Geomechanical, Hydraulic and Thermal Characteristics of Deep Oceanic Sandy Sediments Recovered during the Second Ulleung Basin Gas Hydrate Expedition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (a)
- physical properties (e.g., density, hydrate saturation, porosity, and particle size distribution);
- (b)
- thermal properties (e.g., thermal conductivity and heat capacity);
- (c)
- transport properties (e.g., absolute permeability and relative permeability for gas and water phases); and
- (d)
- mechanical properties (e.g., stiffness and strength).
2. Study Area
2.1. Site of Interest
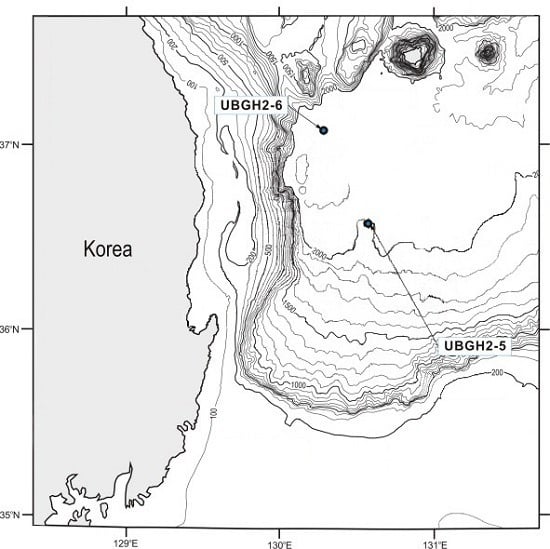
2.2. Sampling Location
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Description of Sediment Core Samples: Physical and Index Properties
3.1.1. Particle Size Distribution and Soil Classification
3.1.2. Mineralogy from X-Ray Diffraction Analysis
3.1.3. Particle-Scale Observations in Scanning Electron Microscope Images
3.2. Setup and Procedure for Triaxial Compression Test
3.3. Setup and Procedure for Thermal Water Retention Test
4. Results
4.1. Stress-Strain Responses and Mohr-Coulomb Strength Parameters
4.2. Stress- and Strain-Dependent Young’s Modulus
4.3. Water Retention Curves and Parameters for Water Permeability
4.4. Variations in Thermal Conductivity and Electrical Resistance with Water Saturation
5. Discussion: Implications for Hydrate-Bearing Sediments
5.1. Thermal Conductivity
5.2. Bulk Permeability
5.3. Relative Permeability
5.4. Geomechanical Properties
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, K.P.; Bahk, J.J.; Kwon, Y.; Kim, G.Y.; Riedel, M.; Holland, M.; Schultheiss, P.; Rose, K. Korean National Program Expedition Confirms Rich Gas Hydrate Deposit in the Ulleung Basin, East Sea. 2008. Available online: https://www.netl.doe.gov/File%20Library/Research/Oil-as/methane%20hydrates/HMNewsSpring08.pdf (accessed on 23 September 2016). [Google Scholar]
- Kim, G.Y.; Yi, B.Y.; Yoo, D.G.; Ryu, B.J.; Riedel, M. Evidence of gas hydrate from downhole logging data in the Ulleung Basin, East Sea. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 2011, 28, 1979–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, B.J.; Collett, T.S.; Riedel, M.; Kim, G.Y.; Chun, J.H.; Bahk, J.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Yoo, D.G. Scientific results of the Second Gas Hydrate Drilling Expedition in the Ulleung Basin (UBGH2). Mar. Pet. Geol. 2013, 47, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, B.J.; Kim, G.Y.; Chun, J.H.; Bahk, J.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Yoo, D.G.; Collett, T.S.; Riedel, M.; Torres, M.E.; et al. The Second Ulleung Basin Gas Hydrate Drilling Expedition (UBGH2) Expedition Report; Korea Institute of Geosciences and Mineral Resources (KIGAM): Daejeon, Korea, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.S.; Cho, G.C.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, S.J. Geotechnical and geophysical properties of deep marine fine-grained sediments recovered during the second Ulleung Basin Gas Hydrate expedition, East Sea, Korea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2013, 47, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, T.H.; Lee, K.R.; Cho, G.C.; Lee, J.Y. Geotechnical properties of deep oceanic sediments recovered from the hydrate occurrence region in the Ulleung Basin, East Sea, offshore Korea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2011, 28, 1870–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Yun, T.S.; Lee, J.S.; Bahk, J.J.; Santamarina, J.C. Geotechnical characterization of marine sediments in the Ulleung Basin, East Sea. Eng. Geol. 2011, 117, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, Y.M.; Lee, C. Stress-dependent and strength properties of gas hydrate-bearing marine sediments from the Ulleung Basin, East Sea, Korea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2013, 47, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Yun, T.S. Thermal conductivity of methane hydrate-bearing Ulleung Basin marine sediments: Laboratory testing and numerical evaluation. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2013, 47, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, S.H.; Dallimore, S.R.; Collett, T.S.; Carle, D.; Weatherill, B.; Satoh, T.; Inoue, T. Overview of Pressure-Drawdown Production-Test Results for the JAPEX/JNOC/GSC et al. Mallik 5L-38 Gas Hydrate Production Research Well; Geological Survey of Canada Bulletin: Dartmouth, NS, Canada, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Schoderbek, D.; Farrell, H.; Hester, K.; Howard, J.; Raterman, K.; Silpngarmlert, S.; Martin, K.L.; Smith, B.; Klein, P. ConocoPhillips Gas Hydrate Production Test Final Technical Report. 2013. Available online: http://www.netl.doe.gov/File%20Library/Research/Oil-Gas/methane%20hydrates/nt0006553-final-report-hydrates.pdf (accessed on 20 July 2013). [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, K. 2013 Methane hydrate offshore production test in the eastern Nankai Trough: a milestone on the path to real energy resource. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Gas Hydrates (ICGH8-2014), Beijing, China, 28 July–1 August 2014.
- Oyama, H.; Abe, S.; Sato, T. Experimental study of mud erosion phenomena at sand mud alternate layer. In Proceedings of the 25th International Ocean and Polar Engineering Conference, Kona, Big Island, HI, USA, 21–26 June 2015.
- Bahk, J.J.; Chough, S.K.; Han, S.J. Origins and paleoceanographic significance of laminated muds from the Ulleung Basin, East Sea (Sea of Japan). Mar. Geol. 2000, 162, 459–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chough, S.K.; Lee, H.J.; Yoon, S.H. Marine Geology of Korean Seas, 2nd ed.; Elsvier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, G.H.; Kim, B. Infill history of the Ulleung Basin, East Sea (Sea of Japan) and implications on source rocks and hydrocarbons. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2002, 19, 829–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahk, J.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kong, G.S.; Park, Y.; Lee, H.; Park, Y.J.; Park, K.P. Occurrence of near-seafloor gas hydrates and associated cold vents in the Ulleung Basin, East Sea. Geosci. J. 2009, 13, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kim, G.Y.; Kang, N.K.; Yi, B.Y.; Jung, J.W.; Im, J.H.; Son, B.K.; Bahk, J.J.; Chun, J.H.; Ryu, B.J.; et al. Physical properties of sediments from the Ulleung Basin, East Sea: Results from Second Ulleung Basin Gas Hydrate Drilling Expedition, East Sea, Korea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2013, 47, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Chun, S.S.; Yoon, S.H.; Kim, S.R. Slope stability and geotechnical properties of sediment of the southern margin of Ulleung Basin, East Sea (Sea of Japan). Mar. Geol. 1993, 110, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waite, W.F.; Stern, L.A.; Kirby, S.H.; Winters, W.J.; Mason, D.H. Simultaneous determination of thermal conductivity, thermal diffusivity and specific heat in sI methane hydrate. Geophys. J. Int. 2007, 169, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waite, W.F.; Santamarina, J.C.; Cortes, D.D.; Dugan, B.; Espinoza, D.N.; Germaine, J.; Jang, J.; Jung, J.W.; Kneafsey, T.J.; Shin, H.; et al. Physical properties of hydrate-bearing sediments. Rev. Geophys. 2009, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Locat, J. A microstructural investigation of Osaka Bay clay: The impact of microfossils on its mechanical behaviour. Can. Geotech. J. 1999, 36, 493–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tréguer, P.; Nelson, D.M.; Van Bennekorn, A.J.; De Master, D.J.; Leynaert, A.; Quéguiner, B. The silica balance in the world ocean: A reestimate. Science 1995, 268, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiwakoti, D.R.; Tanaka, H.; Tanaka, M.; Locat, J. Influences of diatom microfossils on engineering properties of soils. Soils Found. 2002, 42, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneda, J.; Masui, A.; Konno, Y.; Jin, Y.; Egawa, K.; Kida, M.; Ito, T.; Nagao, J.; Tenma, N. Mechanical properties of hydrate-bearing turbidite reservoir in the first gas production test site of the Eastern Nakai Trough. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2015, 66, 471–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Method for Consolidated Drained Triaxial Compression Test for Soils; ASTM D7181-11; American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011.
- Goto, S.; Tatsuoka, F.; Shibuya, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Sato, T. A simple gauge for local small strain measurements in the laboratory. Soils Found. 1991, 31, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, T.S.; Santamarina, J.C.; Ruppel, C. Mechanical properties of sand, silt, and clay containing tetrahydrofuran hydrate. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, S.E. Transient plane source techniques for thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity measurements of solid materials. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1991, 62, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.-S.; Yun, T.S. Thermal and electrical response of unsaturated hydrophilic and hydrophobic granular materials. Geotech. Test. J. 2011, 34, 562–570. [Google Scholar]
- Santamarina, J.C.; Klein, K.A.; Fam, M.A. Soils and Waves; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann, J.; Horton, R.; Grant, S.A.; Van der Ploeg, R.R. Temperature dependence of water retention curves for wettable and water repellent soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, J.; van der Ploeg, R.R. A review on recent developments in soil water retention theory: Interfacial tension and temperature effects. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2002, 165, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mualem, Y. A new model for predicting hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated porous media. Water Resour. Res. 1976, 12, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Genuchten, M.T. A closed form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamarina, J.C.; Dai, S.; Terzariol, M.; Jang, J.; Waite, W.F.; Winters, W.J.; Nagao, J.; Yoneda, J.; Konno, Y.; Fujii, T.; et al. Hydro-bio-geomechanical properties of hydrate-bearing sediments from Nakai Trough. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2015, 66, 434–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winters, W.J. Physical and geotechnical properties of gas-hydrate-bearing sediment from offshore India and the northern Cascadia Margin compared to other hydrate reservoirs. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Gas Hydrates (ICGH 2011), Edinburgh, UK, 17–21 July 2011.
- Kwon, T.H.; Cho, G.C.; Santamarina, J.C. Gas hydrate dissociation in sediments: Pressure-temperature evolution. Geochem. Geophy. Geosy. 2008, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, T.H.; Song, K.I.; Cho, G.C. Destabilization of marine gas hydrate-bearing sediments induced by a hot wellbore: A numerical approach. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 5493–5507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutqvist, J.; Moridis, G.J. Numerical studies on the geomechanical stability of hydrate-bearing sediments. SPE J. 2009, 14, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutqvist, J.; Moridis, G.J.; Grover, T.; Collet, T. Geomechanical response of permafrost-associated hydrate deposits to depressurization-induced gas production. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2009, 67, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Yang, D.; Moridis, G.J.; Rutqvist, J. Numerical studies on two-way coupled fluid flow and geomechanics in hydrate deposits. In Proceedings of the 2011 Reservoir Simulation Symposium, Woodlands, TX, USA, 21–23 February 2011.
- Kim, A.R. T-H-M Coupled Numerical Analysis of Gas Production from Methane Hydrate Deposits in the Ulleung Basin in Korea. Ph.D. Thesis, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), Daejeon, Korea, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, M.Y.A.; Klar, A.; Soga, K. Coupled soil deformation-flow-thermal analysis of methane production in layered methane hydrate soils. In Proceedings of the Offshore Technology Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 5–8 May 2008.
- Klar, A.; Soga, K.; Ng, M.Y.A. Coupled deformation-flow analysis for methane hydrate extraction. Geotechnique 2010, 60, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klar, A.; Uchida, S.; Soga, K.; Yamamoto, K. Explicitly coupled thermal flow mechanical formulation for gas-hydrate sediments. SPE J. 2013, 18, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs, W.; Meyn, V. Surface tension in the system methane/waters—A glance at numeric and precision of the experimental method (pendent drop) and precise experimental results in comparison with literature. Erdol Erdgas Kohle 1995, 111, 119–121. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Q.Y.; Chen, G.J.; Yan, W.; Guo, T.M. Interfacial tension of (CO2 + CH4) + water from 298 K to 373 K and pressures up to 30 MPa. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2000, 45, 610–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.Y.; Chen, G.J.; Yang, L.Y. Interfacial tension of methane + water with surfactant near the hydrate formation conditions. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2004, 49, 1023–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, D.N.; Santamarina, J.C. Water-CO2-mineral systems: Interfacial tension, contact angle, and diffusion—Implications to CO2 geological storage. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.W.; Wan, J. Supercritical CO2 and ionic strength effects on wettability of silica surfaces: Equilibrium contact angle measurements. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 6053–6059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Fan, S. Measuring and modeling thermal conductivity of gas hydrate-bearing sand. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, G.W.C.; Laby, T.H. Table of Physical and Chemical Constant, 16th ed.; National Physical Laboratory: Middlesex, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Stephan, K.; Laesecke, A. The thermal conductivity of fluid air. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1985, 14, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horai, K.I.; Simmons, G. Thermal conductivity of rock forming minerals. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1969, 6, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinberg, R.; Flaum, C.; Griffin, D.; Brewer, P.; Malby, G.; Peltzer, E.; Yesinowski, J. Deep sea NMR: Methane hydrate growth habit in porous media and its relationship to hydraulic permeability, deposit accumulation, and submarine slope stability. J. Geophys. Res 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Seol, Y. Water permeability in hydrate-bearing sediments: A pore-scale study. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 4176–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konno, Y.; Masuda, Y.; Hariguchi, Y.; Kurihara, M.; Ouchi, H. Key factors for depressurization-induced gas production from oceanic methane hydrates. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 1736–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, S.; Soga, K.; Yamamoto, K. Critical state soil constitutive model for methane hydrate soil. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masui, A.; Haneda, H.; Ogata, Y.; Aoki, K. The effect of saturation degree of methane hydrate on the shear strength of synthetic methane hydrate sediments. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Gas Hydrates, Trondheim, Norway, 13–16 June 2005; pp. 657–663.
- Miyazaki, K.; Masui, A.; Sakamoto, Y.; Aoki, K.; Tenma, N.; Yamaguchi, T. Triaxial compressive properties of artificial methane-hydrate-bearing sediment. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, N.; Garziglia, S. Geomechanical constitutive modelling of gas-hydrate-bearing sediments. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Gas Hydrates (ICGH7), Edinburgh, UK, 17–21 July 2011.











| Hole-Core-Section | 2-6B-22R | 2-5B-22H |
|---|---|---|
| Depth (mbsf) 1 | 145.9–147 | 139.5–147.5 |
| Water depth (m) | 2154 | 1969 |
| Temperature (°C) 1 | ~17 | ~14–15 |
| Pressure (MPa) 1 | ~23 | ~21 |
| Bulk density (kg/m3) 1 | 1604 | ~1600 |
| In situ porosity (%) 1 | 35.4 | 50 |
| Remolded porosity (%) 2 | ~44–46 | ~43 |
| Gs (-) 1 | 2.7 | 2.6 |
| Water content (%) 1 | 20.3 | Not available |
| D50 (mm) 2 | 110 | 220 |
| Cu (-) 2 | 6.3 | 1.7 |
| Cc (-) 2 | 2.9 | 0.96 |
| Sand fraction (%) 2 | 78.1 | 97.6 |
| Silt fraction (%) 2 | 20.6 | 2.4 |
| Clay fraction (%) 2 | 1.3 | Non-measurable |
| USCS 2 | Well-graded SM | SP |
| Effective stress (kPa) 1 | 755 | ~700 |
| Hydrate saturation (%) 1 | >40 | 0 (No infrared anomaly) |
| Mineral | % |
|---|---|
| Quartz | 63.7 |
| Albite | 15 |
| Orthoclase K-feldspar | 6.9 |
| Muscovite/Illite | 5.7 |
| Calcite | 4.4 |
| Chlorite | 2.5 |
| Biotite | 1.8 |
| Effective Confining Stress (MPa) | Deviatoric Stress at Failure (MPa) | Deviatoric Stress at Critical State (MPa) | Pore Water Pressure (MPa) | Etan at 0.1% εa (MPa) | Etan at 1% εa (MPa) | E50 (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.32 | 0.65 | 0.23 | 0.33 | 64 | 22 | 29 |
| 0.63 | 1.04 | 0.39 | 0.63 | 101 | 26 | 39 |
| 1.47 | 2.25 | 1.94 | 0.51 | 122 | 30 | 40 |
| 2.58 | 4.17 | 3.14 | 1.13 | 177 | 76 | 50 |
| 5.25 | 6.69 | - | 1.13 | 527 | 79 | 80 |
| Location | Site-Hole | Test Conditions | Cohesion or Undrained Strength | Internal Friction Angle 1 | Sediment Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ulleung Basin, Korea | UBGH2-6B-22R | Drained triaxial tests | No cohesion intercept | 26° (Peak friction angle) 22° (Critical State friction angle) | SM | This study |
| Ulleung Basin, Korea | UBGH2-10D-8H UBGH2-6B-8H/27H UBGH2-10C-11H | Undrained triaxial tests | 18–30 kPa | 17.6°–24.6° | Clay- and silt-dominant sediments | Lee et al. [8] |
| Ulleung Basin, Korea | UBGH2-6C-10H | Undrained triaxial tests | Not available | 27° | Sediment with a high sand fraction | Lee et al. [8] |
| Krishna-Godavari Basins, India | NGHP-01 KG Basin 21A-2Y | Undrained triaxial tests | Not available | 30°–31° | Maximum friction angle | Winters et al. [37] |
| Krishna-Godavari Basin, India | NGHP-01 KG Basin 10D-10X | Undrained triaxial tests | 7.2 kPa | 21.3° | Fine-grained sediments Composite friction angle | Winters et al. [37] |
| Mahanadi Basin, India | NGHP-01, Mahanadi Basin 18A-5H | Undrained triaxial tests | 9.7 kPa | 24.5° | Fine-grained sediments Composite friction angle | Winters et al. [37] |
| Cascadia, Hydrate Ridge | ODP Leg 204 1249-4H | Undrained triaxial tests | Not available | 29 | Fine-grained sediments | Winters et al. [37] |
| Mckenzie Delta, Canada | Mallik-2L | Undrained triaxial tests | Not available | 34°–44° | Coarse-grained sediment | Winters et al. [37] |
| Nakai Trough, Japan | AT1-C-20P | Direct shear tests | Not available | 27° (Peak friction angle) 25° (Residual friction angle) | Sand-silt mixed sediments, using Pressure core characterization tools | Santamarina et al. [36] |
| Nakai Trough, Japan | AT1-C | Drained and undrained triaxial tests for sandy sediments and for clayey-silty sediments | No or minimal cohesion intercept, but increases with hydrate saturation | 30°–37° (Effective friction angle) | Sandy sediments and clayey-silty sediments | Yoneda et al. [25] |
| Property | Correlation | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Permeability | Dai et al. [57] | |
| Relative permeability | kri0 : Relative permeability of end point to the phase i Ni: Relative permeability index of the phase i Se: Normalized water saturation Swm: Effective water saturation Sii: Irreducible saturation of the phase i | Konno et al. [58] Note: Nw = 3, Ng = 2, krw0 = 1, krg0 = 1, Siw = 0.1, and Sig = 0.1 were used in Kanno et al. (2010) |
| a, b, c: van Genuchten parameters for soil pore structures Swm: Effective water saturation | Klar et al. [45,46] Note: a = 0.92, b = 0.5, c = 0.5 were used in Klar et al. [45,46] | |
| Cohesion | Rutqvist and Moridis [40] Rutqvist et al. [41] | |
| Klar et al. [45,46] | ||
| Ng et al. [44] | ||
| Uchida et al. [59] | ||
| , chfs: Cohesion of hydrate-free sediments | Yoneda et al. [25] Note: α = 1.1 × 10−3, β = 1.8 | |
| Dilation angle | Klar et al. [45,46] | |
| Ng et al. [44] | ||
| Uchida et al. [59] | ||
| Young’s modulus | Rutqvist et al. [41] | |
| Klar et al. [45,46] | ||
| Ng et al. [44] | ||
| Kim [43] |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cha, Y.; Yun, T.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kwon, T.-H. Geomechanical, Hydraulic and Thermal Characteristics of Deep Oceanic Sandy Sediments Recovered during the Second Ulleung Basin Gas Hydrate Expedition. Energies 2016, 9, 775. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9100775
Cha Y, Yun TS, Kim YJ, Lee JY, Kwon T-H. Geomechanical, Hydraulic and Thermal Characteristics of Deep Oceanic Sandy Sediments Recovered during the Second Ulleung Basin Gas Hydrate Expedition. Energies. 2016; 9(10):775. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9100775
Chicago/Turabian StyleCha, Yohan, Tae Sup Yun, Young Jin Kim, Joo Yong Lee, and Tae-Hyuk Kwon. 2016. "Geomechanical, Hydraulic and Thermal Characteristics of Deep Oceanic Sandy Sediments Recovered during the Second Ulleung Basin Gas Hydrate Expedition" Energies 9, no. 10: 775. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9100775
APA StyleCha, Y., Yun, T. S., Kim, Y. J., Lee, J. Y., & Kwon, T.-H. (2016). Geomechanical, Hydraulic and Thermal Characteristics of Deep Oceanic Sandy Sediments Recovered during the Second Ulleung Basin Gas Hydrate Expedition. Energies, 9(10), 775. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9100775