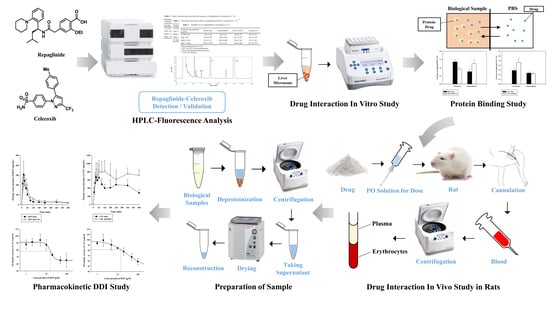
Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of Metabolic Drug Interactions between Repaglinide and Celecoxib by a Bioanalytical HPLC Method for Their Simultaneous Determination with Fluorescence Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Animals
2.3. Calibration Standards and Quality Control Samples
2.4. Sample Preparation
2.5. Chromatographic Conditions
2.6. Method Validation
2.7. In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Study in Rats
2.8. In Vitro Metabolism and Protein Binding Study
2.9. Data Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Method Development
3.2. Method Validation: Selectivity, Linearity, Sensitivity, Precision, and Accuracy
3.3. Method Validation: Recovery, Matrix Effect, and Stability
3.4. Pharmacokinetic Drug Interaction Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Prevention Prevalence of doctor-diagnosed arthritis and arthritis-attributable activity limitation-United States, 2010–2012. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2013, 62, 869–873. [Google Scholar]
- Cefalu, W.T.; Buse, J.B.; Tuomilehto, J.; Fleming, G.A.; Ferrannini, E.; Gerstein, H.C.; Bennett, P.H.; Ramachandran, A.; Raz, I.; Rosenstock, J.; et al. Update and next steps for real-world translation of interventions for type 2 diabetes prevention: Reflections from a diabetes care editors’ expert forum. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 1186–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- March, L.; Smith, E.U.; Hoy, D.G.; Cross, M.J.; Sanchez-Riera, L.; Blyth, F.; Buchbinder, R.; Vos, T.; Woolf, A.D. Burden of disability due to musculoskeletal (MSK) disorders. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2014, 28, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, R.C.; Felson, D.T.; Helmick, C.G.; Arnold, L.M.; Choi, H.; Deyo, R.A.; Gabriel, S.; Hirsch, R.; Hochberg, M.C.; Hunder, G.G.; et al. Estimates of the prevalence of arthritis and other rheumatic conditions in the United States. Part II. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piva, S.R.; Susko, A.M.; Khoja, S.S.; Josbeno, D.A.; Fitzgerald, G.K.; Toledo, F.G. Links between osteoarthritis and diabetes: Implications for management from a physical activity perspective. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2015, 31, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Prevention Arthritis as a potential barrier to physical activity among adults with diabetes-United States, 2005 and 2007. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2008, 57, 486–489. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Q.; Liu, H.; Yang, D.; Zhang, Y. Diabetes mellitus and arthritis: Is it a risk factor or comorbidity? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 2017, 96, e6627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, L.S.; Tomlinson, B.; Chu, T.T.; Li, M.; Leung, Y.Y.; Kwok, L.W.; Li, T.K.; Yu, T.; Zhu, Y.E.; Wong, K.C.; et al. Cardiovascular risk profile of patients with psoriatic arthritis compared to controls-the role of inflammation. Rheumatology 2008, 47, 718–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, J.F.; Gourraud, P.A.; Cantagrel, A.; Davignon, J.L.; Constantin, A. Traditional cardiovascular risk factors in rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis. Joint Bone Spine 2011, 78, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajosaari, L.I.; Niemi, M.; Backman, J.T.; Neuvonen, P.J. Telithromycin, but not montelukast, increases the plasma concentrations and effects of the cytochrome P450 3A4 and 2C8 substrate repaglinide. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 79, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatorp, V.; Hansen, K.T.; Thomsen, M.S. Influence of drugs interacting with CYP3A4 on the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and safety of the prandial glucose regulator repaglinide. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2003, 43, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bidstrup, T.B.; Bjornsdottir, I.; Sidelmann, U.G.; Thomsen, M.S.; Hansen, K.T. CYP2C8 and CYP3A4 are the principal enzymes involved in the human in vitro biotransformation of the insulin secretagogue repaglinide. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2003, 56, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemi, M.; Kajosaari, L.I.; Neuvonen, M.; Backman, J.T.; Neuvonen, P.J. The CYP2C8 inhibitor trimethoprim increases the plasma concentrations of repaglinide in healthy subjects. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2004, 57, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Niemi, M.; Backman, J.T.; Neuvonen, M.; Neuvonen, P.J. Effects of gemfibrozil, itraconazole, and their combination on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of repaglinide: Potentially hazardous interaction between gemfibrozil and repaglinide. Diabetologia 2003, 46, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, H.A.; Kim, D.; Lee, S.H.; Jung, B.H. Simultaneous quantitative determination of celecoxib and its two metabolites using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry in alternating polarity switching mode. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 107, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, J.L.; McKnight, W.; Reuter, B.K.; Vergnolle, N. NSAID-induced gastric damage in rats: Requirement for inhibition of both cyclooxygenase 1 and 2. Gastroenterology 2000, 119, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Gao, S.; Hu, M. Quantitation of celecoxib and four of its metabolites in rat blood by UPLC-MS/MS clarifies their blood distribution patterns and provides more accurate pharmacokinetics profiles. J. Chromatogr. B 2015, 1001, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gong, L.; Thorn, C.F.; Bertagnolli, M.M.; Grosser, T.; Altman, R.B.; Klein, T.E. Celecoxib pathways: Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2012, 22, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, P.; Harisudhan, T.; Choudhury, H.; Mullangi, R.; Srinivas, N.R. Simultaneous estimation of six anti-diabetic drugs-glibenclamide, gliclazide, glipizide, pioglitazone, repaglinide and rosiglitazone: Development of a novel HPLC method for use in the analysis of pharmaceutical formulations and its application to human plasma assay. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2006, 20, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar]
- Ruzilawati, A.B.; Wahab, M.S.; Imran, A.; Ismail, Z.; Gan, S.H. Method development and validation of repaglinide in human plasma by HPLC and its application in pharmacokinetic studies. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 43, 1831–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guirguis, M.S.; Sattari, S.; Jamali, F. Pharmacokinetics of celecoxib in the presence and absence of interferon-induced acute inflammation in the rat: Application of a novel HPLC assay. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Stormer, E.; Bauer, S.; Kirchheiner, J.; Brockmoller, J.; Roots, I. Simultaneous determination of celecoxib, hydroxycelecoxib, and carboxycelecoxib in human plasma using gradient reversed-phase liquid chromatography with ultraviolet absorbance detection. J. Chromatogr. B 2003, 783, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalalizadeh, H.; Amini, M.; Ziaee, V.; Safa, A.; Farsam, H.; Shafiee, A. Determination of celecoxib in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2004, 35, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gao, F.; Guan, X.; Sun, Y.-T.; Gu, J.-K.; Fawcett, J.P. Determination of repaglinide in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2011, 1, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptacek, P.; Klima, J.; Macek, J. Determination of celecoxib in human plasma by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2012, 899, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.S.; Shim, W.S.; Yim, S.V.; Lee, K.T. Development of simple and rapid LC-MS/MS method for determination of celecoxib in human plasma and its application to bioequivalence study. J. Chromatogr. B 2012, 902, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VandenBrink, B.M.; Foti, R.S.; Rock, D.A.; Wienkers, L.C.; Wahlstrom, J.L. Evaluation of CYP2C8 inhibition in vitro: Utility of montelukast as a selective CYP2C8 probe substrate. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2011, 39, 1546–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US-FDA Guidance for Industry: Bioanalytical Method Validation. Center for Drug Evaluation and Research 2018. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/downloads/drugs/guidances/ucm070107.pdf (accessed on 24 May 2018).
- Kim, S.B.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, D.D.; Yoon, I.S. Metabolic interactions of rosmarinic acid with human cytochrome P450 monooxygenases and uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 110, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.B.; Kim, K.S.; Ryu, H.M.; Hong, S.H.; Kim, B.K.; Kim, D.D.; Park, J.W.; Yoon, I.S. Modulation of rat hepatic CYP1A and 2C activity by honokiol and magnolol: Differential effects on phenacetin and diclofenac pharmacokinetics in vivo. Molecules 2018, 23, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.B.; Lee, T.; Lee, H.S.; Song, C.K.; Cho, H.J.; Kim, D.D.; Maeng, H.J.; Yoon, I.S. Development and validation of a highly sensitive LC-MS/MS method for the determination of acacetin in human plasma and its application to a protein binding study. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2016, 39, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avery, B.A.; Pabbisetty, D.; Li, L.; Sharma, A.; Gundluru, M.K.; Chittiboyina, A.G.; Williamson, J.S.; Avery, M.A. A pharmacokinetic comparison of homodimer ARB-92 and heterodimer ARB-89: Novel, potent antimalarial candidates derived from 7β-hydroxyartemisinin. J. Pharm. Investig. 2018, 48, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, U.; Werner, D.; Pahl, A.; Mundkowski, R.; Gillich, M.; Brune, K. Investigation of the pharmacokinetics of celecoxib by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2002, 16, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.S.; Choi, I.; Choi, D.H. Effects of nifedipine on the pharmacokinetics of repaglinide in rats: Possible role of CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein inhibition by nifedipine. Pharmacol. Rep. 2013, 65, 1422–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhou, D.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, M.; Lu, J.; Zhang, H. CYP2C8-mediated interaction between repaglinide and steviol acyl glucuronide: In vitro investigations using rat and human matrices and in vivo pharmacokinetic evaluation in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 94, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulson, S.K.; Zhang, J.Y.; Breau, A.P.; Hribar, J.D.; Liu, N.W.; Jessen, S.M.; Lawal, Y.M.; Cogburn, J.N.; Gresk, C.J.; Markos, C.S.; et al. Pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution, metabolism, and excretion of celecoxib in rats. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2000, 28, 514–521. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kim, S.B.; Chun, J.; Song, K.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Chung, S.J.; Cho, H.J.; Yoon, I.S.; Kim, D.D. High body clearance and low oral bioavailability of alantolactone, isolated from Inula helenium, in rats: Extensive hepatic metabolism and low stability in gastrointestinal fluids. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2016, 37, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Nominal Concentration (ng/mL) | Precision (%) | Accuracy (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intra-Day | Inter-Day | Intra-Day | Inter-Day | |
| Repaglinide (REP) | ||||
| LLOQ (10) | 2.69 | 6.21 | 112 | 101 |
| LQC (30) | 1.20 | 3.99 | 104 | 99.4 |
| MQC (120) | 1.16 | 0.70 | 102 | 101 |
| HQC (1200) | 0.79 | 1.43 | 99.2 | 99.8 |
| Celecoxib (CEL) | ||||
| LLOQ (10) | 4.06 | 8.30 | 111 | 103 |
| LQC (30) | 0.79 | 2.15 | 104 | 103 |
| MQC (120) | 1.19 | 2.18 | 100 | 102 |
| HQC (1200) | 1.55 | 1.63 | 98.6 | 100 |
| Nominal Concentration (ng/mL) | Recovery (%) | Matrix Effect (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Repaglinide (REP) | ||
| LLOQ (10) | 98.5 ± 5.3 | 101 ± 6 |
| LQC (30) | 98.6 ± 1.1 | 102 ± 4 |
| MQC (120) | 103 ± 2 | 95.6 ± 3.0 |
| HQC (1200) | 101 ± 1 | 92.1 ± 2.5 |
| Celecoxib (CEL) | ||
| LLOQ (10) | 104 ± 3 | 97.6 ± 3.0 |
| LQC (30) | 102 ± 4 | 98.5 ± 3.5 |
| MQC (120) | 104 ± 2 | 93.8 ± 1.8 |
| HQC (1200) | 103 ± 2 | 90.7 ± 2.4 |
| IS (Ketoconazole, 50) | 96.7 ± 1.2 | 99.4 ± 1.3 |
| Nominal Concentration (ng/mL) | Bench-Top a | Autosampler b | Freeze‒Thaw c | Long-Term d |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Repaglinide (REP) | ||||
| LLOQ (10) | 102 ± 6 | 106 ± 3 | 106 ± 6. | 96.4 ± 3.4 |
| LQC (30) | 92.7 ± 4.2 | 102 ± 4 | 98.1 ± 3.7 | 97.6 ± 3.7 |
| MQC (120) | 92.9 ± 1.4 | 104 ± 0 | 102 ± 2 | 95.1 ± 1.8 |
| HQC (1200) | 90.6 ± 0.7 | 101 ± 1 | 100 ± 1 | 93.3 ± 0.8 |
| Celecoxib (CEL) | ||||
| LLOQ (10) | 98.3 ± 2.4 | 95.2 ± 2.6 | 90.3 ± 2.4 | 92.7 ± 3.0 |
| LQC (30) | 89.2 ± 2.7 | 97.8 ± 1.8 | 97.9 ± 2.1 | 92.7 ± 3.5 |
| MQC (120) | 93.1 ± 2.2 | 103 ± 1 | 101 ± 2 | 92.9 ± 1.2 |
| HQC (1200) | 89.6 ± 1.9 | 101 ± 1 | 99.6 ± 0.4 | 91.7 ± 0.7 |
| Parameter | REP | CEL | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single | Combined | Single | Combined | |
| AUClast (×103 ng∙min/mL) | 21.1 ± 5.1 | 25.9 ± 2.8 | 189 ± 70 | 333 ± 89 * |
| AUCinf (×103 ng∙min/mL) | 30.5 ± 5.5 | 35.4 ± 8.3 | ND | ND |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 297 ± 103 | 224 ± 102 | 741 ± 299 | 954 ± 196 |
| Tmax (min) | 20 (20–45) | 45 (20–60) | 180 (30–240) | 120 (45–360) |
| t1/2 (min) | 374 ± 45 | 290 ± 123 | ND | ND |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, D.-G.; Kwak, J.; Seo, S.-W.; Kim, J.-M.; Yoo, J.-W.; Jung, Y.; Lee, Y.-H.; Kim, M.-S.; Jung, Y.-S.; Yun, H.; et al. Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of Metabolic Drug Interactions between Repaglinide and Celecoxib by a Bioanalytical HPLC Method for Their Simultaneous Determination with Fluorescence Detection. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11080382
Han D-G, Kwak J, Seo S-W, Kim J-M, Yoo J-W, Jung Y, Lee Y-H, Kim M-S, Jung Y-S, Yun H, et al. Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of Metabolic Drug Interactions between Repaglinide and Celecoxib by a Bioanalytical HPLC Method for Their Simultaneous Determination with Fluorescence Detection. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(8):382. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11080382
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Dong-Gyun, Jinsook Kwak, Seong-Wook Seo, Ji-Min Kim, Jin-Wook Yoo, Yunjin Jung, Yun-Hee Lee, Min-Soo Kim, Young-Suk Jung, Hwayoung Yun, and et al. 2019. "Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of Metabolic Drug Interactions between Repaglinide and Celecoxib by a Bioanalytical HPLC Method for Their Simultaneous Determination with Fluorescence Detection" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 8: 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11080382
APA StyleHan, D.-G., Kwak, J., Seo, S.-W., Kim, J.-M., Yoo, J.-W., Jung, Y., Lee, Y.-H., Kim, M.-S., Jung, Y.-S., Yun, H., & Yoon, I.-S. (2019). Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of Metabolic Drug Interactions between Repaglinide and Celecoxib by a Bioanalytical HPLC Method for Their Simultaneous Determination with Fluorescence Detection. Pharmaceutics, 11(8), 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11080382