Inhibition of Zika Virus Replication by Silvestrol
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. RNA-Isolation
2.3. RT-qPCR
2.4. Cell Viability and Cytotoxicity Assays
2.5. Western Blot
2.6. Plaque Assay
2.7. Immunofluorescence Microscopy
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Silvestrol Shows a Cytostatic rather than a Cytotoxic Effect in A549 Cells
3.2. Silvestrol Impairs ZIKV Infection in A549 Cells
3.3. Inhibition of ZIKV Replication by Silvestrol
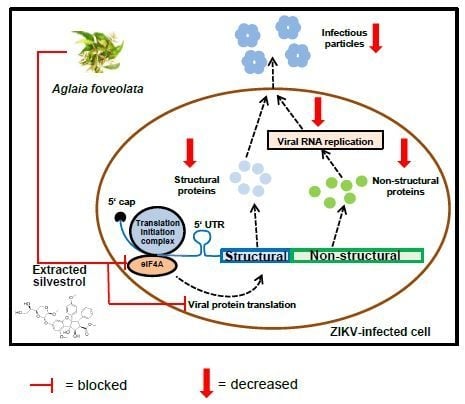
3.4. Silvestrol Inhibits ZIKV Translation by Inhibition of eIF4A
3.5. Silvestrol Inhibits ZIKV Replication in Infected Primary Human Hepatocytes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Göertz, G.P.; Abbo, S.R.; Fros, J.J.; Pijlman, G.P. Functional RNA during Zika virus infection. Virus Res. 2017. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinz, F.X.; Stiasny, K. The Antigenic Structure of Zika Virus and Its Relation to Other Flaviviruses: Implications for Infection and Immunoprophylaxis. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2017, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Chan, J.F.-W.; Tee, K.-M.; Choi, G.K.-Y.; Lau, S.K.-P.; Woo, P.C.-Y.; Tse, H.; Yuen, K.-Y. Comparative genomic analysis of pre-epidemic and epidemic Zika virus strains for virological factors potentially associated with the rapidly expanding epidemic. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2016, 5, e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuno, G.; Chang, G.-J.J. Full-length sequencing and genomic characterization of Bagaza, Kedougou, and Zika viruses. Arch. Virol. 2007, 152, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baronti, C.; Piorkowski, G.; Charrel, R.N.; Boubis, L.; Leparc-Goffart, I.; de Lamballerie, X. Complete coding sequence of zika virus from a French polynesia outbreak in 2013. Genome Announc. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coutard, B.; Barral, K.; Lichière, J.; Selisko, B.; Martin, B.; Aouadi, W.; Lombardia, M.O.; Debart, F.; Vasseur, J.-J.; Guillemot, J.C.; et al. Zika Virus Methyltransferase: Structure and Functions for Drug Design Perspectives. J. Virol. 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao-Lormeau, V.M.; Blake, A.; Mons, S.; Lastere, S.; Roche, C.; Vanhomwegen, J.; Dub, T.; Baudouin, L.; Teissier, A.; Larre, P.; et al. Guillain-Barré Syndrome outbreak associated with Zika virus infection in French Polynesia: A case-control study. Lancet 2016, 387, 1531–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victora, C.G.; Schuler-Faccini, L.; Matijasevich, A.; Ribeiro, E.; Pessoa, A.; Barros, F.C. Microcephaly in Brazil: How to interpret reported numbers? Lancet 2016, 387, 621–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Hwang, B.Y.; Su, B.-N.; Chai, H.; Mi, Q.; Kinghorn, A.D.; Wild, R.; Swanson, S.M. Silvestrol, a potential anticancer rocaglate derivative from Aglaia foveolata, induces apoptosis in LNCaP cells through the mitochondrial/apoptosome pathway without activation of executioner caspase-3 or -7. Anticancer Res. 2007, 27, 2175–2183. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chu, J.; Galicia-Vázquez, G.; Cencic, R.; Mills, J.R.; Katigbak, A.; Porco, J.A.; Pelletier, J. CRISPR-Mediated Drug-Target Validation Reveals Selective Pharmacological Inhibition of the RNA Helicase, eIF4A. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 2340–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordeleau, M.-E.; Robert, F.; Gerard, B.; Lindqvist, L.; Chen, S.M.H.; Wendel, H.-G.; Brem, B.; Greger, H.; Lowe, S.W.; Porco, J.A.; et al. Therapeutic suppression of translation initiation modulates chemosensitivity in a mouse lymphoma model. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 2651–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelletier, J.; Graff, J.; Ruggero, D.; Sonenberg, N. Targeting the eIF4F translation initiation complex: A critical nexus for cancer development. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadlish, H.; Galicia-Vazquez, G.; Paris, C.G.; Aust, T.; Bhullar, B.; Chang, L.; Helliwell, S.B.; Hoepfner, D.; Knapp, B.; Riedl, R.; et al. Evidence for a functionally relevant rocaglamide binding site on the eIF4A-RNA complex. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 1519–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kogure, T.; Kinghorn, A.D.; Yan, I.; Bolon, B.; Lucas, D.M.; Grever, M.R.; Patel, T. Therapeutic potential of the translation inhibitor silvestrol in hepatocellular cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfe, A.L.; Singh, K.; Zhong, Y.; Drewe, P.; Rajasekhar, V.K.; Sanghvi, V.R.; Mavrakis, K.J.; Jiang, M.; Roderick, J.E.; van der Meulen, J.; et al. RNA G-quadruplexes cause eIF4A-dependent oncogene translation in cancer. Nature 2014, 513, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cencic, R.; Carrier, M.; Galicia-Vázquez, G.; Bordeleau, M.-E.; Sukarieh, R.; Bourdeau, A.; Brem, B.; Teodoro, J.G.; Greger, H.; Tremblay, M.L.; et al. Antitumor activity and mechanism of action of the cyclopentabbenzofuran, silvestrol. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinnebusch, A.G.; Ivanov, I.P.; Sonenberg, N. Translational control by 5′-untranslated regions of eukaryotic mRNAs. Science 2016, 352, 1413–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, D.M.; Edwards, R.B.; Lozanski, G.; West, D.A.; Shin, J.D.; Vargo, M.A.; Davis, M.E.; Rozewski, D.M.; Johnson, A.J.; Su, B.-N.; et al. The novel plant-derived agent silvestrol has B-cell selective activity in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia in vitro and in vivo. Blood 2009, 113, 4656–4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schatz, J.H.; Oricchio, E.; Wolfe, A.L.; Jiang, M.; Linkov, I.; Maragulia, J.; Shi, W.; Zhang, Z.; Rajasekhar, V.K.; Pagano, N.C.; et al. Targeting cap-dependent translation blocks converging survival signals by AKT and PIM kinases in lymphoma. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 1799–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biedenkopf, N.; Lange-Grünweller, K.; Schulte, F.W.; Weißer, A.; Müller, C.; Becker, D.; Becker, S.; Hartmann, R.K.; Grünweller, A. The natural compound silvestrol is a potent inhibitor of Ebola virus replication. Antivir. Res. 2017, 137, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, C.; Schulte, F.W.; Lange-Grünweller, K.; Obermann, W.; Madhugiri, R.; Pleschka, S.; Ziebuhr, J.; Hartmann, R.K.; Grünweller, A. Broad-spectrum antiviral activity of the eIF4A inhibitor silvestrol against corona- and picornaviruses. Antivir. Res. 2017, 150, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio, C.A.; Weisburd, B.; Holderfield, M.; Arias, C.; Fang, E.; DeRisi, J.L.; Fanidi, A. Transcriptome-wide characterization of the eIF4A signature highlights plasticity in translation regulation. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himmelsbach, K.; Sauter, D.; Baumert, T.F.; Ludwig, L.; Blum, H.E.; Hildt, E. New aspects of an anti-tumour drug: Sorafenib efficiently inhibits HCV replication. Gut 2009, 58, 1644–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, T.S.; Pahernik, S.; Scheruebl, I.; Jauch, K.-W.; Thasler, W.E. Cellular damage to human hepatocytes through repeated application of 5-aminolevulinic acid. J. Hepatol. 2003, 38, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoudi, S.; Ploen, D.; Kunz, K.; Hildt, E. The adjuvant component α-tocopherol triggers via modulation of Nrf2 the expression and turnover of hypocretin in vitro and its implication to the development of narcolepsy. Vaccine 2014, 32, 2980–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgner, F.; Ren, H.; Medvedev, R.; Ploen, D.; Himmelsbach, K.; Boller, K.; Hildt, E. The intra-cellular cholesterol transport inhibitor U18666A inhibits the exosome-dependent release of mature hepatitis C virus. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 11181–11196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ploen, D.; Hafirassou, M.L.; Himmelsbach, K.; Sauter, D.; Biniossek, M.L.; Weiss, T.S.; Baumert, T.F.; Schuster, C.; Hildt, E. TIP47 plays a crucial role in the life cycle of hepatitis C virus. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bürckstümmer, T.; Kriegs, M.; Lupberger, J.; Pauli, E.K.; Schmittel, S.; Hildt, E. Raf-1 kinase associates with Hepatitis C virus NS5A and regulates viral replication. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himmelsbach, K.; Hildt, E. Identification of various cell culture models for the study of Zika virus. World J. Virol. 2018, 7, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, B.-N.; Chai, H.; Mi, Q.; Riswan, S.; Kardono, L.B.S.; Afriastini, J.J.; Santarsiero, B.D.; Mesecar, A.D.; Farnsworth, N.R.; Cordell, G.A.; et al. Activity-guided isolation of cytotoxic constituents from the bark of Aglaia crassinervia collected in Indonesia. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 960–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Lavrik, I.N.; Mahlknecht, U.; Giaisi, M.; Proksch, P.; Krammer, P.H.; Li-Weber, M. The traditional Chinese herbal compound rocaglamide preferentially induces apoptosis in leukemia cells by modulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase activities. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 121, 1839–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthukrishnan, S.; Both, G.W.; Furuichi, Y.; Shatkin, A.J. 5′-Terminal 7-methylguanosine in eukaryotic mRNA is required for translation. Nature 1975, 255, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dick, G.W.A.; Kitchen, S.F.; Haddow, A.J. Zika Virus (I). Isolations and serological specificity. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1952, 46, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laughhunn, A.; Santa Maria, F.; Broult, J.; Lanteri, M.C.; Stassinopoulos, A.; Musso, D.; Aubry, M. Amustaline (S-303) treatment inactivates high levels of Zika virus in red blood cell components. Transfusion 2017, 57, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, J.; Pelletier, J. Targeting the eIF4A RNA helicase as an anti-neoplastic approach. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1849, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Hao, Q.; Peng, N.; Yue, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhu, Y. Major vault protein: A virus-induced host factor against viral replication through the induction of type-I interferon. Hepatology 2012, 56, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elgner, F.; Sabino, C.; Basic, M.; Ploen, D.; Grünweller, A.; Hildt, E. Inhibition of Zika Virus Replication by Silvestrol. Viruses 2018, 10, 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10040149
Elgner F, Sabino C, Basic M, Ploen D, Grünweller A, Hildt E. Inhibition of Zika Virus Replication by Silvestrol. Viruses. 2018; 10(4):149. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10040149
Chicago/Turabian StyleElgner, Fabian, Catarina Sabino, Michael Basic, Daniela Ploen, Arnold Grünweller, and Eberhard Hildt. 2018. "Inhibition of Zika Virus Replication by Silvestrol" Viruses 10, no. 4: 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10040149
APA StyleElgner, F., Sabino, C., Basic, M., Ploen, D., Grünweller, A., & Hildt, E. (2018). Inhibition of Zika Virus Replication by Silvestrol. Viruses, 10(4), 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10040149