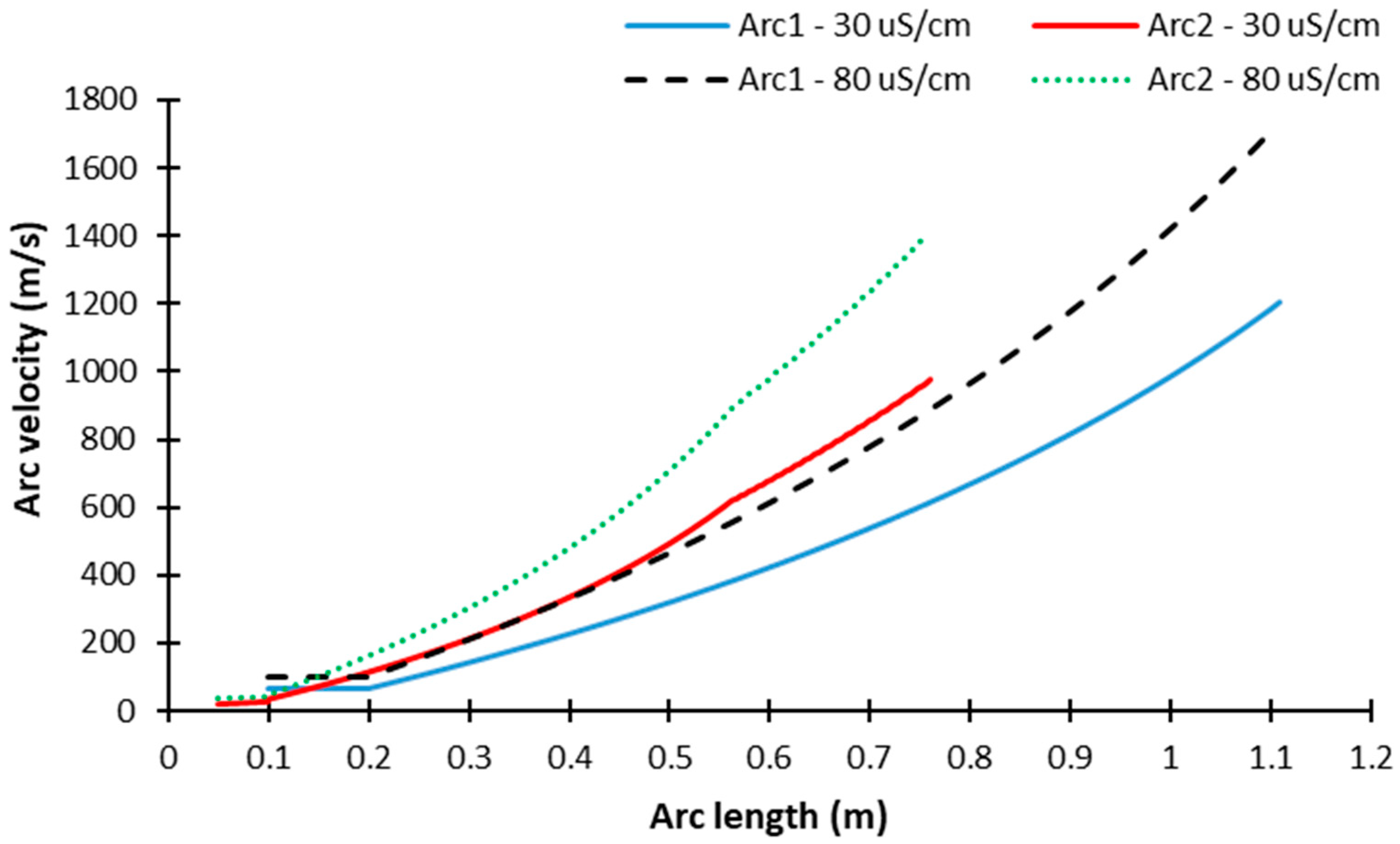
3.3.1. The Effect of Arcing Distance and Freezing Water Conductivity
3.3.2. The Effect of the Initial Partial Arc Length
3.4. Implementation of the Mayr Approach in the Bi-Arc Dynamic Numerical Model
3.4.1. Arc Resistance Formulation by Mayr
3.4.2. Validation of the Implementation of the Mayr Arc Resistance Formulation
4. Discussion
4.1. Validation of the Bi-Arc Dynamic Numerical Model Results
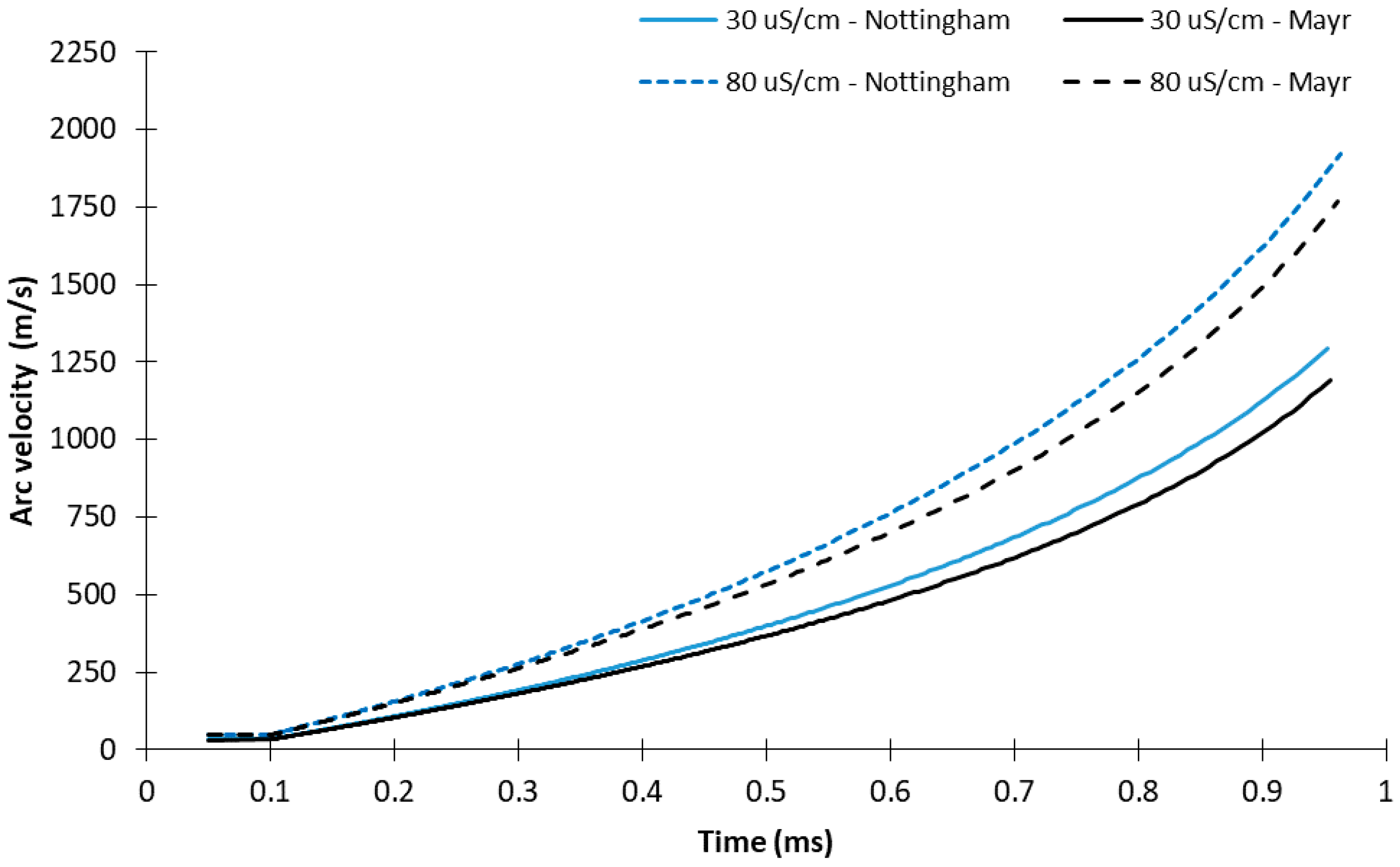
4.2. Comparison of Nottingham and Mayr Approaches
4.3. The Proposition to Extend the Bi-Arc Dynamic Numerical Model to Multi-Arc Flashover Modeling
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khalifa, M.M.; Morris, R.M. Performance of line insulators under rime ice. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 1967, PAS-86, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, A.; Niggli, W.M. The influence of snow and ice deposits on supertension transmission line insulator strings with special reference to high altitude operation. IEEE Conf. Publ. 1968, 44, 386–395. [Google Scholar]
- Kawai, M. AC flashover tests at project UHV on ice- coated insulators. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 1970, PAS-89, 1800–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzaneh, M.; Chisholm, W.A. 50 Years of Icing Performance of Outdoor Insulators. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 2014, 30, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzaneh, M.; Chisholm, W.A. Insulators for Icing and Polluted Environments; IEEE Press Series on Power Engineering; John Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; ISBN 9780470496251. [Google Scholar]
- Fikke, S.M. Possible Effects of Contaminated Ice on Insulator Strength. In Proceedings of the 5th International Workshop on Atmospheric Icing of Structures (IWAIS), Tokyo, Japan, 29 October–1 November 1990; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Makkonen, H.; Komuro, H.; Takasu, K. Withstand voltage characteristics of insulator string covered with snow and ice. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 1991, 6, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar]
- Farzaneh, M.; Kiernicki, J. Flashover problems caused by ice build-up on insulators. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 1995, 11, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volat, C.; Farzaneh, M. 3-D Modeling of Potential and Electric Field Distributions along an EHV Ceramic Post Insulator Covered with Ice—Part I: Simulations During a Melting Period. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2005, 20, 2006–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volat, C.; Farzaneh, M. 3-D Modeling of Potential and Electric Field Distributions along an EHV Ceramic Post Insulator Covered with Ice—Part II: Influence of Air Gaps and Partial Arcs. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2005, 20, 2014–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farokhi, S.; Nekahi, A.; Farzaneh, M. Mechanisms and Processes of Arc Propagation over an Ice-Covered Surface. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2014, 21, 2634–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzaneh, M.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X. Modeling of the AC Arc Discharge on Ice Surfaces. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 1997, 12, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzaneh, M.; Zhang, J. Modeling of DC arc discharge on ice surfaces. IEE Proc. Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2000, 147, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzaneh, M.; Zhang, J. A Multi-Arc Model for Predicting AC Critical Flashover Voltage of Ice-Covered Insulators. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2007, 14, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzaneh, M.; Fofana, I.; Tavakoli, C.; Chen, X. Dynamic modeling of dc arc discharge on ice surfaces. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2003, 10, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, C.; Farzaneh, M.; Fofana, I.; Beroual, A. Dynamics and Modeling of AC Arc on Ice Surfaces. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2006, 13, 1278–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, S.; Farzaneh, M.; Fofana, I. Improved Dynamic Model of DC Arc Discharge on Ice-covered Post Insulator Surfaces. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2014, 21, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, S.; Farzaneh, M.; Fofana, I. Dynamic Modeling of AC Multiple Arcs of EHV Post Station Insulators Covered with Ice. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2015, 22, 2214–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obenaus, F. Fremdschichtüberschlag und KriechwegLange. Dtsch. Elektrotech. 1958, 4, 135–136. [Google Scholar]
- Rizk, F.A.M. Mathematical Models for Pollution Flashover. Electra 1981, 103, 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins, R. Flashover Voltage of High-voltage Insulators with Uniform Surface-pollution Films. Proc. Inst. Electr. Eng. 1969, 116, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volat, C.; Farzaneh, M.; Mhaguen, N. Improved FEM models of one-and two- arcs to predict AC critical flashover voltage of ice covered insulators. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2011, 18, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbari, M.; Volat, C.; Farzaneh, M. A New Single-arc AC Dynamic FEM Model of Arc Propagation on Ice Surfaces. In Proceedings of the IEEE Electrical Insulation Conference (EIC), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 3–7 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jabbari, M.; Volat, C.; Fofana, I. Application of a New Dynamic Numerical Model to Predict Polluted Insulator Flashover Voltage. In Proceedings of the IEEE Electrical Insulation Conference (EIC), Philadephia, PA, USA, 8–11 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Nottingham, W.B. A new equation for the static characteristic of the normal electric arc. J. Am. Inst. Electr. Eng. 1923, 42, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayr, O. BeitragzurTheorie der Statischen und der Dynamischen Lichtbogens. Arch. Elektrotech. 1943, 37, 588–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessedik, S.A.; Hadi, H.; Volat, C.; Jabbari, M. Refinement of Residual Resistance Calculation Dedicated to Polluted Insulator Flashover Models. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2014, 21, 1207–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampton, B.F. Flashover mechanism of polluted insulation. Inst. Electr. Eng. IEE 1964, 111, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondiou-Clergerie, A.; Gallimberti, I. Theoretical modelling of the development of the positive spark in long gaps. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1994, 27, 1252–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| A | 204.7 |
| n | 0.561 |
| Ve | 0 |
| B | 0.875 |
| α | 0.0675 |
| β | 2.45 |
| K1 | 1118 |
| K2 | 1300 |
| b | 0.528 |
| Ice Thickness (cm) | σ (µs/cm) | Experimental FOV (kVrms) | Numerical Dynamic FOV (kVrms) | Absolute Discrepancy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arcing distance of 139 cm | ||||
| 1.5 | 30 | 130 | 130.4 | 0.31 |
| 1.5 | 80 | 120 | 117.1 | 2.17 |
| 2 | 80 | 120 | 124.0 | 3.3 |
| Arcing distance of 202 cm | ||||
| 1.5 | 30 | 190 | 189.0 | 0.53 |
| 1.5 | 80 | 161 | 160.3 | 0.43 |
| 2 | 80 | 150 | 147.5 | 1.67 |
| Ice Thickness (cm) | σ (µs/cm) | FOV for x01 = x02 (kVrms) | FOV for x01 = 2x02 (kVrms) | Absolute Discrepancy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arcing distance of 139 cm | ||||
| 1.5 | 30 | 130.4 | 130.7 | 0.23 |
| 1.5 | 80 | 117.1 | 117.5 | 0.34 |
| Arcing distance of 202 cm | ||||
| 1.5 | 30 | 189.0 | 187.2 | 0.95 |
| 1.5 | 80 | 160.3 | 157.7 | 1.61 |
| σ (µs/cm) | Experimental FOV (kVrms) | FOV with Nottingham (kVrms) | FOV with Mayr (kVrms) | Absolute Discrepancy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | (%) | ||||
| Arcing distance of 139 cm | |||||
| 30 | 130 | 130.4 | 136.4 | 0.31 | 4.92 |
| 80 | 120 | 117.1 | 125.0 | 2.17 | 4.17 |
| Arcing distance of 202 cm | |||||
| 30 | 190 | 189.0 | 191.0 | 0.53 | 0.53 |
| 80 | 161 | 160.3 | 160.8 | 0.43 | 0.12 |
| σ (µs/cm) | Experimental FOV (kVrms) | FOV with Nottingham (kVrms) | FOV with Mayr (kVrms) | Absolute Discrepancy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | (%) | ||||
| Arcing distance of 139 cm | |||||
| 30 | 130 | 130.7 | 132.3 | 0.53 | 1.77 |
| 80 | 120 | 117.5 | 122.8 | 2.08 | 2.33 |
| Arcing distance of 202 cm | |||||
| 30 | 190 | 187.2 | 182.7 | 1.47 | 3.84 |
| 80 | 161 | 157.7 | 163.5 | 2.05 | 1.55 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jabbari, M.; Volat, C.; Fofana, I. Development of a New Bi-Arc Dynamic Numerical Model for Modeling AC Flashover Processes of EHV Ice-Covered Insulators. Energies 2018, 11, 2792. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11102792
Jabbari M, Volat C, Fofana I. Development of a New Bi-Arc Dynamic Numerical Model for Modeling AC Flashover Processes of EHV Ice-Covered Insulators. Energies. 2018; 11(10):2792. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11102792
Chicago/Turabian StyleJabbari, Marouane, Christophe Volat, and Issouf Fofana. 2018. "Development of a New Bi-Arc Dynamic Numerical Model for Modeling AC Flashover Processes of EHV Ice-Covered Insulators" Energies 11, no. 10: 2792. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11102792
APA StyleJabbari, M., Volat, C., & Fofana, I. (2018). Development of a New Bi-Arc Dynamic Numerical Model for Modeling AC Flashover Processes of EHV Ice-Covered Insulators. Energies, 11(10), 2792. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11102792







