Co-Amorphous Screening for the Solubility Enhancement of Poorly Water-Soluble Mirabegron and Investigation of Their Intermolecular Interactions and Dissolution Behaviors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Mirabegron (MBR) Co-Amorphous Screening Using Vacuum Evaporation Crystallization
2.3. Powder X-ray Diffraction (PXRD)
2.4. Solution-State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (Solution-State NMR) Spectroscopy
2.5. Solid-State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (Solid-State CP/MAS 13C-NMR) Spectroscopy
2.6. Attenuated Total Reflectance Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR)
2.7. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.8. Dissolution Test of MBR Co-Amorphous
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mirabegron Co-Amorphous Screening and Intermolecular Interactions
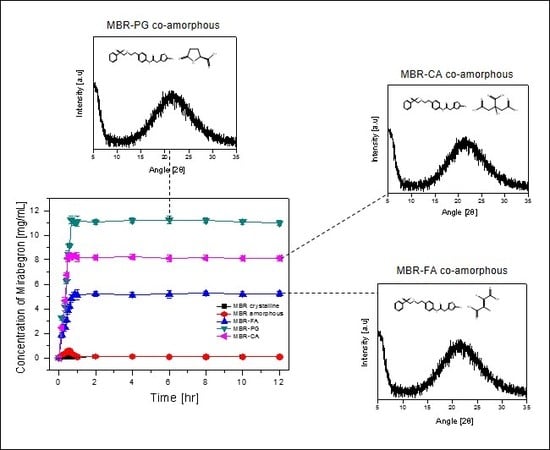
3.2. Dissolution Test for MBR Co-Amorphous and Investigation of Their Phase Transformation to Crystalline Solid
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hilfiker, R. Polymorphism in the Pharmaceutical Industry; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2006; pp. 259–281. ISBN 13-978-3-527-31146-0. [Google Scholar]
- Aaltonen, J.; Rades, T. Towards physico-relevant dissolution testing: The importance of solid-state analysis in dissolution. Dissolut. Technol. 2009, 16, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, B.C.; Zografi, G. Characteristics and significance of the amorphous state in pharmaceutical systems. J. Pharm. Sci. 1997, 86, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiou, W.L.; Riegelman, S. Pharmaceutical applications of solid dispersion systems. J. Pharm. Sci. 1971, 60, 1281–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leuner, C.; Dressman, J. Improving drug solubility for oral delivery using solid dispersions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 50, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsac, P.J.; Shamblin, S.L.; Taylor, L.S. Theoretical and practical approaches for prediction of drug–polymer miscibility and solubility. Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 2417–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, B.C.; Shamblin, S.L.; Zografi, G. Molecular mobility of amorphous pharmaceutical solids below their glass transition temperatures. Pharm. Res. 1995, 12, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Zografi, G. Phase behavior of binary and ternary amorphous mixtures containing indomethacin, citric acid, and PVP. Pharm. Res. 1998, 15, 1202–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serajuddin, A.T.M. Solid dispersion of poorly water-soluble drugs: Early promises, subsequent problems, and recent breakthroughs. J. Pharm. Sci. 1999, 88, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconcelos, T.; Sarmento, B.; Costa, P. Solid dispersions as strategy to improve oral bioavailability of poor water soluble drugs. Drug Discov. Today 2007, 12, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laitinen, R.; Löbmann, K.; Strachan, C.J.; Grohganz, H.; Rades, T. Emerging trends in the stabilization of amorphous drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chieng, N.; Aaltonen, J.; Saville, D.; Rades, T. Physical characterization and stability of amorphous indomethacin and ranitidine hydrochloride binary systems prepared by mechanical activation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 71, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, S.; Zografi, G.; Engers, D.; Morris, K.; Crowley, K.; Newman, A. Analysis of amorphous and nanocrystalline solids from their X-ray diffraction patterns. Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 2333–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dengale, S.J.; Grohganz, H.; Rades, T.; Löbmann, K. Recent advances in co-amorphous drug formulations. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 100, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamura, S.; Gotoh, H.; Sakamoto, Y.; Momose, Y. Physicochemical properties of amorphous salt of cimetidine and diflunisal system. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 241, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamura, S.; Gotoh, H.; Sakamoto, Y.; Momose, Y. Physicochemical properties of amorphous precipitates of cimetidine–indomethacin binary system. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 49, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantishaiyakul, V.; Suknuntha, K.; Vao-Soongnern, V. Characterization of cimetidine–piroxicam coprecipitate interaction using experimental studies and molecular dynamic simulations. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 952–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skieneh, J.M.; Sathisaran, I.; Dalvi, S.V.; Rohani, S. Co-amorphous form of Curcumin−Folic Acid dehydrate with increased dissolution rate. Cryst. Growth Des. 2017, 17, 6273–6280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodagekar, A.; Chavan, R.B.; Chella, N.; Shastri, N.R. Role of Valsartan as an Antiplasticizer in development of therapeutically viable drug—Drug coamorphous system. Cryst. Growth Des. 2018, 18, 1944–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, K.T.; Larsen, F.H.; Cornett, C.; Löbmann, K.; Grohganz, H.; Rades, T. Formation mechanism of co-amorphous drug–amino acid mixtures. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 2484–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allesø, M.; Chieng, N.; Rehder, S.; Rantanen, J.; Rades, T.; Aaltonen, J. Enhanced dissolution rate and synchronized release of drugs in binary systems through formulation: Amorphous naproxen–cimetidine mixtures prepared by mechanical activation. J. Control. Release 2009, 136, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama, T.; Suzuki, T.; Onda, K.; Hayakawa, M.; Moritomo, H.; Kimizuka, T.; Matsui, T. Amide Derivatives or Salts Thereof. U.S. Patent 6346532B1, 12 February 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Takasu, T.; Sato, S.; Ukai, M.; Maruyama, T. Remedy for Overactive Bladder Comprising Acetic Acid Anilide Derivative as the Active Ingredient. U.S. Patent 8835474B2, 16 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Teijlingen, R.V.; Meijer, J.; Takusagawa, S.; Gelderen, M.V.; Beld, C.V.D.; Usui, T. Development and validation of LC–MS/MS methods for the determination of mirabegron and its metabolites in human plasma and their application to a clinical pharmacokinetic study. J. Chromatogr. B 2012, 887–888, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patal, D.A.; Patal, D.J. Physicochemical characterization and in vitro dissolution enhancement of Mirabegron using solid dispersion method. World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 7, 973–991. [Google Scholar]
- Yuuki, T.; Hiroyasu, T.; Tadashi, H. Orally Administered Medical Composition. U.S. Patent 20150306090A1, 29 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Alessio, B.; Pietro, A.; Emanuele, A. Crystalline Forms of Mirabegron Acetate Salt. EP Patent 2857389A1, 8 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rey, A.W.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Gerster, J.; Duncan, S.; Raheem, M.A.; Wang, F.; Green, S.P. Solid Forms of Mirabegron. WO Patent 2016/049749A1, 7 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sangwan, S.; Kaushik, P.; Ali, I.; Thaimattam, R.; Prasad, M. Crystalline Form of Mirabegron. WO Patent 2015/040605A1, 26 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Stahl, P.H.; Wermuth, C.G. Handbook of Pharmaceutical Salt Properties, Selection, and Use; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2002; pp. 269–302. ISBN 3-906390-26-8. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, R.K. Application of solid-state NMR to pharmaceutical polymorphism and related matters. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2007, 59, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Su, Y.; Zhu, L.; Brown, C.D.; Rosen, L.A.; Rosenberg, K.J. Rheological and solid-state NMR assessments of copovidone/clotrimazole model solid dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 500, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löbmann, K.; Laitinen, R.; Strachan, C.; Rades, T.; Grohganz, H. Amino acids as coamorphous stabilizers for poorly water-soluble drugs—Part 2: Molecular interactions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 85, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
An, J.-H.; Lim, C.; Kiyonga, A.N.; Chung, I.H.; Lee, I.K.; Mo, K.; Park, M.; Youn, W.; Choi, W.R.; Suh, Y.-G.; et al. Co-Amorphous Screening for the Solubility Enhancement of Poorly Water-Soluble Mirabegron and Investigation of Their Intermolecular Interactions and Dissolution Behaviors. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030149
An J-H, Lim C, Kiyonga AN, Chung IH, Lee IK, Mo K, Park M, Youn W, Choi WR, Suh Y-G, et al. Co-Amorphous Screening for the Solubility Enhancement of Poorly Water-Soluble Mirabegron and Investigation of Their Intermolecular Interactions and Dissolution Behaviors. Pharmaceutics. 2018; 10(3):149. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030149
Chicago/Turabian StyleAn, Ji-Hun, Changjin Lim, Alice Nguvoko Kiyonga, In Hwa Chung, In Kyu Lee, Kilwoong Mo, Minho Park, Wonno Youn, Won Rak Choi, Young-Ger Suh, and et al. 2018. "Co-Amorphous Screening for the Solubility Enhancement of Poorly Water-Soluble Mirabegron and Investigation of Their Intermolecular Interactions and Dissolution Behaviors" Pharmaceutics 10, no. 3: 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030149
APA StyleAn, J.-H., Lim, C., Kiyonga, A. N., Chung, I. H., Lee, I. K., Mo, K., Park, M., Youn, W., Choi, W. R., Suh, Y.-G., & Jung, K. (2018). Co-Amorphous Screening for the Solubility Enhancement of Poorly Water-Soluble Mirabegron and Investigation of Their Intermolecular Interactions and Dissolution Behaviors. Pharmaceutics, 10(3), 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030149