Calcium Silicate/Chitosan-Coated Electrospun Poly (Lactic Acid) Fibers for Bone Tissue Engineering
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fabrication of PLA Nanofiber Mat
2.2. Calcium Silicate/Chitosan Coating
2.3. Characterization of CS/CH-PLA Mat
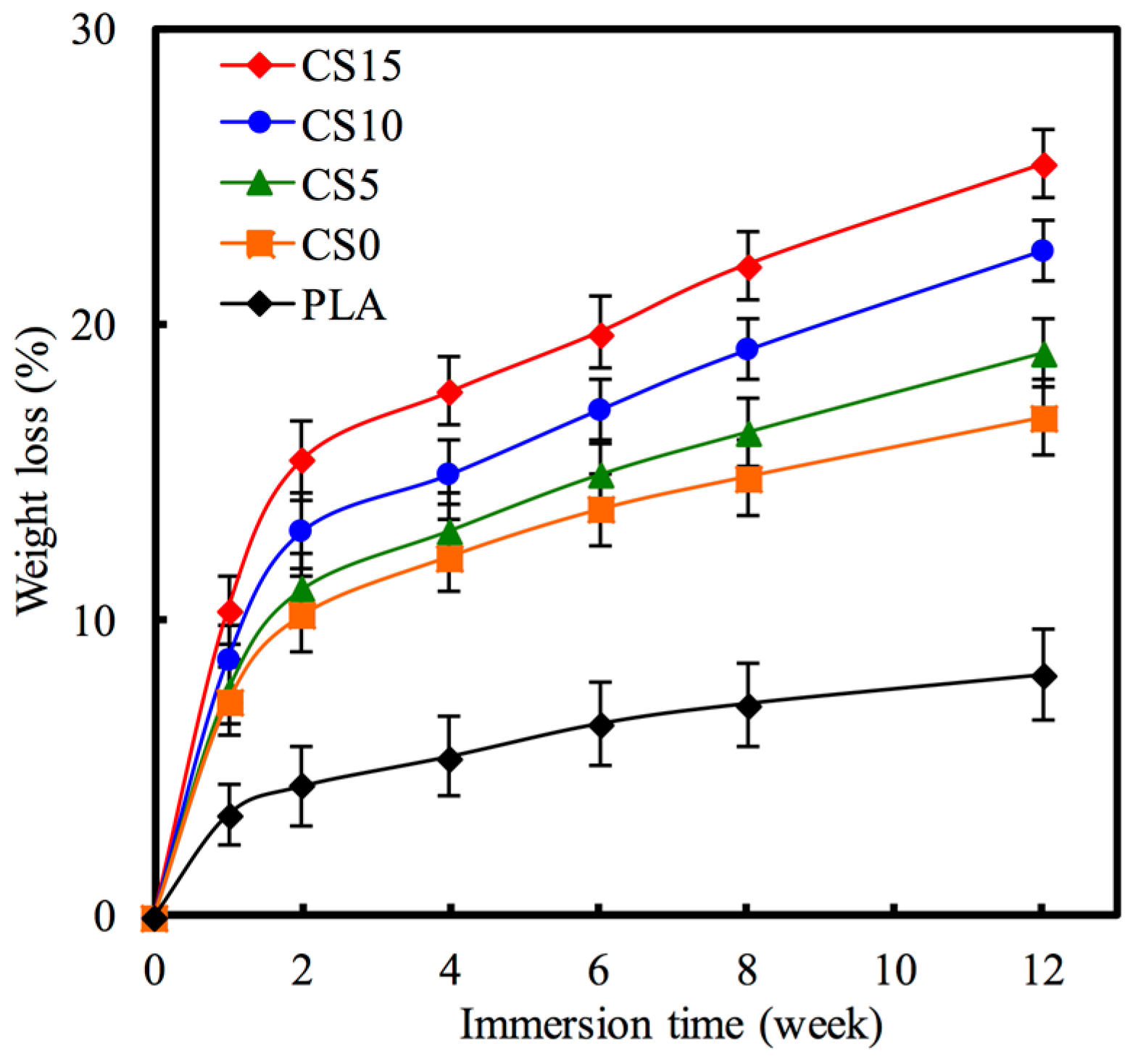
2.4. Weight Loss and Ion Concentration
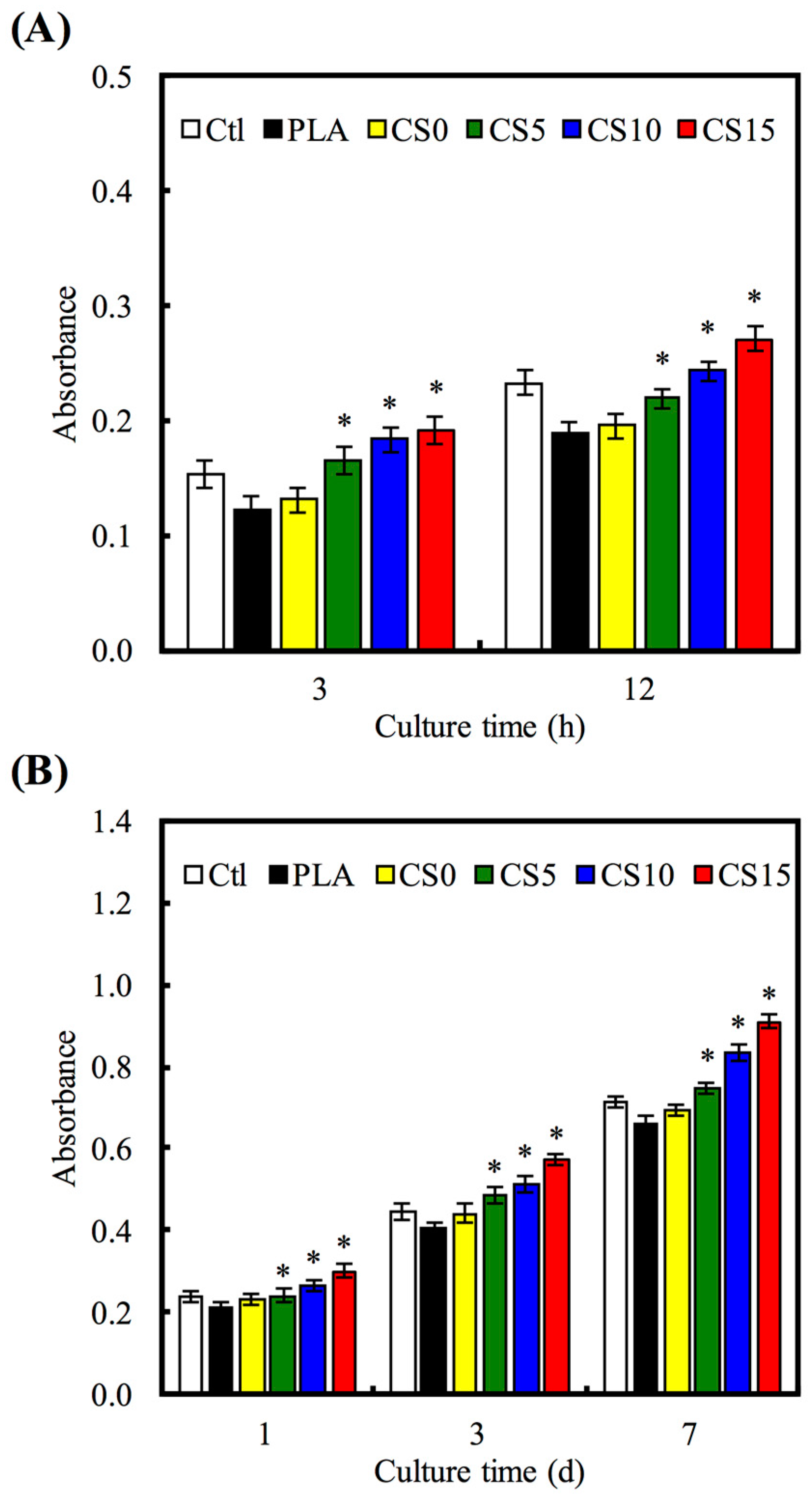
2.5. Cell Adhesion and Proliferation
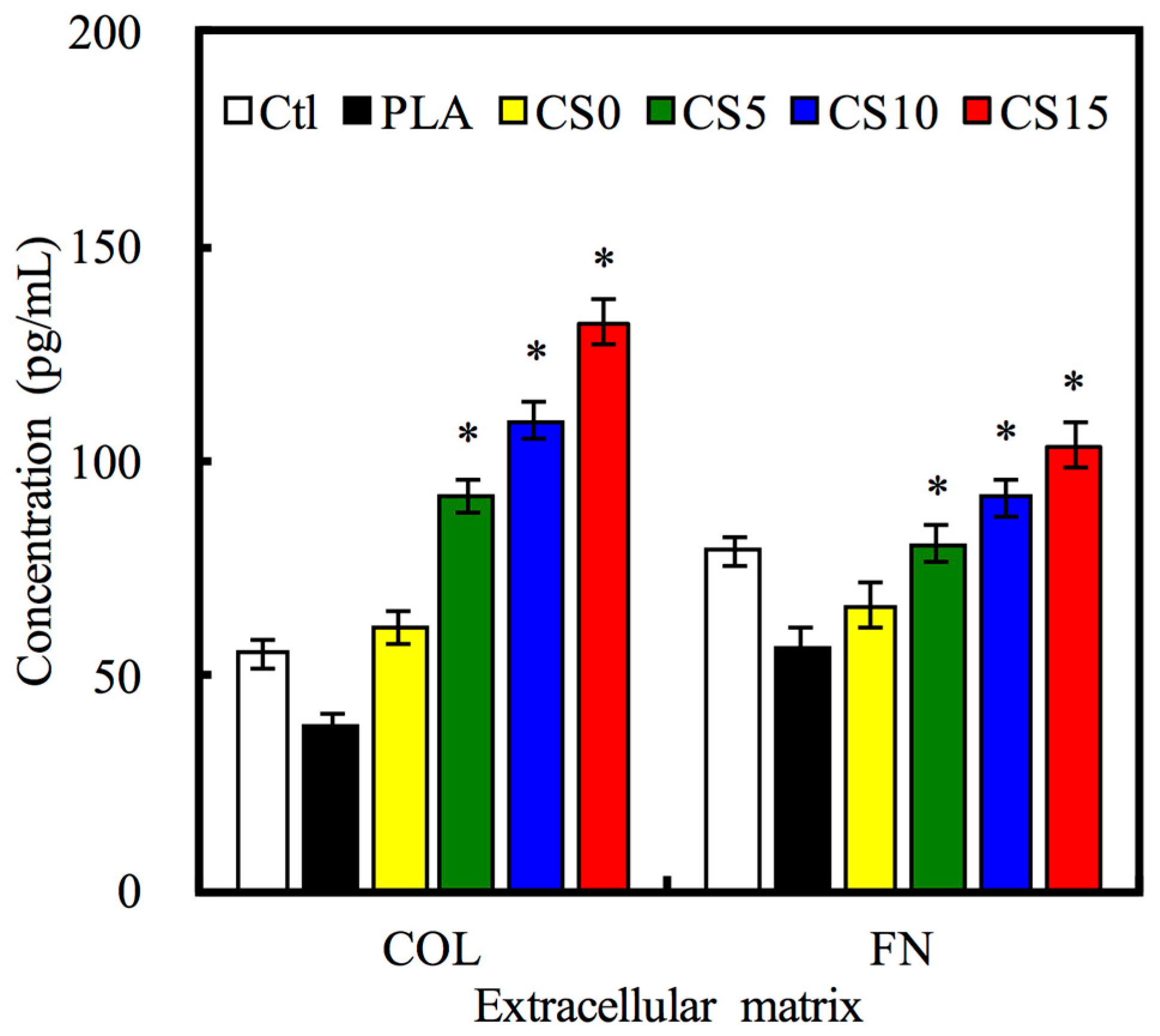
2.6. Protein Adsorption on Substrates
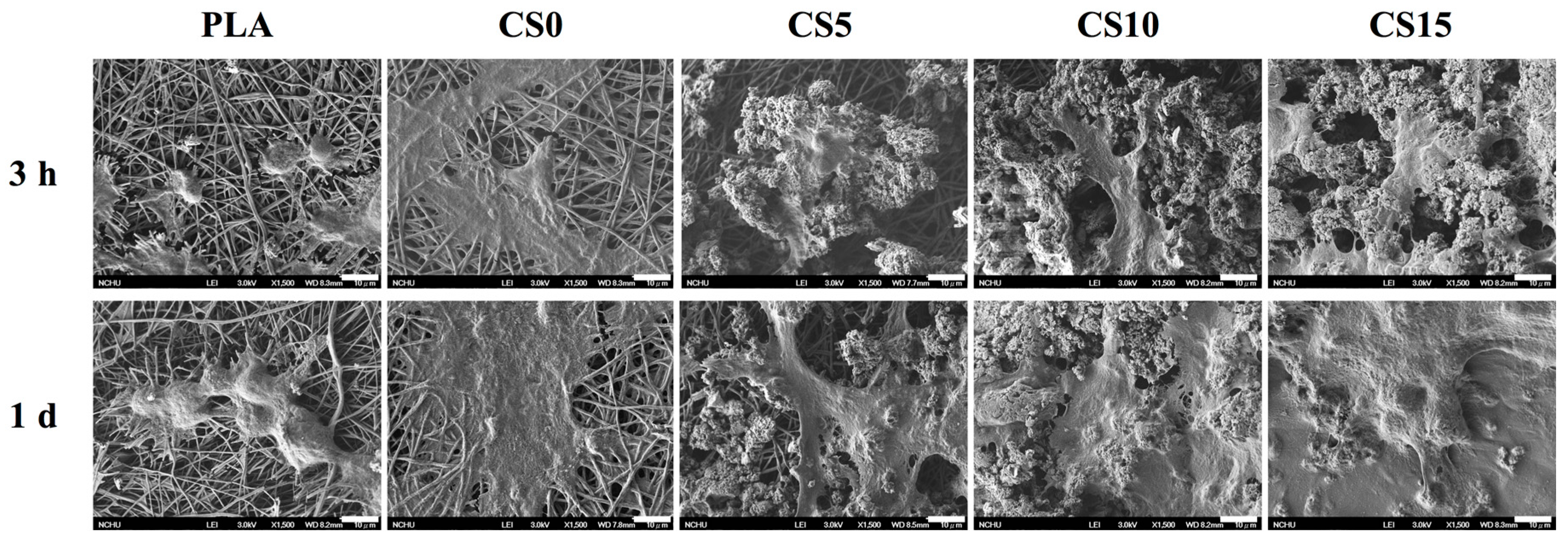
2.7. Cell Morphology
2.8. Real-Time PCR
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
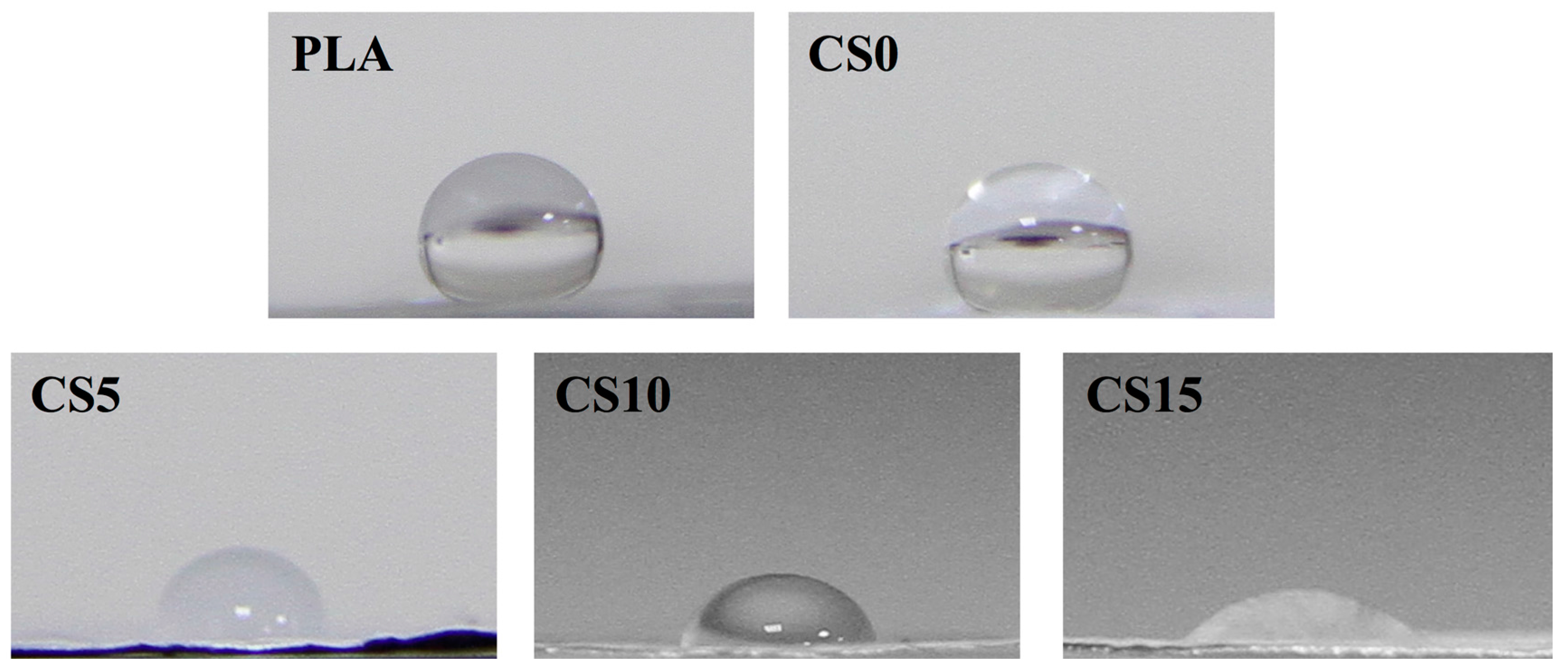
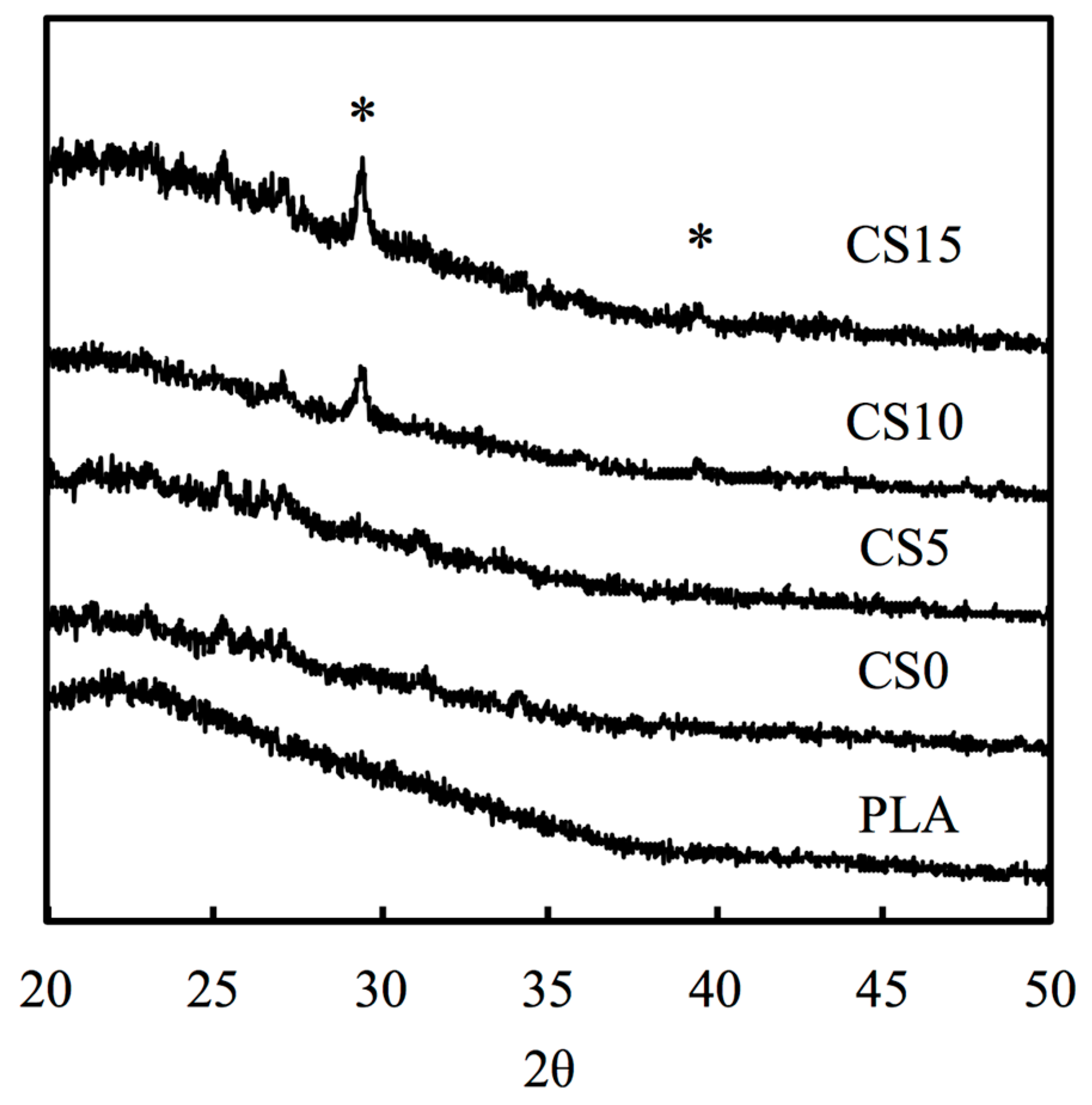
3.1. Characterization of CS/CH-Coated PLA Mats
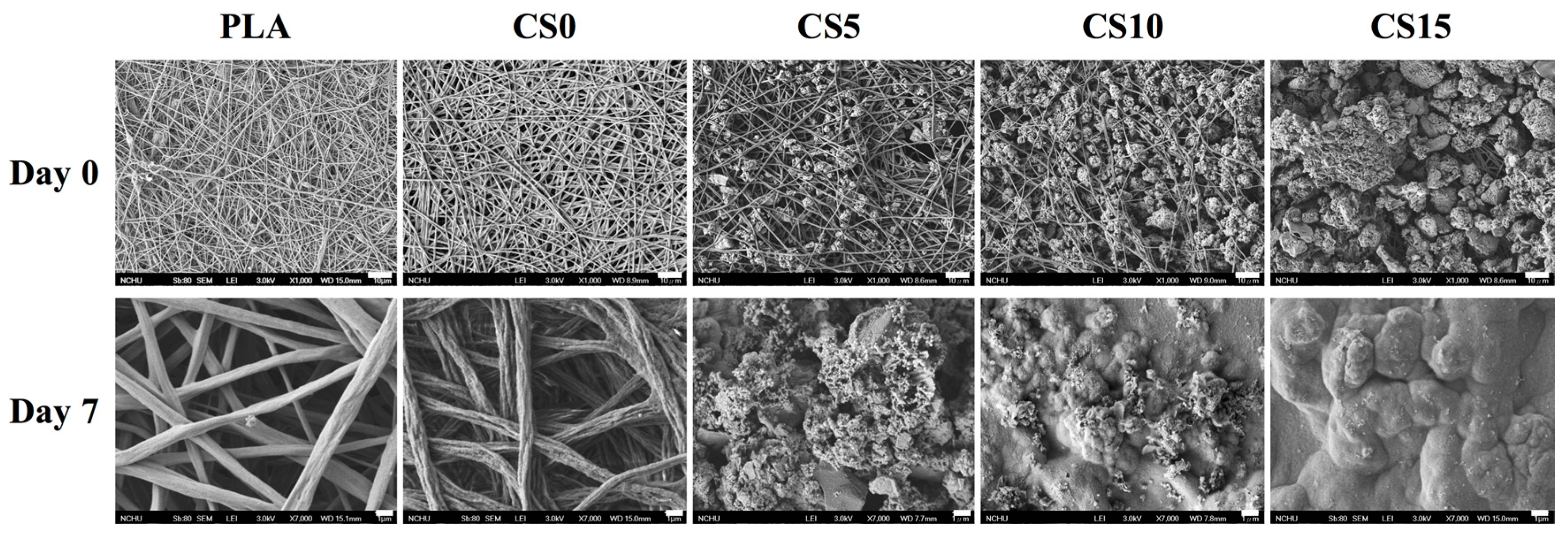
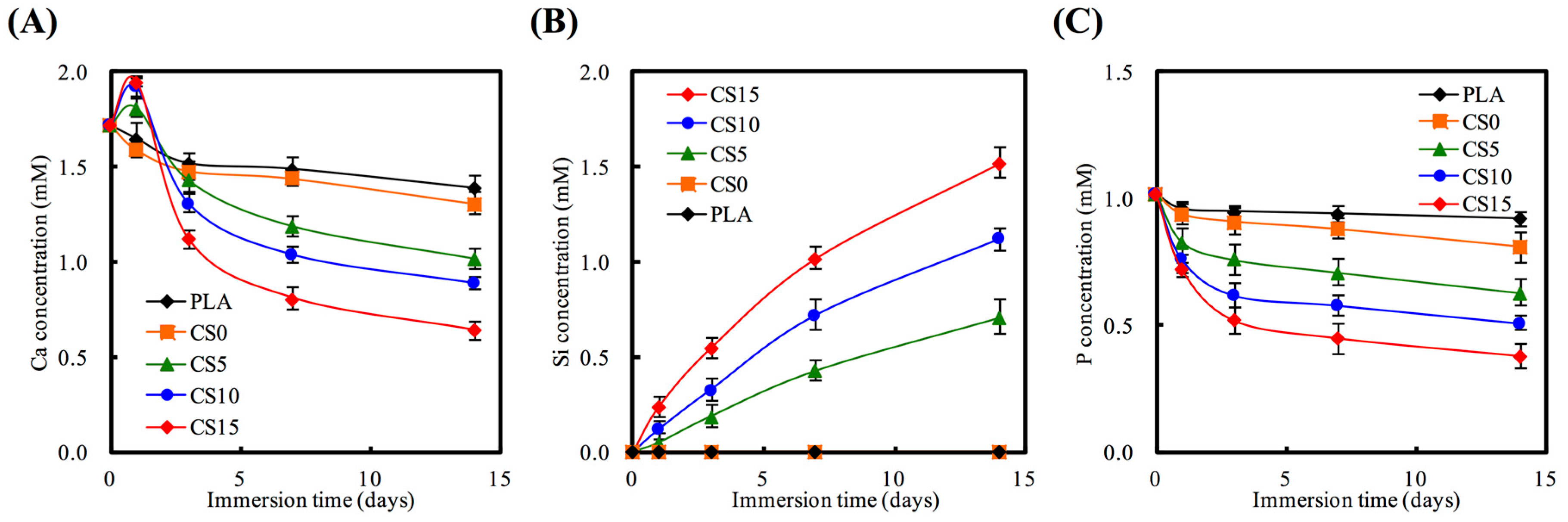
3.2. Bioactivity
3.3. Protein Adsorption
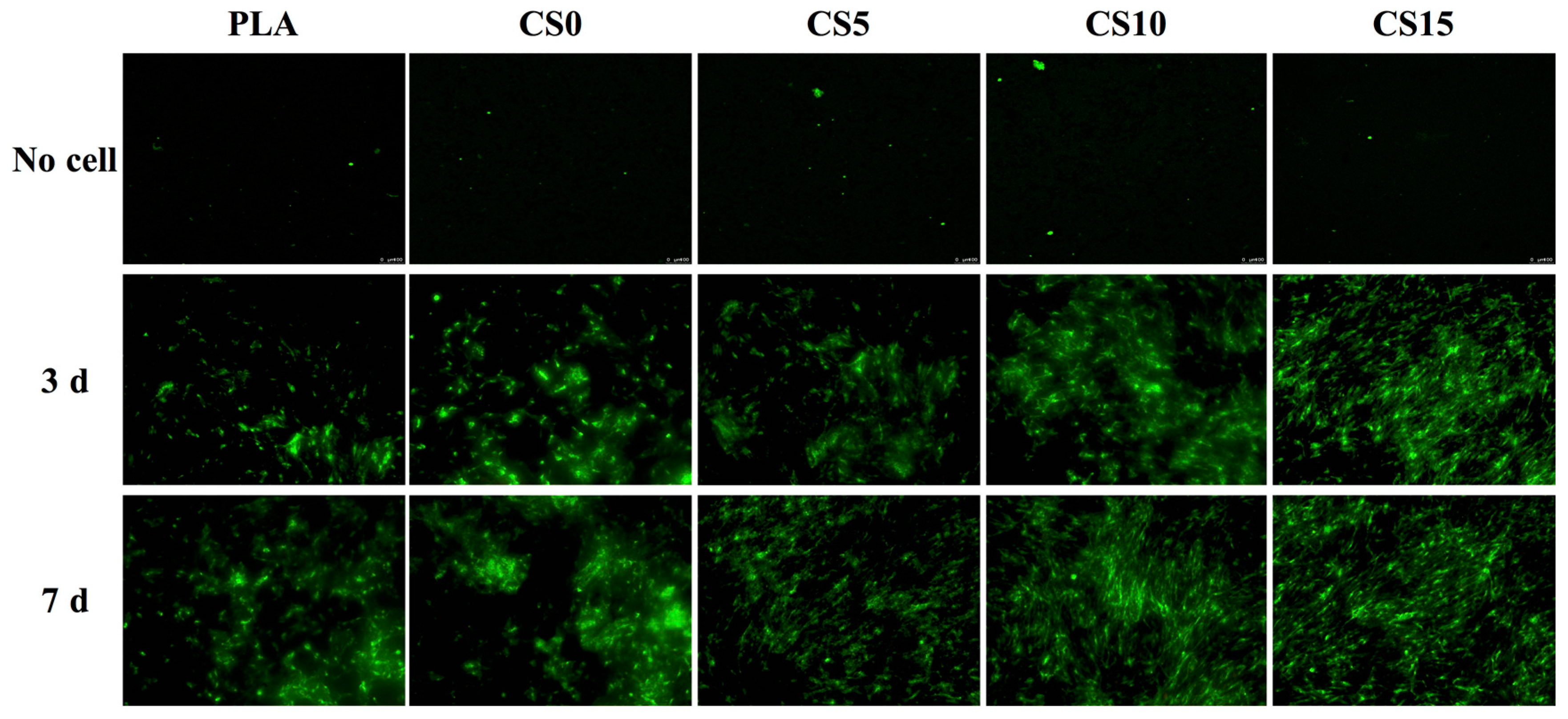
3.4. Cell Adhesion and Proliferation
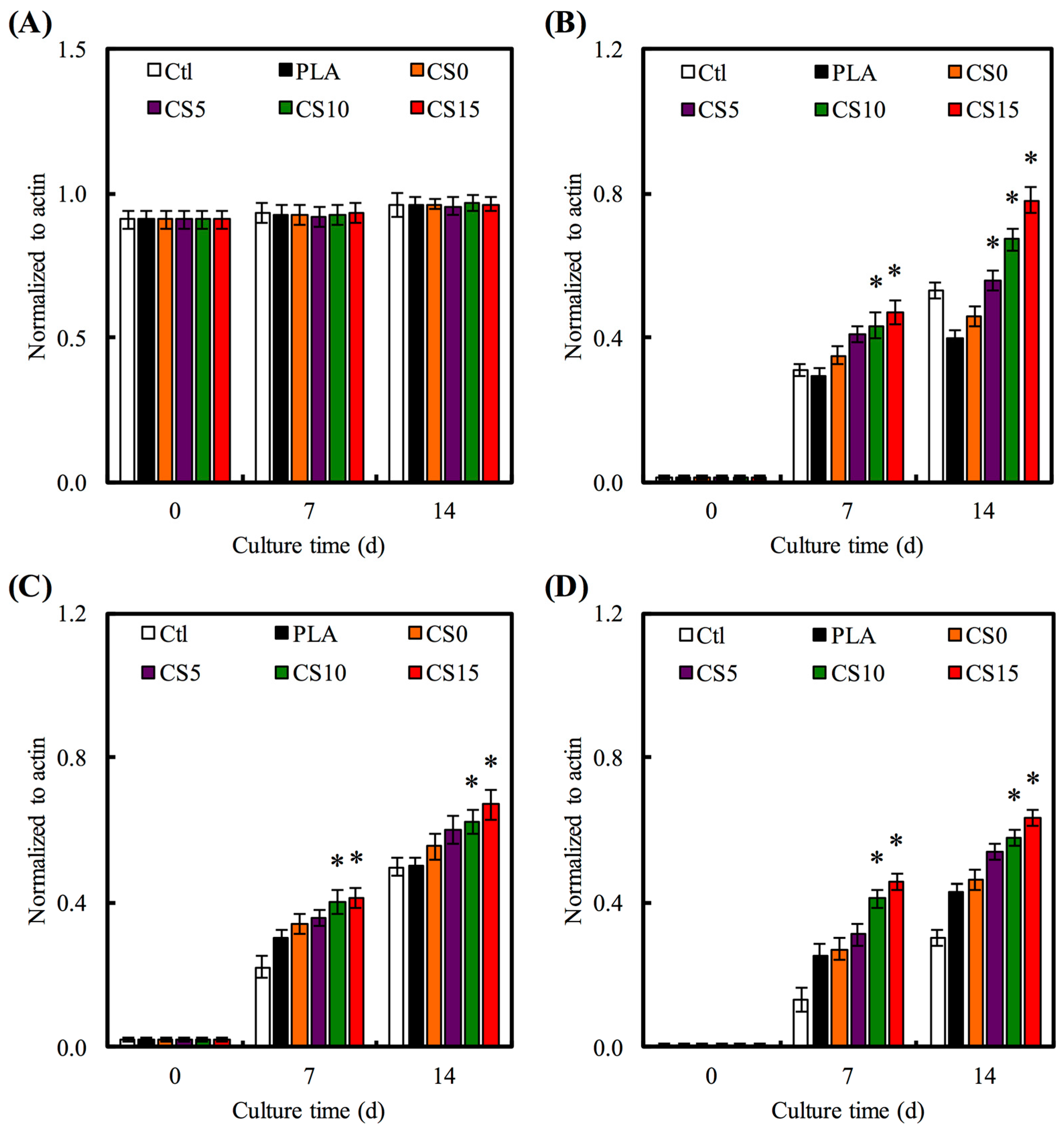
3.5. Osteogenesis Gene Expression
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mikos, A.; Herring, S.; Ochareon, P. Engineering complex tissues. Tissue Eng. 2006, 12, 3307–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.C.; Fu, S.J.; Lin, Y.C.; Yang, I.K.; Gu, Y. Chitosan-coated electrospun PLA fibers for rapid mineralization of calcium phosphate. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 68, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, B.; Wu, C.; Chang, J. Dual drug release from electrospun poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)/mesoporous silica nanoparticles composite mats with distinct release profiles. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 1901–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Liao, S.; Ngiam, M.; Chan, C.K.; Ramakrishna, S. Degradation behaviors of electrospun resorbable polyester nanofibers. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2009, 15, 333–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzwarth, J.M.; Ma, P.X. Biomimetic nanofibrous scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 9622–9629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Murugan, R.; Wang, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospinning of nano/micro scale poly(l-lactic acid) aligned fibers and their potential in neural tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 2603–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Liu, W.; Sun, J.; Xianyu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, W.; Huang, D.; Di, S.; Long, Y.-Z.; et al. Culturing primary human osteoblasts on electrospun poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) and poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)/nanohydroxyapatite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 5921–5926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Cheng, L.; Zhao, J.; Jin, R.; Sun, B.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, W. bFGF-grafted electrospun fibrous scaffolds via poly(dopamine) for skin wound healing. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 3636–3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajzer, I.; Menaszek, E.; Kwiatkowski, R.; Planell, J.A.; Castaño, O. Electrospun gelatin/poly(ε-caprolactone) fibrous scaffold modified with calcium phosphate for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2014, 44, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kai, D.; Liow, S.S.; Loh, X.J. Biodegradable polymers for electrospinning: Towards biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2014, 45, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wang, M. Electrospun multicomponent and multifunctional nanofibrous bone tissue engineering scaffolds. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 1388–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; He, J.; Sang, F.; Ding, B.; Chen, L.; Cui, S.; Li, K.; Han, Q.; Tan, W. Coaxial electrospun aligned tussah silk fibroin nanostructured fiber scaffolds embedded with hydroxyapatite–tussah silk fibroin nanoparticles for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 58, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, S.; Li, J.J.; Li, X.; Ma, Y.; Hou, Y.; Jiang, N.; Xu, C.; Zhang, S.; et al. Novel bone substitute composed of chitosan and strontium-doped α-calcium sulfate hemihydrate: Fabrication, characterisation and evaluation of biocompatibility. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 66, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Cui, Z.-K.; Fan, J.; Fartash, A.; Aghaloo, T.L.; Lee, M. Photocrosslinkable chitosan hydrogels functionalized with the RGD peptide and phosphoserine to enhance osteogenesis. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 5289–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Q.; Li, W.; Yu, S.; Ma, L.; Jin, D.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Liu, Y. Multifunctional chitosan/polyvinyl pyrrolidone/45S5 Bioglass® scaffolds for MC3T3-E1 cell stimulation and drug release. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2015, 56, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arunkumar, P.; Indulekha, S.; Vijayalakshmi, S.; Srivastava, R. Poly (caprolactone) microparticles and chitosan thermogels based injectable formulation of etoricoxib for the potential treatment of osteoarthritis. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 61, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Li, X. Development of porous Ti6Al4V/chitosan sponge composite scaffold for orthopedic applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 58, 1177–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.P.; Guan, J.J.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.Q.; Ke, Q.F. Hybrid nanostructured hydroxyapatite–Chitosan composite scaffold: Bioinspired fabrication, mechanical properties and biological properties. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 4679–4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Xu, Z.; Ke, Q.; Yin, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, C.; Guo, Y. Strontium hydroxyapatite/chitosan nanohybrid scaffolds with enhanced osteoinductivity for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 72, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Huang, X.; Han, Y. Formation mechanism and cytocompatibility of nano-shaped calcium silicate hydrate/calcium titanium silicate/TiO2 composite coatings on titanium. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 6734–6745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, F.; Sousa Gomes, P.; Fernandes, M.H. Osteogenic and angiogenic response to calcium silicate-based endodontic sealers. J. Endod. 2016, 42, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.W.; Hsu, T.T.; Wang, K.; Shie, M.Y. Preparation of the fast setting and degrading Ca-Si-Mg cement with both odontogenesis and angiogenesis differentiation of human periodontal ligament cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 60, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.H.; Shen, Y.F.; Hsu, T.T.; Huang, T.H.; Shie, M.Y. Physical characteristics, antimicrobial and odontogenesis potentials of calcium silicate cement containing hinokitiol. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 65, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shie, M.Y.; Chiang, W.H.; Chen, I.W. P.; Liu, W.Y.; Chen, Y.W. Synergistic acceleration in the osteogenic and angiogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells by calcium silicate–graphene composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 73, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, N.J.; Chen, Y.W.; Shieh, D.E.; Fang, H.Y.; Shie, M.Y. The effects of injectable calcium silicate-based composites with the Chinese herb on an osteogenic accelerator in vitro. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 10, 055004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, T.T.; Kao, C.T.; Chen, Y.W.; Huang, T.H.; Yang, J.J.; Shie, M.Y. The synergistic effects of CO2 laser treatment with calcium silicate cement of antibacterial, osteogenesis and cementogenesis efficacy. Laser Phys. Lett. 2015, 12, 055602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.Y.; Huang, T.H.; Kao, C.T.; Wu, Y.H.; Chen, W.C.; Shie, M.Y. Mesoporous calcium silicate nanoparticles with drug delivery and odontogenesis properties. J. Endod. 2017, 43, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shie, M.Y.; Ding, S.J.; Chang, H.C. The role of silicon in osteoblast-like cell proliferation and apoptosis. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 2604–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.W.; Ho, C.C.; Huang, T.H.; Hsu, T.T.; Shie, M.Y. The ionic products from mineral trioxide aggregate–induced odontogenic differentiation of dental pulp cells via activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J. Endod. 2016, 42, 1062–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.C.; Fu, S.J. Osteogenesis of human adipose-derived stem cells on poly(dopamine)-coated electrospun poly(lactic acid) fiber mats. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 58, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.L.; Chen, Y.W.; Wang, K.; Shie, M.Y. Enhanced adhesion and differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cell inside apatite-mineralized/poly(dopamine)-coated poly(ε-caprolactone) scaffolds by stereolithography. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 6307–6315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, K.Y.; Lin, H.Y.; Chen, Y.W.; Lin, C.Y.; Hsu, T.T.; Kao, C.T. Laser sintered magnesium-calcium silicate/poly-ε-caprolactone scaffold for bone tissue ngineering. Materials 2017, 10, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.W.; Yeh, C.H.; Shie, M.Y. Stimulatory effects of the fast setting and degradable Ca–Si–Mg cement on both cementogenesis and angiogenesis differentiation of human periodontal ligament cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 7099–7108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawelec, K.M.; Shepherd, J.; Jugdaohsingh, R.; Best, S.M.; Cameron, R.E.; Brooks, R.A. Collagen scaffolds as a tool for understanding the biological effect of silicates. Mater. Lett. 2015, 157, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Walsh, J.; Wei, M. Covalent immobilization of collagen on titanium through polydopamine coating to improve cellular performances of MC3T3-E1 cells. RSC Adv. 2013, 4, 7185–7192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Osaka, A.; Ikoma, T.; Morita, H.; Li, J.; Takeguchi, M.; Hanagata, N. Fabrication, microstructure, and BMP-2 delivery of novel biodegradable and biocompatible silicate-collagen hybrid fibril sheets. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 10942–10948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Fan, J.; Ye, W.; Zhang, H.; Cong, Y.; Xiao, J. A highly specific graphene platform for sensing collagen triple helix. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 1064–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lode, A.; Meyer, M.; Brüggemeier, S.; Paul, B.; Baltzer, H.; Schröpfer, M.; Winkelmann, C.; Sonntag, F.; Gelinsky, M. Additive manufacturing of collagen scaffolds by three-dimensional plotting of highly viscous dispersions. Biofabrication 2016, 8, 015015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shie, M.Y.; Ding, S.J. Integrin binding and MAPK signal pathways in primary cell responses to surface chemistry of calcium silicate cements. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 6589–6606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, W.Y.; Chen, Y.W.; Kao, C.T.; Hsu, T.T.; Huang, T.H.; Shie, M.Y. Human dental pulp cells responses to apatite precipitation from dicalcium silicates. Materials 2015, 8, 4491–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zheng, K.; Zhang, J.; Tang, T.; Guo, H.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Wei, J. Effects of magnesium silicate on the mechanical properties, biocompatibility, bioactivity, degradability, and osteogenesis of poly(butylene succinate)-based composite scaffolds for bone repair. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 7974–7988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.H.; Hung, C.J.; Huang, T.H.; Lin, C.C.; Kao, C.T.; Shie, M.Y. Odontogenic differentiation of human dental pulp cells by calcium silicate materials stimulating via FGFR/ERK signaling pathway. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2014, 43, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, C.J.; Hsu, H.I.; Lin, C.C.; Huang, T.H.; Wu, B.C.; Kao, C.T.; Shie, M.Y. The role of integrin αv in proliferation and differentiation of human dental pulp cell response to calcium silicate cement. J. Endod. 2014, 40, 1802–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.C.; Kao, C.T.; Huang, T.H.; Hung, C.J.; Shie, M.Y.; Chung, H.Y. Effect of verapamil, a calcium channel blocker, on the odontogenic activity of human dental pulp cells cultured with silicate-based materials. J. Endod. 2014, 40, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, C.-J.; Tu, M.-G.; Wei, L.-J.; Hsu, T.-T.; Kao, C.-T.; Chen, T.-H.; Huang, T.-H. Calcium Silicate/Chitosan-Coated Electrospun Poly (Lactic Acid) Fibers for Bone Tissue Engineering. Materials 2017, 10, 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10050501
Su C-J, Tu M-G, Wei L-J, Hsu T-T, Kao C-T, Chen T-H, Huang T-H. Calcium Silicate/Chitosan-Coated Electrospun Poly (Lactic Acid) Fibers for Bone Tissue Engineering. Materials. 2017; 10(5):501. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10050501
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Chu-Jung, Ming-Gene Tu, Li-Ju Wei, Tuan-Ti Hsu, Chia-Tze Kao, Tsui-Han Chen, and Tsui-Hsien Huang. 2017. "Calcium Silicate/Chitosan-Coated Electrospun Poly (Lactic Acid) Fibers for Bone Tissue Engineering" Materials 10, no. 5: 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10050501
APA StyleSu, C.-J., Tu, M.-G., Wei, L.-J., Hsu, T.-T., Kao, C.-T., Chen, T.-H., & Huang, T.-H. (2017). Calcium Silicate/Chitosan-Coated Electrospun Poly (Lactic Acid) Fibers for Bone Tissue Engineering. Materials, 10(5), 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10050501




