Wind Power Prediction Considering Nonlinear Atmospheric Disturbances
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Lorenz System and Wind Power Forecasting

3. Wind Power Prediction Based on a Nonlinear Lorenz Disturbance
3.1. Data Description

3.2. Modeling Process for Wind Power Prediction

| Perturbation models | Lorenz disturbance | Data or charts |
|---|---|---|
| LSWNN | Disturbance coefficient | 0.0253 |
| Disturbance intensity | 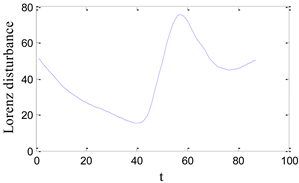 | |
| LSBP | Disturbance coefficient | −0.0384 |
| Disturbance intensity |  | |
| LSSVM | Disturbance coefficient | −0.0131 |
| Disturbance intensity | 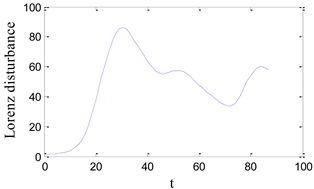 |
4. Wind Speed and Power Prediction Results and Error Analysis
| Wind speed prediction models (symbols) | Error | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| MAE (m/s) | MSE (m2/s2) | MAPE (%) | |
| WNN (Vf1) | 1.0298 | 1.2635 | 9.4189 |
| LSWNN (V1) | 0.2123 | 0.0697 | 1.8209 |
| BP (Vf2) | 1.8030 | 3.3591 | 14.9113 |
| LSBP (V2) | 0.2902 | 0.1141 | 2.5353 |
| SVM (Vf3) | 0.6709 | 0.6751 | 5.5984 |
| LSSVM (V3) | 0.3778 | 0.2223 | 3.1729 |
| PM | 0.8694 | 1.2757 | 7.0925 |
| Error | Wind power prediction models | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM | WNN | BP | SVM | ||||
| Vf1 | V1 | Vf2 | V2 | Vf3 | V3 | ||
| MAE (MW) | 0.1593 | 0.2476 | 0.0980 | 0.3147 | 0.0825 | 0.1475 | 0.0872 |
| MSE (MW2) | 0.0431 | 0.0819 | 0.0150 | 0.1320 | 0.0106 | 0.0309 | 0.0122 |
| MAPE (%) | 10.8252 | 18.3653 | 6.7683 | 24.3340 | 5.1664 | 9.7209 | 5.9801 |
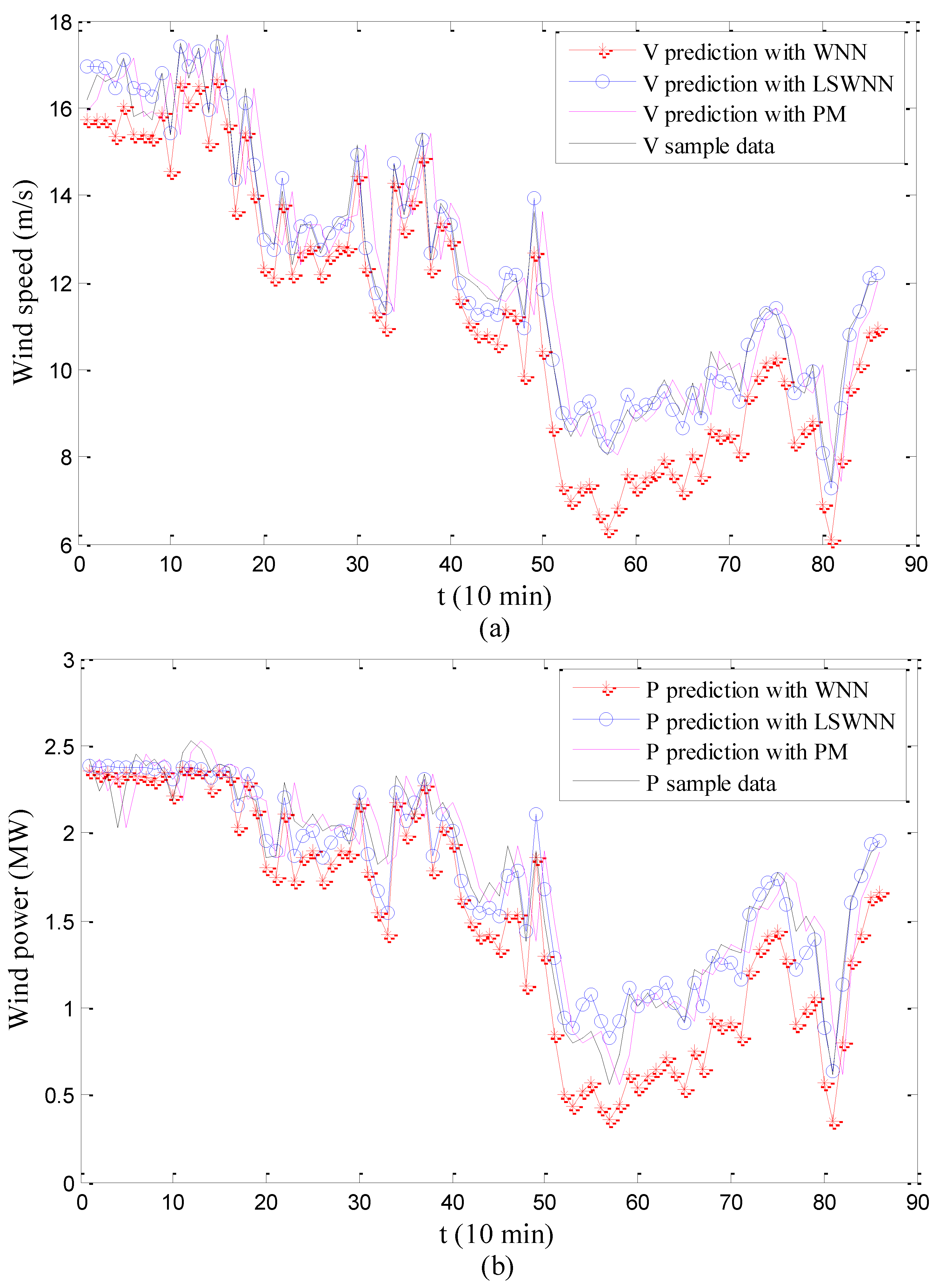


5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Global Wind Energy Council (GWEC). Available online: http://www.gwec.net/global-figures/graphs/ (accessed on 9 March 2014).
- Hu, J.M.; Wang, J.Z.; Zeng, G.W. A hybrid forecasting approach applied to wind speed time series. Renew. Energy 2013, 60, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.Y.; Wang, J.J.; Wang, J.Z.; Zhao, Z.B.; Tian, M. Short-term wind speed forecasting based on a hybrid model. Appl. Soft. Comput. 2013, 13, 3225–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.C.; Guo, P.; Huang, X.B. A review of wind power forecasting models. Energy Proced. 2011, 12, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, A.M.; Leahy, P.G.; Marvuglia, A.; Mckeogh, E.J. Current methods and advances in forecasting of wind power generation. Renew. Energy 2011, 37, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.H.; Xu, Y.; Xu, P.H.; Yang, H.Q.; Xiong, S.Q. Principle of Wind Power Prediction Technology and Business Systems, 1st ed.; China Meteorological Press: Beijing, China, 2013; pp. 18–41. [Google Scholar]
- Bouzgou, H.; Benoudjit, N. Multiple architecture system for wind speed prediction. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 2463–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesilbudak, M.; Sagiroglu, S.; Colak, I. A new approach to very short term wind speed prediction using k-nearest neighbor classification. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 69, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Tian, H.Q.; Chen, C.; Li, Y.F. A hybrid statistical method to predict wind speed and wind power. Renew. Energy 2010, 35, 1857–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tascikaraoglu, A.; Uzunoglu, M. A review of combined approaches for prediction of short-term wind speed and power. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 34, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, M.; Ding, M.; Huang, Y.Z.; Dong, X.P. The effect of different state sizes on Mycielski approach for wind speed prediction. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2012, 109, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Morales, J.D.; Palacios, E.; Velazquez-Carrillo, G.A. Wavelet neural networks for predicting engine emissions. Proced. Technol. 2013, 7, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.Y.; Shi, J.; Li, G. Fine tuning support vector machines for short-term wind speed forecasting. Energy Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 1990–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monfared, M.; Rastegar, H.; Kojabadi, H.M. A new strategy for wind speed forecasting using artificial intelligent methods. Renew. Energy 2008, 34, 845–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Tian, H.Q.; Li, Y.F. Comparison of two new ARIMA-ANN and ARIMA-Kalman hybrid methods for wind speed prediction. Appl. Energy 2010, 98, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheela, K.G.; Deepa, S.N. Neural network based hybrid computing model for wind speed prediction. Neurocomputing 2013, 122, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Tian, H.Q.; Pan, D.F.; Li, Y.F. Forecasting models for wind speed using wavelet, wavelet packet, time series and artificial neural networks. Appl. Energy 2013, 107, 191–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.X.; Wang, X.F. Review on probabilistic forecasting of wind power generation. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 32, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.H.; Chi, D.Z.; Wu, J.; Zhang, W.Y. A new wind speed forecasting strategy based on the chaotic time series modelling technique and the Apriori algorithm. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 84, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.G.; Yang, J.Y.; Wang, K.C.; Wang, Y.D. Lorenz wind disturbance model based on grey generated components. Energies 2014, 7, 7178–7193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.Z.; Peng, J.H. Nonlinear Dynamics, 1st ed.; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 120–143. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz, E.N. The Butterfly Effect; Premio Felice Pietro Chisesi e Caterina Tomassoni award lecture; University of Rome: Rome, Italy, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz, E.N. Deterministic nonperiodic flow. J. Atmos. Sci. 1963, 20, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algaba, A.; Fernandez-Sanchez, F.; Merino, M.; Rodriguez-Luis, A.J. Comments on ‘Global dynamics of the generalized Lorenz systems having invariant algebraic surfaces’. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 2014, 266, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghtadaei, M.; Hashemi Golpayegani, M.R. Complex dynamic behaviors of the complex Lorenz system. Sci. Iran. D 2012, 19, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, E.N. The Essence of Chaos, 1st ed.; China Meteorological Press: Beijing, China, 1997; pp. 127–137. [Google Scholar]
- Saltzman, B. Finite amplitude free convection as an initial value problem-I. J. Atmos. Sci. 1962, 19, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, K.; Wang, Z. Wind Power Prediction Considering Nonlinear Atmospheric Disturbances. Energies 2015, 8, 475-489. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8010475
Zhang Y, Yang J, Wang K, Wang Z. Wind Power Prediction Considering Nonlinear Atmospheric Disturbances. Energies. 2015; 8(1):475-489. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8010475
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yagang, Jingyun Yang, Kangcheng Wang, and Zengping Wang. 2015. "Wind Power Prediction Considering Nonlinear Atmospheric Disturbances" Energies 8, no. 1: 475-489. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8010475
APA StyleZhang, Y., Yang, J., Wang, K., & Wang, Z. (2015). Wind Power Prediction Considering Nonlinear Atmospheric Disturbances. Energies, 8(1), 475-489. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8010475






