Dynamic Equivalent Modeling for Small and Medium Hydropower Generator Group Based on Measurements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
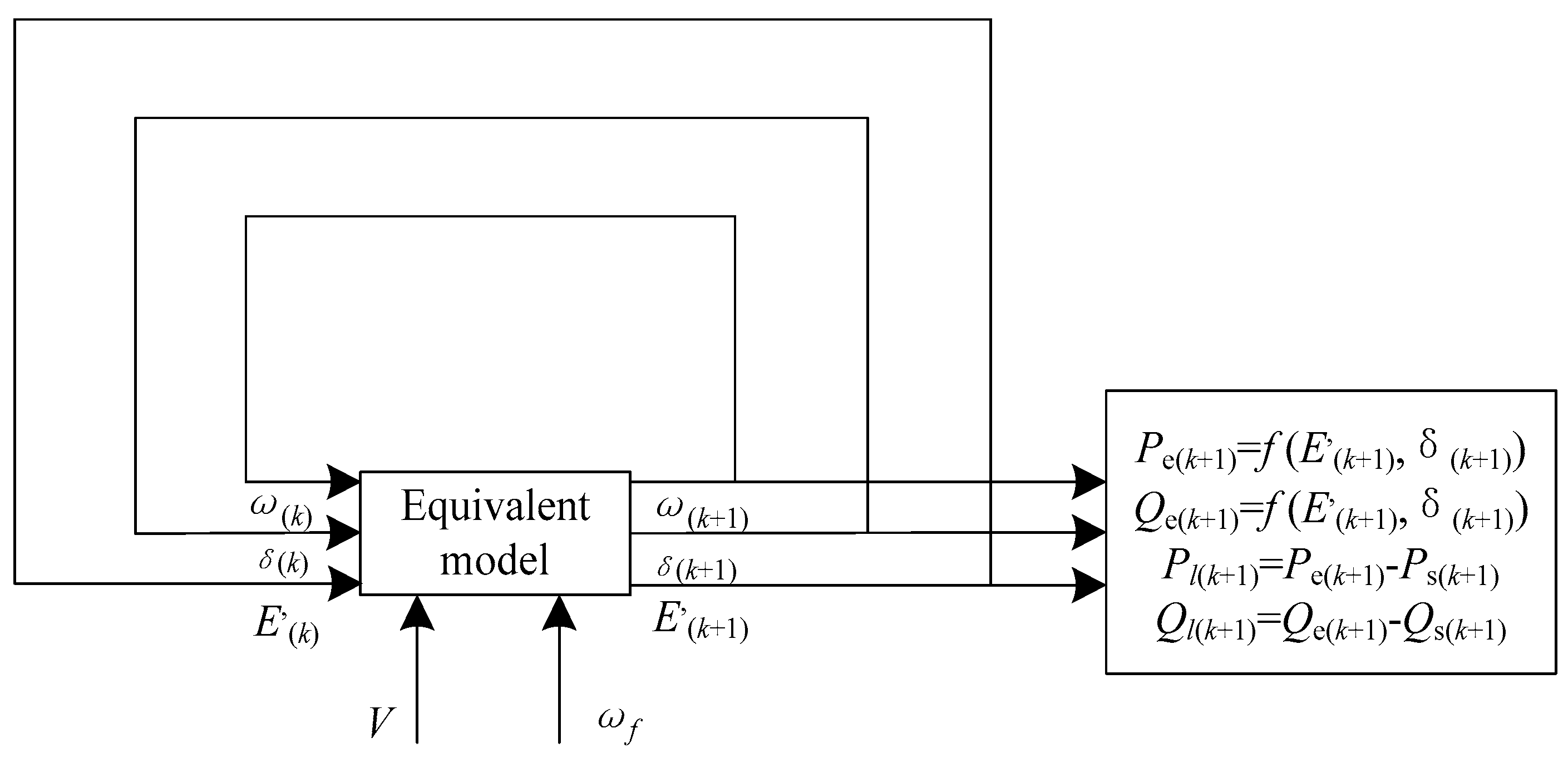
2. Equivalent Model for the Hydropower Generator Group
2.1. Equivalent Generator Model
2.2. Equivalent Load Model
3. Methodology of the Proposed Equivalence
3.1. Frame of the Equivalence Method
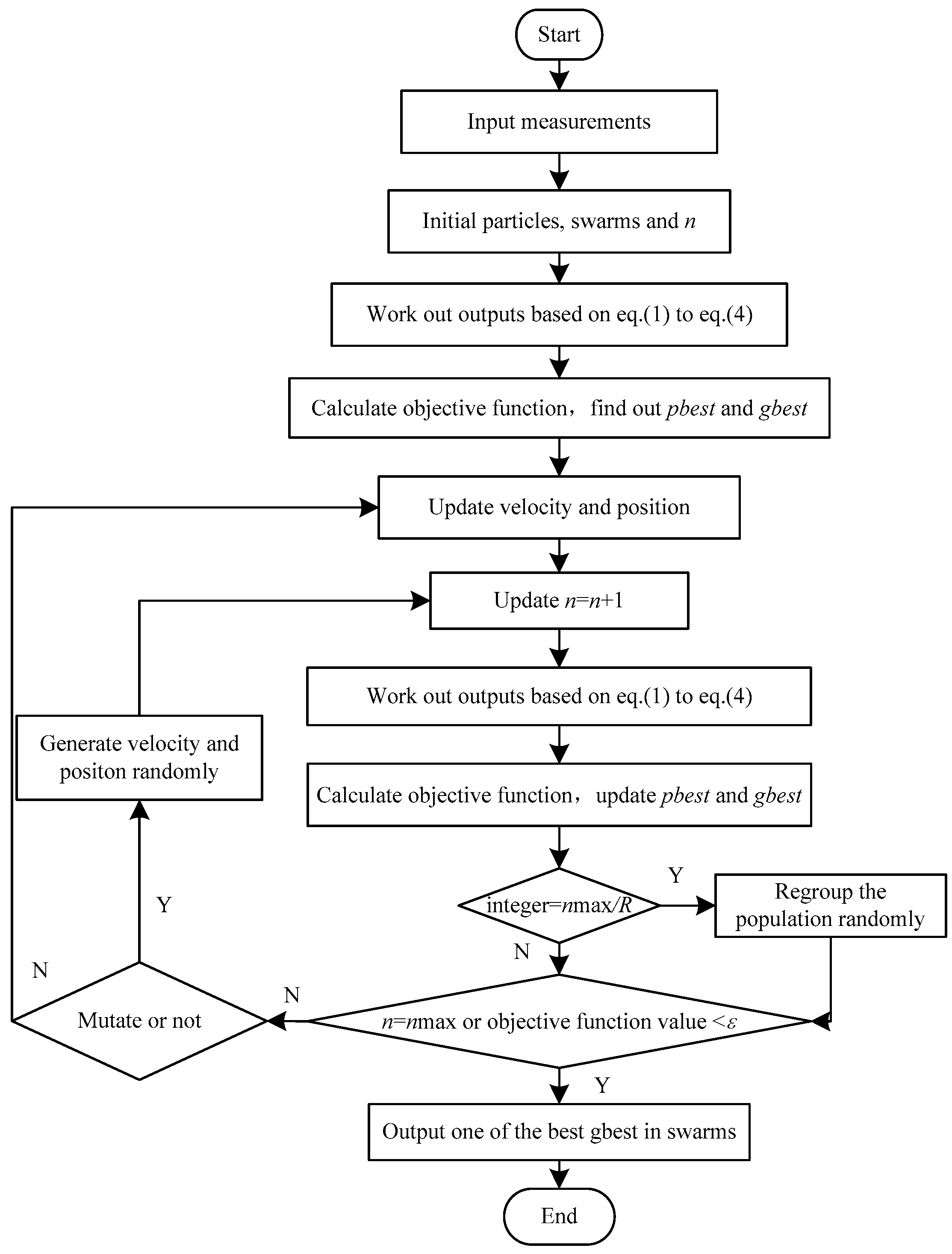
3.2. Dynamic Multi-Swarm Particle Swarm Optimizer Algorithm
4. Case Study
4.1. Sensitivity Analysis of Equivalent Model Parameters
4.2. Identifiability Verification
4.3. Equivalence with Simulation Data
4.4. Equivalence with PMU Data
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ni, Y.X.; Chen, S.S.; Zhang, B.L. Theory and Analysis of Dynamic Power System; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2002; pp. 197–208. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Y. Research on small signal stability of power system with distributed small hydropower. In Proceedings of the Innovative Smart Grid Technologies-Asia, Tianjin, China, 21–24 May 2012; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.P.; Zhi, D.; Yang, D.J.; Zhao, H.S.; Zhang, Y.F.; Yang, H. An equivalent modeling for small and medium-sized hydropower generator group considering excitation and governor system. In Proceedings of the Power and Energy Engineering Conference, Hong Kong, China, 6–10 December 2014; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.D.; Sun, G.C.; Pan, R.R.; Xu, N.; Li, C.Q.; Ma, H.Z. An equivalent modeling for synthesis load of distributed network with small hydropower. In Proceedings of the 2014 4th International Workshop on Computer Science and Engineering, WCSE 2014, Dubai, UAE, 22–23 August 2014; Science and Engineering Institute: Bristol, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Wen, J.Y.; Hu, W.B.; Ruan, S.W.; Li, X.P.; Sun, J.B. A dynamic equivalent modeling for regional small hydropower generator group. Power Syst. Prot. Control 2013, 41, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Joo, S.K.; Liu, C.C.; Choe, J.W. Enhancement of coherency identification techniques for power system dynamic equivalents. In Proceedings of the Power Engineering Society Summer Meeting, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 15–19 July 2001; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Oscar, Y.L.; Fette, M. Electromechanical identity recognition as alternative to the coherency identification. In Proceedings of the 39th International Universities Power Engineering Conference, Bristol, UK, 8 September 2004; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Nath, R.; Lamba, S.S. Development of coherency-based time-domain equivalent model using structure constraints. IEEE Proc. C Gener. Trans. Distrib. 1986, 133, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ourari, M.L.; Dessaint, L.A.; Van-Que, D. Dynamic equivalent modeling of large power systems using structure preservation technique. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2006, 21, 1284–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ourari, M.L.; Dessaint, L.A.; Van-Que, D. Generating units aggregation for dynamic equivalent of large power systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE Power Engineering Society General Meeting, Denver, CO, USA, 10 June 2004; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Valle, R.J. Identification of dynamic equivalents preserving the internal modes. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE Bologna Power Tech Conference Proceedings, Bologna, Italy, 23–26 June 2004; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Price, W.W.; Ewart, D.N.; Gulachenski, E.M. Dynamic equivalents from on-line measurements. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 1975, 94, 1349–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmy, A.M.; Erlich, I. Identification of dynamic equivalents for distribution power networks using recurrent ANNS. In Proceedings of the Power Systems Conference and Exposition, Bristol, UK, 10–13 October 2004; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Azmy, A.M.; Erlich, I.; Sowa, P. Artificial neural network-based dynamic equivalents for distribution systems containing active sources. IEEE Proc. Gener. Trans. Distrib. 2004, 151, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, A.H.M.A.; Al-Ramadhan, A.J. Dynamic equivalent of external power system and its parameter estimation through artificial neural network. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2002, 24, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zali, S.M.; Milanovic, J.V. Dynamic equivalent model of Distribution Network Cell using Prony analysis and Nonlinear least square optimization. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Bucharest Power Tech, Bucharest, Roman, 28 June 2009; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhang, B.H. A real-time dynamic equivalent solution for large interconnected power systems. In Proceedings of the Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies, 2011 4th International Conference, Weihai, China, 6–9 July 2011; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.B.; Hu, B.W.; Sun, J.T. Research on hydropower generator group equivalence and parameter identification based on PSASP calling and optimization algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Power and Energy, Shanghai, China, 29–30 November 2014; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, P. Theory and Method of Power System Modeling; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2010; pp. 276–291. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Guan, L.; Wang, T.W. Influence on the performance of dynamic equivalence based on equivalent model. In Proceedings of the 24th Annual Conference Proceedings about Power System and Automation in China, Beijing, China, 10 October 2008.
- Shi, D.; Tylavsky, D.J.; Koellner, M.; Logic, N.; Wheeler, D.E. Transmission line parameter identification using PMU measurements. Eur. Trans. Electr. Power 2011, 21, 1574–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.X.; Zhang, B.M.; Wu, W.C.; Sun, H.B. Identification and validation for synchronous generator parameters based on recorded on-line disturbance data. Power Syst. Technol. 2012, 36, 87–93. [Google Scholar]
- Chakhchoukh, Y.; Vittal, V.; Heydt, G.T. PMU based state estimation by integrating correlation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2014, 29, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, D.M. Numerical Method; China Machine Press: Beijing, China, 2009; pp. 208–217. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.H. Identification Based Dynamic Equivalents of Power Systems Interconnected with Three Areas. Master’s Thesis, Hohai University, Nanjing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N. Research on the Identification of Synchronous Generator Parameters Based on Phasor Measurement. Master’s Thesis, North China Electric Power University, Baoding, Hebei, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, L.X. Parameters Identification for Power Load Models Based on Improved Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm. Master’s Thesis, Dalian Maritime University, Dalian, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kermedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks, Piscataway, NJ, USA, 27 November 1995; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.K.; Chen, X.Y.; Yu, K. Hybrid particle swarm optimization for distribution network reconfiguration. Proc. CSEE 2008, 28, 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.W.; Shi, X.C.; Dan, Y.Q.; Li, P.; Liu, W.Y.; Wei, D.B.; Fu, C. Application of PSO algorithm in global MPPT for PV array. Proc. CSEE 2012, 32, 42–48. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.Z.; Liang, J.J.; Suganthan, P.N. Dynamic multi-swarm particle swarm optimizer with local search for large scale global optimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Hong Kong, China, 1–6 June 2008; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.J.; Suganthan, P.N. Dynamic multi-swarm particle swarm optimizer. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Swarm Intelligence Symposium, SIS 2005, New York, NY, USA, 8–10 June 2005; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]











| Parameter | Identified Value | Actual Value | Parameter | Identified Value | Actual Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tj | 50.96 | 49.50 | D | 0.165 | 0.2 |
| xd | 0.1038 | 0.1460 | Ps | 0.987 | 1 |
| x′d | 0.0512 | 0.0523 | Qs | 0.298 | 0.5 |
| T″d0 | 8.682 | 10.430 | Np | 1.143 | 1.5 |
| Kv | 0.3672 | - | Nq | 1.767 | 1.2 |
| Parameter | Identified Value | Actual Value | Parameter | Identified Value | Actual Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tj | 52.34 | 49.50 | D | 0.1297 | 0.2 |
| xd | 0.2156 | 0.1460 | Ps | 1.1681 | 1 |
| x′d | 0.0586 | 0.0523 | Qs | 0.2743 | 0.5 |
| T″d0 | 17.35 | 10.430 | Np | 2.292 | 1.5 |
| Kv | 2.2693 | - | Nq | 1.987 | 1.2 |
| Parameter | Tj | xd | x′d | T′d0 | Kv |
| Value | 68.3137 | 0.5811 | 0.0455 | 15.3374 | 13.8422 |
| Parameter | D | Ps0 | Qs0 | Np | Nq |
| Value | 0.3093 | 0.7765 | 0.5897 | 0.5982 | 1.8078 |
| Position | Type | Before Equivalence | After Equivalence | Relative Errors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jiulong500–Shimian500 | Active power | 14.5465 | 14.55 | 0.024% |
| Reactive power | −0.34845 | −0.34935 | 0.25% | |
| Jiulong500 | Voltage amplitude | 1.00641 | 1.00637 | −0.0039% |
| Jianshan500–Pengzhu500 | Active power | 4.41634 | 4.41727 | 0.0047% |
| Reactive power | 1.41196 | 1.41087 | 0.079% | |
| Jianshan500 | Voltage amplitude | 0.97591 | 0.97589 | −0.0020% |
| Huangyan500–Wanxian500 | Active power | 15.90473 | 15.90617 | 0.0091% |
| Reactive power | −1.177 | −1.17682 | 0.015% | |
| Huangyan500 | Voltage amplitude | 0.98683 | 0.98682 | −0.001% |
| Meiguhe220–Puti220 | Active power | 0.53659 | 0.53659 | 0% |
| Reactive power | 0.49844 | 0.49845 | 0.0020% | |
| Puti220 | Voltage amplitude | 0.9913 | 0.9913 | 0% |
| Caoba220–Mingshan220 | Active power | 0.29271 | 0.29271 | 0% |
| Reactive power | −0.16314 | −0.16313 | 0.0061% | |
| Caoba220 | Voltage amplitude | 0.98993 | 0.98991 | −0.0020% |
| grid | Frequency | 1 | 1 | 0% |
| Number | Fault Descriptions | Relative Errors |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Three phase short circuit occurred in 1 s in a 500 kV Yuecheng-Puti transmission line and broke this line in 1.1 s | 40.49 |
| 2 | Three phase short circuit occurred in 1 s in a 500 kV Nantian-Dongpo transmission line and broke this line in 1.1 s | 39.65 |
| 3 | Three phase short circuit occurred in 1 s in a 500 kV Shuzhou-Danjing transmission line and broke this line in 1.1 s | 34.17 |
| 4 | Three phase short circuit occurred in 1 s in a 500 kV Ya’an-Jianshan transmission line and broke this line in 1.1 s | 37.48 |
| 5 | Three phase short circuit occurred in 1 s in a 500 kV Tanjiawan-Nanchong transmission line and broke this line in 1.1 s | 28.56 |
| Parameter | Tj | xd | x′d | T′d0 | Kv |
| Value | 6.0684 | 0.5548 | 0.1475 | 1.6488 | 4.2420 |
| Parameter | D | Ps0 | Qs0 | Np | Nq |
| Value | 0.1982 | 1.1065 | 3.1636 | 0.8321 | 0.6005 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, B.; Sun, J.; Ding, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, X. Dynamic Equivalent Modeling for Small and Medium Hydropower Generator Group Based on Measurements. Energies 2016, 9, 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9050362
Hu B, Sun J, Ding L, Liu X, Wang X. Dynamic Equivalent Modeling for Small and Medium Hydropower Generator Group Based on Measurements. Energies. 2016; 9(5):362. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9050362
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Bowei, Jingtao Sun, Lijie Ding, Xinyu Liu, and Xiaoru Wang. 2016. "Dynamic Equivalent Modeling for Small and Medium Hydropower Generator Group Based on Measurements" Energies 9, no. 5: 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9050362
APA StyleHu, B., Sun, J., Ding, L., Liu, X., & Wang, X. (2016). Dynamic Equivalent Modeling for Small and Medium Hydropower Generator Group Based on Measurements. Energies, 9(5), 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9050362





