Chemically Surface Tunable Solubility Parameter for Controllable Drug Delivery—An Example and Perspective from Hollow PAA-Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles with R6G Model Drug
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Hollow Fe3O4 NPs
2.2. The Surface Coating and Decoration of Hollow Magnetic Composite Particles
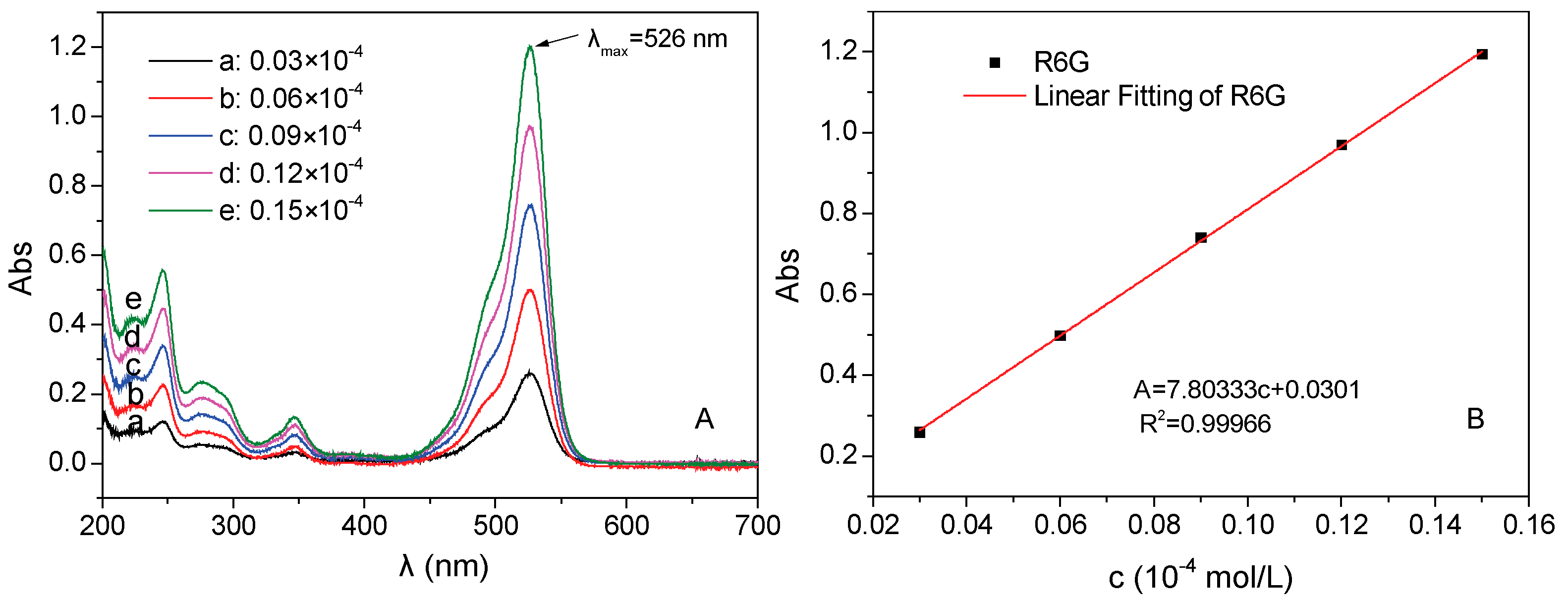
2.3. The Preparation of Standard Curve of Rhodamine 6G
2.4. Drug Loadings and Releasing Tests of Fe3O4/PAA
3. Result and Discussion
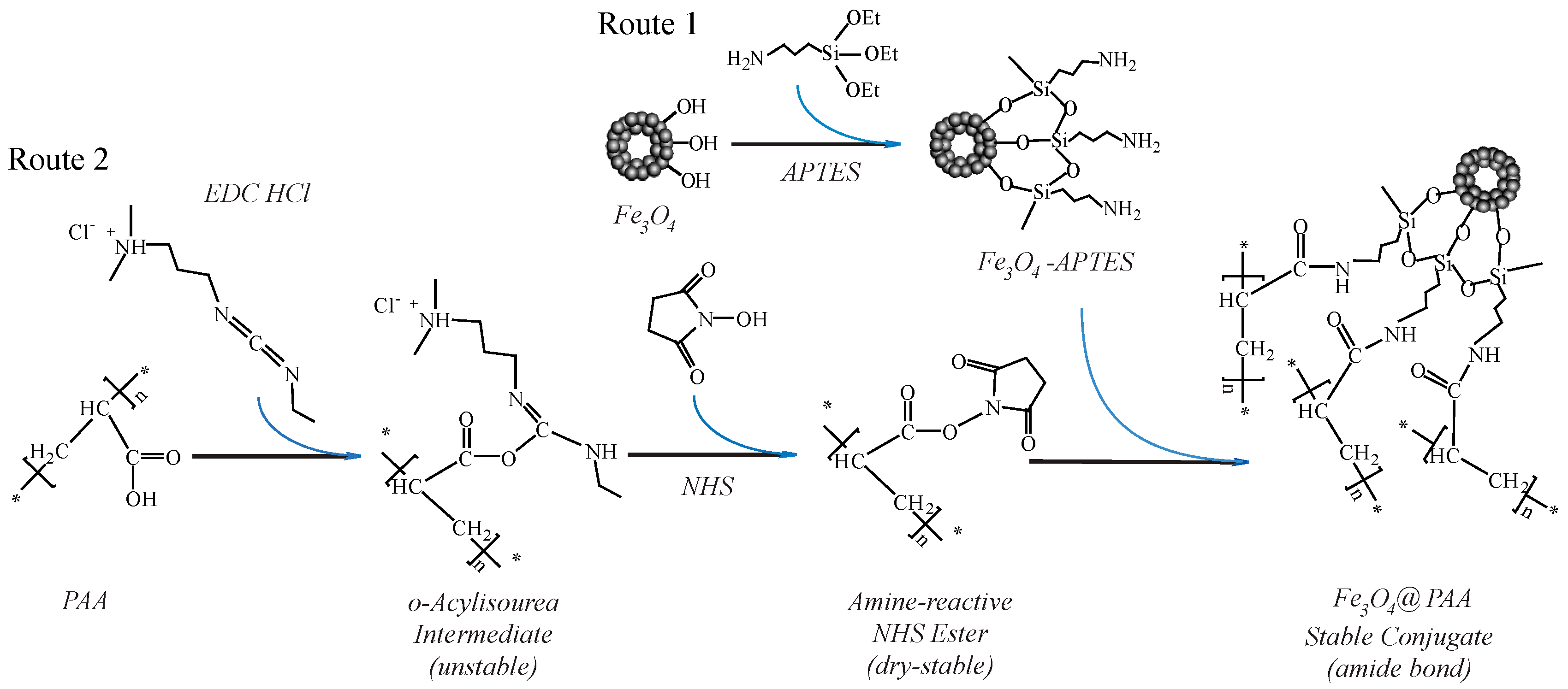
3.1. The Principle of the Preparation of Fe3O4/PAA Composite Magnetic NPs
3.2. The Morphologies of the Fe3O4/PAA Composited NPs
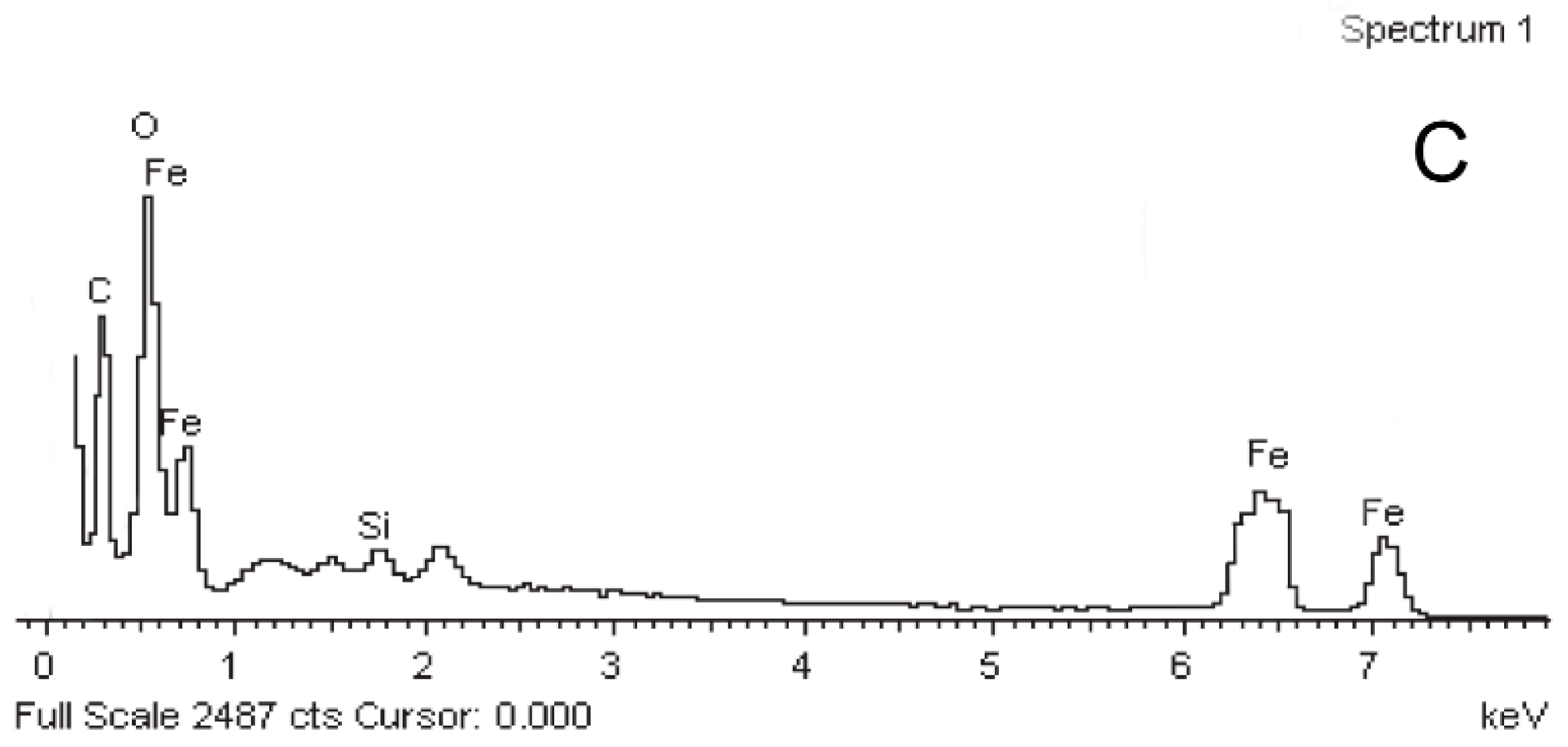
3.3. The Structure and Element Analysis of the Fe3O4/PAA Composited NPs
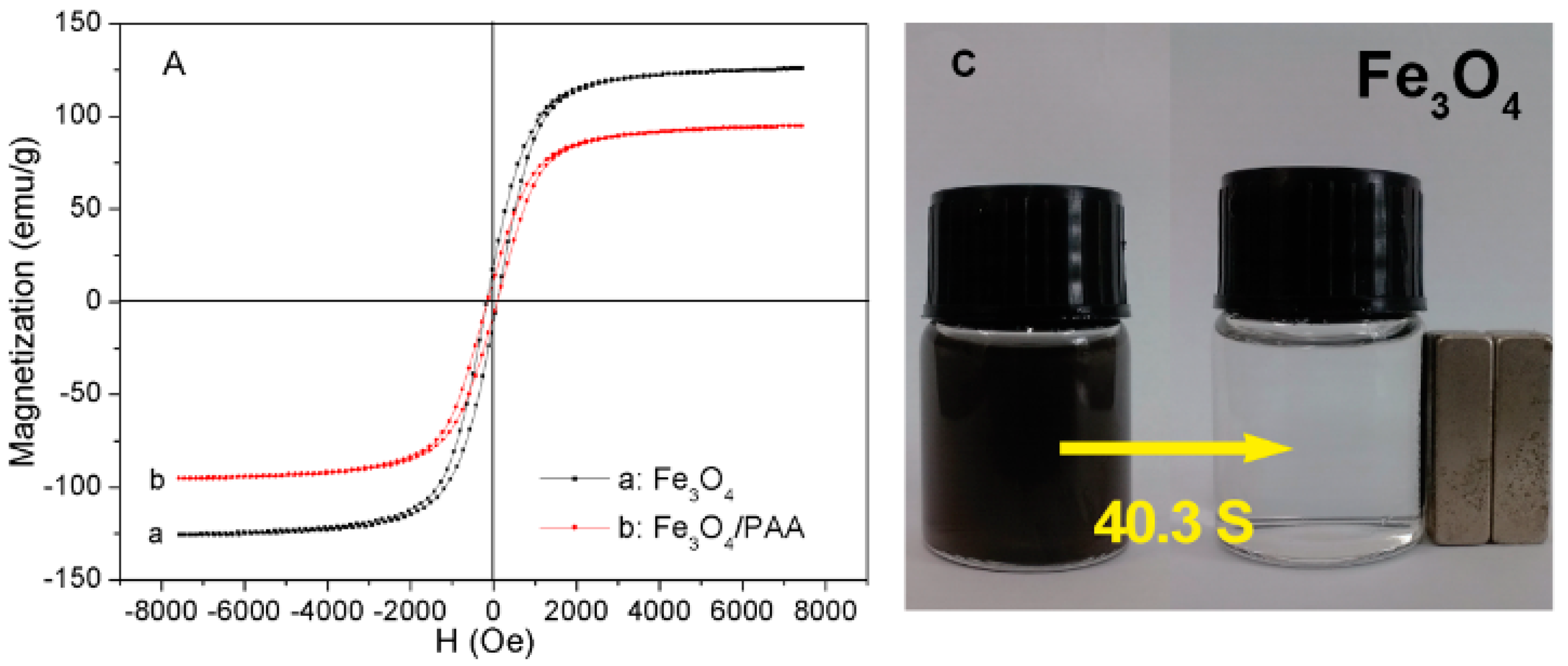
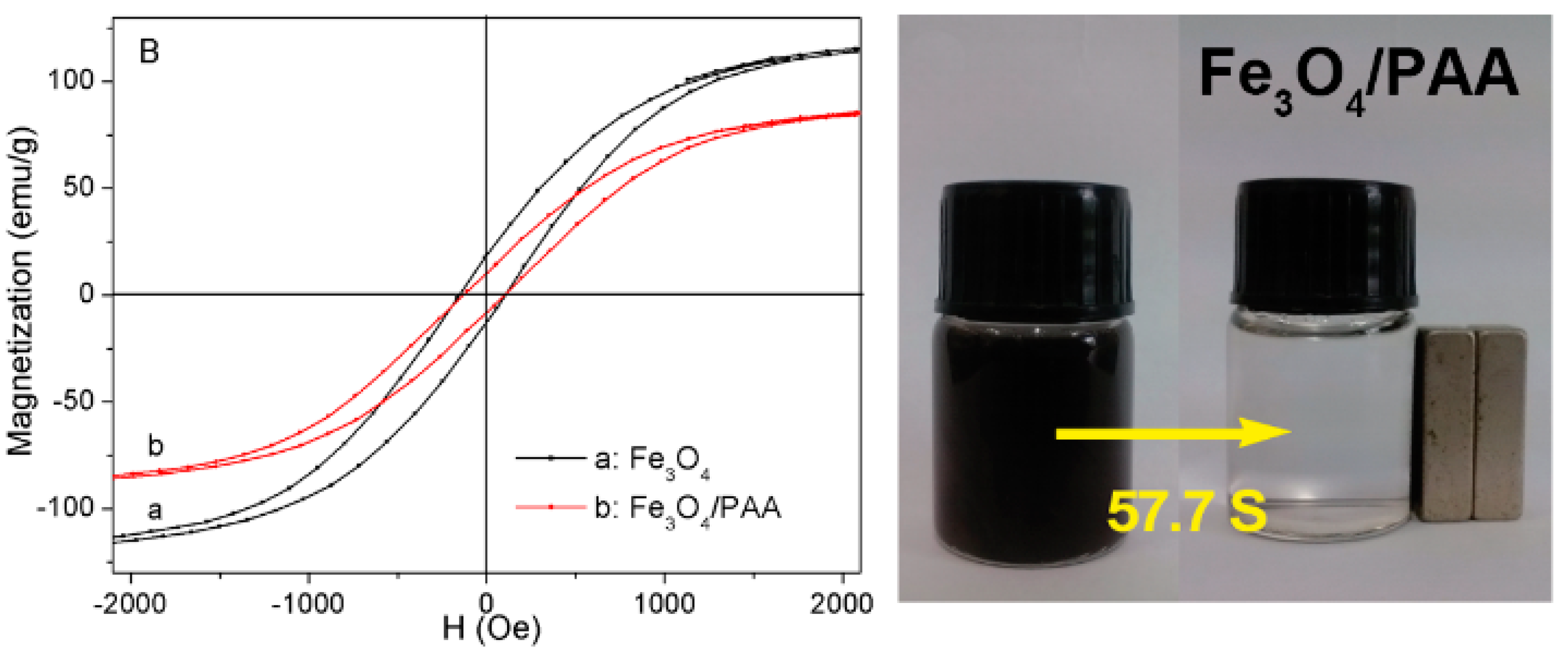
3.4. The Magnetic Properties of the Fe3O4/PAA Composited NPs
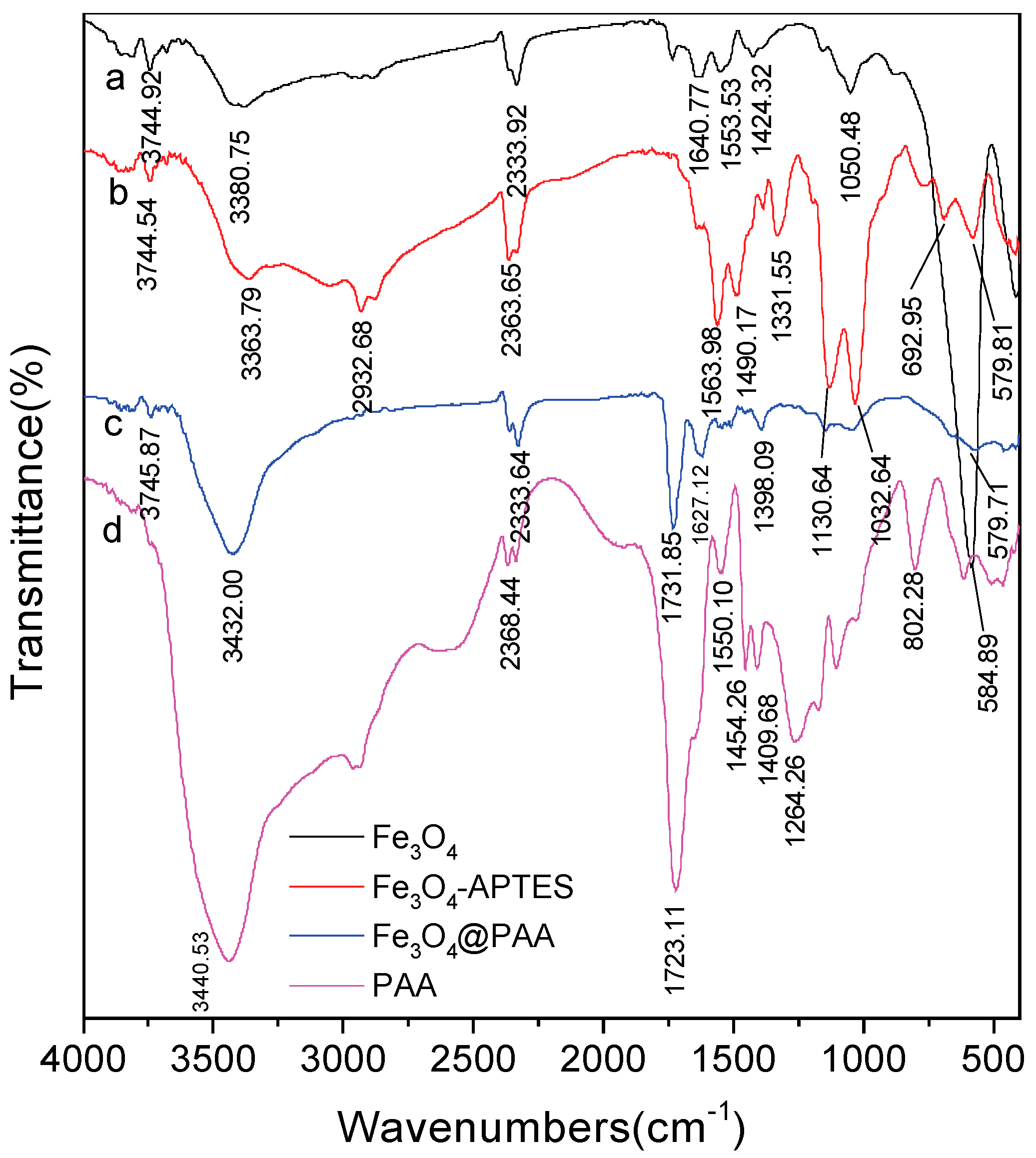
3.5. The FT-IR Spectra of the Fe3O4/PAA Composited NPs
3.6. The Thermogravimetry of the Fe3O4/PAA Composited NPs
3.7. Drug Loadings Tests of the Fe3O4/PAA Composited NPs
3.8. The Influence Factors for Adsorption Properties of the Fe3O4/PAA Composited NPs
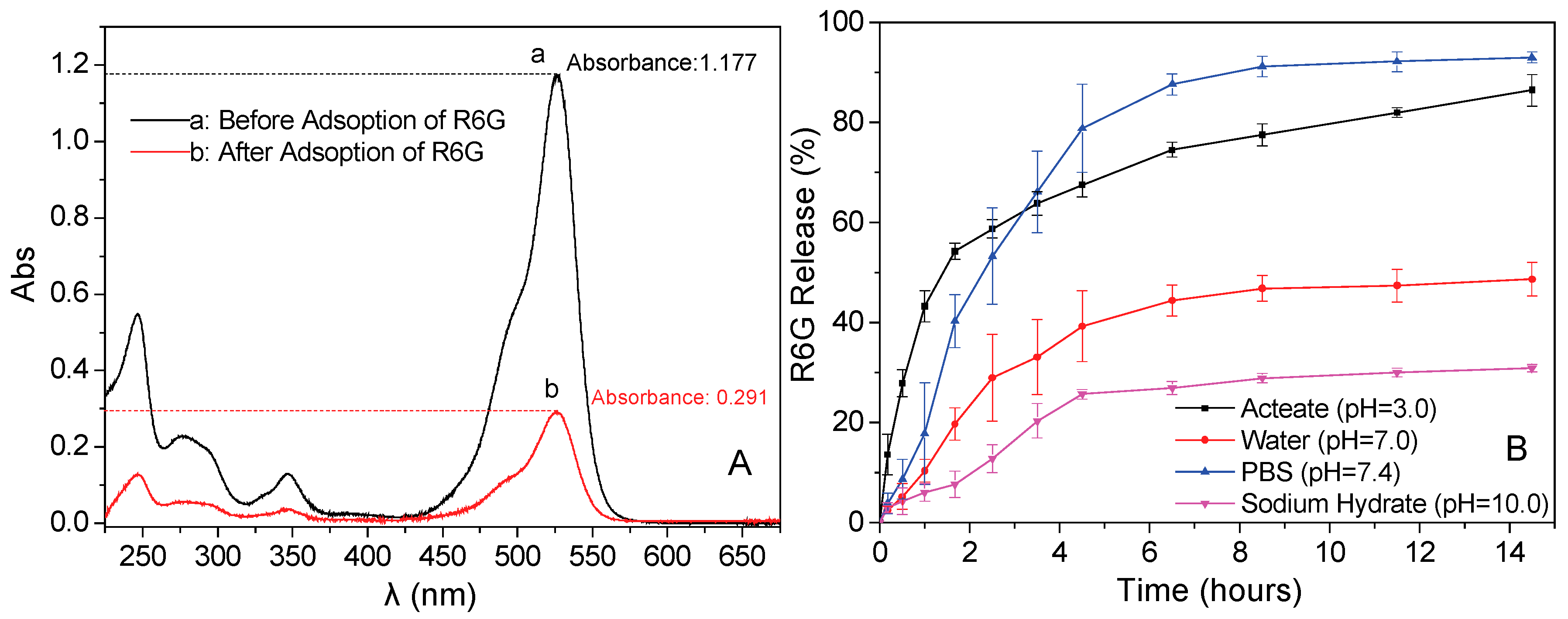
3.9. In Vitro Release Properties of Rhodamine (R6G)
3.10. Release Mechanism of Rhodamine 6G (R6G)
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xia, Y. Nanomaterials at work in biomedical research. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 758–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Huang, C.; He, Q. Pharmaceutical application of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2015, 7, 672–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douziech-Eyrolles, L.; Marchais, H.; Herve, K.; Munnier, E.; Soucé, M.; Linassier, C.; Dubois, P.; Chourpaet, I. Nanovectors for anticancer agents based on superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2007, 2, 541–550. [Google Scholar]
- Katsnelson, B.A.; Degtyareva, T.D.; Minigalieva, I.I.; Privaloca, L.I.; Kuzmin, S.V.; Yeremenko, O.S.; Kireyeva, E.P.; Sutunkoca, M.P.; Valamina, I.I.; Khodos, M.Y.; et al. Subchronic systemic toxicity and bioaccumulation of Fe3O4 nano-and microparticles following repeated intraperitoneal administration to rats. Int. J. Toxicol. 2011, 30, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorniani, D.; Hussein, M.Z.B.; Kura, A.U.; Fakurazi, S.; Shaari, A.H.; Ahmad, Z. Preparation of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles coated with gallic acid for drug delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 5745–5756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, L.; Hu, G.; Sun, Z.; Yang, W. Dose-dependent cytotoxicity and oxidative stress induced by “naked” Fe3O4 Nanoparticles in human hepatocyte. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2012, 28, 114–118. [Google Scholar]
- Jeng, H.A.; Swanson, J. Toxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles in mammalian cells. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2006, 41, 2699–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, B.; Chen, J.; Cai, X.; Xia, G.; Liu, R.; Chen, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Synthesis and antitumor efficacy of daunorubicin-loaded magnetic nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 203–211. [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.; Liu, J.; Huang, C.; Wu, Z. A nanoscale system for remarkably enhanced drug delivery based on hollow magnetic particles encapsulated within temperature-responsive poly (methylmethacrylate). Sci. Adv. Mater. 2014, 6, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahajuddin, S.A. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Magnetic nanoplatforms as drug carriers. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 3445–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein-Al-Ali, S.H.; El Zowalaty, M.E.; Hussein, M.Z.; Ismail, M.; Webster, T.J. Synthesis, characterization, controlled release, and antibacterial studies of a novel streptomycin chitosan magnetic nanoantibiotic. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 549–557. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Ikoma, T.; Hanagata, N.; Kaskel, S. Rattle-type Fe3O4@ SiO2 hollow mesoporous spheres as carriers for drug delivery. Small 2010, 6, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.Y.; Liu, K.H.; Liu, D.M.; Chen, S.Y.; Chen, I.W. Temperature-Sensitive Nanocapsules for Controlled Drug Release Caused by Magnetically Triggered Structural Disruption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isojima, T.; Lattuada, M.; Vander Sande, J.B.; Hatton, T.A. Reversible clustering of pH-and temperature-responsive Janus magnetic nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 1799–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, H.; Wang, F.; Zeng, L. Design of yolk–shell Fe3O4@ PMAA composite microspheres for adsorption of metal ions and pH-controlled drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2014, 2, 7065–7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmares, M.; Blanco, M.; Goddard, W.A.; Ross, R.B.; Caldwell, G.; Chou, S.-H.; Pham, J.; Olofson, P.M.; Thomas, C. Hildebrand and Hansen solubility parameters from Molecular Dynamics with applications to electronic nose polymer sensors. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1814–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, C.M. Polymer science applied to biological problems: Prediction of cytotoxic drug interactions with DNA. Eur. Polym. J. 2008, 44, 2741–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.Z.; Lan, H.L.; Wang, F.F.; Chang, S.J.; Wang, Y.J. Cell encapsulation with alginate and α-phenoxycinnamylidene-acetylated poly(allylamine). Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2000, 70, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daou, T.; Greneche, J.; Pourroy, G.; Buathong, S.; Derory, A.; Ulhaq-Bouillet, C.; Donnio, B.; Guillon, D.; Begin-Colin, S. Coupling agent effect on magnetic properties of functionalized magnetite-based nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 5869–5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestal, C.R.; Zhang, Z.J. Synthesis and magnetic characterization of Mn and Co spinel ferrite-silica nanoparticles with tunable magnetic core. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 1739–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, P. Some factors affecting the solubility of polymers. J. Appl. Chem. 1953, 3, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelatos, A.S.; Wang, Y.; Caruso, F. Probing the conformation of polyelectrolytes in mesoporous silica spheres. Langmuir 2008, 24, 4224–4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Shi, J.; Shen, W.; Dong, X.; Feng, J.; Ruan, M.; Li, Y. Stimuli-Responsive Controlled Drug Release from a Hollow Mesoporous Silica Sphere/Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Core–Shell Structure. Angew. Chem. 2005, 117, 5213–5217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





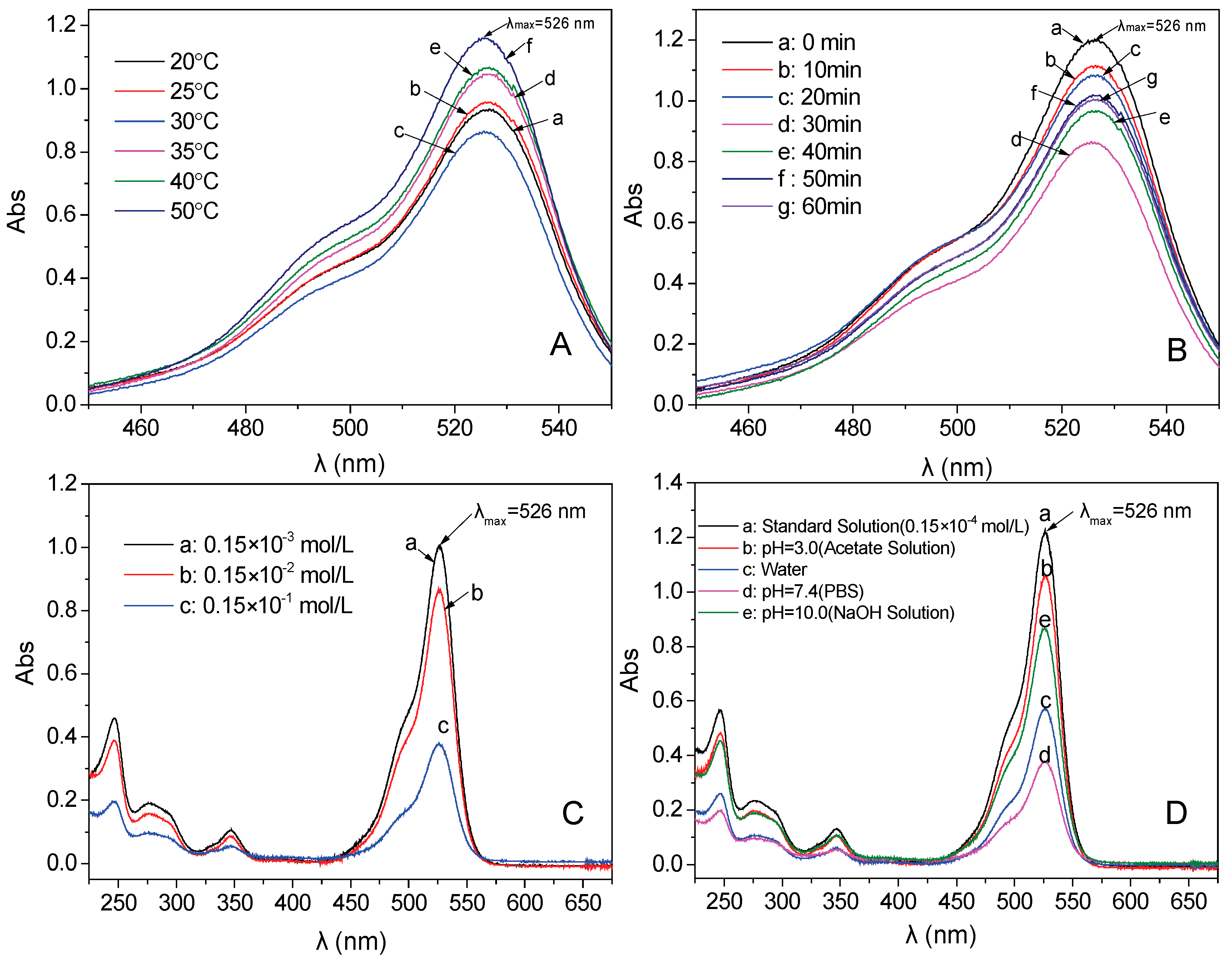
| Temperature (°C) | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 50 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absorbance | 0.926 | 0.955 | 0.860 | 1.046 | 1.064 | 1.159 |
| Drug concentration (×10−2 mol/L) | 0.115 | 0.119 | 0.106 | 0.130 | 0.132 | 0.145 |
| The remaining amount of R6G in 20 mL solution (mg) | 11.017 | 11.355 | 10.189 | 12.472 | 12.693 | 13.860 |
| The amount of the adsorbed drug by 0.010 g particles (mg) | 3.257 | 2.919 | 4.085 | 1.802 | 1.581 | 0.414 |
| The amount of the adsorbed drug by 1.0 g particles (mg) | 325.7 | 291.9 | 408.5 | 180.2 | 158.1 | 41.4 |
| Adsorption Time (min) | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absorbance | 1.109 | 1.083 | 0.860 | 0.964 | 1.018 | 1.006 |
| Drug concentration (×10−2 mol/L) | 0.138 | 0.135 | 0.106 | 0.120 | 0.127 | 0.125 |
| The remaining amount of R6G in 20 mL solution (mg) | 13.246 | 12.927 | 10.189 | 11.466 | 12.129 | 11.981 |
| The amount of the adsorbed drug by 0.010 g particles (mg) | 1.028 | 1.347 | 4.085 | 2.808 | 2.145 | 2.293 |
| The amount of the adsorbed drug by 1.0 g particles (mg) | 102.8 | 134.7 | 408.5 | 280.8 | 214.5 | 229.3 |
| Adsorption Concentration (mol/L) | 10−3 | 10−2 | 10−1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Absorbance | 1.004 | 0.860 | 0.377 |
| Drug concentration | 0.125 × 10−3 | 0.106 × 10−2 | 0.045 × 10−1 |
| The remaining amount of R6G in 20 mL solution (mg) | 1.198 | 10.189 | 42.589 |
| The amount of added magnetic particles (g) | 0.001 | 0.01 | 0.1 |
| The amount of the adsorbed drug (mg) | 0.239 | 4.085 | 101.114 |
| The amount of the adsorbed drug by 1.0 g particles (mg) | 239.0 | 408.5 | 1011.1 |
| pH | Acetic Acid Solution pH = 3.0 | Aqueous Solution pH = 7.0 | PBS pH = 7.4 | NaOH pH = 10.0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absorbance | 1.054 | 0.569 | 0.377 | 0.866 |
| Drug concentration (×10−1 mol/L) | 0.131 | 0.069 | 0.045 | 0.107 |
| The remaining amount of R6G in 20 mL solution (mg) | 125.501 | 66.103 | 42.589 | 102.508 |
| The amount of the adsorbed drug by 0.010 g particles (mg) | 18.202 | 77.600 | 101.114 | 41.195 |
| The amount of the adsorbed drug by 1.0 g particles (mg) | 182.0 | 776.0 | 1011.1 | 412.0 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, Q.; Liu, J.; Liang, J.; Liu, X.; Tuo, D.; Li, W. Chemically Surface Tunable Solubility Parameter for Controllable Drug Delivery—An Example and Perspective from Hollow PAA-Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles with R6G Model Drug. Materials 2018, 11, 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11020247
He Q, Liu J, Liang J, Liu X, Tuo D, Li W. Chemically Surface Tunable Solubility Parameter for Controllable Drug Delivery—An Example and Perspective from Hollow PAA-Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles with R6G Model Drug. Materials. 2018; 11(2):247. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11020247
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Quanguo, Jun Liu, Jing Liang, Xiaopeng Liu, Du Tuo, and Wen Li. 2018. "Chemically Surface Tunable Solubility Parameter for Controllable Drug Delivery—An Example and Perspective from Hollow PAA-Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles with R6G Model Drug" Materials 11, no. 2: 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11020247
APA StyleHe, Q., Liu, J., Liang, J., Liu, X., Tuo, D., & Li, W. (2018). Chemically Surface Tunable Solubility Parameter for Controllable Drug Delivery—An Example and Perspective from Hollow PAA-Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles with R6G Model Drug. Materials, 11(2), 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11020247





