Neural Network Analysis and Evaluation of the Fetal Heart Rate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
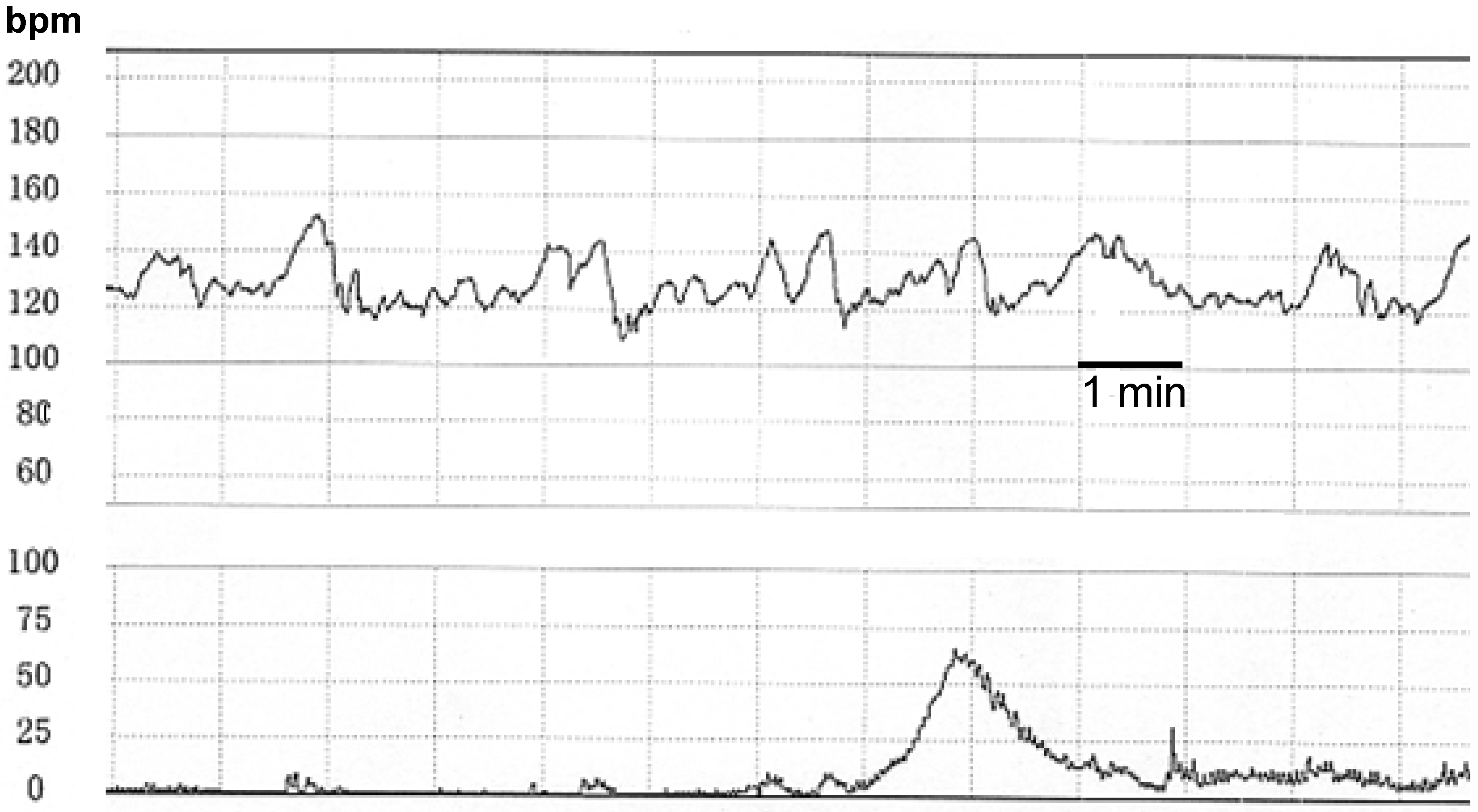
2. Methods
2.1 Acquisition of the Fetal Heart Rate and Uterine Contraction Data
2.2 Detection of Sinusoidal FHR
2.3 The Neural Network Computer
| 1. Baseline FHR (beats/minute) |
| 2. Baseline variability amplitude (beats/minute) |
| 3. Presence of sinusoidal FHR pattern |
| 4. Number of decelerations |
| 5. Duration of decelerations (in seconds) |
| 6. Bottom FHR of decelerations (beats/minute) |
| 7. Lag time of decelerations (in seconds) |
| 8. Recovery time of decelerations (in seconds) |
| 1. Baseline FHR (beats/minute) |
| From 50 to 210, we divided 16 steps, and named from 0 to 15, respectively. |
| 2. Baseline variability amplitude (beats/minute) |
| From 0 to 63, we divided 16 steps, and named from 0 to 15, respectively. |
| 3. Presence of sinusoidal FHR pattern |
| Absent: 0, Present: 15 |
| 4. Number of decelerations |
| No deceleration: 0, 1-2: 5, 3-4: 10, 5 and over: 15 |
| 5. Duration of decelerations (in seconds) |
| From 0 to 320, we divided 16 steps, and named from 0 to 15, respectively. |
| 6. Bottom FHR of decelerations (beats/minute) |
| From 0 to 160, we divided 16 steps, and named from 0 to 15, respectively. |
| 7. Lag time of decelerations (in seconds) |
| From 0 to 240, we divided 16 steps, and named from 0 to 15, respectively. |
| 8. Recovery time of decelerations (in seconds) |
| From 0 to 240, we divided 16 steps, and named from 0 to 15, respectively. |
3. Results and Discussion
3.1 Performance of the Neural Network Computer
| Example No. | Probability | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| name | normal | intermediate | pathologic | |
| 1 | svd* | 0 | 0.001 | 0.999 |
| 2 | mvd** | 0.001 | 0.999 | 0 |
| 3 | normal | 0.998 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| 4 | normal | 0.998 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| 5 | ssp*** | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 6 | bdc**** | 0.001 | 0 | 0.999 |
| 7 | svd* | 0 | 0.001 | 0.999 |
| 8 | ld***** | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 9 | lv *6 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 10 | normal | 0.998 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| 11 | mvd** | 0.001 | 0.999 | 0.001 |
| 12 | mvd** | 0.001 | 0.998 | 0.001 |
| 13 | lv *6 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 14 | lv *6 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 15 | ld***** | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 16 | ld***** | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 17 | bdc**** | 0.001 | 0 | 0.999 |
| 18 | bdc**** | 0.001 | 0 | 0.999 |
| 19 | ssp*** | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 20 | svd* | 0 | 0.001 | 0.999 |
3.2 Comparison of Neural Computer Results to Clinical Data
3.2.1 Neural Computer Results and Neonatal State
3.2.2 The FHR Score of the Experts’ System Strongly Correlates with the Outcome Probability

3.3 The Neural Index
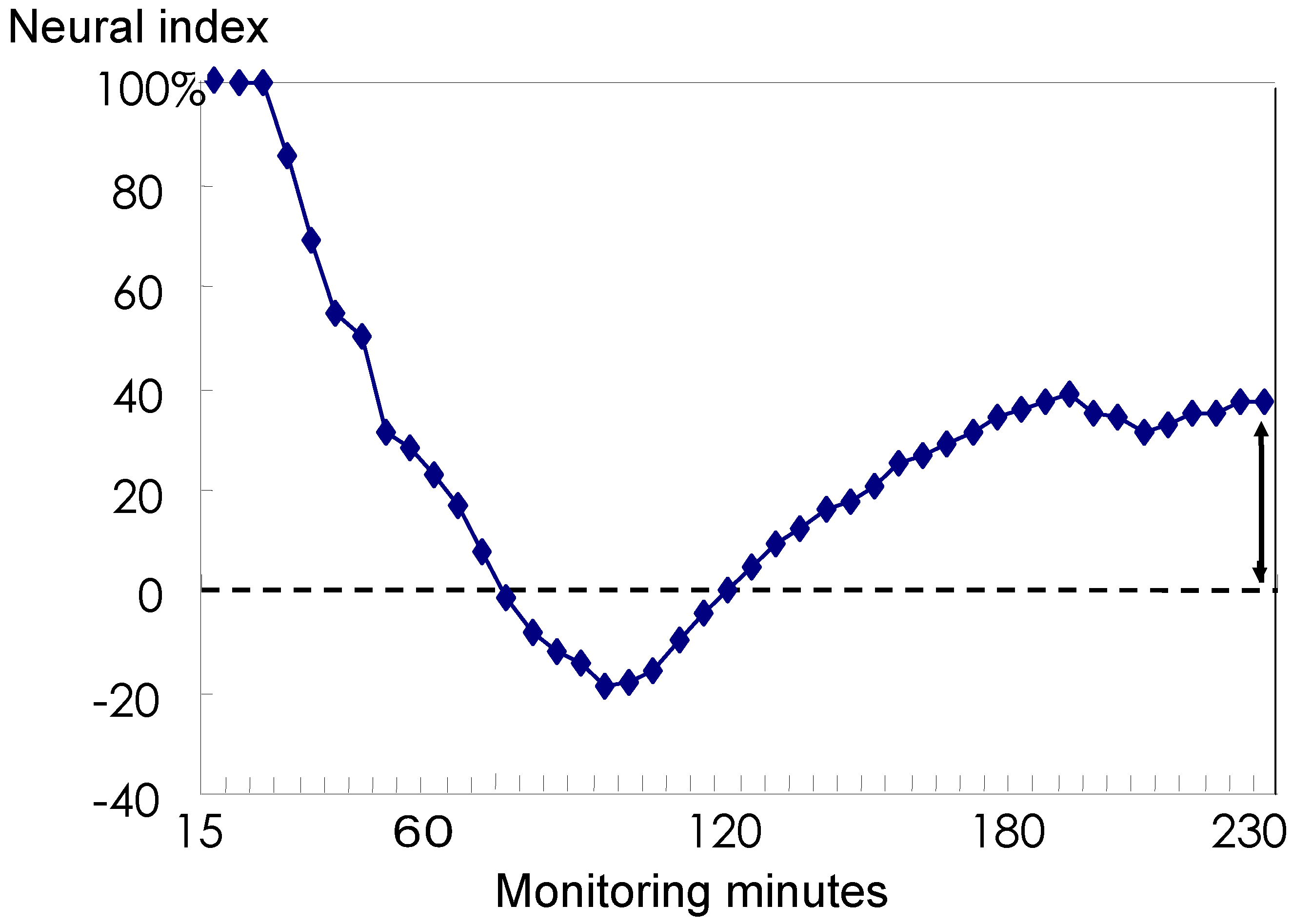
3.4 Discussion
Conclusion
Acknowledgements
References
- Maeda, K. Fetal heart sound recorded by using slow down tape technique. In Proc. 8th Int. Conf. Med. Biol. Eng. 1969. Session 19-2. [Google Scholar]
- Symonds, E.M. Configuration of the fetal electrocardiogram in relation to the fetal acid-base balance and plasma electrolytes. J. Obstetet. Gynaecol. Brit. Commonw. 1971, 78, 957–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentner, O.; Hammacher, K. An improved method for the determination of the instantaneous fetal heart frequency from the fetal phonocardiogram. In Proc. 7th Int. Conf. Med. Biol. Eng. 1967. No. 140. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, K.; Ezaki, I. Fetal cardiotachography recorded with fetal heart sound during pregnancy and labor. In Proc. 7th Int. Conf. Med. Biol. Eng. 1967. No. 144. [Google Scholar]
- Hammacher, K. Einführung in die Cardiotokographie. 5. Teil: Die Herzfrequenzmessung mit US = Ultraschall. Die Schweizer Hebamme 1976, 74, 17–21. (in German). [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi, Y.; Hogaki, N. Auto correlation method for fetal heart rate measurement from ultrasonic Doppler fetal signal. In Ultrasound in Medicine; White, D., Brown, R.E., Eds.; Plenum Press: New York, 1977; Vol. 3B “Engineering Aspect”, pp. 1327–1332. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuzaki, T.; Sekijima, A.; Morishita, K.; Takeuchi, Y.; Mizuta, M.; Minagawa, Y.; Nakajima, K.; Maeda, K. Survey on the perinatal variables and the incidence of cerebral palsy for 12 years before and after the application of the fetal monitoring system. Nippon Sanka Fujinka Gakkai Zasshi 1990, 42, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takeshita, K.; Ando, Y.; Ohtani, K.; Takashima, S. Cerebral palsy in Tottori, Japan. Benefits and risks of progress in perinatal medicine. Neuroepidemiology 1989, 4, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K.; Arima, T.; Tatsumura, M.; Nagasawa, T. Computer-aided fetal heart rate analysis and automatic fetal-distress diagnosis during labor and pregnancy utilizing external techniques in fetal monitoring. MEDINFO 1980, 80, 1214–1219. [Google Scholar]
- Dawes, G.S.; Moulden, M.; Redman, C.W. System 8000: computerized antenatal FHR analysis. J. Perinat. Med. 1991, 19, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardes, J.; Moura, C.; de Sa, J.P.; Leite, L.P. The Porto system for automated cardiotocogaphic signal analysis. J. Perinat. Med. 1991, 19, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keith, R.D.; Westgate, J.; Ifeachor, E.C.; Greene, K.R. Suitability of artificial neural networks for feature extraction from cardiotocogram during labor. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 1994, 32, S51–S57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulbricht, C.; Dorfner, G.; Lee, A. Neural networks for recognizing patterns in cardiotocograms. Artif. Intell. Med. 1998, 12, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupka, T.; Wrobel, J.; Jerewski, J.; Gacek, A.; Jerewski, M. Evalation of fetal heart rate baseline estimation method using testing signals based on a statistical model. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2006, 1, 3728–3731. [Google Scholar]
- Jezewski, M.; Wrobel, J.; Labaj, P.; Leski, J.; Henzel, N.; Horoba, K.; Jezewski, J. Some practical remarks on neural networks approach to fetal cardiotocograms classification. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2007, 5170–5173. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, K.; Noguchi, Y.; Matsumoto, F.; Nagasawa, T. Quantitative fetal heart rate evaluation without pattern classification: FHR score and artificial neural network analysis. In Textbook of Perinatal Medicine, 2nd Ed.; Kurjak, A., Chervenak, F.A., Eds.; Informa: London, UK, 2006; Vol. 2, pp. 1487–1495. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, K. Computerized automatic diagnosis of fetal distress with the use of external monitoring technique. In Computerdiagnostik in der Geburtsmedizin; Krause, W., Ed.; Friedrich-Schiller-Universität: Jena, Germany, 1981; pp. 28–49. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, T.; Maeda, K.; Takahashi, H.; Nagata, N.; Nakajima, K.; Terakawa, N. Differentiation between physiologic and pathologic sinusoidal FHR pattern by fetal actocardiogram. J. Perinat. Med. 1994, 221, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K.; Nagasawa, T. Automatic computerized diagnosis of fetal sinusoidal heart rate. Fetal Diag. Ther. 2006, 20, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; McClelland, J.L. Parallel Distributed Processing; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, 1986; Vol. 1 & 2. [Google Scholar]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning Internal Representations by Error Propagation. In Parallel Distributed Processing; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, 1986; Vol. 1, pp. 318–362. [Google Scholar]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning Representations by Back-Propagating Errors. Nature 1986, 323, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K.; Utsu, M.; Makio, A.; Serizawa, M.; Noguchi, Y.; Hamada, T.; Mariko, K,; Matsumoto, F. Neural network computer analysis of fetal heart rate. J. Matern. Fetal Invest. 1998, 8, 163–171. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, K.; Kimura, S.; Fukui, Y.; Ozawa, S.; Kosaka, T.; Wang, C.F.M.; Tamura, M.; Takata, D.; Nakano, H.; Mitoma, M. Pathophysiology of Fetus; Fukuoka Printing: Fukuoka, Japan, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Irie, T. Automated fetal heart rate analysis and its trend gram in relation to the gas analysis and acid-base balance of umbilical arterial blood. Nippon Sanka Fujinka Gakkai Zasshi 1986, 38, 1623–1631. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maeda, K.; Noguchi, Y.; Matsumoto, F. Evaluation of prolonged fetal monitoring with normal and pathologic outcome probabilities determined by artificial neural network. Fetal Diag. Ther. 2003, 18, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuda, I.; Nagashima, T.; Aihara, K. Global bifurcation structure of chaotic neural networks and its application to traveling salesman problems. Neural Networks 1997, 10, 1673–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, W.; Khorasani, K. An adaptive structure neural networks application to EEG automatic seizure detection. Neural Networks 1996, 9, 1223–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moul, J.W.; Snow, P.H.; Fernandez, E.B.; Maher, P.D.; Sesterhenn, I.A. Neural network analysis of quantitative histological factors to predict pathological stage in clinical stage I nonseminomatous testicular cancer. J. Urol. 1995, 153, 1674–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruppin, E.; Reggia, J.A. A neural model of memory impairment in diffuse cerebral atrophy. Br. J. Psychiatry 1995, 166, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arle, J.E.; Moriss, C.; Wang, Z.J.; Zimmerman, R.A.; Philipps, P.G.; Sutton, L.N. Prediction of posterior fossa tumor type in children by means of magnetic resonance image properties, spectroscopy, and neural networks. J. Neurosurg. 1997, 86, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brickley, M.R.; Cowpe, J.G.; Shepherd, J.P. Performance of a computer-simulated neural network trained to categorize normal, premalignant and malignant oral smears. J. Oral. Pathol. Med. 1996, 25, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutlukan, E.; Keating, D. Visual field interpretation with a personal computer-aided neural network. Eye 1994, 8, 321–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westenskow, D.R.; Orr, J.A.; Simon, F.H.; Bender, H.J.; Frankenberger, H. Intelligent alarms reduce anesthesiologist’s response time to critical faults. Anesthesiology 1992, 77, 1074–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, H.; Katafuchi, T.; Uehara, T.; Nishimura, T. Application of artificial neural network to computer-aided diagnosis of coronary artery disease in myocardial SPECT bull’s eye images. J. Nucl. Med. 1992, 33, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Andreassen, H.; Bohr, H.; Bohr, J.; Brunak, S.; Bugge, T. Analysis of the secondary structure of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) proteins p17, gp120 and gp41 by computer modeling based on neural network methods. J. Acquir. Immune Def. Syndr. 1990, 3, 615–622. [Google Scholar]
- De Voe, L.D.; Samuel, S.; Prescott, P.; Work, B.A. Predicting the duration of the first stage of spontaneous labor using a neural network. J. Mat. Fet. Med. 1996, 5, 256–261. [Google Scholar]
- Farmer, R.M.; Medearis, A.L.; Hirata, G.I.; Platt, L.D. The use of a neural network for the ultrasonographic estimation of fetal weight in the macrosomic fetus. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1992, 166, 1467–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, M.; Signorini, M.G.; Magenes, G. Comparison of entropy-bases regularity estimators: application to the fetal heart rate signal for the identification of fetal distress. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 53, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattani, C.; Doubrovina, O.; Rogosin, S.; Voskresensky, S.L.; Zelianko, E. On the creation of a new diagnostic model for fetal well-being on the base of wavelet analysis of cardiotocograms. J. Med. Sys. 2006, 30, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Angari, H.M.; Sahakian, A.V. Use of sample entropy approach to study heart rate variability in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 54, 1900–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assaleh, K. Extraction of fetal electrocardiogram using adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference systems. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 54, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2009 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Noguchi, Y.; Matsumoto, F.; Maeda, K.; Nagasawa, T. Neural Network Analysis and Evaluation of the Fetal Heart Rate. Algorithms 2009, 2, 19-30. https://doi.org/10.3390/a2010019
Noguchi Y, Matsumoto F, Maeda K, Nagasawa T. Neural Network Analysis and Evaluation of the Fetal Heart Rate. Algorithms. 2009; 2(1):19-30. https://doi.org/10.3390/a2010019
Chicago/Turabian StyleNoguchi, Yasuaki, Fujihiko Matsumoto, Kazuo Maeda, and Takashi Nagasawa. 2009. "Neural Network Analysis and Evaluation of the Fetal Heart Rate" Algorithms 2, no. 1: 19-30. https://doi.org/10.3390/a2010019
APA StyleNoguchi, Y., Matsumoto, F., Maeda, K., & Nagasawa, T. (2009). Neural Network Analysis and Evaluation of the Fetal Heart Rate. Algorithms, 2(1), 19-30. https://doi.org/10.3390/a2010019




