Biology of the BKPyV: An Update
Abstract
:1. Introduction
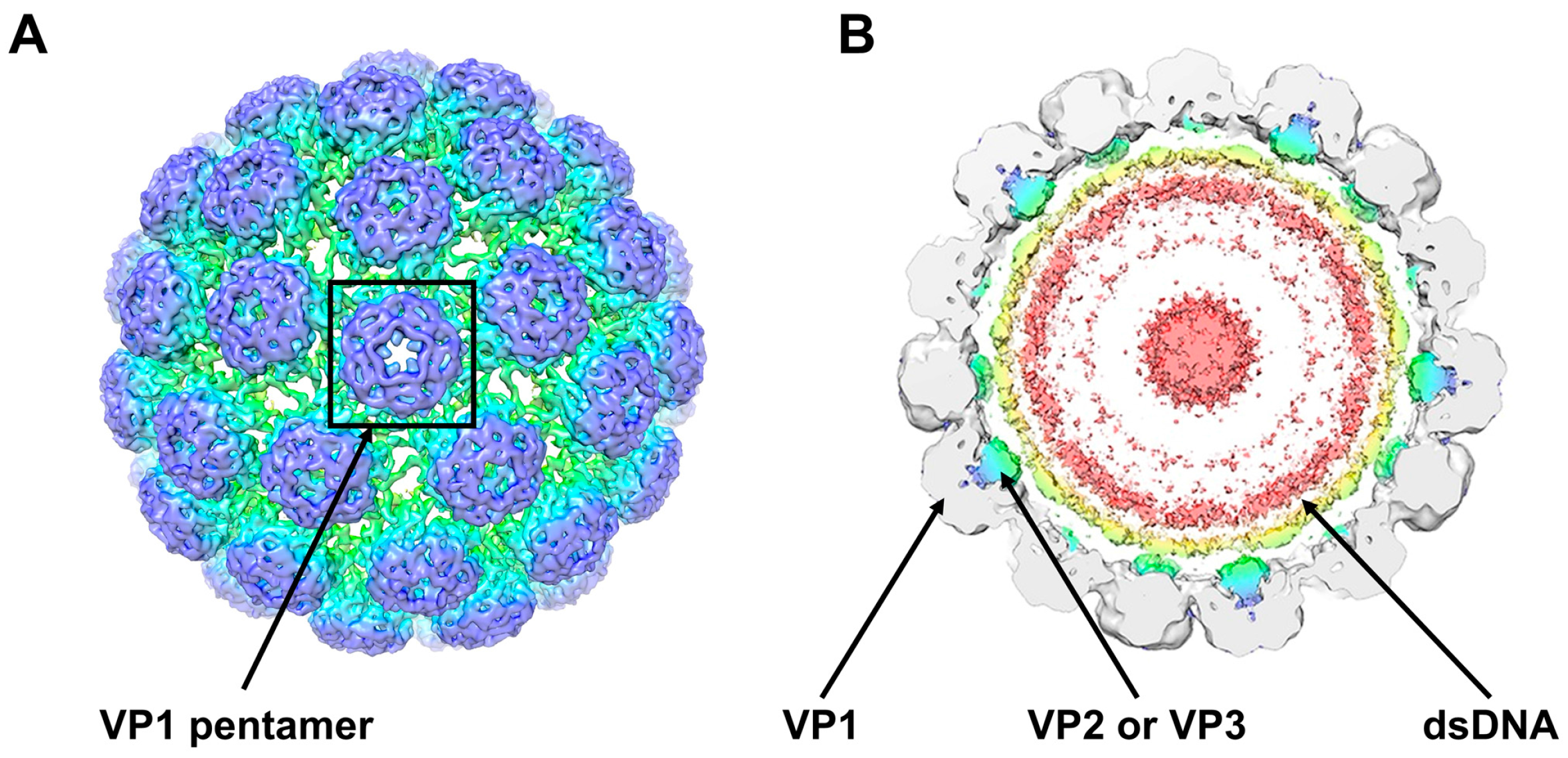
2. The BKPyV Particle
3. The BKPyV Genome
4. The BKPyV Proteins
4.1. TAg, tAg and truncTAg
4.2. VP1, VP2 and VP3
4.3. Agno
4.4. Putative VP4
5. BKPyV-Encoded MicroRNAs
6. In Vitro Model Systems for BKPyV Research
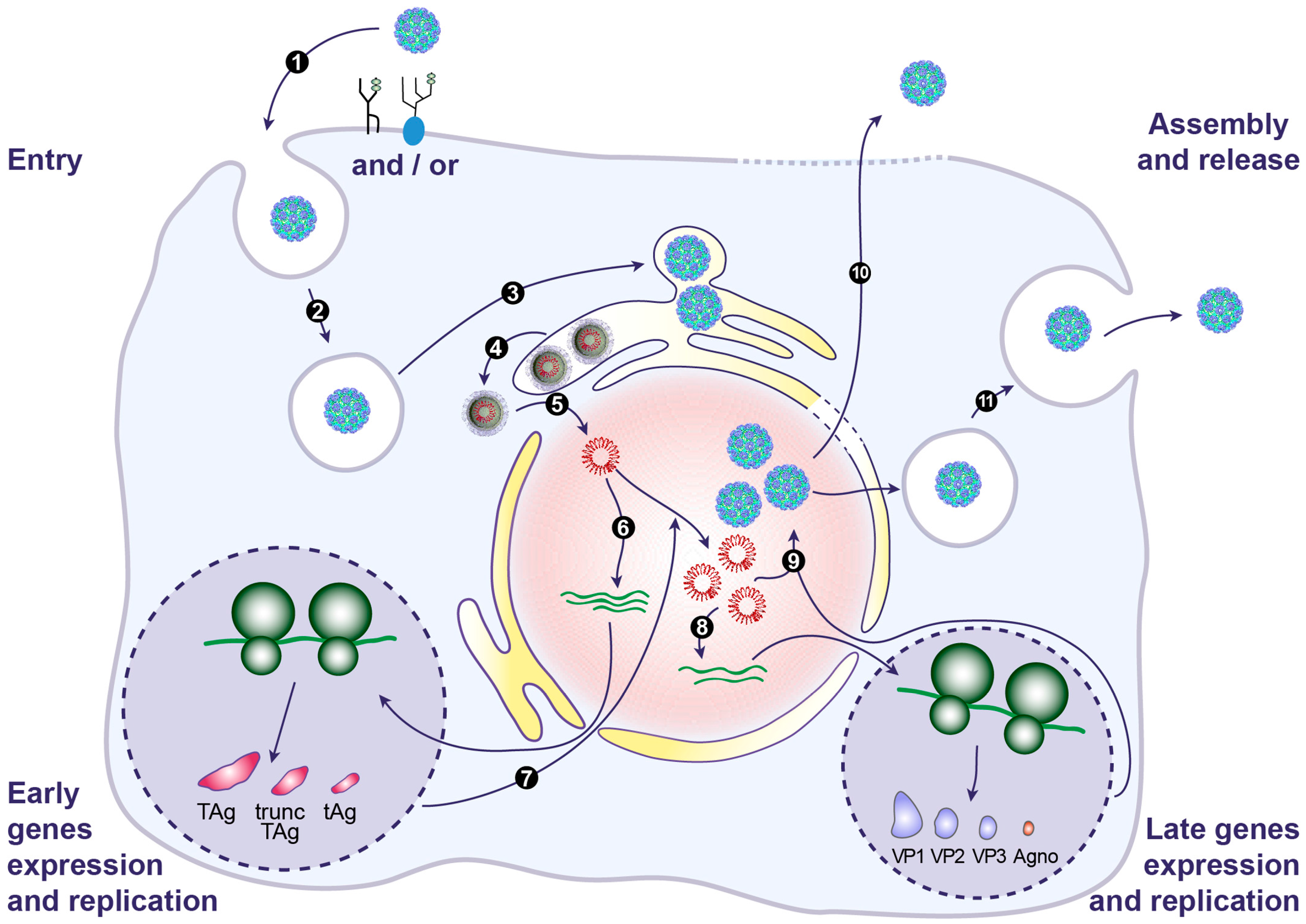
7. BKPyV Entry
7.1. Attachment
7.2. Internalization
7.3. Trafficking through the Endoplasmic Reticulum
7.4. Release from the ER and Nuclear Entry
8. BKPyV Gene Expression and Genome Replication
9. BKPyV Assembly and Release
10. Concluding Remarks and Future Directions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gardner, S.D.; Field, A.M.; Coleman, D.V.; Hulme, B. New human papovavirus (B.K.) isolated from urine after renal transplantation. Lancet 1971, 1, 1253–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moens, U.; Calvignac-Spencer, S.; Lauber, C.; Ramqvist, T.; Feltkamp, M.C.W.; Daugherty, M.D.; Verschoor, E.J.; Ehlers, B.; Ictv Report Consortium. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Polyomaviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 1159–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cubitt, C.L. Molecular genetics of the BK virus. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2006, 577, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Gibson, P.E.; Knowles, W.A.; Clewley, J.P. BK virus antigenic variants: Sequence analysis within the capsid VP1 epitope. J. Med. Virol. 1993, 39, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yogo, Y.; Sugimoto, C.; Zhong, S.; Homma, Y. Evolution of the BK polyomavirus: Epidemiological, anthropological and clinical implications. Rev. Med. Virol. 2009, 19, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastrana, D.V.; Ray, U.; Magaldi, T.G.; Schowalter, R.M.; Cuburu, N.; Buck, C.B. BK polyomavirus genotypes represent distinct serotypes with distinct entry tropism. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 10105–10113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kean, J.M.; Rao, S.; Wang, M.; Garcea, R.L. Seroepidemiology of human polyomaviruses. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, H.H.; Steiger, J. Polyomavirus BK. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2003, 3, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambalathingal, G.R.; Francis, R.S.; Smyth, M.J.; Smith, C.; Khanna, R. BK Polyomavirus: Clinical Aspects, Immune Regulation and Emerging Therapies. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 30, 503–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barth, H.; Solis, M.; Lepiller, Q.; Sueur, C.; Soulier, E.; Caillard, S.; Stoll-Keller, F.; Fafi-Kremer, S. 45 years after the discovery of human polyomaviruses BK and JC: Time to speed up the understanding of associated diseases and treatment approaches. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 43, 178–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurdiss, D.L.; Morgan, E.L.; Thompson, R.F.; Prescott, E.L.; Panou, M.M.; Macdonald, A.; Ranson, N.A. New Structural Insights into the Genome and Minor Capsid Proteins of BK Polyomavirus using Cryo-Electron Microscopy. Structure 2016, 24, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seehafer, J.; Salmi, A.; Scraba, D.G.; Colter, J.S. A comparative study of BK and polyoma viruses. Virology 1975, 66, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, P.J.; Di Mayorca, G. Virion polypeptide composition of the human papovavirus BK: Comparison with simian virus 40 and polyoma virus. J. Virol. 1975, 15, 828–835. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.Y.; Chen, H.Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, P.L.; Chang, C.F.; Chen, L.S.; Shen, C.H.; Ou, W.C.; Tsai, M.D.; Hsu, P.H.; et al. Global analysis of modifications of the human BK virus structural proteins by LC-MS/MS. Virology 2010, 402, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meneguzzi, G.; Pignatti, P.F.; Barbanti-Brodano, G.; Milanesi, G. Minichromosome from BK virus as a template for transcription in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1978, 75, 1126–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayment, I.; Baker, T.S.; Caspar, D.L.; Murakami, W.T. Polyoma virus capsid structure at 22.5 A resolution. Nature 1982, 295, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liddington, R.C.; Yan, Y.; Moulai, J.; Sahli, R.; Benjamin, T.L.; Harrison, S.C. Structure of simian virus 40 at 3.8-A resolution. Nature 1991, 354, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, J.; Miyazaki, N.; Xing, L.; Wu, B.; Hammar, L.; Li, T.C.; Takeda, N.; Miyamura, T.; Cheng, R.H. Structure and assembly of a T = 1 virus-like particle in BK polyomavirus. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 5337–5345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.S.; Stehle, T.; Harrison, S.C. Interaction of polyomavirus internal protein VP2 with the major capsid protein VP1 and implications for participation of VP2 in viral entry. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 3233–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.C.; Takeda, N.; Kato, K.; Nilsson, J.; Xing, L.; Haag, L.; Cheng, R.H.; Miyamura, T. Characterization of self-assembled virus-like particles of human polyomavirus BK generated by recombinant baculoviruses. Virology 2003, 311, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinstein, R.; Pare, N.; Harley, E.H. Structure and function of the transcriptional control region of nonpassaged BK virus. J. Virol. 1987, 61, 1747–1750. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yogo, Y.; Zhong, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, M.; Chao, Y.; Sugimoto, C.; Ikegaya, H.; Shibuya, A.; Kitamura, T. Conserved archetypal configuration of the transcriptional control region during the course of BK polyomavirus evolution. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 1849–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bethge, T.; Hachemi, H.A.; Manzetti, J.; Gosert, R.; Schaffner, W.; Hirsch, H.H. Sp1 sites in the noncoding control region of BK polyomavirus are key regulators of bidirectional viral early and late gene expression. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 3396–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bethge, T.; Ajuh, E.; Hirsch, H.H. Imperfect Symmetry of Sp1 and Core Promoter Sequences Regulates Early and Late Virus Gene Expression of the Bidirectional BK Polyomavirus Noncoding Control Region. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 10083–10101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moens, U.; Johansen, T.; Johnsen, J.I.; Seternes, O.M.; Traavik, T. Noncoding control region of naturally occurring BK virus variants: Sequence comparison and functional analysis. Virus Genes 1995, 10, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnsen, J.I.; Seternes, O.M.; Johansen, T.; Moens, U.; Mantyjarvi, R.; Traavik, T. Subpopulations of non-coding control region variants within a cell culture-passaged stock of BK virus: Sequence comparisons and biological characteristics. J. Gen. Virol. 1995, 76, 1571–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorrill, T.S.; Khalili, K. Cooperative interaction of p65 and C/EBPβ modulates transcription of BKV early promoter. Virology 2005, 335, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moens, U.; Sundsfjord, A.; Flaegstad, T.; Traavik, T. BK virus early RNA transcripts in stably transformed cells: enhanced levels induced by dibutyryl cyclic AMP, forskolin and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate treatment. J. Gen. Virol. 1990, 71, 1461–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moens, U.; Subramaniam, N.; Johansen, B.; Johansen, T.; Traavik, T. A steroid hormone response unit in the late leader of the noncoding control region of the human polyomavirus BK confers enhanced host cell permissivity. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 2398–2408. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moens, U.; Van Ghelue, M. Polymorphism in the genome of non-passaged human polyomavirus BK: Implications for cell tropism and the pathological role of the virus. Virology 2005, 331, 209–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowitz, R.B.; Tolbert, S.; Dynan, W.S. Promoter evolution in BK virus: Functional elements are created at sequence junctions. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 2411–2415. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gosert, R.; Rinaldo, C.H.; Funk, G.A.; Egli, A.; Ramos, E.; Drachenberg, C.B.; Hirsch, H.H. Polyomavirus BK with rearranged noncoding control region emerge in vivo in renal transplant patients and increase viral replication and cytopathology. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Broekema, N.M.; Abend, J.R.; Bennett, S.M.; Butel, J.S.; Vanchiere, J.A.; Imperiale, M.J. A system for the analysis of BKV non-coding control regions: application to clinical isolates from an HIV/AIDS patient. Virology 2010, 407, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broekema, N.M.; Imperiale, M.J. Efficient propagation of archetype BK and JC polyomaviruses. Virology 2012, 422, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abend, J.R.; Joseph, A.E.; Das, D.; Campbell-Cecen, D.B.; Imperiale, M.J. A truncated T antigen expressed from an alternatively spliced BK virus early mRNA. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, W.L.; Georgopoulos, C. The T/t common exon of simian virus 40, JC and BK polyomavirus T antigens can functionally replace the J-domain of the Escherichia coli DnaJ molecular chaperone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 3679–3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, P.; Saenz Robles, M.T.; Pipas, J.M. Large T antigens of polyomaviruses: Amazing molecular machines. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 66, 213–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeCaprio, J.A.; Garcea, R.L. A cornucopia of human polyomaviruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, K.F.; Christensen, J.B.; Imperiale, M.J. BK virus large T antigen: Interactions with the retinoblastoma family of tumour suppressor proteins and effects on cellular growth control. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 2378–2386. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Harris, K.F.; Christensen, J.B.; Radany, E.H.; Imperiale, M.J. Novel mechanisms of E2F induction by BK virus large-T antigen: Requirement of both the pRb-binding and the J domains. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 1746–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakshatri, H.; Pater, M.M.; Pater, A. Functional role of BK virus tumour antigens in transformation. J. Virol. 1988, 62, 4613–4621. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Major, E.O.; Di Mayorca, G. Malignant transformation of BHK21 clone 13 cells by BK virus—A human papovavirus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1973, 70, 3210–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portolani, M.; Barbanti-Brodano, G.; Placa, M.L. Malignant transformation of hamster kidney cells by BK virus. J. Virol. 1975, 15, 420–422. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takemoto, K.K.; Martin, M.A. Transformation of hamster kidney cells by BK papovavirus DNA. J. Virol. 1975, 17, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tognon, M.; Corallini, A.; Martini, F.; Negrini, M.; Barbanti-Brodano, G. Oncogenic transformation by BK virus and association with human tumors. Oncogene 2003, 22, 5192–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tognon, M.; Provenzano, M. New insights on the association between the prostate cancer and the small DNA tumour virus, BK polyomavirus. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kenan, D.J.; Mieczkowski, P.A.; Burger-Calderon, R.; Singh, H.K.; Nickeleit, V. The oncogenic potential of BK-polyomavirus is linked to viral integration into the human genome. J. Pathol. 2015, 237, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouvard, V.; Baan, R.A.; Grosse, Y.; Lauby-Secretan, B.; El Ghissassi, F.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Guha, N.; Straif, K. Carcinogenicity of malaria and of some polyomaviruses. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 339–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, E.A.; de Raad, M.; Mastrobattista, E. Production and biomedical applications of virus-like particles derived from polyomaviruses. J. Control. Release 2013, 172, 305–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugan, A.S.; Gasparovic, M.L.; Tsomaia, N.; Mierke, D.F.; O’Hara, B.A.; Manley, K.; Atwood, W.J. Identification of amino acid residues in BK virus VP1 that are critical for viability and growth. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 11798–11808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neu, U.; Allen, S.A.; Blaum, B.S.; Liu, Y.; Frank, M.; Palma, A.S.; Stroh, L.J.; Feizi, T.; Peters, T.; Atwood, W.J.; et al. A structure-guided mutation in the major capsid protein retargets BK polyomavirus. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.L.; Hsu, P.H.; Fang, C.Y.; Chang, C.F.; Ou, W.C.; Wang, M.; Chang, D. Phosphorylation of Ser-80 of VP1 and Ser-254 of VP2 is essential for human BK virus propagation in tissue culture. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 2637–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morel, V.; Martin, E.; Francois, C.; Helle, F.; Faucher, J.; Mourez, T.; Choukroun, G.; Duverlie, G.; Castelain, S.; Brochot, E. A Simple and Reliable Strategy for BK Virus Subtyping and Subgrouping. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 1177–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriksen, S.; Hansen, T.; Bruun, J.A.; Rinaldo, C.H. The Presumed Polyomavirus Viroporin VP4 of Simian Virus 40 or Human BK Polyomavirus Is Not Required for Viral Progeny Release. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 10398–10413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaldo, C.H.; Traavik, T.; Hey, A. The agnogene of the human polyomavirus BK is expressed. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 6233–6236. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leuenberger, D.; Andresen, P.A.; Gosert, R.; Binggeli, S.; Strom, E.H.; Bodaghi, S.; Rinaldo, C.H.; Hirsch, H.H. Human polyomavirus type 1 (BK virus) agnoprotein is abundantly expressed but immunologically ignored. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2007, 14, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johannessen, M.; Myhre, M.R.; Dragset, M.; Tummler, C.; Moens, U. Phosphorylation of human polyomavirus BK agnoprotein at Ser-11 is mediated by PKC and has an important regulative function. Virology 2008, 379, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unterstab, G.; Gosert, R.; Leuenberger, D.; Lorentz, P.; Rinaldo, C.H.; Hirsch, H.H. The polyomavirus BK agnoprotein co-localizes with lipid droplets. Virology 2010, 399, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saribas, A.S.; Arachea, B.T.; White, M.K.; Viola, R.E.; Safak, M. Human polyomavirus JC small regulatory agnoprotein forms highly stable dimers and oligomers: Implications for their roles in agnoprotein function. Virology 2011, 420, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saribas, A.S.; Coric, P.; Hamazaspyan, A.; Davis, W.; Axman, R.; White, M.K.; Abou-Gharbia, M.; Childers, W.; Condra, J.H.; Bouaziz, S.; et al. Emerging From the Unknown: Structural and Functional Features of Agnoprotein of Polyomaviruses. J. Cell. Physiol. 2016, 231, 2115–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myhre, M.R.; Olsen, G.H.; Gosert, R.; Hirsch, H.H.; Rinaldo, C.H. Clinical polyomavirus BK variants with agnogene deletion are non-functional but rescued by trans-complementation. Virology 2010, 398, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Sunden, Y.; Orba, Y.; Kose, S.; Imamoto, N.; Takahashi, H.; Tanaka, S.; Hall, W.W.; Nagashima, K.; et al. Dissociation of heterochromatin protein 1 from lamin B receptor induced by human polyomavirus agnoprotein: Role in nuclear egress of viral particles. EMBO Rep. 2005, 6, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johannessen, M.; Walquist, M.; Gerits, N.; Dragset, M.; Spang, A.; Moens, U. BKV agnoprotein interacts with α-soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion attachment protein and negatively influences transport of VSVG-EGFP. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gerits, N.; Johannessen, M.; Tummler, C.; Walquist, M.; Kostenko, S.; Snapkov, I.; van Loon, B.; Ferrari, E.; Hubscher, U.; Moens, U. Agnoprotein of polyomavirus BK interacts with proliferating cell nuclear antigen and inhibits DNA replication. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Darbinyan, A.; Siddiqui, K.M.; Slonina, D.; Darbinian, N.; Amini, S.; White, M.K.; Khalili, K. Role of JC virus agnoprotein in DNA repair. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 8593–8600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, R.; Sadowicz, D.; Hebert, D.N. A very late viral protein triggers the lytic release of SV40. PLoS Pathog. 2007, 3, e98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, G.J.; Fink, L.H.; O’Hara, B.; Atwood, W.J.; Sullivan, C.S. Evolutionarily conserved function of a viral microRNA. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 9823–9828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, C.S.; Grundhoff, A.T.; Tevethia, S.; Pipas, J.M.; Ganem, D. SV40-encoded microRNAs regulate viral gene expression and reduce susceptibility to cytotoxic T cells. Nature 2005, 435, 682–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broekema, N.M.; Imperiale, M.J. miRNA regulation of BK polyomavirus replication during early infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8200–8205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauman, Y.; Nachmani, D.; Vitenshtein, A.; Tsukerman, P.; Drayman, N.; Stern-Ginossar, N.; Lankry, D.; Gruda, R.; Mandelboim, O. An identical miRNA of the human JC and BK polyoma viruses targets the stress-induced ligand ULBP3 to escape immune elimination. Cell Host Microbe 2011, 9, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, S.M.; Jiang, M.; Imperiale, M.J. Role of cell-type-specific endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation in polyomavirus trafficking. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 8843–8852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, W.F.; Telenti, A.; Proper, J.; Aksamit, A.J.; Smith, T.F. Rapid detection of polyomavirus BK by a shell vial cell culture assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1990, 28, 1613–1615. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Low, J.; Humes, H.D.; Szczypka, M.; Imperiale, M. BKV and SV40 infection of human kidney tubular epithelial cells in vitro. Virology 2004, 323, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaldo, C.H.; Hansen, H.; Traavik, T. Human endothelial cells allow passage of an archetypal BK virus (BKV) strain—A tool for cultivation and functional studies of natural BKV strains. Arch. Virol. 2005, 150, 1449–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffers, L.K.; Madden, V.; Webster-Cyriaque, J. BK virus has tropism for human salivary gland cells in vitro: Implications for transmission. Virology 2009, 394, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seamone, M.E.; Wang, W.; Acott, P.; Beck, P.L.; Tibbles, L.A.; Muruve, D.A. MAP kinase activation increases BK polyomavirus replication and facilitates viral propagation in vitro. J. Virol. Methods 2010, 170, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husseiny, M.I.; Lacey, S.F. Development of infectious recombinant BK virus. Virus Res. 2011, 161, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahon, C.; Liang, B.; Tikhanovich, I.; Abend, J.R.; Imperiale, M.J.; Nasheuer, H.P.; Folk, W.R. Restriction of human polyomavirus BK virus DNA replication in murine cells and extracts. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 5708–5717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seganti, L.; Mastromarino, P.; Superti, F.; Sinibaldi, L.; Orsi, N. Receptors for BK virus on human erythrocytes. Acta Virol. 1981, 25, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sinibaldi, L.; Goldoni, P.; Pietropaolo, V.; Longhi, C.; Orsi, N. Involvement of gangliosides in the interaction between BK virus and Vero cells. Arch. Virol. 1990, 113, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinibaldi, L.; Viti, D.; Goldoni, P.; Cavallo, G.; Caroni, C.; Orsi, N. Inhibition of BK virus haemagglutination by gangliosides. J. Gen. Virol. 1987, 68, 879–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groux-Degroote, S.; Guerardel, Y.; Delannoy, P. Gangliosides: Structures, Biosynthesis, Analysis and Roles in Cancer. ChemBioChem 2017, 18, 1146–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, J.A.; Magnuson, B.; Tsai, B.; Imperiale, M.J. Identification of gangliosides GD1b and GT1b as receptors for BK virus. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 1361–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swimm, A.I.; Bornmann, W.; Jiang, M.; Imperiale, M.J.; Lukacher, A.E.; Kalman, D. Abl family tyrosine kinases regulate sialylated ganglioside receptors for polyomavirus. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 4243–42451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugan, A.S.; Eash, S.; Atwood, W.J. An N-linked glycoprotein with α(2,3)-linked sialic acid is a receptor for BK virus. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 14442–14445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eash, S.; Querbes, W.; Atwood, W.J. Infection of vero cells by BK virus is dependent on caveolae. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 11583–11590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriyama, T.; Marquez, J.P.; Wakatsuki, T.; Sorokin, A. Caveolar endocytosis is critical for BK virus infection of human renal proximal tubular epithelial cells. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 8552–8562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriyama, T.; Sorokin, A. Repression of BK virus infection of human renal proximal tubular epithelial cells by pravastatin. Transplantation 2008, 85, 1311–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Marciano, A.T.; Rivet, C.R.; Imperiale, M.J. Caveolin- and clathrin-independent entry of BKPyV into primary human proximal tubule epithelial cells. Virology 2016, 492, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Imperiale, M.J. Identification of Rab18 as an Essential Host Factor for BK Polyomavirus Infection Using a Whole-Genome RNA Interference Screen. mSphere 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drachenberg, C.B.; Papadimitriou, J.C.; Wali, R.; Cubitt, C.L.; Ramos, E. BK polyoma virus allograft nephropathy: Ultrastructural features from viral cell entry to lysis. Am. J. Transplant. 2003, 3, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eash, S.; Atwood, W.J. Involvement of cytoskeletal components in BK virus infectious entry. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 11734–11741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriyama, T.; Sorokin, A. Intracellular trafficking pathway of BK Virus in human renal proximal tubular epithelial cells. Virology 2008, 371, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Abend, J.R.; Tsai, B.; Imperiale, M.J. Early events during BK virus entry and disassembly. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 1350–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, C.D.; Carney, D.W.; Derdowski, A.; Lipovsky, A.; Gee, G.V.; O’Hara, B.; Williard, P.; DiMaio, D.; Sello, J.K.; Atwood, W.J. A retrograde trafficking inhibitor of ricin and Shiga-like toxins inhibits infection of cells by human and monkey polyomaviruses. MBio 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouley, S.J.; Maginnis, M.S.; Derdowski, A.; Gee, G.V.; O’Hara, B.A.; Nelson, C.D.; Bara, A.M.; Atwood, W.J.; Dugan, A.S. Host cell autophagy promotes BK virus infection. Virology 2014, 456–457, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, H.H.; Yakhontova, K.; Lu, M.; Manzetti, J. BK Polyomavirus Replication in Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells Is Inhibited by Sirolimus but Activated by Tacrolimus Through a Pathway Involving FKBP-12. Am. J. Transplant. 2016, 16, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, T.; Dosey, A.; Herbstman, J.F.; Ravindran, M.S.; Skiniotis, G.; Tsai, B. ERdj5 Reductase Cooperates with Protein Disulphide Isomerase To Promote Simian Virus 40 Endoplasmic Reticulum Membrane Translocation. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 8897–8908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupzyk, A.; Tsai, B. How Polyomaviruses Exploit the ERAD Machinery to Cause Infection. Viruses 2016, 8, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, T.; Tsai, B. A nucleotide exchange factor promotes endoplasmic reticulum-to-cytosol membrane penetration of the nonenveloped virus simian virus 40. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 4069–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodwin, E.C.; Lipovsky, A.; Inoue, T.; Magaldi, T.G.; Edwards, A.P.; Van Goor, K.E.; Paton, A.W.; Paton, J.C.; Atwood, W.J.; Tsai, B.; et al. BiP and multiple DNAJ molecular chaperones in the endoplasmic reticulum are required for efficient simian virus 40 infection. MBio 2011, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravindran, M.S.; Bagchi, P.; Inoue, T.; Tsai, B. A Non-enveloped Virus Hijacks Host Disaggregation Machinery to Translocate across the Endoplasmic Reticulum Membrane. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walczak, C.P.; Ravindran, M.S.; Inoue, T.; Tsai, B. A cytosolic chaperone complexes with dynamic membrane J-proteins and mobilizes a nonenveloped virus out of the endoplasmic reticulum. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, S.M.; Zhao, L.; Bosard, C.; Imperiale, M.J. Role of a nuclear localization signal on the minor capsid proteins VP2 and VP3 in BKPyV nuclear entry. Virology 2015, 474, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liacini, A.; Seamone, M.E.; Muruve, D.A.; Tibbles, L.A. Anti-BK virus mechanisms of sirolimus and leflunomide alone and in combination: toward a new therapy for BK virus infection. Transplantation 2010, 90, 1450–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tikhanovich, I.; Nasheuer, H.P. Host-specific replication of BK virus DNA in mouse cell extracts is independently controlled by DNA polymerase α-primase and inhibitory activities. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 6636–6644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tikhanovich, I.; Liang, B.; Seoighe, C.; Folk, W.R.; Nasheuer, H.P. Inhibition of human BK polyomavirus replication by small noncoding RNAs. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 6930–6940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grinde, B.; Gayorfar, M.; Rinaldo, C.H. Impact of a polyomavirus (BKV) infection on mRNA expression in human endothelial cells. Virus Res. 2007, 123, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abend, J.R.; Low, J.A.; Imperiale, M.J. Global effects of BKV infection on gene expression in human primary kidney epithelial cells. Virology 2010, 397, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Zhao, L.; Gamez, M.; Imperiale, M.J. Roles of ATM and ATR-mediated DNA damage responses during lytic BK polyomavirus infection. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhalen, B.; Justice, J.L.; Imperiale, M.J.; Jiang, M. Viral DNA replication-dependent DNA damage response activation during BK polyomavirus infection. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 5032–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Entezami, P.; Gamez, M.; Stamminger, T.; Imperiale, M.J. Functional reorganization of promyelocytic leukemia nuclear bodies during BK virus infection. MBio 2011, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, G.L.; Caller, L.G.; Foster, V.; Crump, C.M. Anion homeostasis is important for non-lytic release of BK polyomavirus from infected cells. Open Biol. 2015, 5, 150041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Helle, F.; Brochot, E.; Handala, L.; Martin, E.; Castelain, S.; Francois, C.; Duverlie, G. Biology of the BKPyV: An Update. Viruses 2017, 9, 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9110327
Helle F, Brochot E, Handala L, Martin E, Castelain S, Francois C, Duverlie G. Biology of the BKPyV: An Update. Viruses. 2017; 9(11):327. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9110327
Chicago/Turabian StyleHelle, Francois, Etienne Brochot, Lynda Handala, Elodie Martin, Sandrine Castelain, Catherine Francois, and Gilles Duverlie. 2017. "Biology of the BKPyV: An Update" Viruses 9, no. 11: 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9110327
APA StyleHelle, F., Brochot, E., Handala, L., Martin, E., Castelain, S., Francois, C., & Duverlie, G. (2017). Biology of the BKPyV: An Update. Viruses, 9(11), 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9110327







