Luminescence in Sulfides: A Rich History and a Bright Future
Abstract
:- Sulfide phosphors: A short history
- Electroluminescent powders
- Lamp and CRT phosphors
- Thin film electroluminescence
- Color conversion phosphors
- Persistent and storage phosphors
- Luminescent sulfide nanoparticles
- Conclusions
1. Sulfide phosphors: A Short History
2. Electroluminescent Powders
- The absolute brightness is quite low. As large areas can emit quite homogeneously, the total light output can be considerable, but making a sunlight readable device, requiring high surface brightness, is a problem.
- The lifetime of moderate to high luminance devices is limited. The brightness of an ACPEL device can be increased by increasing the applied voltage, but this in turn decreases the lifetime. Thus a low luminance device can last for many 1000s of hours, but this lifetime decreases drastically at increased luminance. With improvements in technology, a lifetime of about 2500 h (at 50% relative luminance) with an initial luminance of 100 cd/m2 can now be achieved [22]. Probably, the degradation is related to diffusion of copper or blunting of the copper needles in the phosphor layer, but this is still a matter of debate. Chen et al. showed that the degradation rate increases at higher operating temperatures and almost drops to zero when operated at -67 °C, suggesting diffusion related degradation [23]. Heating of degraded devices to 200 °C leads to a partial rejuvenation [24].
- The stability, and thus the lifetime, is highly dependent on the encapsulation of the layers. As these are moisture sensitive, they should be very well shielded from the ambient. First, the layers were encapsulated as a whole, but more recently, micro-encapsulation has been performed, the particles being coated individually. Obviously, this kind of additional process increases the cost of the material.
- The overall external efficiency of ACPEL devices is very low, of the order of only a few lm/W, which makes the technology unsuited for general lighting applications, and certainly not a match for CFL’s (compact fluorescent lamps) and LEDs.
3. Lamp and CRT Phosphors
4. Thin Film Electroluminescence
4.1. Working principle

- ACTFEL displays can have an unsurpassed lifetime of the order of 50.000 hours.
- As this is a fully solid state display, it can be made very rugged to withstand harsh environments, in industrial, medical, military or aviation applications.
- The tunneling mechanism, which is the cornerstone of the device operation, is essentially independent of temperature. Therefore, these displays can be made to work at extremely low and high temperatures, the temperature range of the drive electronics being the main limiting factor. An EL device has been reported to work down to 15 K [36].
- ACTFEL is an emissive display technology; therefore, the viewing angle can be very large, of the order of 170°, both horizontally and vertically.
- The active layer is very thin – of the order of 500 nm – therefore the display resolution can be high. A microdisplay with a pixel pitch of 24 µm was presented by Planar Systems [38].
4.2. Towards full-color EL
- A wide band gap semiconductor is needed, as it has to be transparent to the emitted light. However, the band gap should not be too high, allowing avalanche multiplication processes.
- The dopant chosen should show an efficient emission under high electric fields, which excludes donor-acceptor based emission. Therefore ions with internal transitions are preferred, such as encountered in Mn2+ and the rare earth ions (both 4f-4f and 5d-4f emittors).
- The host’s cation size should match the size of the dopant ions to facilitate the substitutional incorporation in the host lattice. In addition, its oxidation state should preferably be the same as that of the dopant, although charge compensating co-dopants can be used. The ideal concentration of the dopants depends on the type of dopant, but is typically in the order of 1%. At higher concentration, non-radiative decay becomes more important because of an increased energy transfer between dopant ions. Also, high dopant concentrations can distort the host lattice thus lowering the excitation efficiency. This will especially be important for dopant ions with deviating valence state and/or ionic radius compared to the substituted ion.
- A very important parameter, which precludes the use of almost all oxides, is the need for a crystalline layer. In the applied electric field, electrons should be accelerated ballistically [53]. If the layer is amorphous, electrons are scattered at numerous grain boundaries and thus cannot gain sufficient energy to impact/excite the activator ions. While sulfides quite easily crystallize at moderate temperatures (around 500 °C), very high processing temperatures are typically needed for crystallizing oxide materials. Another effect favors the use of sulfide materials. At high electric fields (in the order of MV/cm), electron-phonon interaction is the main scattering mechanism. Hence, host compounds having low optical-phonon energies are favored. Benalloul et al. compared phonon energies of sulfides and oxides and observed significantly lower values for sulfides compared to oxides [54]. The optical-phonon energy for ZnS (44meV) is similar to the one in BaAl2S4 (30-40meV) [55], both being efficient EL hosts.
| Material | Color | λd (nm) | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZnS:Mn | Amber | 585 | [29] |
| ZnS:Tb | Green | 545 | [46,78,79] |
| ZnS:Ho | White | 550 | [44,48] |
| ZnS:Sm | Red | 651 | [47] |
| CaS:Ce | Green | 505 | [56] |
| SrS:Ce | Blue-green | 480 | [57] |
| CaS:Eu | Red | 660 | [58] |
| SrS:Eu | Orange | 610 | [59] |
| SrS1-xSex:Ce | Blue | 465 | [64] |
| CaS1-xSex:Eu | Orange-red | 630 | [62,63,80] |
| CaSr1-xSx:Eu | Orange-red | 640 | [61] |
| CaS:Pb | Blue | 450 | [73,81,82,83,84] |
| CaS:Bi | Blue | 450 | [85] |
| BaAl2S4:Eu | Blue | 475 | [86,87,88,89] |
| CaGa2S4:Ce | Blue | 460 | [90] |
| CaGa2S4:Eu | Yellow | 565 | [91] |
| SrGa2S4:Ce | Blue | 445 | [90,92,93,94] |
| SrGa2S4:Eu | Green | 532 | [71,75,94,95] |
| SrS:Cu | Blue-green | 480 | [36,77] |
| SrS:Cu,Ag | Blue | 440 | [36,76,77] |
| CaS:Cu,Ag | Blue | 450 | [96] |
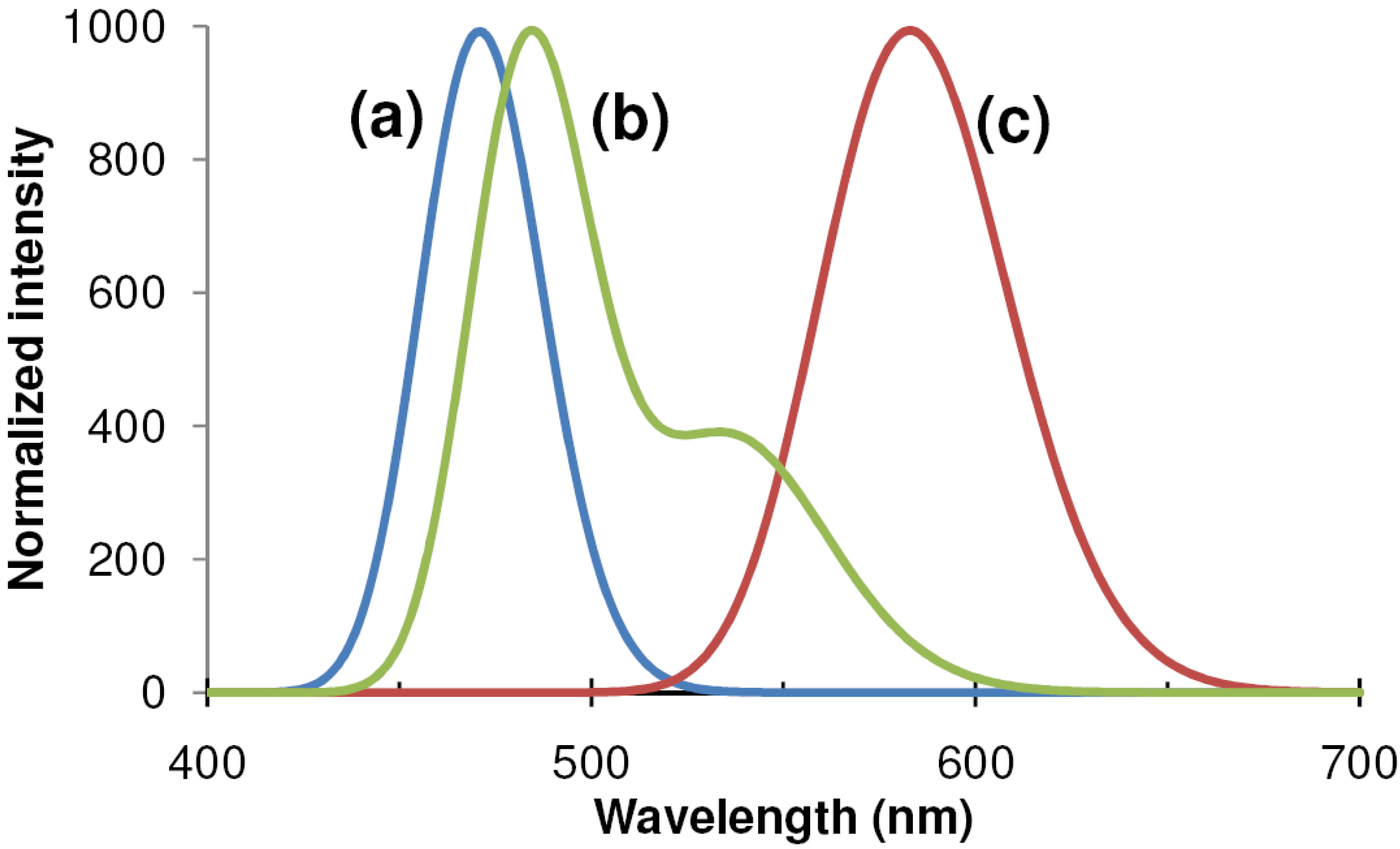
4.3. BaAl2S4:Eu and color-by-blue
4.3.1. Deposition techniques
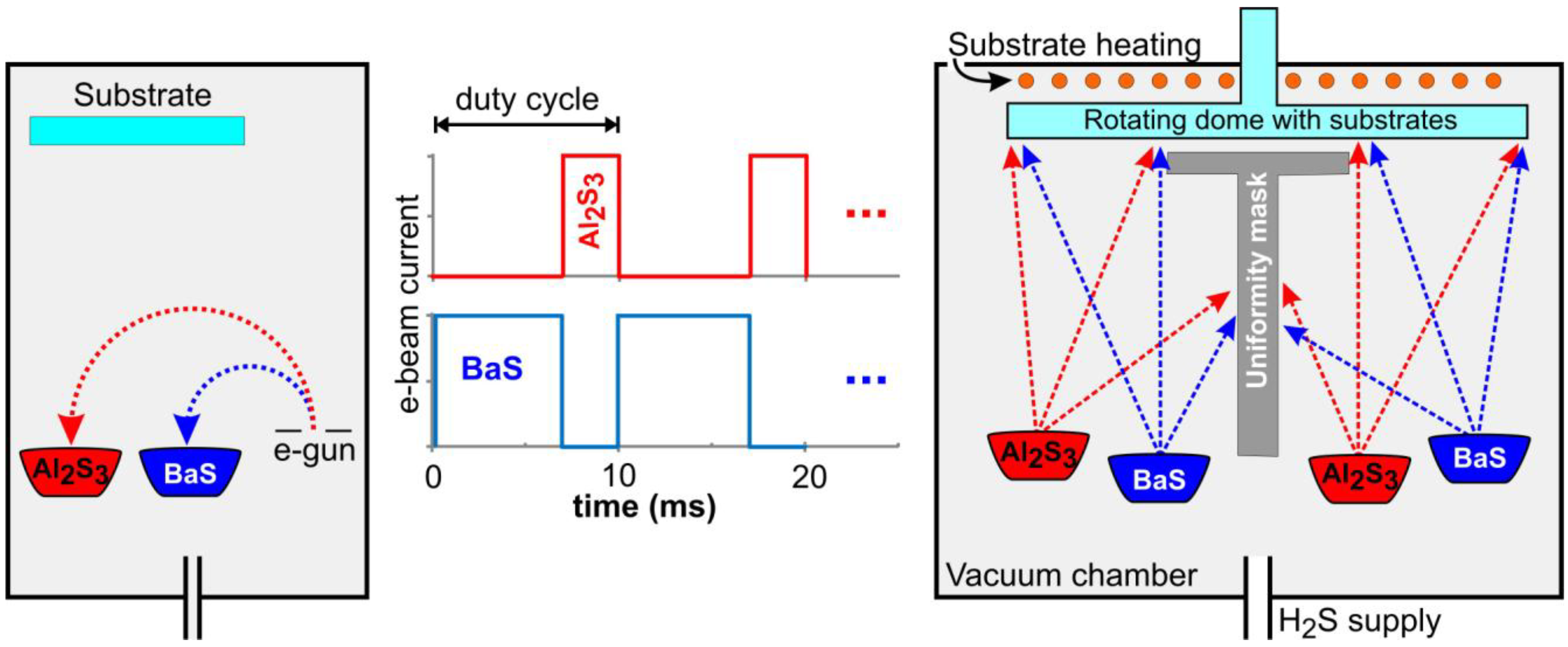
4.3.2. TDEL and CBB
4.3.3. Current research activities.
4.4. Other hosts and approaches
4.5. Future of iEL.
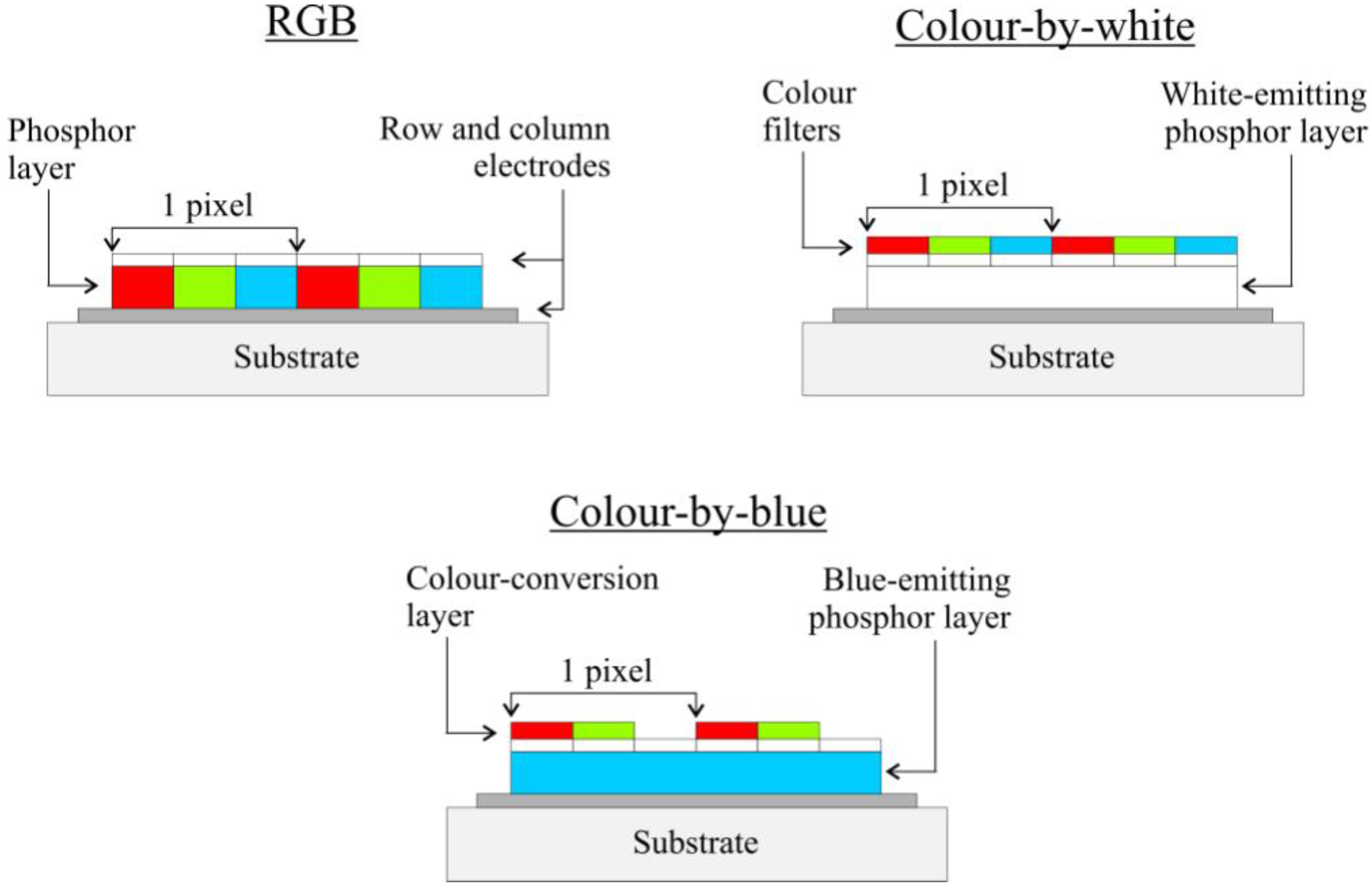
5. Color Conversion Phosphors
5.1. Requirements for LED phosphors.
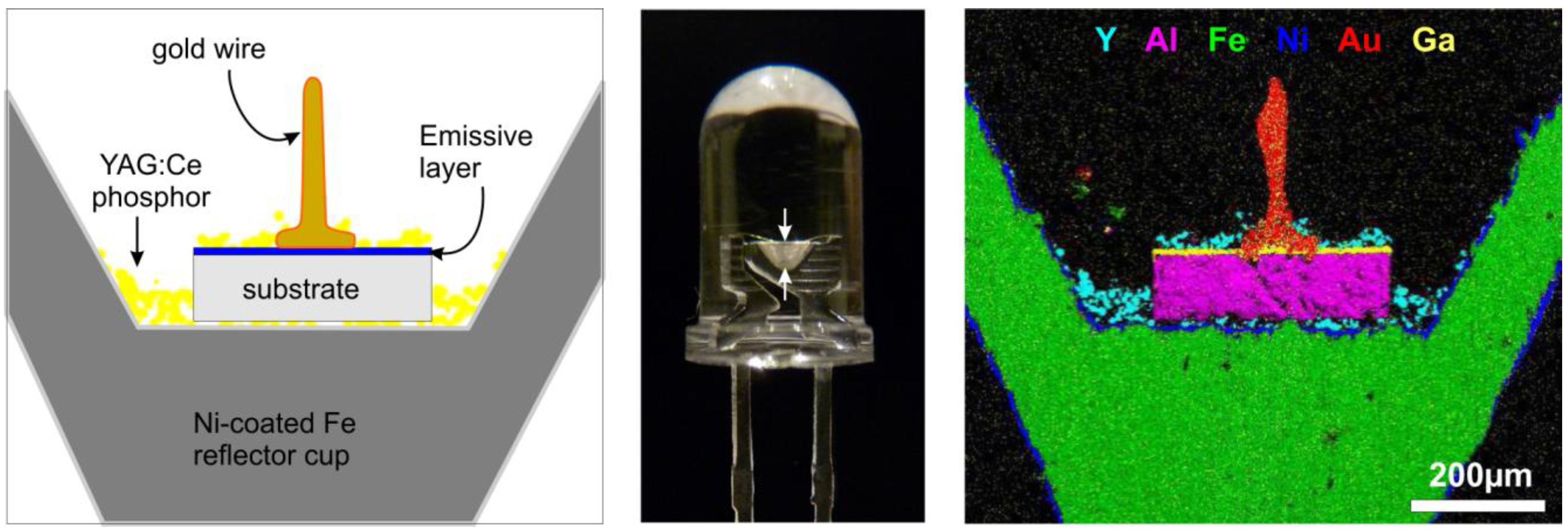
- An appropriate emission spectrum to achieve a true white emission when mixed with the remaining (visible) LED emission and possible other phosphors. To achieve a high color rendering index (CRI) for high-quality illumination applications (typically 90 or higher), broad band emission is required.
- High quantum efficiency for the conversion process. YAG:Ce can be considered as a benchmark, with a quantum efficiency exceeding 90% [136].
- The excitation spectrum should show sufficient overlap with the LED’s emission spectrum. As the LED’s emission spectrum can significantly change as a function of temperature and/or driving current, a broad excitation band overlapping the LED’s emission is preferred to avoid color shifts of the LED-phosphor combination.
- A relatively short decay time, to prevent saturation in high flux devices.
- A high thermal quenching temperature, as LED chips can reach relatively high temperatures of 450 K [137] during operation.
- Good stability during the full lifetime of an LED (typically over 50,000 hours)
5.2. Binary sulfides
| HostDopant | Eu2+ | Ce3+ | Cu+ | Sb3+ | ||||
| MgS | 591 | [145] | 521 | [146] | 472 | [147] | 539 | [148] |
| CaS | 652 663 | [145] [149,150] | 509 520 | [151] [146] | 413 | [147] | 549 | [148] |
| SrS | 620 | [145] | 483 503 | [151] [146] | 478 | [147] | 600 | [148] |
| BaS | 878 | [152] | 480 | [146] | 585 | [147] |
5.3. Thiogallates.
| Host | Dopant | λmax(nm) | Quenching | Remarks | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MgGa2S4 | Eu2+ | 660 | [168] | ||
| CaGa2S4 | Eu2+ Ce3+ | 565 459 | 410 K | [91] [169] | |
| SrGa2S4 | Eu2+ Ce3+ | 534 445 | 470 K | [95] [170] | |
| Sr2Ga2S5 | Eu2+ | 553 (90 K) | 280 K | [166] | |
| BaGa4S7 | Eu2+ | 482 (90 K) | 70% | [166] | |
| BaGa2S4 | Eu2+ Ce3+ | 493 448 | 420 K | [171] [170] | |
| Ba2Ga2S5 | Eu2+ | - | No emission at 90 K | [167] | |
| Ba3Ga2S6 | Eu2+ | 538 (90 K) | 140 K | [167] | |
| Ba4Ga2S7 | Eu2+ | 654 (90 K) | 110 K | [167] | |
| Ba5Ga2S8 | Eu2+ | - | No emission at 90 K | [167] | |
| EuGa2S4 | Eu2+ | 546 | +/- 150 K | [166,172] | |
| ZnGa2S4 | Eu2+ | 540 | [173] |
5.4. Thioaluminates and thioindates.
| Host | Dopant | λmax(nm) | Quenching | Remarks | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MgAl2S4 | Eu2+ | 499 | [131] | ||
| CaAl2S4 | Eu2+ Ce3+ | 516 436 | 93-98% | [97,181] [126] | |
| SrAl2S4 | Eu2+ | 495 | 90% | [97] | |
| Sr2Al2S5 | Eu2+ | 521 | [97] | ||
| BaAl4S7 | Eu2+ | 470 | 490 K | [97] | |
| BaAl2S4 | Eu2+ | 467-473 473 | >550 K | Cubic Orthorhombic | [55,89,97] [89] |
| Ba2Al2S5 | Eu2+ | 487 | [97] | ||
| Ba4Al2S7 | Eu2+ | 534 | 330 K | [97] | |
| Ba5Al2S8 | Eu2+ | 540 | [97] | ||
| EuAl2S4 | Eu2+ | 508 | [166] | ||
| CaIn2S4 | Eu2+ | 731 | strong | 95 nm FWHM | [183] |
| SrIn2S4 | Eu2+ | 640 (80 K) 614 | strong | [166] [183] | |
| BaIn2S4 | Eu2+ | 680 (80 K) 663 | strong | 145 nm FWHM | [166] [183] |
5.5. Thiosilicates and thiogermanates.
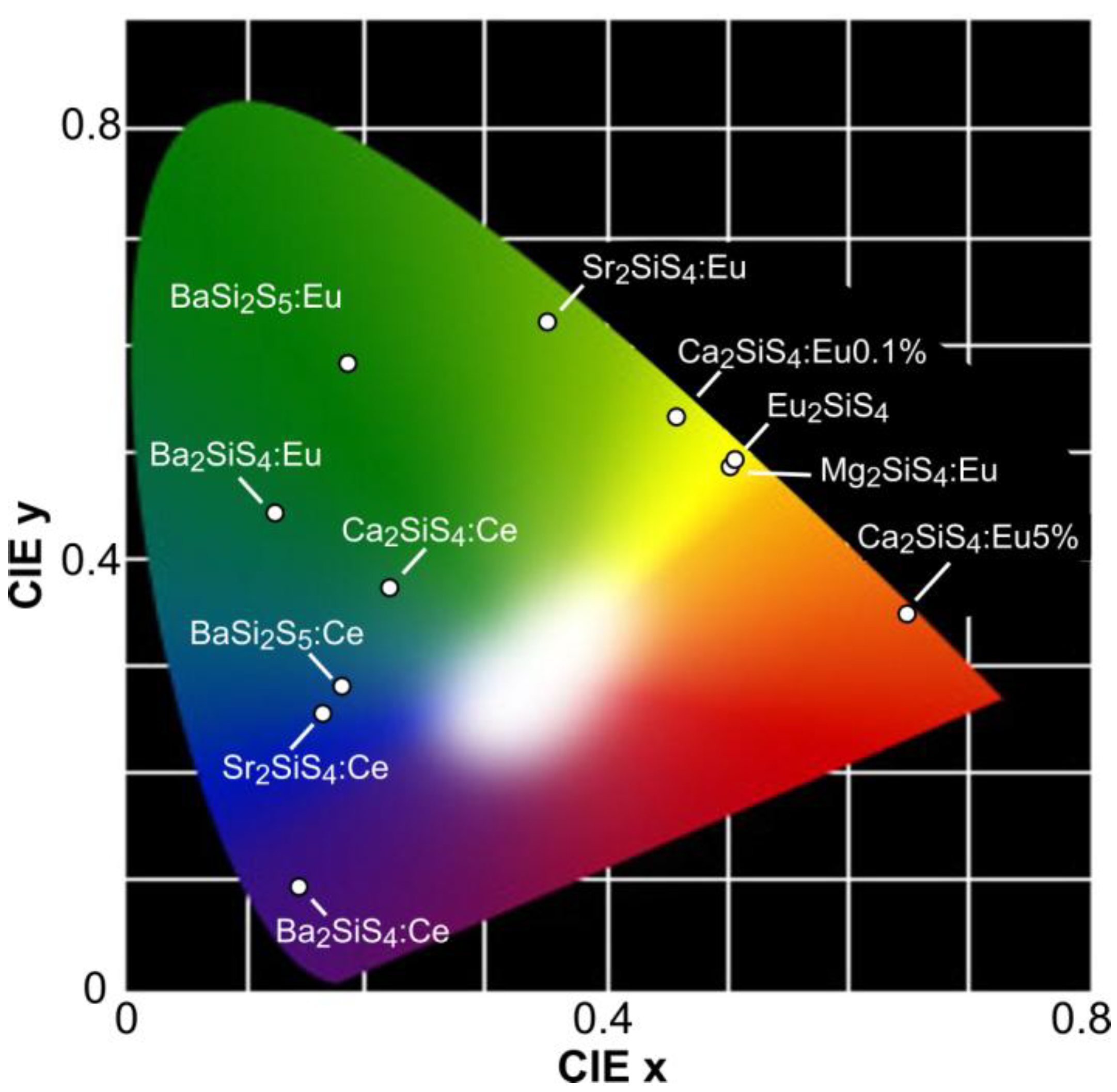
| Host | Dopant | λmax(nm) | Quenching | Remarks | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na2Si2S5 | Eu2+ | 488 | Weak emission | [185] | |
| Na4SiS4 | Eu2+ | 460 | [185] | ||
| Mg2SiS4 | Eu2+ | 660 | [168] | ||
| Ca2SiS4 | Eu2+ | 565 | 445 K | [Eu] < 1 mol % | [186,187] |
| CaEuSiS4 | Eu2+ | 614 | [186] | ||
| Sr2SiS4 | Eu2+ | 545 | 380 K | [168,188] | |
| SrSi2S5 | Eu2+ | 490 | [185] | ||
| Ba2SiS4 | Eu2+ | 495 | [129,185] | ||
| BaSi2S5 | Eu2+ | 505 | [129,185] | ||
| Ba3SiS5 | Eu2+ | - | No emission at RT | [128] | |
| Eu2SiS4 | 577 | [186] | |||
| Sr2GeS4 | Eu2+ | - | No emission at RT | [185] | |
| Ba2GeS4 | Eu2+ | - | No emission at RT | [185] |
5.7. Future
6. Persistent Luminescence and Storage Phosphors
7. Luminescent Sulfide Nanoparticles
7.1. Undoped nanoparticles
7.1.1. Introduction
7.1.2. Brief historic overview of sulfide Qdots
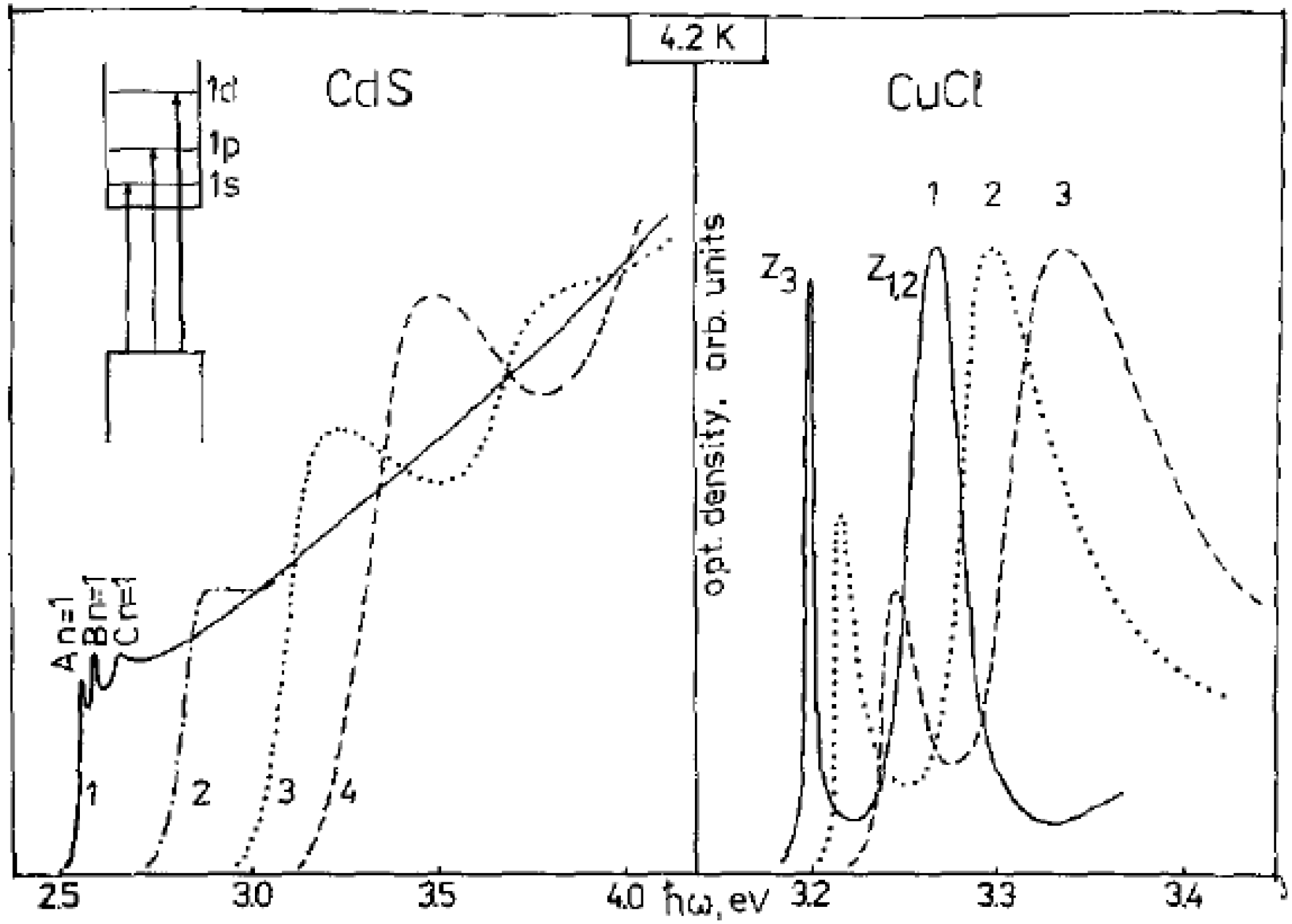
7.1.3. State-of-the-art


7.1.4. Applications of luminescent metal sulfide Qdots
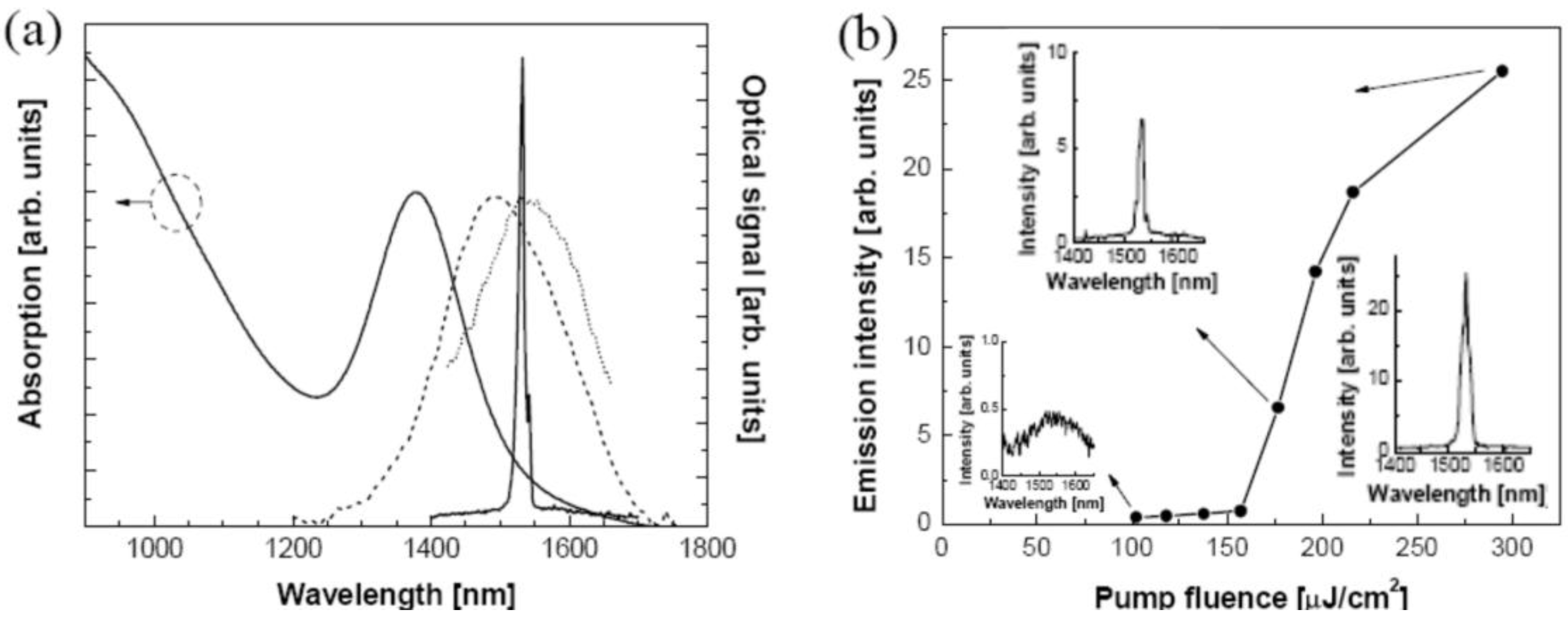

7.2. Doped nanoparticles
8. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References and Notes
- Yen, W.M.; Weber, M.J. Inorganic Phosphors: Compositions, Preparation and Optical Properties; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Yen, W.M.; Shionoya, S.; Yamamoto, H. Phosphor Handbook, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, E.N. A History of Luminescence From the Earliest Times Until 1900; American Philosophical Society: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Leverenz, H.W. An Introduction to Luminescence of Solids; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1950. [Google Scholar]
- Sidot, T. Recherches sur la crystallisation de quelque sulphures métalliques et sur les propriétés de la blende hexagonale. Comptes Rend. Ac. Sci. 1866, 62, 999–1001. [Google Scholar]
- Wiedemann, E. Uber Fluorescenz und Phosphorescenz. Ann. der Physik 1888, 34, 446–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheludev, N. The life and times of the LED - a 100-year history. Nat. Photonics 2007, 1, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destriau, G. Recherches sur les scintillations des sulfures de zinc aux rayons. J. Chim. Phys. 1936, 33, 587–625. [Google Scholar]
- Chadha, S.S. Powder electroluminescence. In Solid State Luminescence Theory, Materials and Devices; Kitai, A., Ed.; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1993; pp. 159–227. [Google Scholar]
- Mission Evaluation Team NASA manned spacecraft center. Apollo 11 Mission Report; National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Washington D.C., USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Thornton, W.A. Electroluminescence in zinc sulfide. Phys. Rev. 1956, 102, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, W.W.; Williams, F.E. Theory of Electroluminescence. Phys. Rev. 1955, 98, 1809–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecht, A.; Werring, N.J.; Smith, P.J.F. High-efficiency DC electroluminescence in ZnS:Mn,Cu. J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 1968, 1, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusano, D.A. Cathodo-, photo-, and D.C.-Electroluminescence in Zinc Sulphide Layers. In Luminescence of Organic and Inorganic Materials; Kallman, H.P., Spruch, G.M., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1962; pp. 494–522. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, A.G. Electroluminescence in II-VI Compounds. In Luminescence in Inorganic Solids; Goldberg, P., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1966; pp. 541–602. [Google Scholar]
- Curie, D. Luminescence in Solids; Methuen: London, UK, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Morehead, F.F. Electroluminescence. In Physics and Chemistry of II-VI Compounds; Aven, M., Prener, J.S., Eds.; North-Holland: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1967; pp. 611–656. [Google Scholar]
- Cusano, D.A. Thin film studies and electro-optical effects. In Physics and Chemistry of II-VI Compounds; Aven, M., Prener, J.S., Eds.; North-Holland: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1967; pp. 707–766. [Google Scholar]
- Vecht, A. Methods of activating and recrystallizing thin films of II-VI compounds. In Physics of Thin Films; Hass, G., Thun, R.E., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1966; Volume 3, pp. 165–210. [Google Scholar]
- Ivey, H.F. Electroluminescence and Related Effects (Advances in Electronics and Electron Physics. Supplement); Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Henish, H.K. Electroluminescence; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Xiang, Y. AC Powder Electroluminescence. In Luminescent Materials and Applications; Kitai, A., Ed.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2008; pp. 249–268. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Kitai, A.H.; Xiang, Y.W. Temperature-Dependent Degradation of AC Powder EL. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2009, 156, H585–H587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warkentin, M.; Bridges, F.; Carter, S.A.; Anderson, M. Electroluminescence materials ZnS : Cu,Cl and ZnS : Cu,Mn,Cl studied by EXAFS spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 75, 075301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredol, M.; Dieckhoff, H.S. Materials for Powder-Based AC-Electroluminescence. Materials 2010, 3, 1353–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasse, G.; Grabmaier, B.C. Luminescent Materials; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Inaho, S.; Hase, T. Phosphors for cathode-ray tubes. In Phosphor Handbook, 2nd ed.; Yen, W.M., Shionoya, S., Yamamoto, H., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto, K.; Itoh, S. Phosphor for vacuum fluorescent displays. In Phosphor Handbook, 2nd ed.; Yen, W.M., Shionoya, S., Yamamoto, H., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; pp. 667–685. [Google Scholar]
- Vlasenko, N.A.; Popkov, Y.A. Study of electroluminescence of a sublimated ZnS-Mn phosphor. Opt. Spektroskop. 1960, 8, 81–88. [Google Scholar]
- Russ, M.J.; Kennedy, D.I. The effects of double insulating layers on the electroluminescence of evaporated ZnS:Mn films. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1967, 114, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, R.; Mueller, G.O. Physics and technology of thin-film electroluminescent displays. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 1991, 6, 305–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, R.; Mueller, G.O. Mechanisms of thin-film color electroluminescence. SPIE Proc. Ser. 1993, 1910, 48–64. [Google Scholar]
- Mach, R.; Muller, G.O. Physical concepts of high-field, thin-film electro-luminescence devices. Phys. Status Solidi A - Appl. Res. 1982, 69, 11–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rack, P.D.; Holloway, P.H. The structure, device physics, and material properties of thin film electroluminescent displays. Mater. Sci. Eng. R-Rep. 1998, 21, 171–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoguchi, T.; Takeda, M.; Kakihara, Y.; Nakata, Y.; Yoshida, M. Stable High Luminance Thin Film Electroluminescent Panels. In SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers; San Diego, CA, USA, May 1974; pp. 84–85. [Google Scholar]
- Wauters, D.; Poelman, D.; Van Meirhaeghe, R.L.; Cardon, F. Optical characterisation of SrS : Cu and SrS : Cu,Ag EL devices. J. Lumines. 2000, 91, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inuzuka, H.; Yamauchi, T.; Hattori, Y.; Katayama, M.; Itou, N. EL displays for automotive applications. J. Soc. Inf. Disp. 2001, 9, 197–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuenge, R.; Goodman, J.; Koyama, R.; Ping, K.; Vetanen, W. A QVGA AMEL microdisplay with improved color performance. In Proceedings of the 21st Int. Display Research Conf. and 8th International Display Workshops, Nagoya, Japan, October 2001; pp. 1071–1074.
- Laakso, C.; Khormaei, R.; King, C.; Harkonen, G.; Pakkala, A.; Pitkanen, T.; Surma-aho, M.; Törnqvist, R. A 9 inch diagonal, compact, multicolor TFEL display. In Conference Record of the 1991 International Display Research Conference; San Diego, CA, USA, October 1991; pp. 43–44. [Google Scholar]
- Smet, P.F.; Poelman, D.; Van Meirhaeghe, R.L. Blue electroluminescence from multilayered BaS : Eu/Al2S3 thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 95, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Mikami, Y.; Deguchi, H.; Kobayashi, H. White-light emitting thin-film electroluminescent devices with SrS:Ce,Cl/ZnS:Mn double phosphor layers. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. Part 2 - Lett. 1986, 25, L225–L227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, E.W.; Hepplewhite, R.T.; Krupka, D.C.; Kahng, D. Electroluminescence of ZnS Lumocen devices containing rare-earth and transition-metal fluorides. J. Appl. Phys. 1969, 40, 2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Tanaka, S.; Shanker, V.; Shiiki, M.; Kunou, T.; Mita, J.; Sasakura, H. Multicolor electroluminescent ZnS thin-films doped with rare-earth fluorides. Phys. Status Solidi A - Appl. Res. 1985, 88, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suyama, T.; Sawara, N.; Okamoto, K.; Hamakawa, Y. Multi-coloring of thin-film electroluminescent device. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1982, 21, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenbossche, J.; Neyts, K.A.; Devisschere, P.; Corlatan, D.; Pauwels, H.; Vercaemst, R.; Fiermans, L.; Poelman, D.; Vanmeirhaeghe, R.L.; Laflere, W.H.; Cardon, F. Xps Study of TbF3 and TbOF Centers in ZnS. Phys. Status Solidi A - Appl. Res. 1994, 146, K67–K70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, K.; Hamakawa, Y. Bright green electroluminescence in thin-film ZnS-TbF3. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1979, 35, 508–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohda, T.; Fujita, Y.; Matsuoka, T.; Abe, A. New efficient phosphor material ZnS:Sm,P for red electroluminescent devices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1986, 48, 95–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuk, V.K.; Kynev, K.D. Luminescence of ZnS:Dy,Cu, ZnS:Pr,Cu and ZnS:Ho,Cu phosphors depending on the activator and coactivator concentration. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1989, 8, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, K.; Yoshimi, T.; Miura, S. TbOF complex centers in ZnS thin-film electroluminescent devices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1988, 53, 678–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, Y.A. Electroluminescent Displays; World Scientific Publishing: Singapore, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Electroluminescence II. In Semiconductors and Semimetals; Mueller, G. (Ed.) Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000; Volume 65, Chapter 2-4.
- Inoguchi, T.; Mito, S. Electroluminescence. In Topics in Applied Physics; Pankove, J.I., Ed.; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1977; Volume 17. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, G.O.; Mach, R.; Halden, E.; Fitting, H.J. Direct evidence of ballistic acceleration of electrons in ZnS. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on the Physics of Semiconductors, Thessaloniki, Greece, August 1990; pp. 2510–2513.
- Benalloul, P.; Barthou, C.; Benoit, J. SrGa2S4: RE phosphors for full colour electroluminescent displays. J. Alloy. Compd. 1998, 275, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthou, C.; Jabbarov, R.B.; Benalloul, P.; Chartier, C.; Musayeva, N.N.; Tagiev, B.G.; Tagiev, O.B. Radiative properties of the blue BaAl2S4:Eu2+ phosphor. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2006, 153, G253–G258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanker, V.; Tanaka, S.; Shiiki, M.; Deguchi, H.; Kobayashi, H.; Sasakura, H. Electroluminescence in thin-film CaS:Ce. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1984, 45, 960–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, W.A.; Coovert, R.E.; King, C.N. Strontium sulphide: the host for a new high-efficiency thin-film EL blue phosphor. In SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers; San Francisco, CA, USA, June 1984; pp. 249–250. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, S.; Shanker, V.; Shiiki, M.; Deguchi, H.; Kobayashi, H. Multicolor Electroluminescence in Alkaline-Earth Sulfide Thin-Film Devices. In SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers; Orlando, FL, USA, May 1985; pp. 255–258. [Google Scholar]
- Kane, J.; Harty, W.E.; Ling, M.; Yocom, P.N. New electroluminescent phosphors based on strontium sulfide. In Conference Record of the 1985 International Display Research Conference; San Diego, CA, USA, October 1985; pp. 163–166. [Google Scholar]
- Van Haecke, J.E.; Smet, P.F.; Poelman, D. The influence of source powder composition on the electroluminescence of Ca1-xSrxS:Eu thin films. Spectroc. Acta Pt. B-Atom. Spectr. 2004, 59, 1759–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Haecke, J.E.; Smet, P.F.; Poelman, D. The formation of Eu2+ clusters in saturated red Ca0.5Sr0.5S:Eu electroluminescent devices. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2005, 152, H225–H228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poelman, D.; Vercaemst, R.; VanMeirhaeghe, R.L.; Laflere, W.H.; Cardon, F. Influence of the growth conditions on the properties of CaS:Eu electroluminescent thin films. J. Lumines. 1997, 75, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, T.; Sano, Y.; Nunomura, K.; Tani, C. Characteristics of red electroluminescent devices using CaS1-xSex:Eu phosphor layers. In SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers; Baltimore, MD, USA, May 1989; pp. 313–316. [Google Scholar]
- Poelman, D.; Vanmeirhaeghe, R.L.; Laflere, W.H.; Cardon, F. The Influence of Se Coevaporation on the Electroluminescent Properties of SrS:Ce Thin-Films. J. Lumines. 1992, 52, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poelman, D.; Vercaemst, R.; Vanmeirhaeghe, R.L.; Laflere, W.H.; Cardon, F. The Influence of Se-Coevaporation on the Emission Spectra of CaS:Eu and SrS:Ce Thin-Film Electroluminescent Devices. J. Lumines. 1995, 65, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poelman, D.; Wauters, D.; Van Meirhaeghe, R.L.; Cardon, F. Photoluminescence of SrS : Cu,Ag and SrS1-xSex : Cu,Ag thin films. Solid State Commun. 2000, 113, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schecter, A.; Shanske, W.; Stenzler, A.; Quintilian, H.; Steinberg, H. Acute hydrogen selenide inhalation. Chest 1980, 77, 554–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leppänen, M.; Härkönen, G.; Pakkala, A.; Soininen, E.; Törnqvist, R. Broadband Double Layer Phosphor for an Inverted Filtered RGB Electroluminescent Display. In Proceedings of the 13th International Display Research Conference, Strasbourg, France, August 31 - September 3 1993; pp. 229–232.
- Poelman, D.; Vercaemst, R.; Vanmeirhaeghe, R.L.; Laflere, W.H.; Cardon, F. Effect of Moisture on Performance of SrS:Ce Thin-Film Electroluminescent Devices. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. Part 1 1993, 32, 3477–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wauters, D.; Poelman, D.; Van Meirhaeghe, R.L.; Cardon, F. Effects of rapid thermal annealing on electron beam evaporated SrS : Ce thin film electroluminescent devices made in H2S ambient. J. Cryst. Growth 1999, 204, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chartier, C.; Barthou, C.; Benalloul, P.; Chenot, S.; Frigerio, J.M. Structural and luminescent properties of green emitting SrGa2S4:Eu thin films prepared by RF-sputtering. J. Cryst. Growth 2003, 256, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leskela, T.; Vasama, K.; Harkonen, G.; Sarkio, P.; Lounasmaa, M. Potential cerium precursors for blue colour in thin film electroluminescent devices grown by atomic layer epitaxy. Adv. Mater. Opt. Electron. 1996, 6, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun Jin, Y.; Yong Shin, K.; Jung-Sook, K.; Sang-Hee Ko, P.; Kyoung-Ik, C.; Dong-Sung, M. High-luminance blue-emitting CaS:Pb electroluminescent devices fabricated using atomic layer deposition. In SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers; San Jose, CA, USA, May 1999; pp. 1142–1145. [Google Scholar]
- Nakano, F.; Uekura, N.; Nakanishi, Y.; Hatanaka, Y.; Shimaoka, G. Preparation of CaGa2S4:Ce thin films for blue emitting thin-film EL device. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1997, 121, 160–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benalloul, P.; Barthou, C.; Benoit, J.; Eichenauer, L.; Zeinert, A. IIa-III2-S4 Ternary Compounds - New Host Matrices for Full-Color Thin-Film Electroluminescence Displays. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1993, 63, 1954–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smet, P.; Wauters, D.; Poelman, D.; Van Meirhaeghe, R.L. Influence of sintering on photoluminescent emission of SrS : Cu,Ag powders and e-beam evaporated phosphor layers. Solid State Commun. 2001, 118, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.S.; Dickey, E.; Kane, J.; Yocom, P.N. A bright and efficient new blue TFEL phosphor. In Proceedings of the 17th Int. Display Research Conference, Toronto, Canada, September 1997; pp. 301–304.
- Krupka, D.C.; Mahoney, D.M. Electroluminescence and photoluminescence of thin-films of ZnS doped with rare-earth metals. J. Appl. Phys. 1972, 43, 2314–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikami, A.; Ogura, T.; Tanaka, K.; Taniguchi, K.; Yoshida, M.; Nakajima, S. Tb-F emission centers in ZnS:Tb,F thin-film electroluminescent devices. J. Appl. Phys. 1987, 61, 3028–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercaemst, R.; Poelman, D.; Vanmeirhaeghe, R.L.; Fiermans, L.; Laflere, W.H.; Cardon, F. An Xps Study of the Dopants Valence States and the Composition of CaS1-xSexEu and SrS1-xSexCe Thin-Film Electroluminescent Devices. J. Lumines. 1995, 63, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poelman, D.; VanMeirhaeghe, R.L.; Vermeersch, B.A.; Cardon, F. Possibilities and limitations of blue electroluminescence in CaS:Pb2+ thin films. J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 1997, 30, 465–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versluys, J.; Poelman, D.; Wauters, D.; Van Meirhaeghe, R.L. Photoluminescent and structural properties of CaS : Pb electron beam deposited thin films. J. Phys.-Condes. Matter 2001, 13, 5709–5716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Park, S.H.K. Fabrication of CaS : Pb blue phosphor by incorporating dimeric Pb2+ luminescent centers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 78, 721–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nykanen, E.; Lehto, S.; Leskela, M.; Niinisto, L.; Soininen, P. Blue electroluminescence in Pb2+ doped CaS and SrS thin films. In Proceedings of the 6th International Workshop on Electroluminescence, El Paso, TX, USA, May 1992; pp. 199–204.
- Smet, P.F.; Van Gheluwe, J.; Poelman, D.; Van Meirhaeghe, R.L. Photoluminescence of electron beam evaporated CaS : Bi thin films. J. Lumines. 2003, 104, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, N.; Kawanishi, M.; Matsumoto, H.; Nakano, R. High-luminance blue-emitting BaAl2S4 : Eu thin-film electroluminescent devices. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. Part 2 - Lett. 1999, 38, L1291–L1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, N.; Kawanishi, M.; Matsumoto, H.; Nakano, R. Blue-emitting BaAl2S4 : Eu thin-film electroiluminescent devices prepared by two targets pulse electron beam evaporation. IEICE Trans. Electron. 2000, E83C, 1618–1621. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, I.; Inoue, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Izumi, Y.; Okamoto, S.; Kawanishi, M.; Miura, N.; Matsumoto, H.; Nakano, R. Crystallographic and luminescent characterizations of blue-emitting BaAl2S4 : Eu electroluminescent thin films. J. Lumines. 2002, 96, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smet, P.F.; Van Haecke, J.E.; Van Meirhaeghe, R.L.; Poelman, D. Crystallographic and luminescent properties of orthorhombic BaAl2S4 : Eu powder and thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 043512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, W.A.; Coovert, R.E.; Dickey, E.; King, C.N.; Laakso, C.; Sun, S.-S.; Tuenge, R.T.; Wentross, W.; Kane, J. A New Class of Blue TFEL Phosphors with Applications to a VGA Full-Color Display. In SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers; Seattle, WA, USA, May 1993; pp. 761–764. [Google Scholar]
- Benalloul, P.; Barthou, C.; Fouassier, C.; Georgobiani, A.N.; Lepnev, L.S.; Emirov, Y.N.; Gruzintsev, A.N.; Tagiev, B.G.; Tagiev, O.B.; Jabbarov, R.B. Luminescence of Eu2+ in calcium thiogallate. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2003, 150, G62–G65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djazovski, O.; Mikami, T.; Ohmi, K.; Tanaka, S.; Kobayashi, H. Microstructural characterization and photoluminescence of SrGa2S4:Ce3+ thin films grown by deposition from binary vapors. IEICE Trans. Electron. 1997, E80C, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar]
- Djazovski, O.N.; Mikami, T.; Ohmi, K.; Tanaka, S.; Kobayashi, H. Luminescence and energy transfer in thin films of SrGa2S4:Ce. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1999, 146, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichenauer, L.; Jarofke, B.; Mertins, H.C.; Dreyhsig, J.; Busse, W.; Gumlich, H.E.; Benalloul, P.; Barthou, C.; Benoit, J.; Fouassier, C.; Garcia, A. Optical characterization of europium and cerium in strontium thiogallate thin films and powders. Phys. Status Solidi A - Appl. Res. 1996, 153, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chartier, C.; Barthou, C.; Benalloul, P.; Frigerio, J.M. Photoluminescence of Eu2+ in SrGa2S4. J. Lumines. 2005, 111, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wauters, D.; Poelman, D.; Van Meirhaeghe, R.L.; Cardon, F. Photoluminescent, electroluminescent and structural properties of CaS : Cu and CaS : Cu, Ag thin films. J. Phys.-Condes. Matter 2000, 12, 3901–3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lethi, K.T.; Garcia, A.; Guillen, F.; Fouassier, C. Investigation of the MS-Al2S3 systems (M = Ca, Sr, Ba) and luminescence properties of europium-doped thioaluminates. Mater. Sci. Eng. B-Solid State Mater. Adv. Technol. 1992, 14, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Hunt, T.; Acchione, J. Multi-Source Deposition of BaAl2S4 Blue Phosphors. In SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers; Seattle, WA, USA, May 2004; pp. 1138–1141. [Google Scholar]
- Kawanishi, M.; Miura, N.; Matsumoto, H.; Nakano, R. Preparation of Efficient Blue Emitting BaAl2S4:Eu Thin Films without High Temperature Annealing. In Proceedings of the 21st International Display Research Conference in conjunction with the 8th International Display Workshops, Nagoya, Japan, October 2001; pp. 1075–1078.
- Wu, X. Recent Development in Hybrid Inorganic Electroluminescent Devices. In Proceedings of the 11th International Workshop on Inorganic and Organic Electroluminescence & 2002 International Conference on the Science and Technology of Emissive Displays, Gent, Belgium, September 2002; pp. 293–297.
- Guo, C.; Tang, Q.; Huang, D.; Zhang, C.; Su, Q. Influence of co-doping different rare earth ions on CaGa2S4:Eu2+, RE3+ (RE = Ln) phosphors. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2007, 68, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiles, J.A.R.; Kamkar, M. Polymorphic barium thioaluminate electroluminescent phosphor materials. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 100, 074508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenmann, B.; Jakowski, M.; Schafer, H. The structures of BaGa2S4 and BaAl2S4. Mater. Res. Bull. 1982, 17, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Xu, Y.; Acchione, J. Development of bright and stable BaAl2S4:Eu blue phosphor. In Proceedings of the 12th International Workshop on Inorganic and Organic Electroluminescence & 2004 International Conference on the Science and Technology of Emissive Displays, Toronto, Canada, September 2004; pp. 84–87.
- Inoue, Y.; Tanaka, I.; Tanaka, K.; Izumi, Y.; Okamoto, S.; Kawanishi, M.; Barada, D.; Miura, N.; Matsumoto, H.; Nakano, R. Atomic composition and structural properties of blue emitting BaAl2S4 : Eu electroluminescent thin films. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. Part 1 2001, 40, 2451–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smet, P.F.; Van Haecke, J.E.; Van Meirhaeghe, R.L.; Poelman, D. An X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study of BaAl2S4 thin films. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 2005, 148, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smet, P.F.; Van Haecke, J.E.; Kitai, A.; Poelman, D. Annealing study on BaAl2S4:Eu EL devices prepared by multi-layered deposition. In Proceedings of the 13th International Workshop on Inorganic and Organic Electroluminescence & 2006 International Conference on the Science and Technology of Emissive Displays, Jeju, Korea, September 2006; pp. 249–251.
- Heikenfeld, J.C.; Steckl, A.J. Inorganic EL displays at the crossroads. Inf. Disp. 2003, 19, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Poelman, D.; Vanmeirhaeghe, R.L.; Laflere, W.H.; Cardon, F. Spectral Shifts in Thin-Film Electroluminescent Devices - an Interference Effect. J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 1992, 25, 1010–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyts, K. Microcavity effects and the outcoupling of light in displays and lighting applications based on thin emitting films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2005, 244, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, T.; Miyata, T.; Takata, S.; Fukuda, I. High-luminance green Zn2SiO4:Mn thin-film electroluminescent devices using an insulating BaTiO3 ceramic sheet. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. Part 2 - Lett. 1991, 30, L117–L119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, T.; Kuroi, Y.; Takata, S. Preparation of ZnGa2O4:Mn phosphor thin films as emitting layers for electroluminescent devices. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 1996, 14, 1736–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Carkner, D.; Hamada, H.; Yoshida, I.; Kutsukake, M.; Dantani, K. Large-screen Flat Panel Displays based on Thick-Dielectric Electroluminescent (TDEL) Technology. In SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers; Seattle, WA, USA, May 2004; pp. 1146–1149. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, Y.J.; Hirakawa, T.; Sakiyama, K.; Okamoto, H.; Hamakawa, Y. EL/PL hybrid device enhanced by UV emission from ZnF2:Gd thin film electroluminescence. J. Korean. Phys. Soc. 1997, 30, S65–S68. [Google Scholar]
- Senda, T.; Cho, Y.J.; Hirakawa, T.; Okamoto, H.; Takakura, H.; Hamakawa, Y. Development of full-color display combined with ultraviolet-electroluminescence/photoluminescence multilayered thin films. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. Part 1 2000, 39, 4716–4720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, N.; Sasaki, T.; Matsumoto, H.; Nakano, R. Strong ultraviolet-emitting ZnF2:Gd thin-film electroluminescent device. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. Part 2 - Lett. 1991, 30, L1815–L1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, H.; Yoshida, I.; Carkner, D.; Wu, X.; Kutsukake, M.; Oda, K. A 34-inch Flat-Panel TV Fabricated by Combining Inorganic EL and Color-Conversion Technologies. Information and Media Technologies 2009, 4, 136–140. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Q.Z.; Mita, J.; Tsuruoka, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Kawamura, K. High luminance white EL devices using SrS:Ce,Eu,K films deposited in a H2 atmosphere. J. Cryst. Growth 1992, 117, 983–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Mikami, Y.; Deguchi, H.; Kobayashi, H. White Light Emitting Thin-Film Electroluminescent Devices with SrS:Ce,Cl/ZnS:Mn Double Phosphor Layers. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1986, 25, L225–L227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, H.; Yoshida, I.; Carkner, D.; Wu, X.W.; Kutsukake, M.; Oda, K. Inorganic EL devices with high-performance blue phosphor and application to 34-in. flat-panel televisions. J. Soc. Inf. Disp. 2008, 16, 1183–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.H.; Park, D.H.; Ahn, B.T. Low-temperature synthesis of Eu-doped cubic phase BaAl2S4 blue phosphor using liquid-phase reaction. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2008, 155, J41–J44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.H.; Chalapathy, R.B.V.; Park, D.H.; Ahn, B.T. Low Temperature Synthesis of Eu-Doped Cubic Phase BaAl2S4 Blue Phosphor Using H3BO3 or B2O3 Flux. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2010, 157, J45–J49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrykin, V.; Kakihana, M. Synthesis of BaAl2S4 : Eu phosphor using BaS : Eu precursor prepared by the polymerizable complex method. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2007, 115, 615–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrykin, V.; Kakihana, M. Synthesis of BaAl2S4:Eu2+ Electroluminescent Material by the Polymerizable Complex Method Combined with CS2 Sulfurization. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2009, 92, S27–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, M.; Westcott, M.; Pugliese, V. Optical band gap measurement of BaAl2S4:Eu thin films. In Proceedings of the 12th International Workshop on Inorganic and Organic Electroluminescence & 2004 International Conference on the Science and Technology of Emissive Displays, Toronto, Canada, September 2004; pp. 351–354.
- Yu, R.J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.M.; Yuan, H.B.; Zhang, J.H.; Su, Q. Eu2+-doped thioaluminates: New candidates for white LEDs. Chem. Lett. 2008, 37, 410–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorenbos, P. Energy of the first 4f(7)-> 4f(6)5d transition of Eu2+ in inorganic compounds. J. Lumines. 2003, 104, 239–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samura, Y.; Usui, S.; Ohmi, K.; Kobayashi, H. Ce3+ doped alkaline-earth thiosilicate blue EL phosphors. In Proceedings of the 12th International Workshop on Inorganic and Organic Electroluminescence & 2004 International Conference on the Science and Technology of Emissive Displays, Toronto, Canada, September 2004; pp. 132–135.
- Smet, P.F.; Korthout, K.; Van Haecke, J.E.; Poelman, D. Using rare earth doped thiosilicate phosphors in while light emitting LEDs: Towards low colour temperature and high colour rendering. Mater. Sci. Eng. B-Solid State Mater. Adv. Technol. 2008, 146, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, T.; Ohmi, K. Improvement in Luminescent Characteristics by Al Codoping in Ba2SiS4:Ce Blue Phosphor for White LEDs. J. Light Vis. Env. 2008, 32, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, N. Color Phosphors for Inorganic Electroluminescent Devices. In SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers; Seattle, WA, USA, May 2004; pp. 1142–1145. [Google Scholar]
- Miura, N. Phosphor studies for color EL devices. In Proceedings of the 13th International Workshop on Inorganic and Organic Electroluminescence & 2006 International Conference on the Science and Technology of Emissive Displays, Jeju, Korea, September 2006; pp. 240–242.
- Kitai, A.; Xiang, Y.W.; Cox, B. Sphere-supported thin-film electroluminescence: A new platform technology for displays and lighting. J. Soc. Inf. Disp. 2005, 13, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, E.F.; Kim, J.K. Solid-state light sources getting smart. Science 2005, 308, 1274–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller-Mach, R.; Mueller, G.; Krames, M.R.; Hoppe, H.A.; Stadler, F.; Schnick, W.; Juestel, T.; Schmidt, P. Highly efficient all-nitride phosphor-converted white light emitting diode. Phys. Status Solidi A-Appl. Mat. 2005, 202, 1727–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, V.; Ronda, C.; Meijerink, A. Temperature Quenching of Yellow Ce3+ Luminescence in YAG:Ce. Chem. Mat. 2009, 21, 2077–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, V.; Justel, T.; Meijerink, A.; Ronda, C.; Schmidt, P.J. Luminescence properties of SrSi2O2N2 doped with divalent rare earth ions. J. Lumines. 2006, 121, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorenbos, P. Light output and energy resolution of Ce3+-doped scintillators. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A-Accel. Spectrom. Dect. Assoc. Equip. 2002, 486, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poort, S.H.M.; Meyerink, A.; Blasse, G. Lifetime measurements in Eu2+-doped host lattices. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1997, 58, 1451–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorenbos, P. Anomalous luminescence of Eu2+ and Yb2+ in inorganic compounds. J. Phys. Condes. Matter 2003, 15, 2645–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, R.; Sivaraman, S. Spectroscopic properties of defects in alkaline-earth sulfides. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1991, 52, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennie, J.; Takeuchi, K.; Kaneko, Y.; Koda, T. Color centers in calcium sulfide and strontium sulfide single crystals. J. Lumines. 1991, 48-49, 787–791. [Google Scholar]
- Gruzintsev, A.N.; Volkov, V.T.; Pronin, A.N. Investigation of luminescence centers of unactivated CaS films. J. Cryst. Growth 1992, 117, 975–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Yun, S.J. Photoluminescence properties of Pb2+ centres in CaS : Pb thin films. J. Phys.-Condes. Matter 2004, 16, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, N.; Harada, O.; Nakamura, K. Photoluminescence spectra of Eu2+ centers in Ca(S,Se):Eu and Sr(S,Se):Eu. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. Part 1 1995, 34, 5539–5545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasano, H.; Megumi, K.; Yamamoto, H. Cathodoluminescence of Ca1-xMgxS:Eu, Ca1-xMgxS:Ce. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1984, 131, 1953–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, N. Photoluminescence properties of Cu+ centers in MgS, CaS, SrS and BaS. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. Part 1 1991, 30, 3335–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, N.; Sasaki, Y.; Nakamura, K. Photoluminescence of Sb3+ centers in SrS and SrSe. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. Part 1 1992, 31, 2791–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Haecke, J.E.; Smet, P.F.; De Keyser, K.; Poelman, D. Single crystal CaS : Eu and SrS : Eu luminescent particles obtained by solvothermal synthesis. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2007, 154, J278–J282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Batentschuk, M.; Osvet, A.; Winnacker, A.; Schneider, J. Quantum yield of Eu2+ emission in (Ca1-xSrx)S:Eu light emitting diode converter at 20-420 K. Radiat. Meas. 2010. in Press. [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto, F.; Kato, K. Preparation and cathodoluminescence of CaS:Ce and Ca1-xSrxS:Ce phosphors. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1983, 130, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smet, P.F.; Van Haecke, J.E.; Loncke, F.; Vrielinck, H.; Callens, F.; Poelman, D. Anomalous photoluminescence in BaS : Eu. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 74, 035207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brower, D.T.; Lloyd, I.K. Investigation of the effect of host composition on the photoluminescent properties of SrxBa1-xS doped with Eu and Sm. J. Mater. Res. 1995, 10, 211–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, D.D.; Wang, X.J. Alkali earth sulfide phosphors doped with Eu2+ and Ce3+ for LEDs. Opt. Mater. 2007, 30, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poelman, D.; Van Haecke, J.E.; Smet, P.F. Advances in sulfide phosphors for displays and lighting. J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Electron. 2009, 20, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarov, M.; Yoon, C. Controlled peak wavelength shift of Ca1-xSrx(SySe1-y): Eu2+ phosphor for LED application. J. Solid State Chem. 2006, 179, 2529–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.J.; Cho, Y.S.; Huh, Y.D.; Do, Y.R. Preparation, characterization and photoluminescence properties of Ca1-xSrxS : Eu red-emitting phosphors for a white LED. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2007, 28, 1280–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.N.; Kim, J.M.; Choi, K.J.; Park, J.K.; Kim, C.H. Synthesis, characterization, and luminescent properties of CaS : Eu phosphor. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2006, 89, 3413–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorenbos, P. Thermal quenching of Eu2+ 5d-4f luminescence in inorganic compounds. J. Phys.-Condes. Matter 2005, 17, 8103–8111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.H.; Kim, J.H.; Han, B.Y.; Yoo, J.S. Failure Analysis of a Phosphor-Converted White Light-Emitting Diode due to the CaS:Eu Phosphor. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 47, 3524–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avci, N.; Musschoot, J.; Smet, P.F.; Korthout, K.; Avci, A.; Detavernier, C.; Poelman, D. Microencapsulation of Moisture-Sensitive CaS:Eu2+ Particles with Aluminum Oxide. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2009, 156, J333–J337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.H.; Kim, C.K. Nanocomposite Encapsulation of CuS:Eu Light-Emitting Diode Phosphors for the Enhancement of the Stability Against Moisture. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2009, 156, J170–J173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.W.; Kim, J.H.; Yoo, J.S.; Shin, H.H.; Kim, C.K.; Choi, C.K. Longevity improvement of CaS : Eu phosphor using polymer binder coating for white LED application. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2008, 155, J132–J135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Huang, Y.; Bando, Y.; Tang, C.C.; Golberg, D. BN tubular layer-sheathed CaS:Eu2+ nanowires as stable red-light-emitting nanophosphors. Chem. Commun. 2009, 6631–6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, T.E.; Baglio, J.A. Luminescence and structural properties of thiogallate phosphors: Ce+3 and Eu+2 activated phosphors. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1972, 119, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donohue, P.C.; Hanlon, J.E. Synthesis and photoluminescence of MIIM2III(S,Se)4. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1974, 121, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davolos, M.R.; Garcia, A.; Fouassier, C.; Hagenmuller, P. Luminescence of Eu2+ in strontium and barium thiogallates. J. Solid State Chem. 1989, 83, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avella, F.J. Cathodoluminescence of alkaline earth thiosilicate phosphors. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1971, 118, 1862–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.S.; Tuenge, R.T.; Kane, J.; Ling, M. Electroluminescence and photoluminescence of cerium-activated alkaline-earth thiogallate thin-films and devices. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1994, 141, 2877–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marceddu, M.; Anedda, A.; Corpino, R.; Georgobiani, A.N.; Ricci, P.C. Energy transfer in Ce and Eu co-doped barium thiogallate: A photoluminescence characterization. Mater. Sci. Eng. B-Solid State Mater. Adv. Technol. 2008, 146, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbarov, R.B.; Chartier, C.; Tagiev, B.G.; Tagiev, O.B.; Musayeva, N.N.; Barthou, C.; Benalloul, P. Radiative properties of Eu2+ in BaGa2S4. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2005, 66, 1049–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgobiani, A.N.; Tagiev, B.G.; Tagiev, O.B.; Abushov, S.A.; Kazymova, F.A.; Gashimova, T.S.; Xu, X.R. Temperature effect on the photoluminescence intensity and Eu2+ excited state lifetime in EuGa2S4 and EuGa2S4:Er3+. Inorg. Mater. 2009, 45, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Kim, Y.J. Synthesis and luminescent characterization of zinc thiogallate. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2007, 27, 3667–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Yuan, H.B.; Ding, W.J.; An, Y.; Su, Q. Luminescence properties of Ca1-xSrx(Ga1-yAly)2S4 : Eu2+ and their potential application for white LEDs. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2008, 155, J290–J292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.M.; Wang, J.; Wu, H.; Zhang, J.H.; Su, Q. One-step synthesis and double emission (Ca(1+x-y)Euy)Ga2S4+x phosphor for white LEDs. Mater. Lett. 2009, 63, 340–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarov, M.; Noh, D.Y.; Byeon, C.C.; Kim, H. Efficient multiphase green phosphor based on strontium thiogallate. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 073518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbarov, R.; Musayeva, N.; Scholz, F.; Wunderer, T.; Turkin, A.N.; Shirokov, S.S.; Yunovich, A.E. Preparation and optical properties of Eu2+ doped CaGa2S4-CaS composite bicolor phosphor for white LED. Phys. Status Solidi A-Appl. Mat. 2009, 206, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, Y.R.; Ko, K.Y.; Na, S.H.; Huh, Y.D. Luminescence properties of potential Sr1-xCaxGa2S4:Eu green- and greenish-yellow-emitting phosphors for white LED. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2006, 153, H142–H146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Takahashi, M.; Tokuda, Y.; Yoko, T. Preparation of Eu-doped CaGa2S4-CaS composite bicolor phosphor for white light emitting diode. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2004, 112, 511–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benalloul, P.; Barthou, C.; Benoit, J.; Georgobiani, A.; Lepnev, L.; Gruzintsev, A.; Tagiev, B.; Tagiev, O.; Dzhabborrov, R. Luminescence of Eu2+ in CaGa2S4 mono and polycrystals. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 39S1, 121–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Haecke, J.E.; Smet, P.F.; Poelman, D. Luminescent characterization of CaAl2S4 : Eu powder. J. Lumines. 2007, 126, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.H.; Yuan, H.B.; Su, Q. Luminescence properties of Eu2+- and Ce3+-doped CaAl2S4 and application in white LEDs. J. Solid State Chem. 2008, 181, 658–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawanishi, M.; Ono, Y.; Nakagawa, R.; Miura, N.; Matsumoto, H.; Nakano, R. Possibility of RGB Emission by Eu2+ ion doped IIa-IIIb2-S4 phosphors for Full Color Inorganic Electroluminescent Displays. In Proceedings of the 11th International Workshop on Inorganic and Organic Electroluminescence & 2002 International Conference on the Science and Technology of Emissive Displays, Gent, Belgium, September 2002; pp. 239–242.
- Kim, M.Y.; Baik, S.J.; Kim, W.T.; Jin, M.S.; Kim, H.G.; Choe, S.H.; Yoon, C.S. Optical properties of undoped and Co2+-, Ho3+-, Er3+-, and Tm3+-doped CaGa2S4, CaGa2Se4, CaIn2S4, and CaIn2Se4 single crystals. J. Korean. Phys. Soc. 2003, 43, 128–134. [Google Scholar]
- Olivierfourcade, J.; Ribes, M.; Philippot, E.; Merle, P.; Maurin, M. Emission characteristics of alkaline thiosilicates and alkaline-earth thiosilicates. Mater. Res. Bull. 1975, 10, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smet, P.F.; Avci, N.; Loos, B.; Van Haecke, J.E.; Poelman, D. Structure and photoluminescence of (Ca, Eu) 2SiS4 powders. J. Phys.-Condes. Matter 2007, 19, 246223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smet, P.F.; Avci, N.; Poelman, D. Red Persistent Luminescence in Ca2SiS4:Eu,Nd. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2009, 156, H243–H248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmentier, A.; Smet, P.F.; Bertram, F.; Christen, J.; Poelman, D. Structure and luminescence of (Ca,Sr)2SiS4:Eu2+ phosphors. J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 2010, 43, 085401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johrendt, D.; Pocha, R. Europium thiosilicate at 100 K. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. E.-Struct Rep. Online 2001, 57, i57–i59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, M.; Nanai, Y.; Bohda, T.; Okuno, T. Yellow Photoluminescence of Europium Thiosilicate on Silicon Substrate. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 48. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, K.; Okamoto, S. Green electroluminescence of EuGa2S4 thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 83, 647–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, X.H.; Huang, Y.N. Luminescence enhancement of EuS nanoclusters in zeolite. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2000, 76, 2328–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Naitou, T.; Izuno, K.; Tamaki, H.; Murazaki, Y.; Kameshima, M.; Mukai, T. Red-enhanced white-light-emitting diode using a new red phosphor. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. Part 2 - Lett. 2003, 42, L20–L23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.J.; Hirosaki, N.; Suehiro, T.; Xu, F.F.; Mitomo, M. A simple, efficient synthetic route to Sr2Si5N8 : Eu2+-based red phosphors for white light-emitting diodes. Chem. Mat. 2006, 18, 5578–5583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirosaki, N.; Xie, R.J.; Kimoto, K.; Sekiguchi, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Suehiro, T.; Mitomo, M. Characterization and properties of green-emitting beta-SiAlON : Eu2+ powder phosphors for white light-emitting diodes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, R.J.; Hirosaki, N.; Mitomo, M.; Takahashi, K.; Sakuma, K. Highly efficient white-light-emitting diodes fabricated with short-wavelength yellow oxynitride phosphors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 101104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clabau, F.; Rocquefelte, X.; Jobic, S.; Deniard, P.; Whangbo, M.H.; Garcia, A.; Le Mercier, T. On the phosphorescence mechanism in SrAl2O4:Eu2+ and its codoped derivatives. Solid State Sci. 2007, 9, 608–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.Y.; Yuan, H.B.; Lu, L.Z.; Liu, H.M.; Yen, W.M. Crystal growth and characterization of Eu2+, Dy3+: SrAl2O4 and Eu2+, Nd3+: CaAl2O4 by the LHPG method. J. Cryst. Growth 1999, 200, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitasalo, T.; Hassinen, J.; Holsa, J.; Laamanen, T.; Lastusaari, M.; Malkamaki, M.; Niittykoski, J.; Novak, P. Synchrotron radiation investigations of the Sr2MgSi2O7:Eu2+,R3+ persistent luminescence materials. J. Rare Earths 2009, 27, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Eeckhout, K.; Smet, P.F.; Poelman, D. Persistent luminescence in Eu2+ doped compounds: a review. Materials 2010, 3, 2536–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poelman, D.; Avci, N.; Smet, P.F. Measured luminance and visual appearance of multi-color persistent phosphors. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rea, M.S.; Bullough, J.D. Making the move to a unified system of photometry. Lighting Res. Technol. 2007, 39, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Eeckhout, K.; Smet, P.F.; Poelman, D. Persistent luminescence in rare-earth codoped Ca2Si5N8:Eu2+. J. Lumines. 2009, 129, 1140–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.S.; Zhuang, W.D.; Ye, H.Q.; Zhang, S.S.; Fang, Y.; Huang, X.W. Preparation and luminescent properties of (Ca1-xSrx)S : Eu2+ red-emitting phosphor for white LED. J. Lumines. 2005, 111, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.X.; Huang, S.H.; You, F.T.; Kang, K. Hydrothermal preparation and persistence characteristics of nanosized phosphor SrS:Eu2+, Dy3+. J. Rare Earths 2009, 27, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Wang, H.Q.; Tan, X.L.; Cheng, B.C.; Zhang, L.D.; Xiao, Z.D. One-dimensional hollow SrS nanostructure with red long-lasting phosphorescence. J. Alloy. Compd. 2008, 457, 413–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, D.D.; Zhu, J.; Wu, B.Q. Influence of co-doping with Cl- on the luminescence of CaS : Eu2+. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2000, 147, 3948–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, D.D. Enhancement of long-persistence by Ce co-doping in CaS : Eu2+, Tm3+ red phosphor. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2006, 153, H198–H201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, D.D.; Jia, W.Y.; Evans, D.R.; Dennis, W.M.; Liu, H.M.; Zhu, J.; Yen, W.M. Trapping processes in CaS : Eu2+,Tm3+. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 88, 3402–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, Y.; Shibukawa, A. Optical studies of CaS:Eu,Sm infrared stimulable phosphors. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. Part 1 1993, 32, 3187–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidner, M.; Osvet, A.; Schierning, G.; Batentschuka, M.; Winnackera, A. Influence of dopant compounds on the storage mechanism of CaS : Eu2+,Sm3+. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 100, 5. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.S.; Sun, L.; Xu, X.R. Optical absorption studies on the trapping states of CaS : Eu,Sm. J. Phys.-Condes. Matter 2001, 13, 3665–3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.P.; Newman, D.; Viney, I.V.F. Study on relationship of luminescence in CaS : Eu,Sm and dopants concentration. J. Lumines. 2002, 99, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, D.D.; Zhu, J.; Wu, B.Q. Improvement of persistent phosphorescence of Ca0.9Sr0.1S : Bi3+ by codoping Tm3+. J. Lumines. 2000, 91, 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka, C.; Shiino, M.; Takizawa, T. Role of rare earth elements as co-activators on both PL and afterglow of CaGa2S4:Eu. In Physica Status Solidi C - Current Topics in Solid State Physics, Vol 6, No 5; Sadewasser, S., AbouRas, D., Lake, B., Schock, H.W., Eds.; Wiley-V C H Verlag Gmbh: Weinheim, 2009; Volume 6, pp. 1166–1169. [Google Scholar]
- Brus, L.E. Electron Electron and Electron-Hole Interactions in Small Semiconductor Crystallites - the Size Dependence of the Lowest Excited Electronic State. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 80, 4403–4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.W.; Peng, X.G. Formation of high-quality CdS and other II-VI semiconductor nanocrystals in noncoordinating solvents: Tunable reactivity of monomers. Angew. Chem.-Int. Edit. 2002, 41, 2368–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.A.; Peng, X.G. Formation of high-quality CdTe, CdSe, and CdS nanocrystals using CdO as precursor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 183–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiss, P.; Protiere, M.; Li, L. Core/Shell Semiconductor Nanocrystals. Small 2009, 5, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalet, X.; Pinaud, F.F.; Bentolila, L.A.; Tsay, J.M.; Doose, S.; Li, J.J.; Sundaresan, G.; Wu, A.M.; Gambhir, S.S.; Weiss, S. Quantum dots for live cells, in vivo imaging, and diagnostics. Science 2005, 307, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, R.; Zayats, M.; Willner, I. Semiconductor quantum dots for bioanalysis. Angew. Chem.-Int. Edit. 2008, 47, 7602–7625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.N.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, T.; Xu, J.; Wang, A.Y.; Dixon, D.; Li, L.S.; Zhang, Q.; Mohney, S.E.; Ruzyllo, J. Bright and color-saturated emission from blue light-emitting diodes based on solution-processed colloidal nanocrystal quantum dots. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 3803–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourdakos, K.N.; Dissanayake, D.M.N.M.; Lutz, T.; Silva, S.R.P.; Curry, R.J. Highly efficient near-infrared hybrid organic-inorganic nanocrystal electroluminescence device. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 153311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anikeeva, P.O.; Halpert, J.E.; Bawendi, M.G.; Bulovic, V. Quantum Dot Light-Emitting Devices with Electroluminescence Tunable over the Entire Visible Spectrum. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 2532–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogach, A.L.; Gaponik, N.; Lupton, J.M.; Bertoni, C.; Gallardo, D.E.; Dunn, S.; Pira, N.L.; Paderi, M.; Repetto, P.; Romanov, S.G.; O'Dwyer, C.; Torres, C.M.S.; Eychmuller, A. Light-emitting diodes with semiconductor nanocrystals. Angew. Chem.-Int. Edit. 2008, 47, 6538–6549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisler, H.J.; Sundar, V.C.; Bawendi, M.G.; Walsh, M.; Smith, H.I.; Klimov, V. Color-selective semiconductor nanocrystal laser. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 80, 4614–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogland, S.; Sukhovatkin, V.; Howard, I.; Cauchi, S.; Levina, L.; Sargent, E.H. A solution-processed 1.53 mu m quantum dot laser with temperature-invariant emission wavelength. Opt. Express 2006, 14, 3273–3281. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, Y.; Steckel, J.S.; Snee, P.T.; Caruge, J.M.; Hodgkiss, J.M.; Nocera, D.G.; Bawendi, M.G. Blue semiconductor nanocrystal laser. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 073102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, D.; Qian, L.; Tseng, T.-K.; Holloway, P.H. Quantum Dots and Their Multimodal Applications: A Review. Materials 2010, 3, 2260–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efros, A.L.; Efros, A.L. Interband Absorption of Light in a Semiconductor Sphere. Soviet Physics Semiconductors-Ussr 1982, 16, 772–775. [Google Scholar]
- Brus, L. Electronic Wave-Functions in Semiconductor Clusters - Experiment and Theory. J. Phys. Chem. 1986, 90, 2555–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henglein, A. Small-Particle Research - Physicochemical Properties of Extremely Small Colloidal Metal and Semiconductor Particles. Chem. Rev. 1989, 89, 1861–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossetti, R.; Hull, R.; Gibson, J.M.; Brus, L.E. Excited Electronic States and Optical-Spectra of Zns and Cds Crystallites in the Almost-Equal-to-15 to 50-a Size Range - Evolution from Molecular to Bulk Semiconducting Properties. J. Chem. Phys. 1985, 82, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossetti, R.; Hull, R.; Gibson, J.M.; Brus, L.E. Hybrid Electronic-Properties between the Molecular and Solid-State Limits - Lead Sulfide and Silver-Halide Crystallites. J. Chem. Phys. 1985, 83, 1406–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Herron, N. Quantum Size Effects on the Exciton Energy of CdS Clusters. Phys. Rev. B 1990, 42, 7253–7255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Suna, A.; Mahler, W.; Kasowski, R. Pbs in Polymers - from Molecules to Bulk Solids. J. Chem. Phys. 1987, 87, 7315–7322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekimov, A.I.; Efros, A.L.; Onushchenko, A.A. Quantum Size Effect in Semiconductor Microcrystals. Solid State Commun. 1985, 56, 921–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, I.; Wise, F.W. Electronic structure and optical properties of PbS and PbSe quantum dots. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B-Opt. Phys. 1997, 14, 1632–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, B.G.; Simmons, J.H. Quantum Size Effects in Optical-Properties of Cds-Glass Composites. Phys. Rev. B 1988, 37, 10838–10845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, F.W. Lead salt quantum dots: The limit of strong quantum confinement. Accounts Chem. Res. 2000, 33, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.B.; Norris, D.J.; Bawendi, M.G. Synthesis and Characterization of Nearly Monodisperse CdE (E = S, Se, Te) Semiconductor Nanocrystallites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 8706–8715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, S. Optical Properties of Crystalline and Amorphous Semiconductors; Kluwer Academic: Boston, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.C.; Wang, J.H. One-pot synthesis of high-quality zinc-blende CdS nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 14336–14337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steckel, J.S.; Zimmer, J.P.; Coe-Sullivan, S.; Stott, N.E.; Bulovic, V.; Bawendi, M.G. Blue luminescence from (CdS)ZnS core-shell nanocrystals. Angew. Chem.-Int. Edit. 2004, 43, 2154–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protiere, M.; Reiss, P. Facile synthesis of monodisperse ZnS capped CdS nanocrystals exhibiting efficient blue emission. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2006, 1, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, H.Y.; Kas, R.; Yurtsever, E.; Ozen, C.; Lieberwirth, I. Emergence of 2MPA as an Effective Coating for Highly Stable and Luminescent Quantum Dots. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 10005–10012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cademartiri, L.; Bertolotti, J.; Sapienza, R.; Wiersma, D.S.; von Freymann, G.; Ozin, G.A. Multigram scale, solventless, and diffusion-controlled route to highly monodisperse PbS nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 671–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, B.R.; Chen, H.Y.; Rey, D.A.; Wise, F.W.; Batt, C.A. Near-infrared fluorescence imaging with water-soluble lead salt quantum dots. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 5726–5730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luther, J.M.; Law, M.; Beard, M.C.; Song, Q.; Reese, M.O.; Ellingson, R.J.; Nozik, A.J. Schottky Solar Cells Based on Colloidal Nanocrystal Films. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 3488–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, S.A.; Konstantatos, G.; Zhang, S.G.; Cyr, P.W.; Klem, E.J.D.; Levina, L.; Sargent, E.H. Solution-processed PbS quantum dot infrared photodetectors and photovoltaics. Nat. Mater. 2005, 4, 138-U114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sargent, E.H. Infrared photovoltaics made by solution processing. Nat. Photonics 2009, 3, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozik, A.J. Exciton multiplication and relaxation dynamics in quantum dots: Applications to ultrahigh-efficiency solar photon conversion. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 44, 6893–6899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauch, T.; Boberl, M.; Tedde, S.F.; Furst, J.; Kovalenko, M.V.; Hesser, G.N.; Lemmer, U.; Heiss, W.; Hayden, O. Near-infrared imaging with quantum-dot-sensitized organic photodiodes. Nat. Photonics 2009, 3, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreels, I.; De Geyter, B.; Van Thourhout, D.; Hens, Z. Transmission of a quantum-dot-silicon-on-insulator hybrid notch filter. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B-Opt. Phys. 2009, 26, 1243–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, M.A.; Scholes, G.D. Colloidal PbS nanocrystals with size-tunable near-infrared emission: Observation of post-synthesis self-narrowing of the particle size distribution. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 1844–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, J.; Na, H.B.; Yu, T.; Yu, J.H.; Kim, Y.W.; Wu, F.X.; Zhang, J.Z.; Hyeon, T. Generalized and facile synthesis of semiconducting metal sulfide nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 11100–11105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Fritz, K.; Guerin, G.; Bardajee, G.R.; Hinds, S.; Sukhovatkin, V.; Sargent, E.H.; Scholes, G.D.; Winnik, M.A. Highly luminescent lead sulfide nanocrystals in organic solvents and water through ligand exchange with poly(acrylic acid). Langmuir 2008, 24, 8215–8219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner, J.H.; Thomsen, E.; Watt, A.R.; Heckenberg, N.R.; Rubinutein-Dunlop, H. Time-resolved photoluminescence spectroscopy of ligand-capped PbS nanocrystals. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oron, D.; Aharoni, A.; de Mello Donega, C.; van Rijssel, J.; Meijerink, A.; Banin, U. Universal Role of Discrete Acoustic Phonons in the Low-Temperature Optical Emission of Colloidal Quantum Dots. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 177402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darugar, Q.; Qian, W.; El-Sayed, M.A. Observation of optical gain in solutions of CdS quantum dots at room temperature in the blue region. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 261108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Driel, A.F.; Allan, G.; Delerue, C.; Lodahl, P.; Vos, W.L.; Vanmaekelbergh, D. Frequency-dependent spontaneous emission rate from CdSe and CdTe nanocrystals: Influence of dark states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 95, 236804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreels, I.; Lambert, K.; Smeets, D.; De Muynck, D.; Nollet, T.; Martins, J.C.; Vanhaecke, F.; Vantomme, A.; Delerue, C.; Allan, G.; Hens, Z. Size-Dependent Optical Properties of Colloidal PbS Quantum Dots. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 3023–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimov, V.I.; Mikhailovsky, A.A.; Xu, S.; Malko, A.; Hollingsworth, J.A.; Leatherdale, C.A.; Eisler, H.J.; Bawendi, M.G. Optical gain and stimulated emission in nanocrystal quantum dots. Science 2000, 290, 314–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malko, A.V.; Mikhailovsky, A.A.; Petruska, M.A.; Hollingsworth, J.A.; Htoon, H.; Bawendi, M.G.; Klimov, V.I. From amplified spontaneous emission to microring lasing using nanocrystal quantum dot solids. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 81, 1303–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Rapaport, R.; Fuchs, D.T.; Lucas, L.; Lovinger, A.J.; Vilan, S.; Aharoni, A.; Banin, U. Optical gain from InAs nanocrystal quantum dots in a polymer matrix. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 251108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaller, R.D.; Petruska, M.A.; Klimov, V.I. Tunable near-infrared optical gain and amplified spontaneous emission using PbSe nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 13765–13768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhovatkin, V.; Musikhin, S.; Gorelikov, I.; Cauchi, S.; Bakueva, L.; Kumacheva, E.; Sargent, E.H. Room-temperature amplified spontaneous emission at 1300 nm in solution-processed PbS quantum-dot films. Opt. Lett. 2005, 30, 171–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakueva, L.; Musikhin, S.; Hines, M.A.; Chang, T.W.F.; Tzolov, M.; Scholes, G.D.; Sargent, E.H. Size-tunable infrared (1000-1600 nm) electroluminescence from PbS quantum-dot nanocrystals in a semiconducting polymer. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 82, 2895–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coe, S.; Woo, W.K.; Bawendi, M.; Bulovic, V. Electroluminescence from single monolayers of nanocrystals in molecular organic devices. Nature 2002, 420, 800–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstantatos, G.; Huang, C.J.; Levina, L.; Lu, Z.H.; Sargent, E.H. Efficient infrared electroluminescent devices using solution-processed colloidal quantum dots. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2005, 15, 1865–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamaguchi, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Kobayashi, M. Synthesis of Ternary Compound Sulfide Nanoparticles. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 48, 04C131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.S.; Santra, S.; Holloway, P.H. Syntheses and applications of Mn-doped II-VI semiconductor nanocrystals. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2005, 5, 1364–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bol, A.A.; Meijerink, A. Luminescence quantum efficiency of nanocrystalline ZnS:Mn2+. 1. Surface passivation and Mn2+ concentration. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 10197–10202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bol, A.A.; Meijerink, A. Long-lived Mn2+ emission in nanocrystalline ZnS:Mn2+. Phys. Rev. B 1998, 58, 15997–16000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, R.N.; Gallagher, D.; Hong, X.; Nurmikko, A. Optical properties of manganese doped nanocrystals of ZnS. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1994, 72, 416–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, Z.W.; Wang, Z.L.; Yang, P.P.; Lin, J.; Fang, J.Y. Synthesis and characterization of high-quality ZnS, ZnS:Mn2+, and ZnS:Mn2+/ZnS (core/shell) luminescent nanocrystals. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 1354–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, J.Z.; Joly, A.G. Optical properties and potential applications of doped semiconductor nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2004, 4, 919–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, S.; Kar, S. Fabrication of ZnS nanoparticles and nanorods with cubic and hexagonal crystal structures: a simple solvothermal approach. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 045710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Malm, J.O.; Zwiller, V.; Huang, Y.N.; Liu, S.M.; Wallenberg, R.; Bovin, J.O.; Samuelson, L. Energy structure and fluorescence of Eu2+ in ZnS:Eu nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 61, 11021–11024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.C.; Wang, Z.G. Synthesis and optical properties of europium-doped ZnS: Long-lasting phosphorescence from aligned nanowires. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2005, 15, 1883–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.D.; Yan, C.H.; Liu, C.H.; Liao, C.S.; Li, D.; Yu, J.Q. Study of the optical properties of Eu3+-doped ZnS nanocrystals. J. Alloy. Compd. 1998, 275, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bol, A.A.; van Beek, R.; Meijerink, A. On the incorporation of trivalent rare earth ions in II-VI semiconductor nanocrystals. Chem. Mat. 2002, 14, 1121–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, V.; Halpert, J.E.; Panzer, M.J.; Bawendi, M.G.; Bulovic, V. Alternating Current Driven Electroluminescence from ZnSe/ZnS:Mn/ZnS Nanocrystals. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 2367–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyama, T.; Hama, T.; Adachi, D.; Nakashizu, Y.; Okamoto, H. An electroluminescence device for printable electronics using coprecipitated ZnS:Mn nanocrystal ink. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 055203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawada, N.; Chen, Y.; Isobe, T. Low-temperature synthesis and photoluminescence of IIA-VIB nano-phosphors doped with rare earth ions. J. Alloy. Compd. 2006, 408, 824–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.Q.; Yi, G.S.; Chen, D.P.; Zhou, Y.X.; Cheng, J. Synthesis and characterization of strongly fluorescent europium-doped calcium sulfide nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. 2002, 12, 1194–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anila, E.I.; Aravind, A.; Jayaraj, M.K. The photoluminescence of SrS : Cu nanophosphor. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 145604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.R.; Tang, K.B.; Yang, Q.; An, C.H.; Hai, B.; Shen, G.Z.; Qian, Y.T. Blue-light emission of nanocrystalline CaS and SrS synthesized via a solvothermal route. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2002, 351, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.R.; Tang, K.B.; Yang, Q.; Qian, Y.T. Preparation and photoluminescence of CaS : Bi, CaS : Ag, CaS : Pb, and Sr1-xCaxS nanocrystallites. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2003, 150, G163–G166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korthout, K.; Smet, P.F.; Poelman, D. Whispering gallery modes in micron-sized SrS:Eu octahedrons. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 051104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smet, P.F.; Poelman, D. Templated growth of textured and luminescent CaS:Eu thin films by a low-temperature solvothermal process. J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 095306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Smet, P.F.; Moreels, I.; Hens, Z.; Poelman, D. Luminescence in Sulfides: A Rich History and a Bright Future. Materials 2010, 3, 2834-2883. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma3042834
Smet PF, Moreels I, Hens Z, Poelman D. Luminescence in Sulfides: A Rich History and a Bright Future. Materials. 2010; 3(4):2834-2883. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma3042834
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmet, Philippe F., Iwan Moreels, Zeger Hens, and Dirk Poelman. 2010. "Luminescence in Sulfides: A Rich History and a Bright Future" Materials 3, no. 4: 2834-2883. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma3042834
APA StyleSmet, P. F., Moreels, I., Hens, Z., & Poelman, D. (2010). Luminescence in Sulfides: A Rich History and a Bright Future. Materials, 3(4), 2834-2883. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma3042834