Advances in Retinal Tissue Engineering
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Candidates for Cell Therapy
3. Retinal Transplantation via Bolus Injection
4. A Tissue Engineering Approach: Potential Polymers
5. Histologic Analysis of Subretinal Transplantation
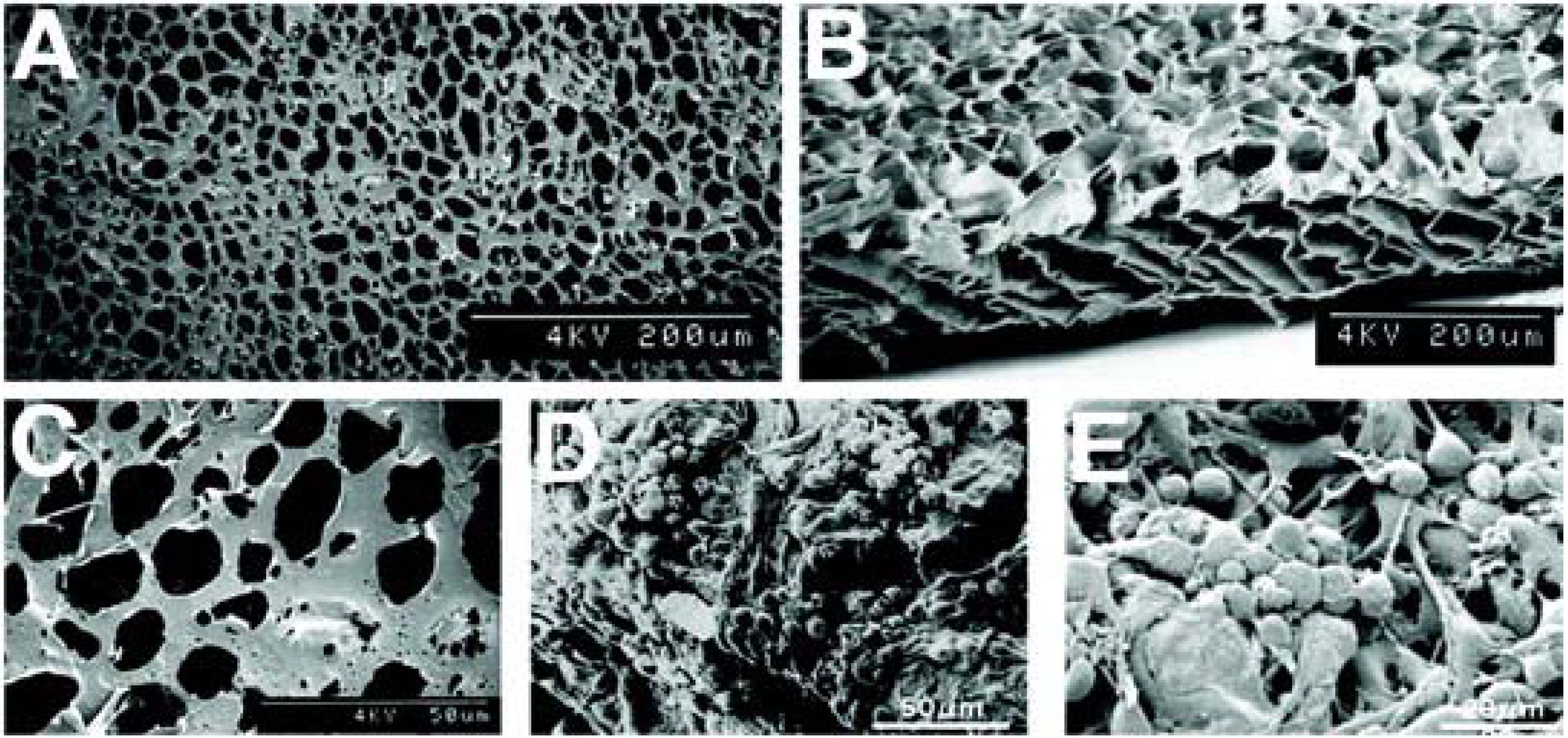

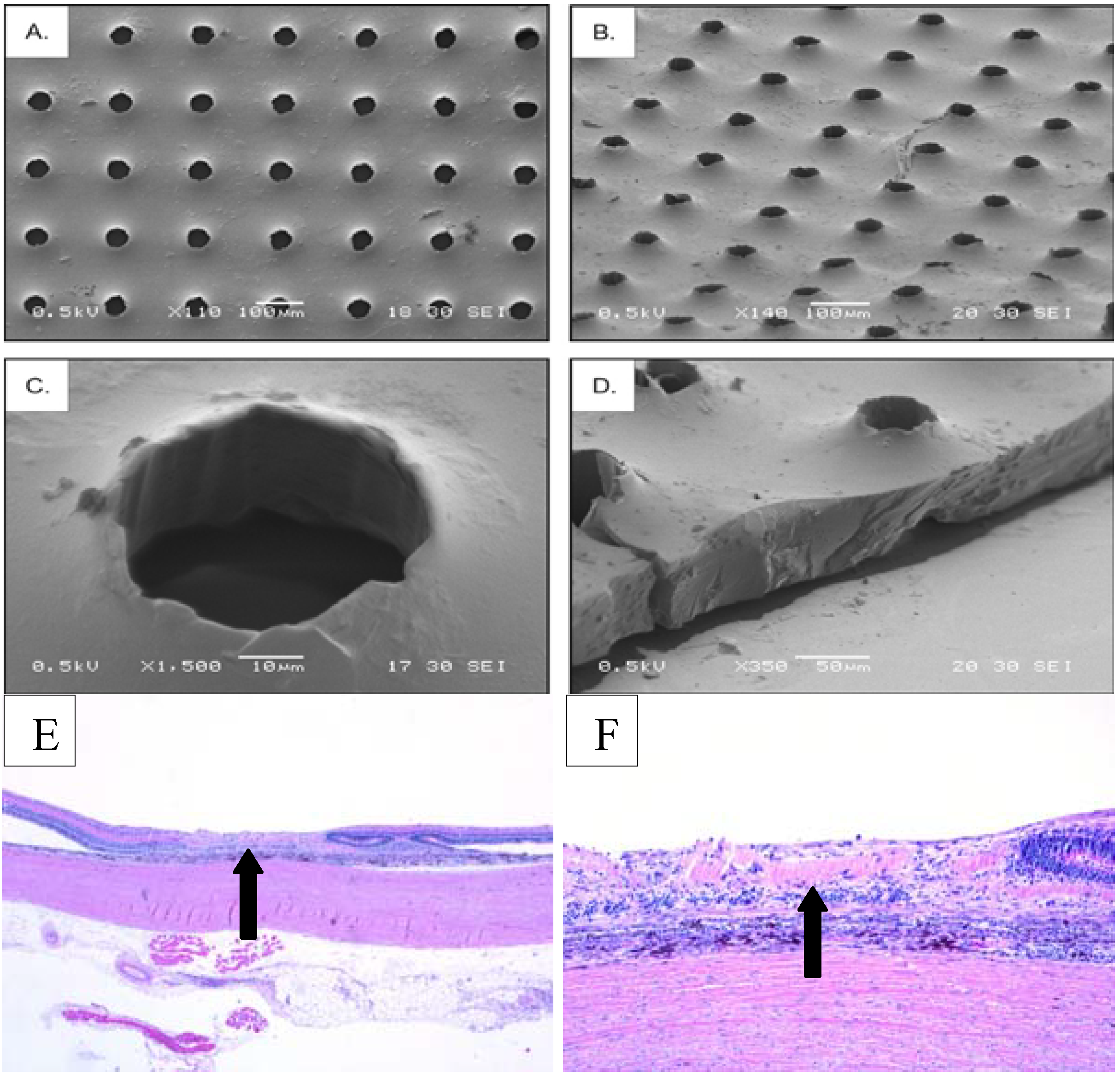
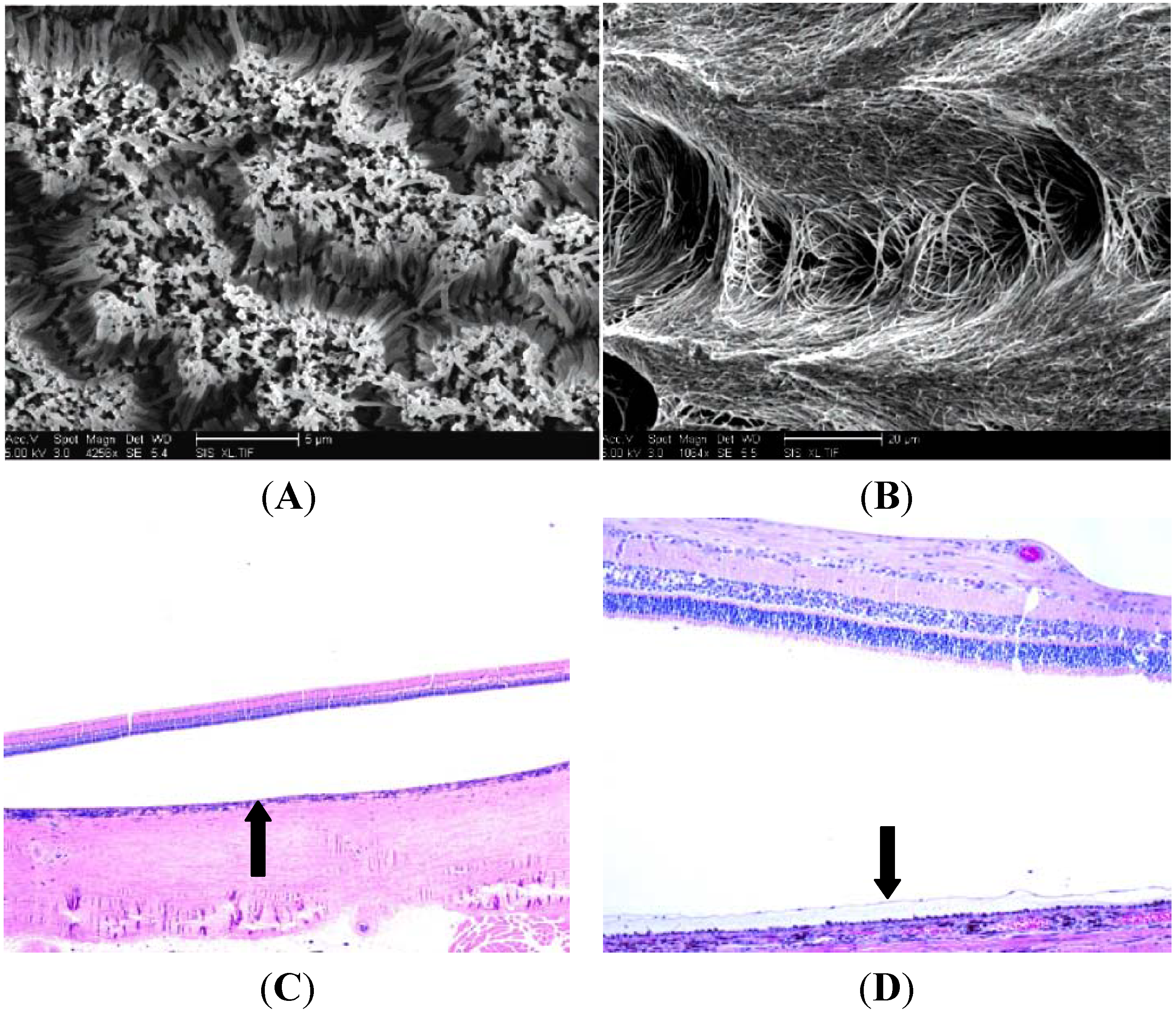
6. Limitations and Future Directions
7. Final Remarks
References
- Cook, H.L.; Patel, P.J.; Tufail, A. Age-related macular degeneration: Diagnosis and management. Br. Med. Bull. 2008, 85, 127–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, D.S.; O’Colmain, B.J.; Munoz, B.; Tomany, S.C.; McCarty, C.; de Jong, P.T.; Nemesure, B.; Mitchell, P.; Kempen, J. Eye diseases prevalence research group. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2004, 122, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamel, C. Retinitis pigmentosa. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2006, 1, 40:1–40:12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnadev, N.; Meleth, A.D.; Chew, E.Y. Nutritional supplements for age-related macular degeneration. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2010, 21, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, J.W. Preliminary results of gene therapy for retinal degeneration. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 2282–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, J.L.; Barlow, W.E.; Humayun, M.S.; de Juan, E., Jr.; Milam, A.H. Morphometric analysis of macular photoreceptors and ganglion cells in retinas with retinitis pigmentosa. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1992, 110, 1634–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.; Humayun, M.S.; de Juan, E., Jr.; Greenburg, R.J.; Marsh, M.J.; Klock, I.B.; Milam, A.H. Preservation of the inner retina in retinitis pigmentosa. A morphometric analysis. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1997, 115, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humayun, M.S.; Prince, M.; de Juan, E., Jr.; Barron, Y.; Moskowitz, M.; Klock, I.B.; Milam, A.H. Morphometric analysis of the extramacular retina from postmortem eyes with retinitis pigmentosa. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1999, 40, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Michaelson, I.C. Disturbance of the chorio-capillaris and retinal dehiscence. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1954, 38, 632–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, B., Jr.; McIntosh, H.D. Retinal circulation. Annu. Rev. Med. 1967, 18, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grisanti, S.; Tatar, O. The role of vascular endothelial growth factor and other endogenous interplayers in age-related macular degeneration. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2008, 27, 372–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, J.A.; Itskovitz-Eldor, J.; Shapiro, S.S.; Waknitz, M.A.; Swiergiel, J.J.; Marshall, V.S.; Jones, J.M. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science 1998, 282, 1145–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amit, M.; Carpenter, M.K.; Inokuma, M.S.; Chiu, C.P.; Harris, C.P.; Waknitz, M.A.; Itskovitz-Eldor, J.; Thomson, J.A. Clonally derived human embryonic stem cell lines maintain pluripotency and proliferative potential for prolonged periods of culture. Dev. Biol. 2000, 227, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwaka, T.P.; Thomson, J.A. Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells occurs through symmetric cell division. Stem Cells 2005, 23, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, M.K.; Rosler, E.; Rao, M.S. Characterization and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells. Cloning Stem Cells 2003, 5, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, M.J.; Kaufman, M.H. Establishment in culture of pluripotential cells from mouse embryos. Nature 1981, 292, 154–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonoda, S.; Spee, C.; Barron, E.; Ryan, S.J.; Kannan, R.; Hinton, D.R. A protocol for the culture and differentiation of highly polarized human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 662–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banin, E.; Obolensky, A.; Idelson, M.; Hemo, I.; Reinhardtz, E.; Pikarsky, E.; Ben-Hur, T.; Reubinoff, B. Retinal incorporation and differentiation of neural precursors derived from human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 2005, 24, 256–257. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 2006, 126, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haruta, M.; Sasai, Y.; Kawasaki, H.; Amemiya, K.; Ooto, S.; Kitada, M.; Suemori, H.; Nakatsuji, N.; Ide, C.; Honda, Y.; Takahashi, M. In vitro and in vivo characterization of pigment epithelial cells differentiated from primate embryonic stem cells. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 1020–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, R.D.; Wang, S.; Klimanskaya, I.; Holmes, T.; Ramos-Kelsey, R.; Lu, B.; Girman, S.; Bischoff, N.; Sauve, Y.; Lanza, R. Human embryonic stem cell-derived cells rescue visual function in dystrophic RCS rats. Cloning Stem Cells 2006, 8, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vugler, A.; Carr, A.J.; Lawrence, J.; Chen, L.L.; Burrell, K.; Wright, A.; Lundh, P.; Semo, M.; Ahmado, A.; Gias, C.; et al. Elucidating the phenomenon of HESC-derived RPE: anatomy of cell genesis, expansion and retinal transplantation. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 214, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, M.J.; Ray, J.; Whiteley, S.J.; Klassen, H.; Gage, F.H. Neuronal differentiation and morphological integration of hippocampal progenitor cells transplanted to the retina of immature and mature dystrophic rats. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2000, 16, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klassen, H.J.; Ng, T.F.; Kurimoto, Y.; Kirov, I.; Shatos, M.; Coffey, P.; Young, M.J. Multipotent retinal progenitors express developmental markers, differentiate into retinal neurons, and preserve light-mediated behavior. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 4167–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLaren, R.E.; Pearson, R.A.; MacNeil, A.; Douglas, R.H.; Salt, T.E.; Akimoto, M.; Swaroop, A.; Sowden, J.C.; Ali, R.R. Retinal repair by transplantation of photoreceptor precursors. Nature 2006, 444, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, M.; Lavik, E.; Klassen, H.; Zahir, T.; Langer, R.; Young, M.J. Biodegradable polymer composite grafts promote the survival and differentiation of retinal progenitor cells. Stem Cells 2005, 23, 1579–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballios, B.G.; Cooke, M.J.; van der Kooy, D.; Shoichet, M.S. A hydrogel-based stem cell delivery system to treat retinal degenerative diseases. Biomaterials 2010, 9, 2555–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aramant, R.B.; Seiler, M.J. Retinal transplantation—Advantages of intact fetal sheets. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2002, 21, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, R.D.; Coffey, P.J.; Sauve, Y.; Lawrence, J.M. Intraretinal transplantation to prevent photoreceptor degeneration. Ophthalmic Res. 1997, 29, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mooney, D.J.; Mazzoni, C.L.; Breuer, C.; McNamara, K.; Hern, D.; Vacanti, J.P.; Langer, R. Stabilized polyglycolic acid fibre-based tubes for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 1996, 17, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niklason, L.E.; Gao, J.; Abbott, W.M.; Hirschi, K.K.; Houser, S.; Marini, R.; Langer, R. Functional arteries grown in vitro. Science 1999, 284, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaszemski, M.J.; Payne, R.G.; Hayes, W.C.; Langer, R.; Mikos, A.G. Evolution of bone transplantation: Molecular, cellular and tissue strategies to engineer human bone. Biomaterials 1996, 17, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redenti, S.; Neeley, W.L.; Rompani, S.; Saigal, S.; Yang, J.; Klassen, H.; Langer, R.; Young, M.J. Engineering retinal progenitor cell and scrollable poly(glycerol-sebacate) composites for expansion and subretinal transplantation. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 3405–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, R. Biomaterials in drug delivery and tissue engineering: one laboratory’s experience. Acc. Chem. Res. 2000, 33, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radtke, N.D.; Aramant, R.B.; Seiler, M.J.; Petry, H.M.; Pidwell, D. Vision change after sheet transplant of fetal retina with retinal pigment epithelium to a patient with retinitis pigmentosa. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2004, 122, 1159–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hynes, S.R.; Lavik, E.B. A tissue-engineered approach towards retinal repair: scaffolds for cell transplantation to the subretinal space. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2010, 248, 763–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, G.G.; Thomson, R.C.; Ishaug, S.L.; Mikos, A.G.; Cumber, S.; Garcia, C.A.; Lahiri-Munir, D. Retinal pigment epithelium cells cultured on synthetic biodegradable polymers. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1997, 34, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, H.A.; Treharne, A.J.; Walker, P.; Grossel, M.C.; Lotery, A.J. Optimisation of polymer scaffolds for retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cell transplantation. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2011, 95, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchholz, D.E.; Hikita, S.T.; Rowland, T.J.; Friedrich, A.M.; Hinman, C.R.; Johnson, L.V.; Clegg, D.O. Derivation of functional retinal pigmented epithelium from induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 2427–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Deng, X.; Spee, C.; Sonoda, S.; Hsieh, C.L.; Barron, E.; Pera, M.; Hinton, D.R. Polarized secretion of PEDF from human embryonic stem cell-derived rpe promotes retinal progenitor cell survival. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 52, 1573–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Hikita, S.T.; Deng, X.; Lu, B.; Johnson, L.V.; Clegg, D.O.; Tai, Y.; Ahuja, A.; Humayun, M.; Hinton, D.R.; et al. Culture of polarized embryonic stem cell-derived rpe on synthetic substrates. ARVO Meet. Abstract 2011, 52, 3191. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, B.B.; Liu, L.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, D.; Thomas, P.B.; Hirsch, L.K.; Ahuja, A.; Clegg, D.O.; Hinton, D.R.; et al. Quantitative analysis of possible surgical shear force stress on polymer substrates seeded with human embryonic stem cell (hESC) derived retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) monolayers implanted into the rat subretinal space. ARVO Meet. Abstract 2011, 52, 3187. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, D.; Thomas, PB.; Ford, K.; Ahuja, A.K.; Thomas, B.B.; Clegg, D.O.; Hinton, D.R.; Humayun, M.S. Human embryonic stem cell derived retinal pigment epithelial cells cultured on polymer substrates maintain a confluent monolayer structure in the subretinal space of implanted rats. ARVO Meet. Abstract 2011, 52, 3190. [Google Scholar]
- Lavik, E.B.; Klassen, H.; Warfvinge, K.; Langer, R.; Young, M.J. Fabrication of degradable polymer scaffolds to direct the integration and differentiation of retinal progenitors. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 3187–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redenti, S.; Tao, S.; Yang, J.; Gu, P.; Klassen, H.; Saigal, S.; Desai, T.; Young, M.J. Retinal tissue engineering using mouse retinal progenitor cells and a novel biodegradable, thin-film poly(e-caprolactone) nanowire scaffold. J. Ocul. Biol. Dis. Inform. 2008, 1, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neeley, W.L.; Redenti, S.; Klassen, H.; Tao, S.; Desai, T.; Young, M.J.; Langer, R. A microfabricated scaffold for retinal progenitor cell grafting. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, S.L.; Desai, T.A. Aligned arrays of biodegradable poly(epsilon-caprolactone) nanowires and nanofibers by template synthesis. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 1463–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steedman, M.R.; Tao, S.L.; Klassen, H.; Desai, T.A. Enhanced differentiation of retinal progenitor cells using microfabricated topographical cues. Biomed. Microdevices 2010, 12, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gullapalli, V.K.; Sugino, I.K.; Van Patten, Y.; Shah, S.; Zarbin, M.A. Impaired RPE survival on aged submacular human Bruch’s membrane. Exp. Eye Res. 2005, 80, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Moore, M.J.; Zhang, X.; Klassen, H.; Langer, R.; Young, M. Intravitreal injections of GDNF-loaded biodegradable microspheres are neuroprotective in a rat model of glaucoma. Mol. Vis. 2007, 13, 1783–1792. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Tucker, B.A.; Zhang, X.; Checa-Casalengua, P.; Herrero-Vanrell, R.; Young, M.J. Robust cell integration from co-transplantation of biodegradable MMP2-PLGA microspheres with retinal progenitor cells. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 1041–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csete, M. Translational prospects for human induced pluripotent stem cells. Regen. Med. 2010, 5, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanaka, S. A fresh look at iPS cells. Cell 2009, 137, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Trese, M.; Regatieri, C.V.; Young, M.J. Advances in Retinal Tissue Engineering. Materials 2012, 5, 108-120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma5010108
Trese M, Regatieri CV, Young MJ. Advances in Retinal Tissue Engineering. Materials. 2012; 5(1):108-120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma5010108
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrese, Matthew, Caio V. Regatieri, and Michael J. Young. 2012. "Advances in Retinal Tissue Engineering" Materials 5, no. 1: 108-120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma5010108
APA StyleTrese, M., Regatieri, C. V., & Young, M. J. (2012). Advances in Retinal Tissue Engineering. Materials, 5(1), 108-120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma5010108




