Impeller Optimized Design of the Centrifugal Pump: A Numerical and Experimental Investigation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Basic Parameters of the Impeller
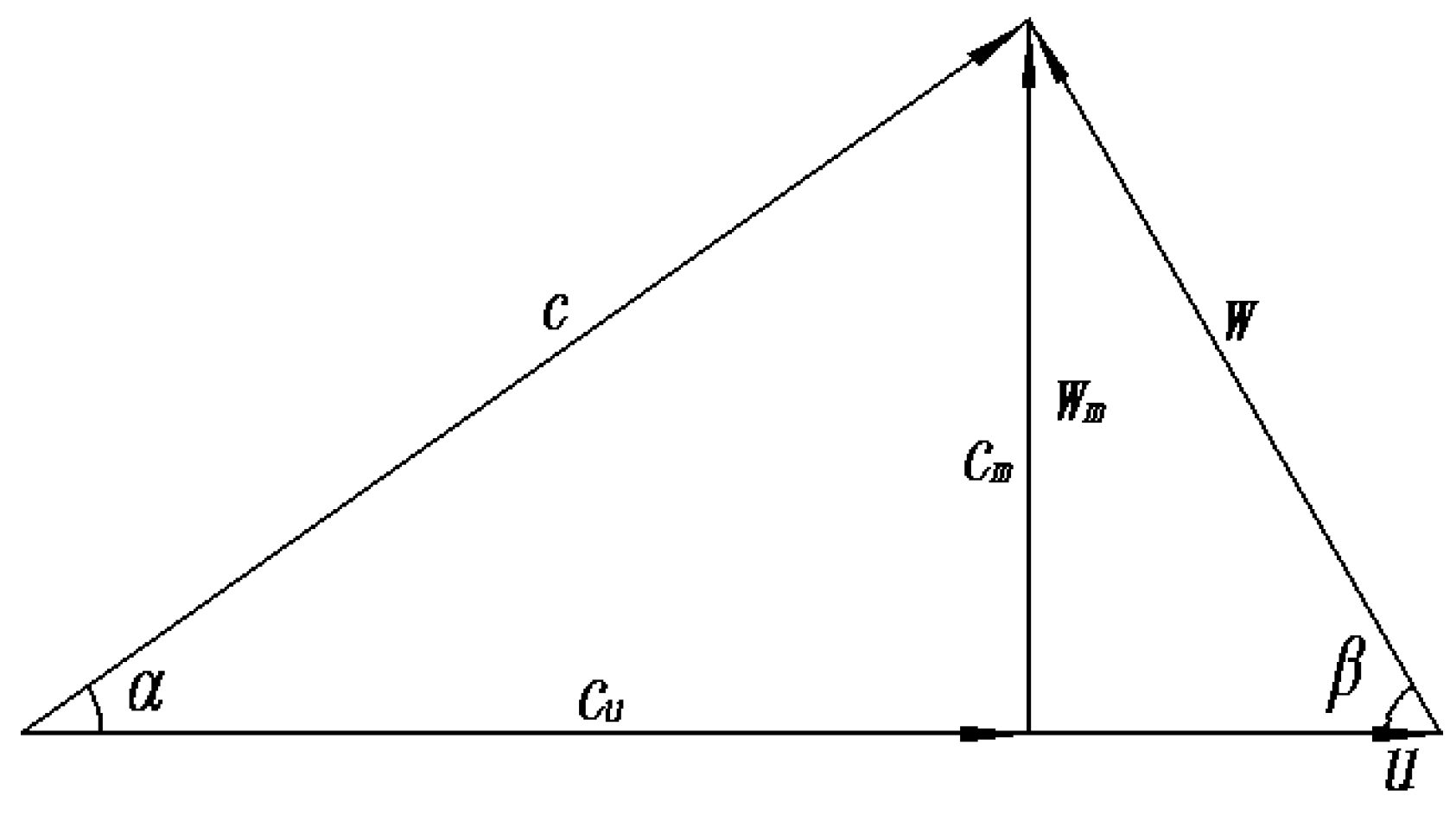
3. Method to Modify the Impeller
- (1)
- β1 is the constant. β2 and Φ are changed.
- (2)
- β1 and β2 are fixed. Φ is varied.
- (3)
- β2 and Φ are invariant. β1 is altered.
4. Numerical Method
4.1. Fundamental Equations
4.2. Turbulent Model
5. Numerical Simulation Setup
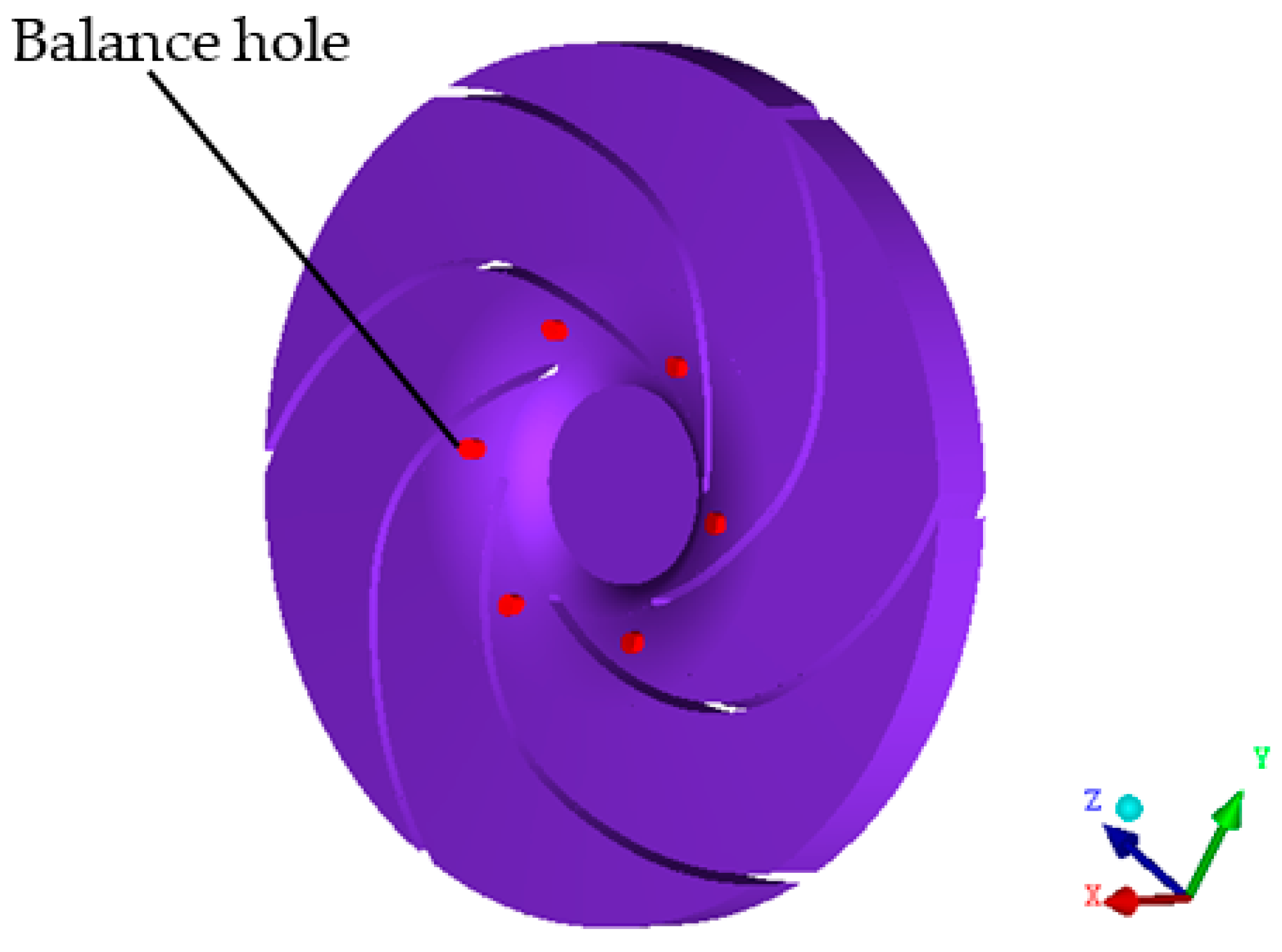
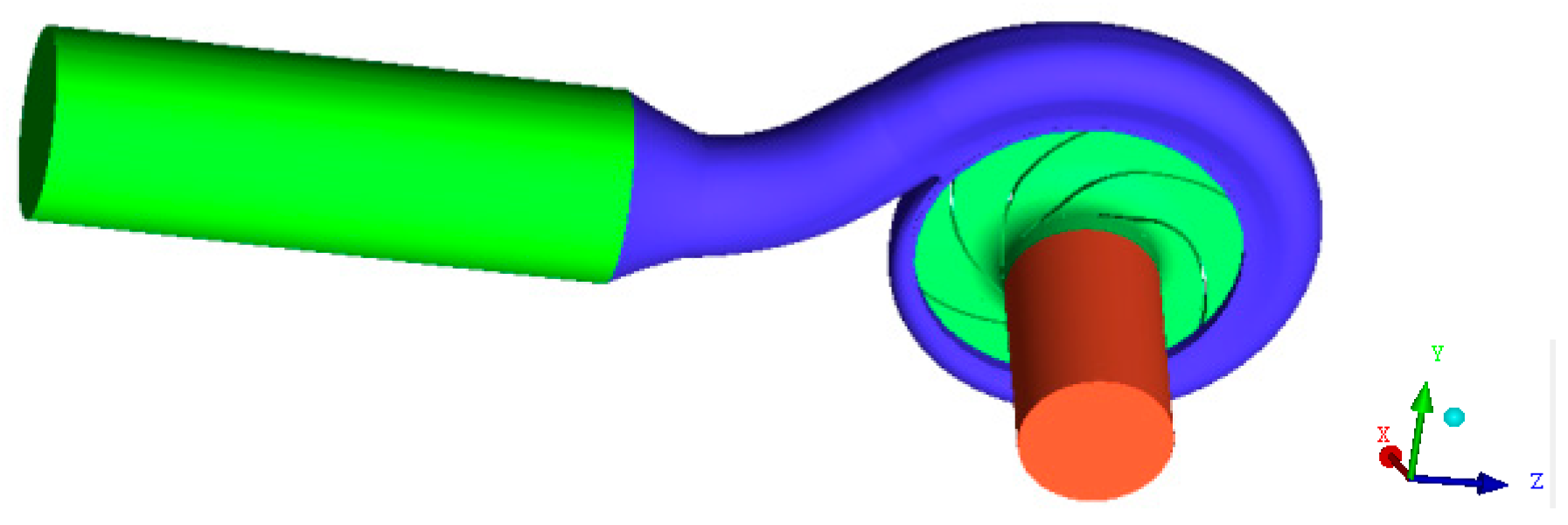
5.1. Physical Model
5.2. Mesh Generation
5.3. Boundary Conditions
5.4. Verification of the Algorithm
6. Numerical Simulation Results Analysis
6.1. Variation of Static Pressure
6.2. Variation of Relative Velocity
6.3. Variation of Streamlines
6.4. Variation of Turbulent Kinetic Energy
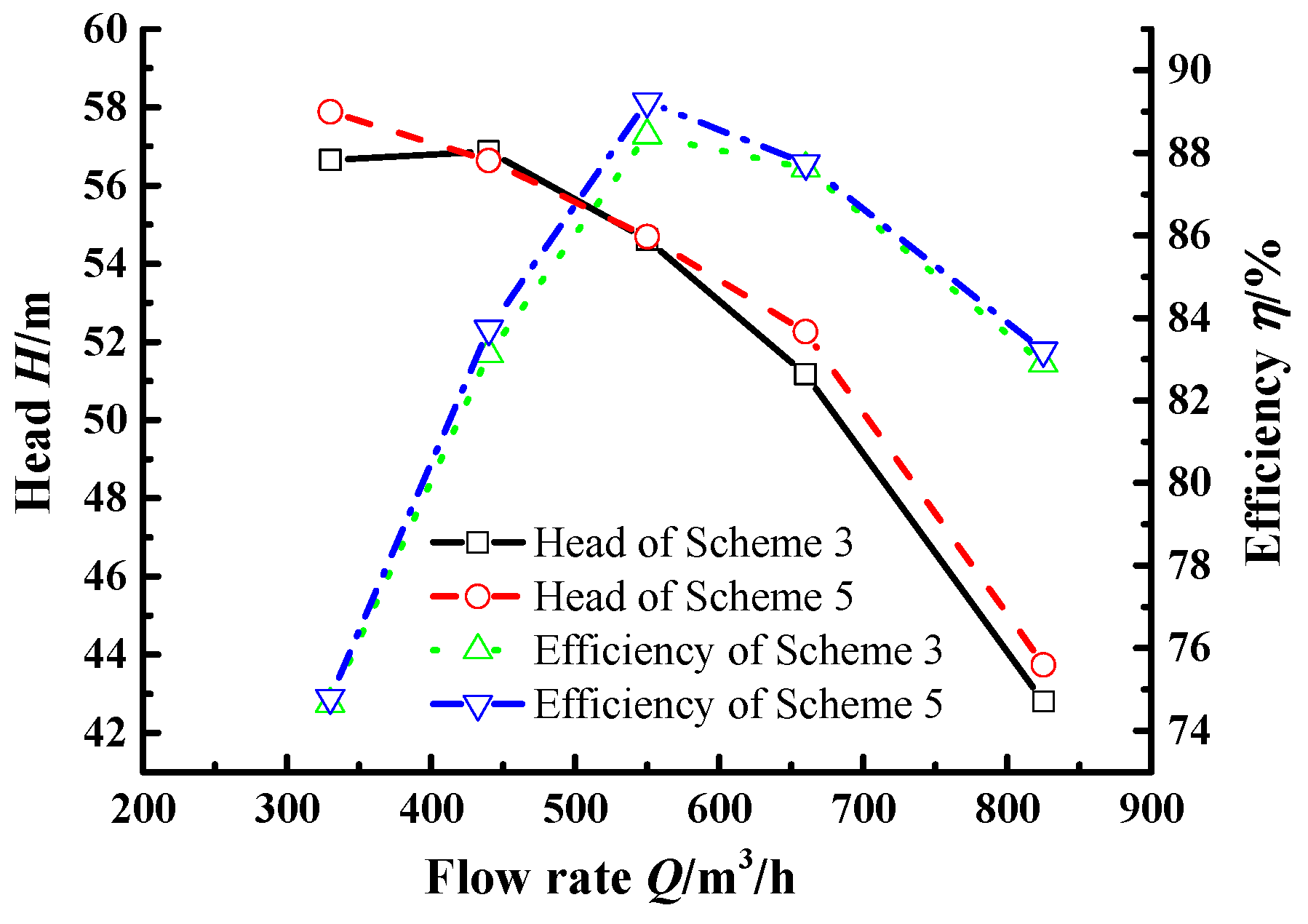
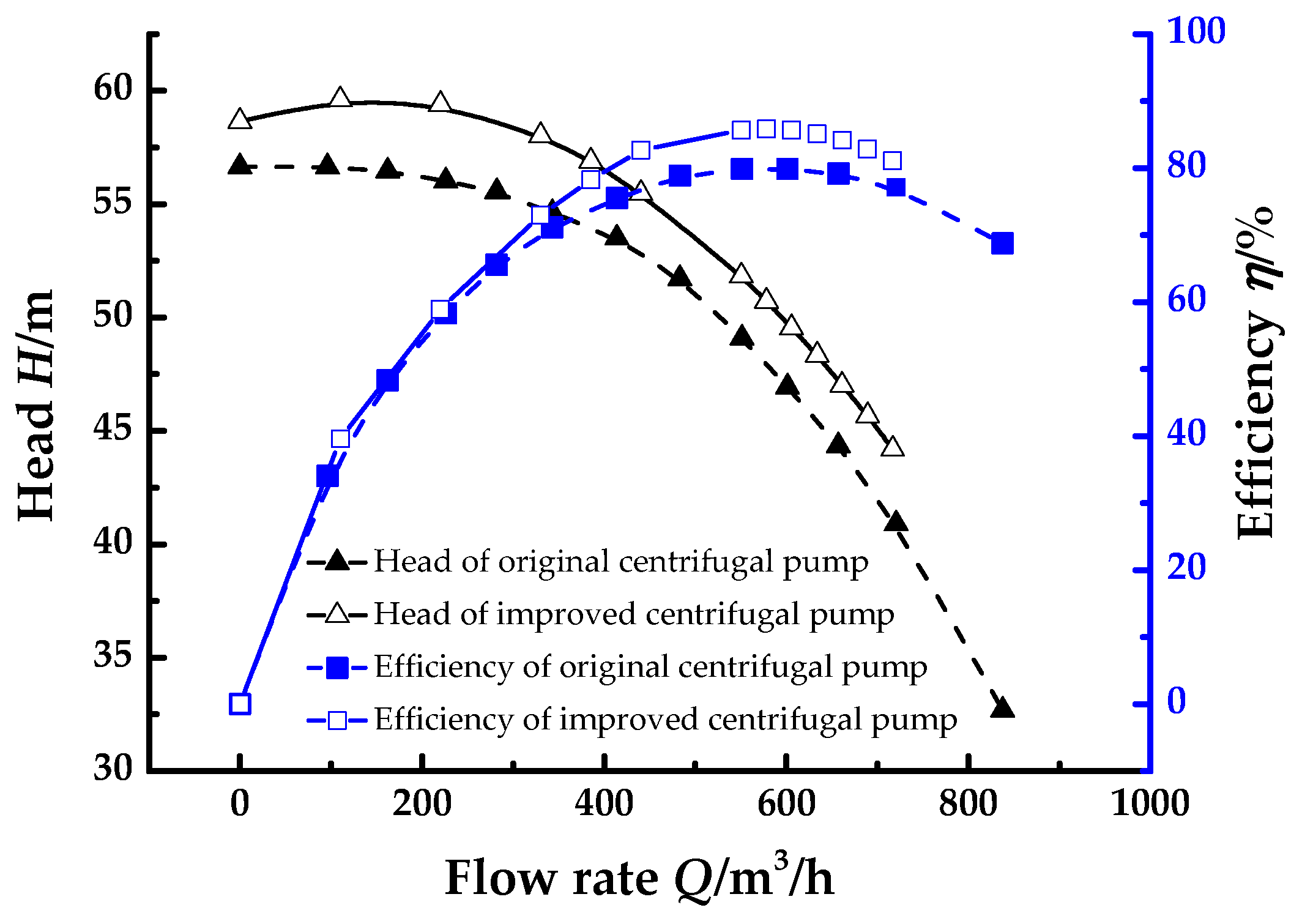
6.5. Variations of Head and Efficiency
7. Experimental Analysis
Experiment Setup
8. Conclusions
- (1)
- The impeller with blade wrap angle 126° and blade exit angle 24° was the best one.
- (2)
- For the best impeller, static pressure and relative velocity was the most uniform distribution. Streamlines were the smoothest and vortices did not exist. Compared with other impellers, the distribution scope of turbulent kinetic energy in the best impeller under all flow rate conditions was the smallest.
- (3)
- For the centrifugal pump with optimized impeller, head and efficiency were higher than that of the original pump. With low flow rate (0.8 Qd), the head and efficiency increased by 3.76 m and 3.84%. With rated flow rate, the head and efficiency increased by 2.74 m and 5.77%. With high flow rate (1.2 Qd), the head and efficiency increased by 2.67 m and 5.0%.
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yedidiah, S. Centrifugal Pump User’s Guidebook: Problems and Solutions; Springer Group: Berlin, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Gülich, J.F. Centrifugal Pumps; Springer Group: Berlin, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Karassik, I.J. Centrifugal Pump Clinic; Taylor Francis Inc.: Oxford, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Tuzson, J. Centrifugal Pump Design; Wiley-Interscience: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Grist, E. Cavitation and the Centrifugal Pump: A Guide for Pump Users; Taylor Francis Inc.: Oxford, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Lobanoff, V.S.; Ross, R.R. Centrifugal Pump: Design and Application; Gulf Professional Publishing: Houston, TX, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Girdhar, P.; Moniz, O. Practical Centrifugal Pumps. Design, Operation, Maintenance; Newnes: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.H. Three-dimensional turbomachine flow equations expressed with respect to non-orthogonal curvilinear coordinates and non-orthogonal velocity components and methods of solution. J. Mech. Eng. 1979, 15, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.H. Streamline similarity method for flow distribution and shock losses at the impeller inlet of the centrifugal pump. J. Hydrodyn. 2018, 30, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Wang, W.J.; Yuan, S.Q.; Zhang, J.F. Optimization on the impeller of a low-specific-speed centrifugal pump for hydraulic performance improvement. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2017, 29, 992–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Zhu, B.S.; Cao, S.L.; Bing, H.; Wang, Y.M. Influence of blade wrap angel on centrifugal pump performance by numerical and experimental study. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2014, 27, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, H.C.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.; Yoon, J.Y.; Choi, Y.S. Design techniques to improve the performance of a centrifugal pump using CFD. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2015, 29, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanoff, A.J. Centrifugal and Axial Pump: Theory, Design and Application; John Wiley Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, A.L.; Lang, D.P.; Li, G.P.; Chen, E.Y.; Dai, R. Numerical research about influence of blade outlet angel on flow-induced noise and vibration for centrifugal pump. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2015, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Heo, M.W.; Kim, J.H.; Seo, T.W.; Kim, K.Y. Aerodynamic and aeroacoustic optimization for design of a forward-curved blades centrifugal fan. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A J. Power Energy 2017, 230, 154–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.F. Modern Pumps Theory and Design; China Astronautic Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2011. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.X.; Kong, F.Y.; Yang, S.S.; Chen, K.; Dai, T. Effect of blade wrap angel in hydraulic turbine with forward-curved blades. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 18709–18717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.J.; Pei, J.; Yuan, S.Q.; Zhang, J.F.; Yuan, J.P.; Xu, C.Z. Application of different surrogate models on the optimization of centrifugal pump. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2016, 30, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Shi, W.D.; Wu, S.Q. Performance optimization in a centrifugal pump impeller by orthogonal experiment and numerical simulation. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2013, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelik, L. Centrifugal and Rotary Pumps: Fundamentals with Applications; CRC Press: London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.G.; Su, F.Z.; Ye, Z.M.; Xia, D.L. Experiment on effect of blade pattern on performance of centrifugal oil pumps. Chin. J. Appl. Mech. 2002, 19, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohner, R. Applied Computational Fluid Dynamics Techniques: An Introduction Based on Finite Element Methods; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Yakhot, V.; Orzag, S.A. Renormalization group analysis of turbulence: Basic theory. J. Sci. Comput. 1986, 1, 3–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Shi, W.D.; Li, W.; Agarwal, R. Numerical and experimental study of axial force and hydraulic performance in a deep-well centrifugal pump with different impeller rear shroud radius. J. Fluid Eng. 2013, 135, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posa, A.; Lippolis, A. A LES investigation of off-design performance of a centrifugal pump with variable-geometry diffuser. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2018, 70, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.X.; He, J.W.; Liu, C. Design and experiment of the centrifugal pump impellers with twisted inlet vice blades. J. Hydrodyn. 2017, 29, 1085–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.L.; Kong, F.Y.; Chen, H.; Su, X.H. Effects of blade wrap angel influencing a pump as turbine. J. Fluid Eng. 2012, 134, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, K.W.; Lee, T.S.; Winoto, S.H.; Zhao, Z.M. Numerical flow simulation in a centrifugal pump at design and off-design conditions. Int. J. Rotating Mach. 2007, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferziger, J.H.; Peric, M. Computational Methods for Fluid Dynamics; Springer Group: Berlin, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
























| Scheme | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Φ | 122° | 126° | 130° | 126° | 126° |
| β2 | 26° | 26° | 26° | 28° | 24° |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Impeller inlet diameter D1, mm | 200 |
| Impeller outlet diameter D2, mm | 420 |
| Impeller exit width b2, mm | 34 |
| Number of blade Z | 6 |
| Base diameter of the volute D3, mm | 435 |
| Volute inlet width b3, mm | 72 |
| Volute outlet diameter D4, mm | 250 |
| Front and Back Chamber | Volute | Suction Pipe | Exit Pipe | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mesh number | 934,607 | 2,238,179 | 498,506 | 327,624 |
| Mesh quality | >0.4 | >0.4 | >0.8 | >0.8 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, X.; Kang, Y.; Li, D.; Zhao, W. Impeller Optimized Design of the Centrifugal Pump: A Numerical and Experimental Investigation. Energies 2018, 11, 1444. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11061444
Han X, Kang Y, Li D, Zhao W. Impeller Optimized Design of the Centrifugal Pump: A Numerical and Experimental Investigation. Energies. 2018; 11(6):1444. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11061444
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Xiangdong, Yong Kang, Deng Li, and Weiguo Zhao. 2018. "Impeller Optimized Design of the Centrifugal Pump: A Numerical and Experimental Investigation" Energies 11, no. 6: 1444. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11061444
APA StyleHan, X., Kang, Y., Li, D., & Zhao, W. (2018). Impeller Optimized Design of the Centrifugal Pump: A Numerical and Experimental Investigation. Energies, 11(6), 1444. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11061444






