Quasi-Static Compression and Low-Velocity Impact Behavior of Tri-Axial Bio-Composite Structural Panels Using a Spherical Head
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Material Properties
2.2. Panel Design and Fabrication
2.3. Quasi-Static Compression Test
2.4. Low-Velocity Impact Test
3. Results and Discussion
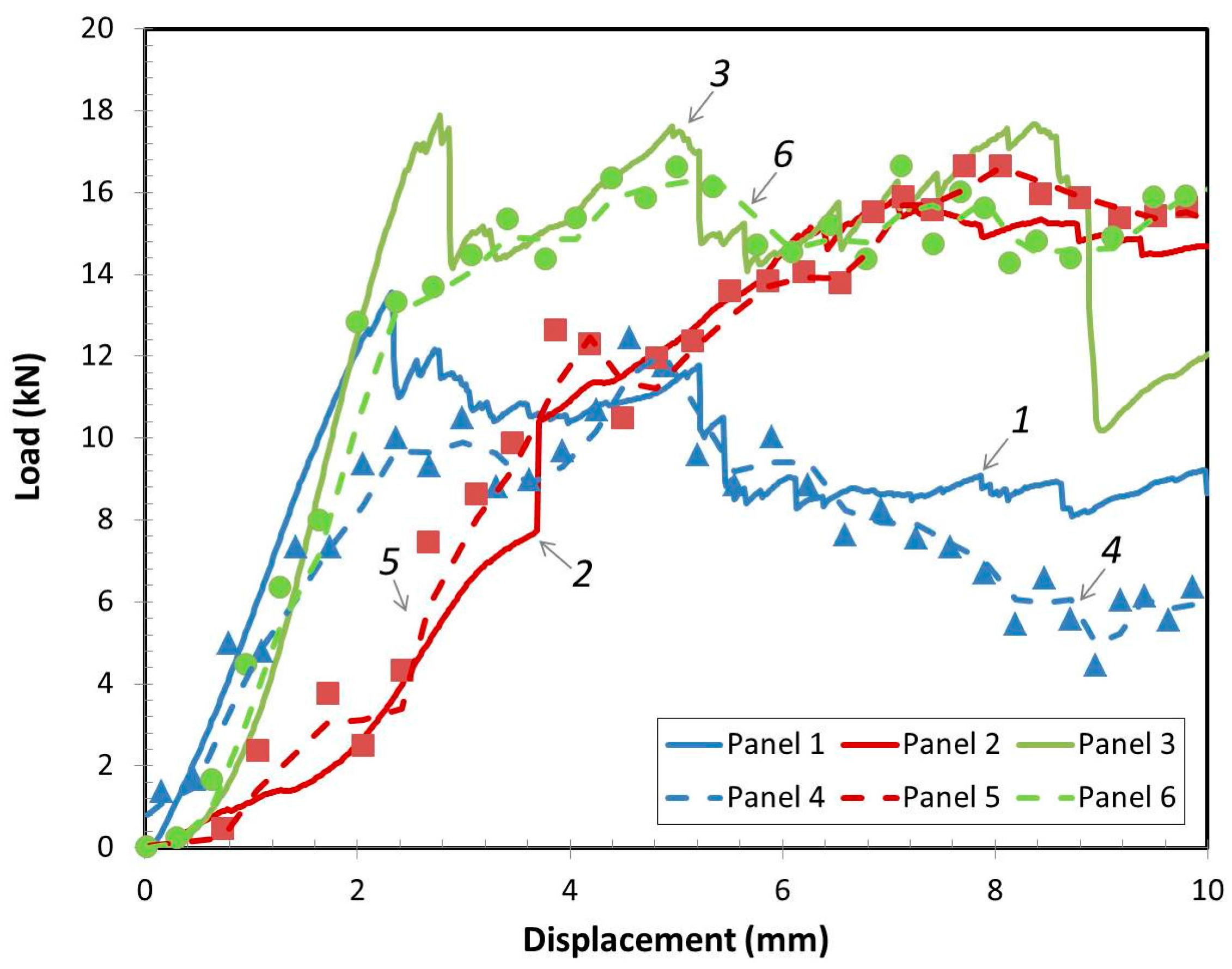
3.1. Quasi-Static Compression Test
3.2. Impact Analyses
3.2.1. Impact Analyses of Panels with Different Configurations
3.2.2. Impact Analyses of Panels under Different Impact Energy
3.2.3. Impact Analyses of Panels with Different Impact Locations
3.2.4. Impact Analyses of Panels with Different Impact Heads
3.2.5. Impact Analyses of Panels with Different Size of Core
3.2.6. Comparison of Quasi-Static Compression and Impact Tests
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vasiliev, V.V.; Barynin, V.A.; Rasin, A.F. Anisogrid lattice structures-survey of development and application. Compos. Struct. 2001, 54, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Tran, P.; de Vaucorbeil, A.; Ramaswamy, R.B.; Latourte, F.; Espinosa, H.D. Three-dimensional numerical modeling of composite panels subjected to underwater blast. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2013, 61, 1319–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davalos, J.F.; Qiao, P.; Xu, X.F.; Robinson, J.; Barth, K.E. Modeling and characterization of fiber-reinforced plastic honeycomb sandwich panels for highway bridge applications. Compos. Struct. 2001, 52, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharaf, T.; Fam, A. Experimental investigation of large-scale cladding sandwich panels under out-of-plane transverse loading for building applications. J. Compos. Constr. 2010, 15, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-J.; Tsai, S.W. Analysis and optimum design of composite grid structures. J. Compos. Mater. 1996, 30, 503–534. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Hunt, J.F.; Cai, Z.; Zhou, X. Bending analyses for 3D engineered structural panels made from laminated paper and carbon fabric. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 53, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, L.J.; Ashby, M.F. Cellular Solids, Structure and Properties; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Meo, M.; Vignjevic, R.; Marengo, G. The response of honeycomb sandwich panels under low-velocity impact loading. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2005, 47, 1301–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubel, P.M.; Luo, J.-J.; Daniel, I.M. Low velocity impact behavior of composite sandwich panels. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2005, 36, 1389–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D. Impact behavior and energy absorption of paper honeycomb sandwich panels. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2009, 36, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Chakka, V.S. Isogrid stiffened syntactic foam cored sandwich structure under low velocity impact. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2010, 41, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hunt, J.F.; Gong, S.; Cai, Z. Testing and Evaluation of a Slot and Tab Construction Technique for Light-Weight Wood-Fiber-Based Structural Panels Under Bending. J. Test. Eval. 2016, 44, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hunt, J.F.; Gong, S.; Cai, Z. High Strength Wood-based Sandwich Panels reinforced with fiberglass and foam. BioResources 2014, 9, 1898–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hunt, J.F.; Gong, S.; Cai, Z. Simplified Analytical Model and Balanced Design Approach for Light-Weight Wood-Based Structural Panel in Bending. Compos. Struct. 2016, 136, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hunt, J.F.; Gong, S.; Cai, Z. Wood-based Tri-Axial Sandwich Composite Materials, Design Fabrication, Testing, Modeling and Application. In Proceedings of the CAMX Conference Proceedings, Orlando, FL, USA, 13–16 October 2014.
- Li, J.; Hunt, J.F.; Gong, S.; Cai, Z. Improved fatigue performance for wood-based structural panels using slot and tab construction. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 82, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hunt, J.F.; Gong, S.; Cai, Z. Fatigue behavior of wood-fiber-based tri-axial engineered sandwich composite panels (ESCP). Holzforschung 2016, 70, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; McDonald, A.G.; Stark, N.M. Grafting of bacterial polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) onto cellulose via in situ reactive extrusion with dicumyl peroxide. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 1040–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Stark, N.M.; McDonald, A.G. Interfacial improvements in biocomposites based on poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) and poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) bioplastics reinforced and grafted with α-cellulose fibers. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 4800–4814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; McDonald, A.G.; Freitag, C.; Morrell, J.J. Effects of wood fiber esterification on properties, weatherability and biodurability of wood plastic composites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 1348–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; McDonald, A.G. A Review on Grafting of Biofibers for Biocomposites. Materials 2016, 9, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Liang, S.; McDonald, A.G. Thermophysical properties and biodegradation behavior of green composites made from polyhydroxybutyrate and potato peel waste fermentation residue. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 69, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard A. D638. Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard A. D695. Standard Test Method for Compressive Properties of Rigid Plastics; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Standard A. C365. Standard Test Method for Flatwise Compressive Properties of Sandwich Cores; ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Standard A. D7136/D7136M-05. Standard Test Method for Measuring the Damage Resistance of a Fiberreinforced Polymer Matrix Composite to a Drop-Weight Impact Event; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]








| Materials | Nominal Thickness (mm) | Comp. Strength MD b (MPa) | Comp. Strength CD c (MPa) | Tensile Strength MD b (MPa) | Tensile Strength CD c (MPa) | MOE MD b (GPa) | MOE CD c (GPa) | Shear Modulus (GPa) | Poisson’s Ratio MD | Poisson’s Ratio CD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laminated papers (LP) | 2.4 | 195.1 | 168.7 | 173.9 | 118.6 | 11.6 | 8.3 | 4.3 | 0.36 | 0.27 |
| Carbon fiber fabric w-L a | 3.2 | 195.1 | 168.7 | 216.6 | 132.2 | 16.3 | 13.6 | 6.0 | 0.36 | 0.46 |
| Epoxy resin | - | 105.9 | - | 31.0 | - | 1.4 | - | 0.54 | 0.3 | - |
| Urethane foam | - | 0.41 | - | 0.48 | - | 0.005 | - | 0.002 | 0.46 | - |
| Group | Test | Panel Density (Kg/m3) | Core Slot Spacing (mm) | Foam | Carbon Fiber Fabric Face | Load Head Diameter (mm) | Impact Energy (J) | Impact Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Panel 1 | Quasi-static compression | 455.8 (7.93) a | 25 | - | - | 38 | - | center |
| Panel 2 | Quasi-static compression | 530.8 (1.83) | 25 | + | - | 38 | - | center |
| Panel 3 | Quasi-static compression | 470.9 (4.01) | 25 | - | + | 38 | - | center |
| Panel 4 | Impact | 455.8 (7.93) | 25 | - | - | 38 | 120 | center |
| Panel 5 | Impact | 530.8 (1.83) | 25 | + | - | 38 | 120 | center |
| Panel 6 | Impact | 470.9 (4.01) | 25 | - | + | 38 | 120 | center |
| Panel 7 | Impact | 322.3 (0.39) | 51 | - | - | 38 | 80 | center |
| Panel 8 | Impact | 327.6 (1.17) | 51 | - | - | 38 | 80 | rib |
| Panel 9 | Impact | 316.9 (1.93) | 51 | - | - | 38 | 80 | node |
| Panel 10 | Impact | 317.9 (1.93) | 51 | - | - | 38 | 120 | center |
| Panel 11 | Impact | 317.0 (5.36) | 51 | - | - | 38 | 40 | center |
| Panel 12 | Impact | 319.7 (1.66) | 51 | - | - | 25 | 40 | center |
| Panel 13 | Impact | 320.3 (1.28) | 51 | - | - | 13 | 40 | center |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Hunt, J.F.; Gong, S.; Cai, Z. Quasi-Static Compression and Low-Velocity Impact Behavior of Tri-Axial Bio-Composite Structural Panels Using a Spherical Head. Materials 2017, 10, 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10020185
Li J, Hunt JF, Gong S, Cai Z. Quasi-Static Compression and Low-Velocity Impact Behavior of Tri-Axial Bio-Composite Structural Panels Using a Spherical Head. Materials. 2017; 10(2):185. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10020185
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jinghao, John F Hunt, Shaoqin Gong, and Zhiyong Cai. 2017. "Quasi-Static Compression and Low-Velocity Impact Behavior of Tri-Axial Bio-Composite Structural Panels Using a Spherical Head" Materials 10, no. 2: 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10020185
APA StyleLi, J., Hunt, J. F., Gong, S., & Cai, Z. (2017). Quasi-Static Compression and Low-Velocity Impact Behavior of Tri-Axial Bio-Composite Structural Panels Using a Spherical Head. Materials, 10(2), 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10020185






