Permanent Magnet Brushless DC Motor and Mechanical Structure Design for the Electric Impact Wrench System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Motor Design Process
2.1. IPMBLDC motor Structure Consideration
2.1.1. Control Type
2.1.2. Motor Structure
2.1.3. Permanent Magnet Material
2.2. Preliminary Stator Sizing
2.3. Stator Core Design
2.4. Stator Slot and Winding Design
2.5. Magnetic Bridge and Rib
2.6. Working Point of a Permanent Magnet and Air Gap Size
2.7. Size of the Permanent Magnet
2.8. Improved Magnet Circuit Model of IPMBLDC motor
3. The Design and Calculation of Impact Wrench
3.1. Working Principle
3.2. Planetary Gear Ration Calculations and Design
3.3. The Main Compression Spring Design
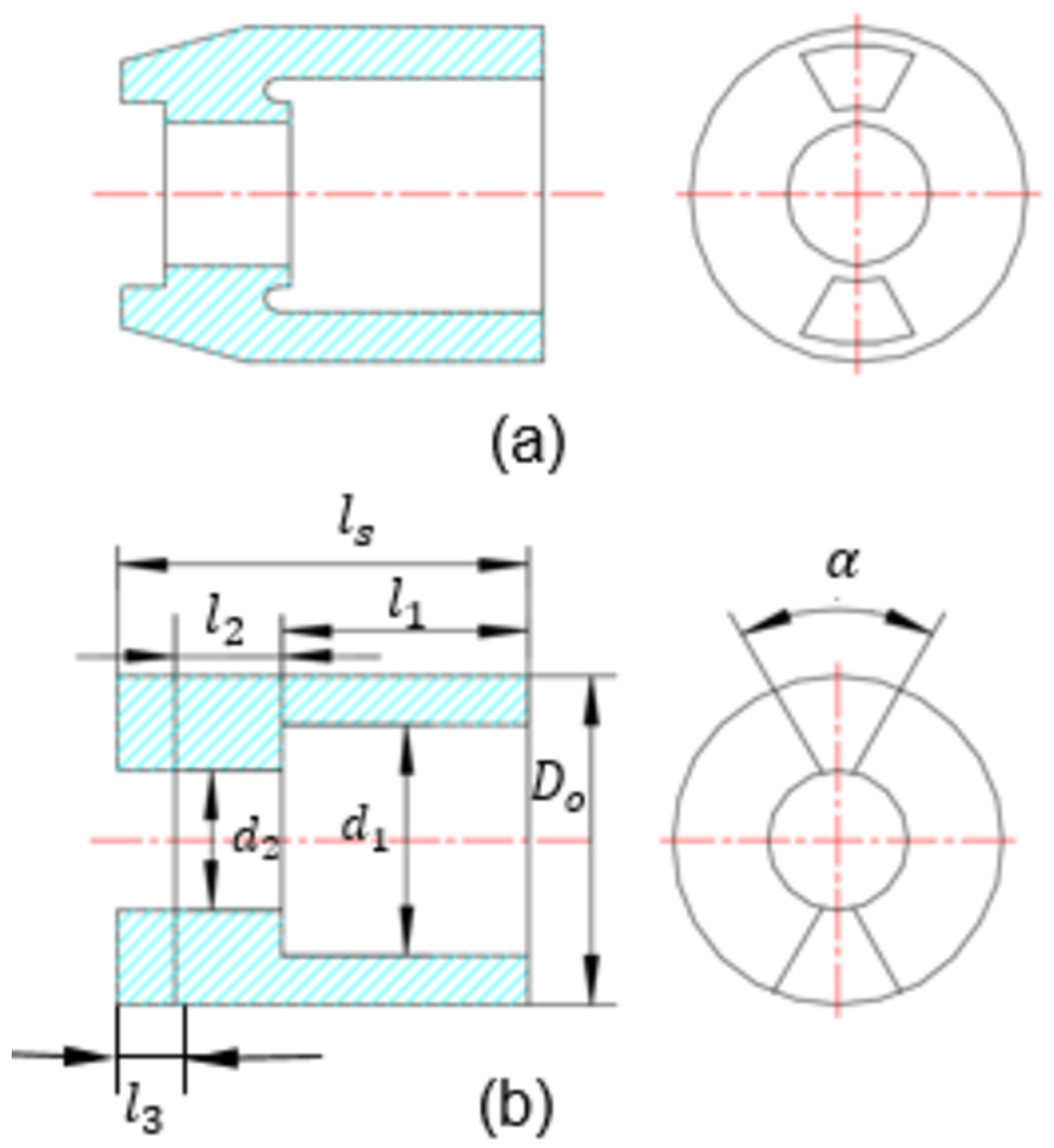
3.4. Shock Block Dynamic Calculation and Design
4. Performance Analysis
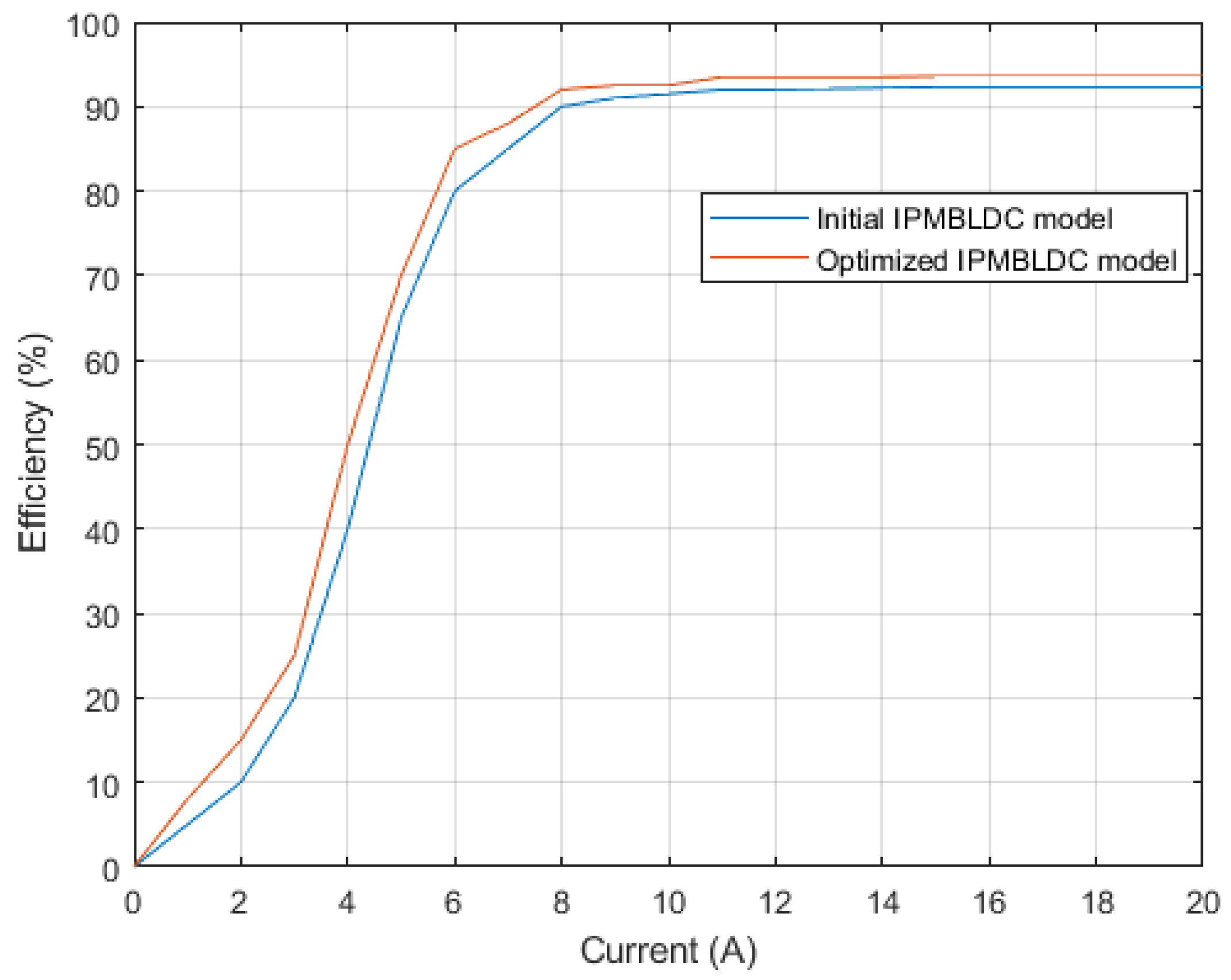
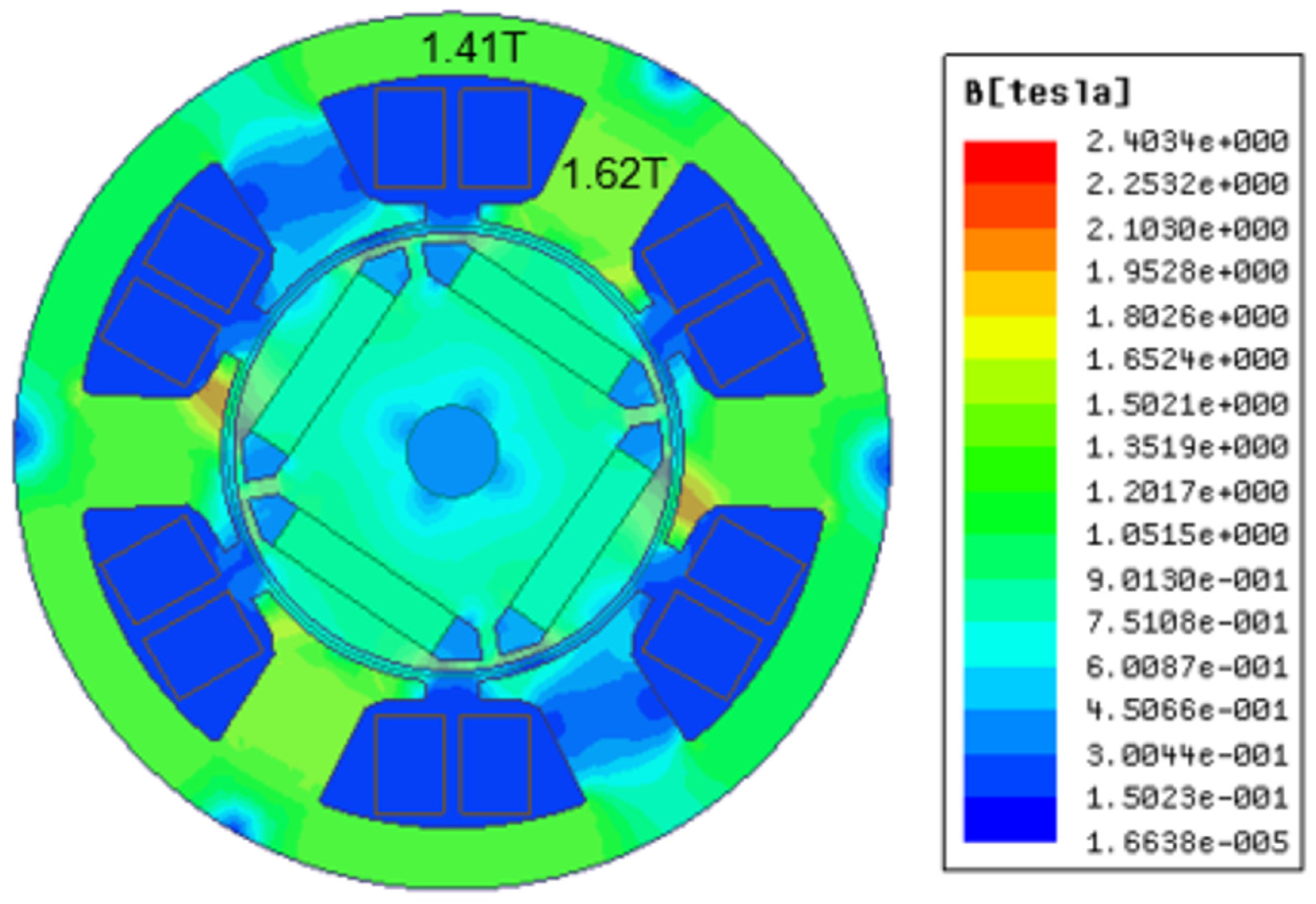
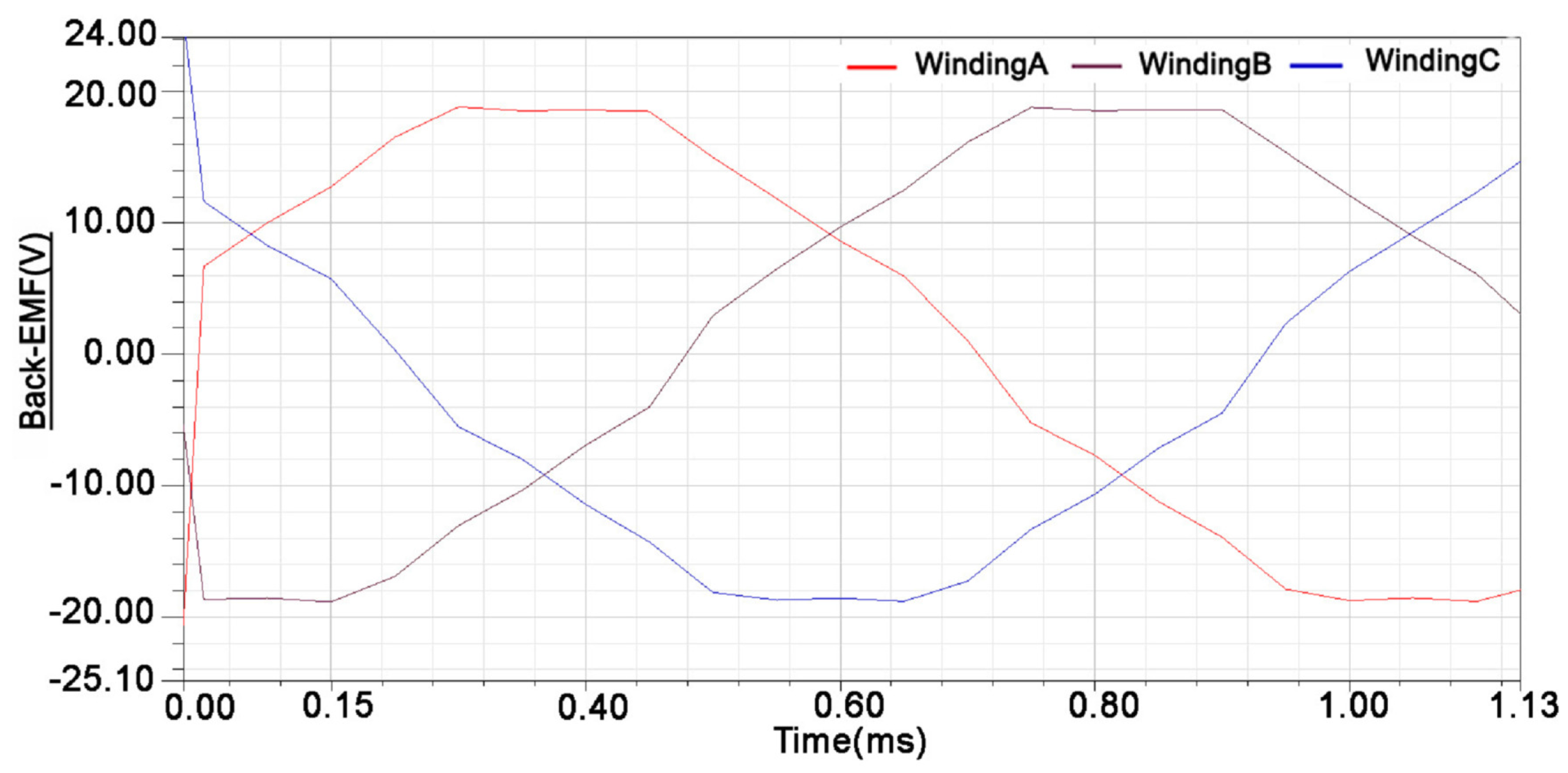
4.1. Optimization and Simulation
4.2. Thermal Analysis and Cooling
5. Experiment
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jang, S.M.; Cho, H.W.; Choi, S.K. Design and Analysis of a High-Speed Brushless DC Motor for Centrifugal Compressor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2007, 43, 2573–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Wu, T.; Wu, W.; Chow, L.; Harms, J.; Taylor, D.R. Design, analysis and experiment of a high efficiency permanent magnet truck alternator. In Proceedings of the 43rd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IECON 2017), Beijing, China, 29 October–1 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Seol, H.S.; Kang, D.W.; Jun, H.W.; Lim, J.; Lee, J. Design of Winding Changeable BLDC Motor Considering Demagnetization in Winding Change Section. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Liu, K.; Wang, Q. Scheme based on buck-converter with three phase H-bridge combinations for high-speed BLDC motors in aerospace applications. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2018, 12, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, W.; Ren, H. Fault-tolerant inverter for high-speed low-inductance BLDC drives in aerospace applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 2452–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batzel, T.D.; Lee, K.Y. Electric Propulsion with Sensorless Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor: Implementation and Performance. IEEE Trans. Energy. Convers. 2005, 20, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.-S.; Choi, J.-S.; Chung, D.-H. Maximum Torque Control of an IPMSM Drive Using an Adaptive Learning Fuzzy-neural Network. J. Power Electron. 2012, 12, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-T.; Kim, K.-S.; Hwang, S.-M.; Kim, T.-J.; Jung, Y.-H. Comparison of Magnetic Forces for IPM and SPM Motor with Rotor Eccentricity. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2001, 37, 3448–3451. [Google Scholar]
- He, C.; Wu, T. Desing and analysis of a V-type fractional-slots IPMSM with distributed winding for electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the XII Internatinal Conference on Electrical Machines(ICEM), Lausanne, Switzerland, 4–7 September 2016; pp. 1459–1465. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.S.; Kwon, B.I. Optimal design of motor shape and magnetisation direction to obtain vibration reduction and average torque improvement in IPM BLDC motor. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2017, 11, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Kim, K.T.; Hur, J. Finite-Element Analysis of the Demagnetization of IPM-Type BLDC Motor with Stator Turn Fault. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, S.; Li, Q. Analytical Calculation of Air-Gap Magnetic Field Distribution and Instantaneous Characteristics of Brushless DC Motors. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2003, 18, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maetani, T.; Morimoto, S.; Yamamoto, K.; Isomura, Y.; Watanabe, A. Comparing brushless dc motors: A method ofsuppressing the shaft voltage even in a grounded motor frame. IEEE Ind. Appl. Mag. 2015, 21, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.K.; Wellawatta, T.R.; Ullah, Z.; Hur, J. New equivalent circui of IPM-type BLDC motor for calculation of shaft voltage by considering electric and magnetic fields. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 3763–3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Cho, H.W. Characteristic analysis of interior permanent-magnet synchronous machine with fractional-slot concentrated winding considering nonlinear magnetic saturation. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2016, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sashidhar, S.; Fernandes, B.G. Braking Torque Due to Cross Magnetization in Unsaturated IPM BLDC Machines and Its Mitigation. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Li, C.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, M. Stator Winding Inter-turn Short Circuit Faults Severity Detection Controlled by OWSVPWM without CMV of Five-phase FTFSCW-IPM. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Gan, L. Orthogonal multiobjective chemical reaction optimization approach for the brushless DC motor design. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri-Zarandi, R.; Mirsalim, M.; Cavagnino, A. Analysis, optimization, and prototyping of a brushless DC limited-angle torque-motor with segmented rotor pole tip structure. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 4985–4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.K.; Yi, K.P.; Jung, S.Y.; Jung, H.K.; Ro, J.S. Optimal design of an interior permanent magnet synchronous motor by using a new surrogate-assisted multi-objective optimization. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhao, X.; Jiao, Z.; Luk, P.C.K.; Jiu, C. Multi-objective optimal design of a toroidally wound radial-flux halbach permanent magnet array limited angle torque motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 2962–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insinga, A.R.; Bjørk, R.; Smith, A.; Bahl, C.R.H. Globally optimal segmentation of permanent-magnet systems. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2016, 5, 064014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhao, X.; Li, C.; Jiao, Z.; Qu, F. Multiobjective Optimization of a Hollow Plunger Type Solenoid for High Speed On/Off Valve. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 3115–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Park, G.J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, Y.J.; Jung, S.Y. Hybridization Algorithm of Fireworks Optimization and Generating Set Search for Optimal Design of IPMSM. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Tran, T.T.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, Y.J.; Jung, S.Y. Mass ionized particle optimization algorithm applied to optimal FEA-based design of electric machine. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2016, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Li, Q.; Lu, H.; Liu, Y.; Gao, H. Analytical model for armature reaction of outer rotor brushless permanent magnet DC motor. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2018, 12, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; You, Y.M.; Kwon, B.I. Rotor shape optimization of interior permanent magnet BLDC motor according to magnetization direction. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 2193–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhoff, S.D.; Krause, P.C. Operation Modes of the Brushless DC Motor with a 120° Inverter. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 1990, 5, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SimPowerSystems: Model and Simulate electrical Power systems. In User’s Guide; The MathWorks Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2010.
- Hendershot, J.R.; Miller, T.J.E. Design of Brushless Permanent-Magnet Machines; Motor Design Books: Venice, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 5–23. [Google Scholar]
- Nagrial, M.H.; Rizk, J.; Hellany, A. Design and Performance of Interior Permanent Magnet Motors with Saturating Magnetic Bridge. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electric Machines and Drives Conference (IEMDC 2009), Miami, FL, USA, 3–6 May 2009; pp. 922–927. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, R.Y. Modern Permanent Magnet Machines Theory and Design; China Machine Press: Beijing, China, 1997; pp. 161–270. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]





















| No-load main flux | |
| Average air-gap flux density | |
| Air-gap MMF | |
| Total MMF | |
| Main magnetic permeability | |
| Per-unit value of the main magnetic permeability | |
| Magnet to magnet flux leakage | |
| Magnet end flux leakage | |
| Total flux leakage | |
| Flux leakage coefficient | |
| Magnet operating point |
| Material | 60Si2MnA |
|---|---|
| Installed length | 60 mm |
| Minimum amount of elastic deformation | 5 mm |
| Maximum amount of elastic deformation | 14 mm |
| Impact stroke length h | 9 mm |
| Angle of spiral | |
| Out diameter of a coil | 71 mm |
| Inner diameter of a coil | 60 mm |
| Total number of winding | 6 |
| Number of active winding | 3 |
| Initial Design Parameters | Calculated Results | FEA | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||||
| IPMBLDC motor Model | Initial Model | Optimized Model |
|---|---|---|
| Number of the slots/poles | ||
| Stator outer diameter/mm | 48 | 48 |
| Stator inner diameter/mm | 24 | 24 |
| Air-gap length/mm | ||
| Magnet width/mm | 2.2 | |
| Magnet length/mm | ||
| Rotor bridge depth/mm | ||
| Tooth width/mm | ||
| /mm | 1 | |
| Rotor magnet web/mm | 1 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, C.; Wu, T. Permanent Magnet Brushless DC Motor and Mechanical Structure Design for the Electric Impact Wrench System. Energies 2018, 11, 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11061360
He C, Wu T. Permanent Magnet Brushless DC Motor and Mechanical Structure Design for the Electric Impact Wrench System. Energies. 2018; 11(6):1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11061360
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Chengyuan, and Thomas Wu. 2018. "Permanent Magnet Brushless DC Motor and Mechanical Structure Design for the Electric Impact Wrench System" Energies 11, no. 6: 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11061360
APA StyleHe, C., & Wu, T. (2018). Permanent Magnet Brushless DC Motor and Mechanical Structure Design for the Electric Impact Wrench System. Energies, 11(6), 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11061360





