Abstract
Invasive, exotic insects and diseases have a devastating effect on North American forests. The rate of spread, or range expansion, is one of the main determinants of an invasive organism’s impact, and can play a major role in structuring management response options. To better understand how exotic organisms have spread through our forests, this study employs a consistent, rigorous analytical framework to analyze a comprehensive geospatial database for the spread of seven exotic insects and six diseases. This study includes new data for six insects and two diseases in combination with five invasive species previously analyzed using the same technique. The quantile regression analysis of over 3000 records of infestation over the preceding century show that the rate of spread of invasive forest insects and diseases ranges from 4.2 km·year−1 to 57.0 km·year−1. The slowest disease spread was white pine blister rust (Cronartium ribicola) at 7.4 km·year−1 while the most rapid disease spread was chestnut blight (Cryphonectria parasitica) at 31.3 km·year−1. The slowest insect spread was balsam woolly adelgid (Adelges piceae) (4.2 km·year−1) while the fastest was emerald ash borer (Agrilus planipennis) at 57.0 km·year−1. Species that can fly long distances or are vectored by flying insects have spread faster than those that are passively dispersed. This analysis highlights the difficulty of estimating spread rates from studies of individual dispersal or flight distances, but the estimated spread rates in this study are generally in line with previous estimates.
1. Introduction
Invasive forest insects and diseases−organisms that damage or kill trees and are not native to the ecosystem−are major threats to forests. Invasive forest insects and diseases have removed dominant tree species, reduced diversity, altered disturbance regimes, and affected ecosystem function in North America. Invasive species can negatively affect forest carbon storage over the long term by altering nutrient availability, primary productivity, and species composition [,]. The effect of invasive organisms is exacerbated by climate change [], more frequent extreme climatic events [,], and forest fragmentation []. In addition to their ecological costs, exotic forest invaders have a large economic impact on both forest products and ecosystem services []. For instance, just three invasive insects (hemlock woolly adelgid—HWA, emerald ash borer—EAB, and gypsy moth—GM) cause approximately $2.1 billion dollars in damages in the United States annually [].
The rate of spread of invasive species through forested ecosystems is a major determinant of management options and response. Understanding the rate and mechanisms of range expansion can help managers reduce transmission, protect areas of special concern, and implement other control measures. For example, understanding rates of spread of invasive species is important in the implementation of biocontrol programs []. Rate of spread is also a key input into risk maps and decision support tools []. The threat of recently discovered forest diseases, such as sudden oak death (Phytophthora ramorum Werres, de Cock and Man in’t Veld), and newly introduced insects, such as Goldspotted Oak Borer (Agrilus auroguttatus Schaeffer), provide a strong motivation for studying how invasive organisms spread through forests. Documenting past spread rates is a key foundation for understanding and reacting to future invasive species, because past spread rates may be the only benchmarks available to guide mitigation decisions until a new invasion can be studied. In addition, climate change is altering the distribution limits of species such that it is reasonable to expect the ranges of forest insects and diseases to shift and in some cases expand [,,]. Forests that have been hostile to the establishment of exotic species may become infested as temperature and moisture regimes change. Documenting past spread rates provides a reference point for future work on the spread of forest insects and diseases into novel and changing environments.
This study adds 1957 geographically specific records of infestation for six exotic insects and two diseases to previously published work using the same methods applied to 1051 records for four forest diseases [] and one insect []. The resulting analysis of 13 forest invaders presents a novel opportunity to test three hypotheses. First, this analysis investigates if diseases spread more rapidly than insects. The second hypothesis is that individual studies of insect or disease dispersal provide a good prediction of long-term range expansion. The third hypothesis based on past studies [], is that previous estimates of spread for these invasive species have generally been overestimates.
1.1. Insects
This analysis covers seven insects that have invaded North American forests, caused ecological disruptions, and for which there are sufficiently detailed records to allow for calculation of a rate of spread. The first insect, the gypsy moth (GM, Lymantria dispar L.), was released in 1868 or 1869 in Medford, Massachusetts []. The second insect is the balsam woolly adelgid (BWA, Adelges piceae Ratzeburg). BWA arrived in western Nova Scotia, Canada from central Europe around the turn of century []. Near its first introduction BWA has made slow progress inland, but continues to cause mortality in balsam fir stands. Hemlock woolly adelgid (HWA, Adelges tsugae Annand) is similar to BWA but feeds on species of hemlock (Tsuga spp.) rather than fir []. HWA was first reported in eastern North America in 1951, though likely arrive much earlier []. The pine shoot beetle (PSB, Tomicus piniperda L.), was introduced from Europe and first discovered in North America in 1992. While the PSB attacks many species of pine, Scotch pine, Pinus sylvestris L. is the most susceptible []. Sirex wood wasp (SWW, Sirex noctilio Fabricus) is considered a high-risk forest insect because of its negative impact on pine plantations in the Southern Hemisphere. First confirmed in North America in 2005, it has the potential to spread throughout North America []. The Emerald ash borer (EAB, Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire), found in 2002 near Detroit, Michigan, originated in China []. EAB has proven to be an aggressive killer of ash (Fraxinus spp.) trees in North America. The final insect in this analysis is the viburnum leaf beetle (VLB, Pyrrhalta viburni Paykull), which was first discovered in Ottawa, Ontario in 1978 and in New York state in 1996 [].
1.2. Diseases
Results for four of the six diseases considered here (Chestnut blight (CB) Cryphonectria parasitica (Murrill) Barr; Dutch elm disease (DED) Ophiostoma ulmi (Buisman) Nannf. and O. novo-ulmi Brasier; Beech bark disease (BBD) Neonectria spp.; and White pine blister rust (WPBR) Cronartium ribicola J.C.Fisch.) are drawn from work by Evans and Finkral []. They are presented here because they use the same analytical method and extend the opportunity to compare spread rates across trophic groups.
CB was first identified in New York City in 1904. The blight had functionally removed American chestnut, Castanea dentata (Marsh.) Borkh., from its ecological role as a dominant tree in eastern forests by the 1950s []. The fungi Ophiostoma ulmi (Buisman) Nannf. and O. novo-ulmi Brasier, commonly known as DED, have killed millions of American elm (Ulmus americana L.) trees since they became established in North America in 1930 []. Exotic bark beetles such as Scolytus multistriatus Marsh., as well as the native species, Hylurgopinus rufipes Eich. spread DED in North America []. BBD is caused by beech scale insect, Cryptococcus fagisuga Lindinger, which feeds on the living outer bark of American beech (Fagus grandifolia Ehrh.) and provides an opportunity for Ascomycete fungi of the genus Neonectria to establish []. This disease was first documented in Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada in 1890 and by 1935 it had expanded into the United States [,]. WPBR is caused by Cronartium ribicola J.C.Fisch., a heteroecious, macrocyclic rust of five needle pine species (Pinus spp.) []. WPBR was first found in North America in 1906, but surveys revealed that infected seedlings had been planted throughout the Northeast as early as 1889 []. Dogwood anthracnose (DA) is caused by the exotic fungus, Discula destructiva Redlin, on dogwood (Cornus spp.) trees and was first detected in North America in the late 1970s []. Laurel wilt (LW) is caused by Raffaelea lauricola T.C. Harr., Aghayeva, and Fraedrich and spread by Xyleborus glabratus Eichhoff, an exotic redbay ambrosia beetle introduced from southern Asia. LW was first detected in 2002 [].
2. Methods
2.1. Geospatial Databases
To estimate rates of spread, I built a geospatial database with the date of infestation and the location for each of the species analyzed. The analysis included data from both the United States and Canada. In the United States, many of the data are at the county level, which average 250,050 ha in size with a median size of 161,183 ha. Tobin and colleagues [] demonstrated the effectiveness of these types of spatially coarse data for measuring spread of invasive insects, even in comparison to estimates obtained from the more costly deployment of extensive trapping grids. Data of invasion that recorded entire counties as infested were summarized with the centroid of the county. Records of invasions reaching individual cities were treated as point locations.
In building the geospatial database of insect and diseases, inconsistencies arose between infestation records. In these cases, I prioritized reports published at the time of the infestation over more modern records, records from peer-review journals over other reports, and specific records over spatially general records. Tracking infection remains difficult because new infections may go unnoticed or unreported and survey methods vary by location and time. However, even with these caveats, the records assembled here represent the best available information on the spread of a diverse suite of invasive species that have substantially changed the composition and structure of North American forests.
2.2. Analytical Methods
The central measure of the rate of spread was distance from point of introduction or first reliable data to each subsequent record of infestation, divided by the number of years between to the two infestations []. Some maps depicted the range of an invasive species with isolines of the limits of infection in a specific year. In order to combine these measures of spread with other point data on infection, I measured the shortest distance in any direction from the start of infection to 10 evenly spaced points along each front of infection, i.e., each isoline for each invasive species. For example, the geospatial database for CB was based on a map showing the geographic limits of CB by decade. I measured the shortest distance from the point of initial infestation to each of the 10 equally spaced points along the isoline for each decade. I measured spread using Euclidean distance on a map in equidistant conic projection (central meridian −96°, first standard parallel 33°, second standard parallel 45°, and latitude of origin 39°). Geospatial analysis was conducted in a geographic information system [].
Geospatial records of invasion require analytical methods that are not adversely affected by spatial correlation or heteroscedasticity. The variation of the distance variable increases with time for all of the organisms in this study and it is likely that at least some of the observed data are spatially correlated. While a regression of distance as a function of time can be fitted to these data with the ordinary least squares method, it will provide inefficient estimates of model parameters if the heteroscedasticity and spatial correlation are ignored in the modeling. Instead, I used quantile regression. Because quantile regression tracks the quantile trend, there is no presumption of uniform variance around the quantile regression line. No distributional assumptions of the model error term are built into quantile regression and the method can generate reliable models for a wide variety of data [,]. Quantile regression can fit a model to portray the change in the 50th (median) or any other quantile of the distribution of distance as a function of time. While the 50th quantile provides a measure of the central trend of the data, the upper quantiles, i.e., the 90th or 95th, can be considered the unconstrained rate of spread [,].
The review of the literature and invasive species databases yielded 3008 records of infection or infestation (Table 1). The spread of GM is well documented and I was able to include 542 county records of infestation [,]. In contrast, there are few records of the spread of BWA and this analysis is based on 30 points taken from the isolines drawn by Greenbank []. The HWA data are at the county level and include 201 locations []. Data from the USDA Forest Service’s Changing Midwest Assessment [] and the Pest Tracker [] provided 368 county records of PSB infestation. Maps from the Canadian Food Inspection Agency added another 50 location records for the Canadian portion of PSB spread [].

Table 1.
Invasive species included in the analysis with the period of record and number of records.
The first 60 infestation records for SWW came from de Groot and colleagues [] while the six additional county infestation records for 2010 through 2012 came from the Pest Tracker. The 308 records of EAB infestation came from the Pest Tracker and the Cooperative Emerald Ash Project []. The Cooperative Emerald Ash Project provides data on Canadian infestations, but does not maintain an archive of historic infestations. Weston and colleagues provided a county level history of VLB infestation in 46 counties []. I used records from Pest Tracker and the Cooperative Pest Survey in Ohio [] to add another 64 infestation locations.
Gravatt’s map [] provided the only records of CB spread by year. Gravatt’s work shows CB infection through 1949, though the entire range of chestnut is now infected. Since no specific infection dates were available after 1949, spread after that year could not be included in the model. Estimates of DED spread were based on 153 records that tied new DED infections to particular counties in the eastern United States (east of the Great Plains) and to 37 point locations in Canada and the United States []. Since the western portion of DED spread may have initiated at a different point of introduction it is included as a separate analysis. There were 22 point locations to analysis DED spread in the western United States.
The database of BBD spread locations included 157 points, of which 60 were derived from Houston’s map of infection between 1929 and 1975 []. The Alien Forest Pest Explorer [] and the Ontario map [] provided the additional infection records. The analysis of eastern WPBR relied on 317 records while the western spread of WPBR was based on 124 points []. As with DED, eastern and western WPBR infections were analyzed separately (the western portion was west of the Great Plains).
To build the database of 380 records of DA infection, I relied on the 1989 through 2006 editions of the Forest insect conditions in the United States report published annually by the USDA Forest Service []. The 103 county records of LW infection come from maps provided by the USDA Forest Service that were based on information from state forestry organizations across the southeast [].
3. Results
The key rates of spread are the central trend or median rate (50th quantile) and unconstrained, or maximum spread rate. The maximum spread rate was identified as the greatest quantile estimable for each organism. In most cases this was the 95th quantile, but some organisms the 95th quantile was undefined so the 90th provided the best estimate of the unconstrained spread rate. Figure 1 presents the median spread rates for each insect and disease and Figure 2 shows the maximum spread rates. The estimate for the median rate of GM spread was 11.7 km·year−1 (90% confidence interval 11.2 to 12.2) while the estimate of the 95th quantile was 14.1 km·year−1 (90% confidence interval 13.9 to 14.2). For BWA, the estimates were 4.2 km·year−1 (90% confidence interval 1.8 to 5.3) for the median rate of spread and 5.7 km·year−1 (90% confidence interval 1.9 to 8.8) for the 90th quantile. The estimates of spread rates for HWA were 12.5 km·year−1 (90% confidence interval 9.0 to 15.0) for the median and 20.8 km·year−1 (90% confidence interval 18.0 to 23.0). The PSB spread rate estimates were 16.5 km·year−1 (90% confidence interval 14.0 to19.2) for the median and 59.0 km·year−1 (90% confidence interval 26.6 to 67.6) for the 95th quantile. Estimates for SWW were 30.3 km·year−1 (90% confidence interval 27.0 to 84.1) for the median and 57.4 km·year−1 (90% confidence interval 26.6 to 67.6) for the 95th quantile. EAB had the highest estimate of median rate of spread at 57.0 km·year−1 (90% confidence interval 53.3 to 59.7) and 95th quantile 69.8 km·year−1 (90% confidence interval 60.9 to 86.9). The estimate for VLB median spread was 20.1 km·year−1 (90% confidence interval 18.3 to 21.4) and the estimate for the 95th quantile was 46.7 km·year−1 (90% confidence interval 17.2 to 48.4).
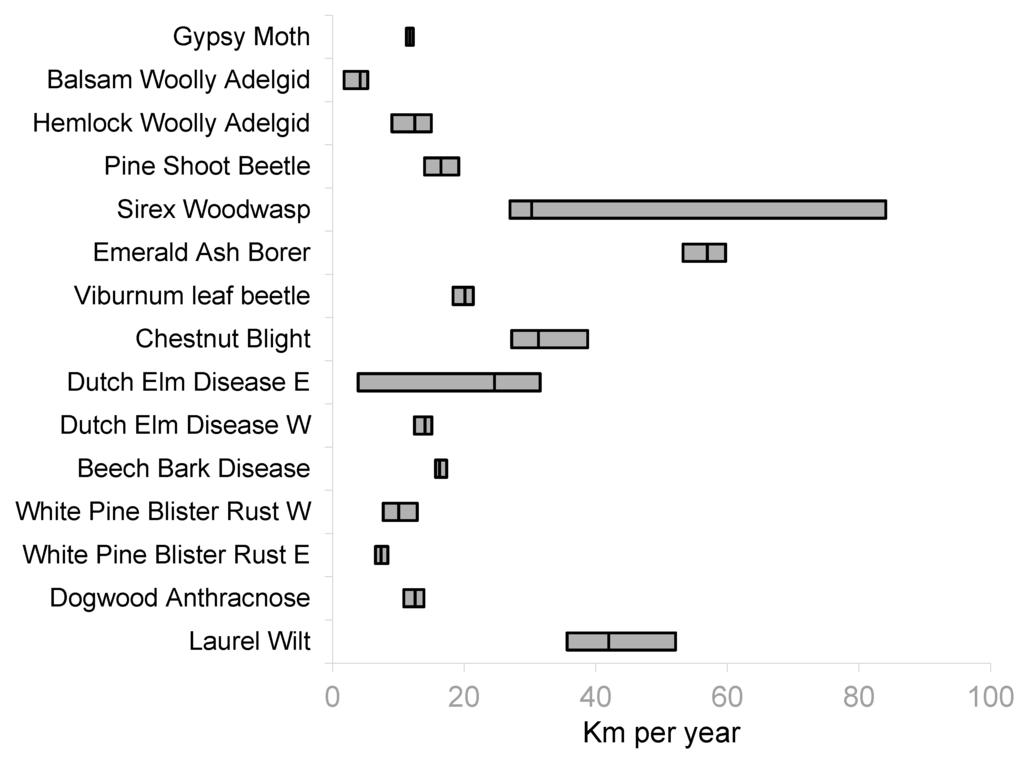
Figure 1.
Center lines of boxes are the 50th quantile estimates for rate of spread with 90% confidence intervals in gray. The eastern and western infections of Dutch Elm Disease (DED) and White Pine Blister Rust (WPBR) were analyzed separately.
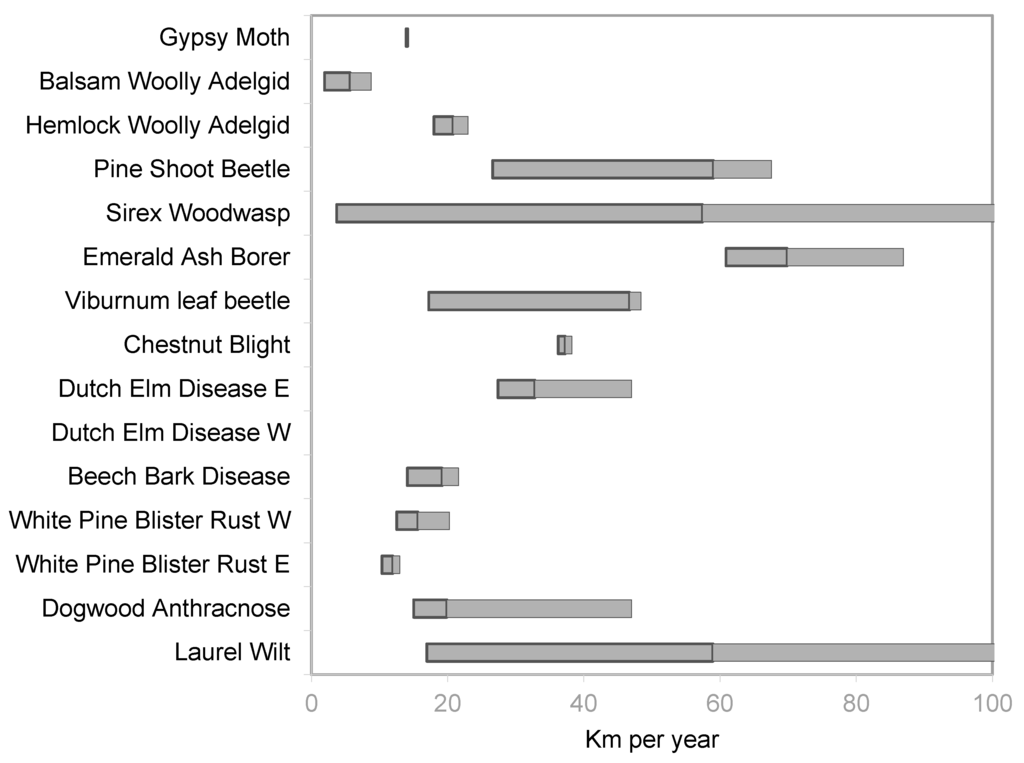
Figure 2.
Center lines of boxes are the estimates for unconstrained rate of spread with 90% confidence intervals in gray. The eastern and western infections of Dutch Elm Disease (DED) and White Pine Blister Rust (WPBR) were analyzed separately. No confidence interval is available for the western subset of DED.
The estimates for the median and unconstrained spread rates for forest diseases were in the same range as those for insects. The estimate of the median spread rate for CB was 31.3 km·year−1 (90% confidence interval 27.2 to 38.8) while the estimate of the 95th quantile was 37.3 km·year−1 (90% confidence interval 37.3 to 37.4). DED was separated into the eastern and western subsets as mentioned above. For DED in the East, the estimate of the median spread was 24.6 km·year−1 (90% confidence interval 3.9 to 31.5) while in the western subset the estimate of the median spread was 14.0 km·year−1 (90% confidence interval 12.5 to 15.1). The estimates for the 95th quantile spread rates for DED was 32.8 km·year−1 (90% confidence interval 27.4 to 47.0) for the East. For the western subset of DED the estimate of the 95th quantile was 25.8 km·year−1 but the confidence interval was undefined. The estimate of the median rate of spread for BBD was 16.3 km·year−1 (90% confidence interval 15.6 to 17.3) and the estimate of the 95th quantile was 19.2 km·year−1 (90% confidence interval 14.1 to 21.6). The results for WPBR are also divided between eastern and western subsets. In the East the estimate of the median WPBR spread was 7.4 km·year−1 (90% confidence interval 6.5 to 8.4) while in the western subset, the estimate of the median spread was 10.0 km·year−1 (90% confidence interval 7.7 to 12.9). Estimates for DA were 12.5 km·year−1 (90% confidence interval 10.8 to 13.9) for the median and 19.9 km·year−1 (90% confidence interval 15.0 to 47.0) for the 95th quantile. For LW, the estimate of median spread rate was 42.0 year−1 (90% confidence interval 35.6 to 52.1) and the estimate of the 95th quantile was 59.0 km·year−1 (90% confidence interval 17.0 to 104.9).
The estimated rates of spread in this analysis indicate individual insects are travelling much farther in a year than studies of individual dispersal for the species suggest. Dispersal of PSB was measured at 900 m [] compared to the spread rate from this study of 16.5 km·year−1. Individual EAB have been documented to travel 4 km [] compared to 57.0 km·year−1 from this study. HWA was documented to travel 2 km [] compared to 12.5 km·year−1 in this analysis. A study of Cryptococcus fagisuga, the insect that facilitates BBD, measured individual dispersal at 10 m [] compared to 16.3 km·year−1 in this analysis.
Of the 12 previous estimated rates of spread for the species in this analysis, three were slower, seven were faster, and four analyses provided ranges which overlapped with those in this analysis. Morin and colleagues [] estimate of BBD spread rate was 14.7 km·year−1 which was outside the 90% confidence interval around the estimate 16.3 km·year−1 from this analysis. The estimate for spread of EAB in this analysis is more than twice as fast as the previous estimate, which may be due to the fact that Prasad and colleagues [] were only able to include range expansion through 2006. Similarly, spread estimates from this analysis of BBD are nearly twice as fast as Gibbs and Wainhouse [] estimated.
In contrast, the estimate from this analysis of LW spread is slower than previous estimates that used three years of data []. The estimates in this study of spread of BWA are slower than Balch’s estimate of 8 km·year−1 [] . Estimates for spread of SWW from South Africa and Australia (48 km·year−1 and between 30 and 40 km·year−1 respectively) are faster but within the 90% confidence interval for spread of SWW from this analysis []. My estimate of 11.7 km·year−1 for GM is slower than Sharov and colleagues’ estimate of 15.8 km·year−1 based on data from the lower peninsula of Michigan []. Gibbs and Wainhouse [] estimated a faster rate of spread for WPBR (30 to 40 km·year−1) than the estimate from this analysis (7.4 km·year−1 for the east and 10.0 km·year−1 for the west). They also suggested a rate of 30 km·year−1 with spot infestations up to 250 km further for CB []. Gravatt estimated CB spread to be 39 km·year−1 [], which is just beyond our 90% confidence interval for the median rate of spread.
Three studies provided ranges that overlapped with the estimates in this analysis. The estimate for HWA from this analysis is in the middle of the range from Morin and colleagues (8.9 to 20.4 km·year−1) []. The estimate of 11.7 km·year−1 for GM from this study is in the middle of the range of previous estimates that range from 2.5 to 28.6 km·year−1 [,,]. For example, Liebhold and colleagues separated GM spread into temporal periods a 1900 to 1915 (9.45 km·year−1), 1916 to 1965 a (2.82 km·year−1), and 1966 to 1990 (20.78 km·year−1) []. Tobin and colleagues give a similar range of spread rates for different time periods in different regions []. Sharov and colleagues also split GM spread into temporal periods with different rates of spread (16.9 km·year−1 in 1984–1990 to 8.8 km·year−1 in 1991–1996) that bracket the estimate from this analysis []. In summary, previous estimates of spread do not appear to systematically over- or under-estimate spread rates in comparison to the rates presented in this analysis.
4. Discussion
The median rate of spread for the 13 insects and diseases was 16.3 km·year−1. The range of spread rates is considerable with the fastest (EAB) spreading at a rate more than ten times the slowest (BWA). Even with this extensive database, comparison between the insects and diseases is difficult. The most obvious confounding factor is that a number of the diseases are vectored by insects. For example, DED is spread by bark beetles and an exotic ambrosia beetle is a vector for LW. The similarity in rates of spread may also be due to the lack of Allee effects in species such as HWA []. However, most of those species that rely on passive dispersal (BWA, HWA, DA, WPBR) have spread more slowly than those species that can fly long distances or are vectored by flying insects. CB is an exception to this pattern which may be due to ease of dispersal and the high density and contiguous distribution of its host throughout eastern forests.
This analysis highlights the difficulty of estimating spread rates from studies of individual dispersal or flight distances. For example, a study of PSB dispersal suggests a dispersal distance of 900 m though the distance could be greater with strong winds []. Based on this analysis, PSB spread is much more rapid, 16.5 km·year−1, than the individual dispersal distance would suggest. Studies of individual EAB dispersal seem in conflict with the 57.0 km·year−1 spread rate estimated here. In one study most EAB larvae (~90%) were found on trees within 100 m of previous infested tree [], but Siegert and colleagues [] found most new infestations within 450 m of the previous infestation and one 683 meters away. Prasad and colleagues [] estimated EAB’s rate of spread to be about 20 km·year−1 or less than half the estimate in this analysis. Their estimate was based on range expansion between 1998 and 2006 and a model of potential flight patterns. Measurements of adult EAB dispersal found only 1% traveled father than 4 km []. These rare, but important instances of long-distance dispersal are particularly hard to predict or build into models of spread (e.g., []). A study of sudden oak death suggests that while most spread occurs via short-distance dispersal (<250 m), rare long-distance dispersal substantially accelerates epidemic spread []. Rare, but influential incidences of long-distance dispersal appear to limit the utility of individual dispersal measurements for the estimation of population spread.
The estimated spread rates in this study are generally in line with previous estimates of spread. However, where there were differences between estimates in this study and previous studies, the treatment of long distance dispersal may be an important factor. For example, Morin and colleagues [] analyzed BBD but excluded disjunct locations and their estimate of spread rate was 14.7 km·year−1, slower than the quantile regression estimate of 16.3 km·year−1. In this analysis, new infestations were included regardless of the mode of transmission and consequently the estimates include human facilitated movement. Recent work has highlighted the importance of human facilitated movement, such as spread of infested firewood, particularly in long-distance dispersal [,].
5. Conclusions
A changing climate and increasing fragmentation mean that the history of invasive insect and disease spread through North American forests is not a perfect predictor of future invasions. In fact, a perfect predictor of the spread of future invasions is beyond reach because of the complexity of ecological interactions and human driven environmental change. However, past spread rates can help managers understand and react to future invasive species before a new invasion can be studied and new models prepared. The range of previous spread rates can provide important context for future models and call into question predictions of range expansion that fall outside the range of past spread rates, once differences between actively and passively dispersed species are taken into account.
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Peltzer, D.A.; Allen, R.B.; Lovett, G.M.; Whitehead, D.; Wardle, D.A. Effects of biological invasions on forest carbon sequestration. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2010, 16, 732–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albani, M.; Moorcroft, P.R.; Ellison, A.M.; Orwig, D.A.; Foster, D.R. Predicting the impact of hemlock woolly adelgid on carbon dynamics of eastern united states forests. Can. J. For. Res. 2010, 40, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, B.; Wilcove, D.; Oppenheimer, M. Climate change increases risk of plant invasion in the Eastern United States. Biol. Invasions 2010, 12, 1855–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez, J.M.; D’Antonio, C.M.; Dukes, J.S.; Grosholz, E.D.; Olden, J.D.; Sorte, C.J.B.; Blumenthal, D.M.; Bradley, B.A.; Early, R.; Ibáñez, I.; et al. Will extreme climatic events facilitate biological invasions? Front. Ecol. Environ. 2012, 10, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasson, M.T.; Livingston, W.H. Relationships among beech bark disease, climate, radial growth response and mortality of American beech in northern Maine, USA. For. Pathol. 2012, 42, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.D. Concurrent management of an exotic species and initial restoration efforts in forests. Restor. Ecol. 2005, 13, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, T.P.; Aukema, J.E.; Holle, B.V.; Liebhold, A.; Sills, E. Economic impacts of invasive species in forests. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1162, 18–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aukema, J.E.; Leung, B.; Kovacs, K.; Chivers, C.; Britton, K.O.; Englin, J.; Frankel, S.J.; Haight, R.G.; Holmes, T.P.; Liebhold, A.M.; et al. Economic impacts of non-native forest insects in the continental united states. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchetto, K.M.; Shea, K.; Kelly, D.; Groenteman, R.; Sezen, Z.; Jongejans, E. Unrecognized impact of a biocontrol agent on the spread rate of an invasive thistle. Ecol. Appl. 2014, 24, 1178–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yemshanov, D.; Koch, F.H.; Ben-Haim, Y.; Smith, W.D. Robustness of risk maps and survey networks to knowledge gaps about a new invasive pest. Risk Anal. 2010, 30, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayres, M.P.; Lombardero, M.J. Assessing the consequences of global change for forest disturbance from herbivores and pathogens. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 262, 263–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, D.R. The gypsy moth life stage model: Landscape-wide estimates of gypsy moth establishment using a multi-generational phenology model. Ecol. Model. 2004, 176, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, A.M.; Finkral, A.J. A new look at spread rates of exotic diseases in north american forests. For. Sci. 2010, 56, 453–459. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, A.M.; Gregoire, T.G. A geographically variable model of hemlock woolly adelgid spread. Biol. Invasions 2007, 9, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebhold, A.M.; Halverson, J.; Elmes, G. Quantitative analysis of the invasion of gypsy moth in North America. J. Biogeogr. 1992, 19, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balch, R.E. Spread of Balsam Woolly Aphid (Adelges piceae) in relation to climate of Newfoundland. In Bi-Monthly Progress Report; Department of Agriculture, Science Service Forest Biology Division: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1954; Volume 10, p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Havill, N.P.; Montgomery, M.E. The role of arboreta in studying the evolution of host resistance to the hemlock woolly adelgid. Arnoldia 2008, 65, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Barak, A.V.; McGervy, D.; Tokaya, G. Dispersal and re-capture of marked, overwintering Tomicus piniperda (coleoptera: Scolytidae) from scotch pine bolts. Gt. Lakes Entomol. 2000, 33, 81–105. [Google Scholar]
- Carnegie, A.J.; Matsuki, M.; Haugen, D.A.; Hurley, B.P.; Ahumada, R.; Klasmer, P.; Sun, J.; Iede, E.T. Predicting the potential distribution of sirex noctilio (hymenoptera: Siricidae), a significant exotic pest of pinus plantations. Ann. For. Sci. 2006, 63, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, A.; Bauer, L.; Poland, T.; Haack, R.; Cognato, A.; Smith, J. Genetic analysis of emerald ash borer (Agrilus planipennis fairmaire) populations in Asia and North America. Biol. Invasions 2011, 13, 2869–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weston, P.A.; Hoebeke, E.R. Viburnum leaf beetle, Pyrrhalta viburni (paykull) (coleoptera: Chrysomelidae): Dispersal pattern of a palearctic landscape pest in New York and its distribution status in the northeastern U.S. and eastern Canada. Proc. Entomol. Soc. Wash. 2003, 105, 4105–4107. [Google Scholar]
- Gravatt, G.F. Chestnut blight in North America. Unasylva 1949, 3, 2–7. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs, J.N. Intercontinental epidemiology of Dutch elm disease. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1978, 16, 287–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houston, D.R. Major new tree disease epidemics: Beech bark disease. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1994, 32, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, J.N.; Wainhouse, D. Spread of forest pests and pathogens in the northern hemisphere. Forestry 1986, 59, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloy, O.C. White pine blister rust control in North America: A case history. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1997, 35, 87–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, D.R.; Kimmey, J.W.; Fowler, M.E. White Pine Blister Rust; Forest Pest Leaflet 36; USDA Forest Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1959; p. 8.
- Hibben, C.; Daughtrey, M. Dogwood anthracnose in Northeastern United States. Plant Dis. 1988, 72, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, T.; Fraedrich, S.; Aghayeva, D. Raffaelea lauricola, a new ambrosia beetle symbiont and pathogen on the lauraceae. Mycotaxon 2008, 104, 399–404. [Google Scholar]
- Tobin, P.C.; Liebhold, A.M.; Roberts, E.A. Comparison of methods for estimating the spread of a non-indigenous species. J. Biogeogr. 2007, 34, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESRI. Arcgis, version 9.3; Environmental Systems Research Institute (ESRI): Redlands, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sas Onlinedoc, version 9; SAS Institute Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2002.
- Gannoun, A.; Saracco, J.; Yuan, A.; Bonney, G. Non-parametric quantile regression with censored data. Scand. J. Stat. 2005, 32, 527–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cade, B.; Noon, B. A gentle introduction to quantile regression for ecologists. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2003, 1, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cade, B.S.; Terrell, J.W.; Schroeder, R.L. Estimating effects of limiting factors with regression quantiles. Ecology 1999, 80, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebhold, A.M. An Atlas of Historical Gypsy Moth Defoliation & Quarantined Areas in the US. Available online: http://www.fs.fed.us/ne/morgantown/4557/gmoth/atlas/#spread (accessed on 8 June 2013).
- Pest Tracker. Available online: http://pest.ceris.purdue.edu/ (accessed on 8 June 2013).
- Greenbank, D.O. Climate and the ecology of the balsam woolly aphid. Can. Entomol. 1970, 102, 546–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA Forest Service. Pine Shoot Beetle, 1992–2001. Available online: http://www.ncrs.fs.fed.us/4153/deltawest/plantanimal/pineshoot.asp (accessed on 8 June 2013).
- Plant Health Surveillance Unit. Plant Protection Survey Report. Available online: http://epe.lac-bac.gc.ca/100/206/301/cfia-acia/2011-09-21/www.inspection.gc.ca/english/plaveg/pestrava/surv/sit2008e.shtml (accessed on 8 June 2013).
- USDA Forest Service. Alien Forest Pest Explorer. Available online: http://www.fs.fed.us/ne/morgantown/4557/AFPE/index.html (accessed on 16 June 2009).
- Eastern Ontario Model Forest. Ecosystem Condition and Productivity. Available online: http://sof.eomf.on.ca/Ecosystem_Condition_and_Productivity/Biotic/Indicators/Disease/Area/i_forest_area_affected_by_disease_e.htm (accessed on 16 June 2009).
- U.S. Forest Service. Forest Insect and Disease Conditions in the United Utates 1999; U.S. Forest Service, Forest Health Protection: Washington, DC, USA, 2007; p. 176.
- Cooperative Emerald Ash Project. Initial County EAB Detections. Available online: http://www.aphis.usda.gov/plant_health/plant_pest_info/emerald_ash_b/downloads/multistateeab.pdf (accessed on 8 June 2013).
- Forest Health Protection. Distribution of Counties with Laurel Wilt Disease by Year of Initial Detection. Available online: http://www.fs.fed.us/r8/foresthealth/laurelwilt/dist_map.shtml (accessed on 8 June 2013).
- De Groot, P.; Nystrom, K.; Scarr, T. Discovery of sirex noctilio (hymenoptera: Siricidae) in Ontario, Canada. Gt. Lakes Entomol. 2006, 39, 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Weston, P.A.; Desurmont, G.; Hoebeke, E.R. Viburnum leaf beetle. Am. Entomol. 2007, 53, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plant Health Division. Viburnum Leaf Beetle. Available online: http://www.agri.ohio.gov/divs/plant/caps/vlb.aspx (accessed on 8 June 2013).
- Taylor, R.A.; Bauer, L.S.; Miller, D.L.; Haack, R.A. Emerald ash borer flight potential. In Proceedings of the Emerald Ash Borer Research and Technology Development Meeting, Romulus, MI, USA, 5–6 October 2004; Mastro, V., Reardon, R., Eds.; U.S. Forest Service, Forest Health Technology Enterprise Team: Morgantown, WV, USA; pp. 15–16.
- McClure, M.S. Role of winds, birds, deer, and humans in the dispersal of hemlock woolly adelgid (homoptera: Adelgidae). Environ. Entomol. 1990, 19, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainhouse, D. Dispersal of first instar larvae of the felted beech scale, Cryptococcus fagisuga. J. Appl. Ecol. 1980, 17, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, R.S.; Liebhold, A.M.; Tobin, P.C.; Gottschalk, K.W.; Luzader, E. Spread of beech bark disease in the eastern United States and its relationship to regional forest composition. Can. J. For. Res. 2007, 37, 726–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.; Iverson, L.; Peters, M.; Bossenbroek, J.; Matthews, S.; Davis Sydnor, T.; Schwartz, M. Modeling the invasive emerald ash borer risk of spread using a spatially explicit cellular model. Landsc. Ecol. 2010, 25, 353–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, F.H.; Smith, W.D. Spatio-temporal analysis of Xyleborus glabratus (coleoptera: Circulionidae: Scolytinae) invasion in eastern U.S. Forests. Environ. Entomol. 2009, 37, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharov, A.A.; Pijanowski, B.C.; Liebhold, A.M.; Gage, S.H. What affects the rate of gypsy moth (lepidoptera: Lymantriidae) spread: Winter temperature or forest susceptibility? Agric. For. Entomol. 1999, 1, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, R.; Liebhold, A.; Gottschalk, K. Anisotropic spread of hemlock woolly adelgid in the eastern United States. Biol. Invasions 2009, 11, 2341–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharov, A.A.; Liebhold, A.M.; Roberts, E.A. Methods for monitoring the spread of gypsy moth (lepidoptera: Lymantriidae) populations in the appalachian mountains. J. Econ. Entomol. 1997, 90, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, P.; Turcotte, R.; Snider, D. When one is not necessarily a lonely number: Initial colonization dynamics of Adelges tsugae on eastern hemlock, Tsuga canadensis. Biol. Invasions 2013, 15, 1925–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercader, R.J.; Siegert, N.W.; Liebhold, A.M.; McCullough, D.G. Dispersal of the emerald ash borer, Agrilus planipennis, in newly-colonized sites. Agric. For. Entomol. 2009, 11, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegert, N.W.; McCullough, D.G.; Williams, D.W.; Fraser, I.; Poland, T.M.; Pierce, S.J. Dispersal of Agrilus planipennis (coleoptera: Buprestidae) from discrete epicenters in two outlier sites. Environ. Entomol. 2010, 39, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzpatrick, M.C.; Preisser, E.L.; Porter, A.; Elkinton, J.; Ellison, A.M. Modeling range dynamics in heterogeneous landscapes: Invasion of the hemlock woolly adelgid in eastern North America. Ecol. Appl. 2011, 22, 472–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meentemeyer, R.K.; Cunniffe, N.J.; Cook, A.R.; Filipe, J.A.N.; Hunter, R.D.; Rizzo, D.M.; Gilligan, C.A. Epidemiological modeling of invasion in heterogeneous landscapes: Spread of sudden oak death in California (1990–2030). Ecosphere 2011, 2, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigsby, K.; Tobin, P.; Sills, E. Anthropogenic drivers of gypsy moth spread. Biol. Invasions 2011, 13, 2077–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, F.H.; Yemshanov, D.; Magarey, R.D.; Smith, W.D. Dispersal of invasive forest insects via recreational firewood: A quantitative analysis. J. Econ. Entomol. 2012, 105, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the author; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).