Mitigation of Salt Stress in Rice by the Halotolerant Plant Growth-Promoting Bacterium Enterobacter asburiae D2
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation of Halotolerant Rhizobacteria from Rice
2.2. Morphological and Biochemical Characteristics
2.3. Identification of the Selected Isolate
2.4. Genome Sequencing and Analysis
2.5. Evaluation of Plant Growth-Promoting Attributes
2.6. Effect of Strain Inoculation on Rice Growth under Salt Stress
2.6.1. Plant Inoculation and Salt Treatment
2.6.2. Biochemical Analysis of Plants
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
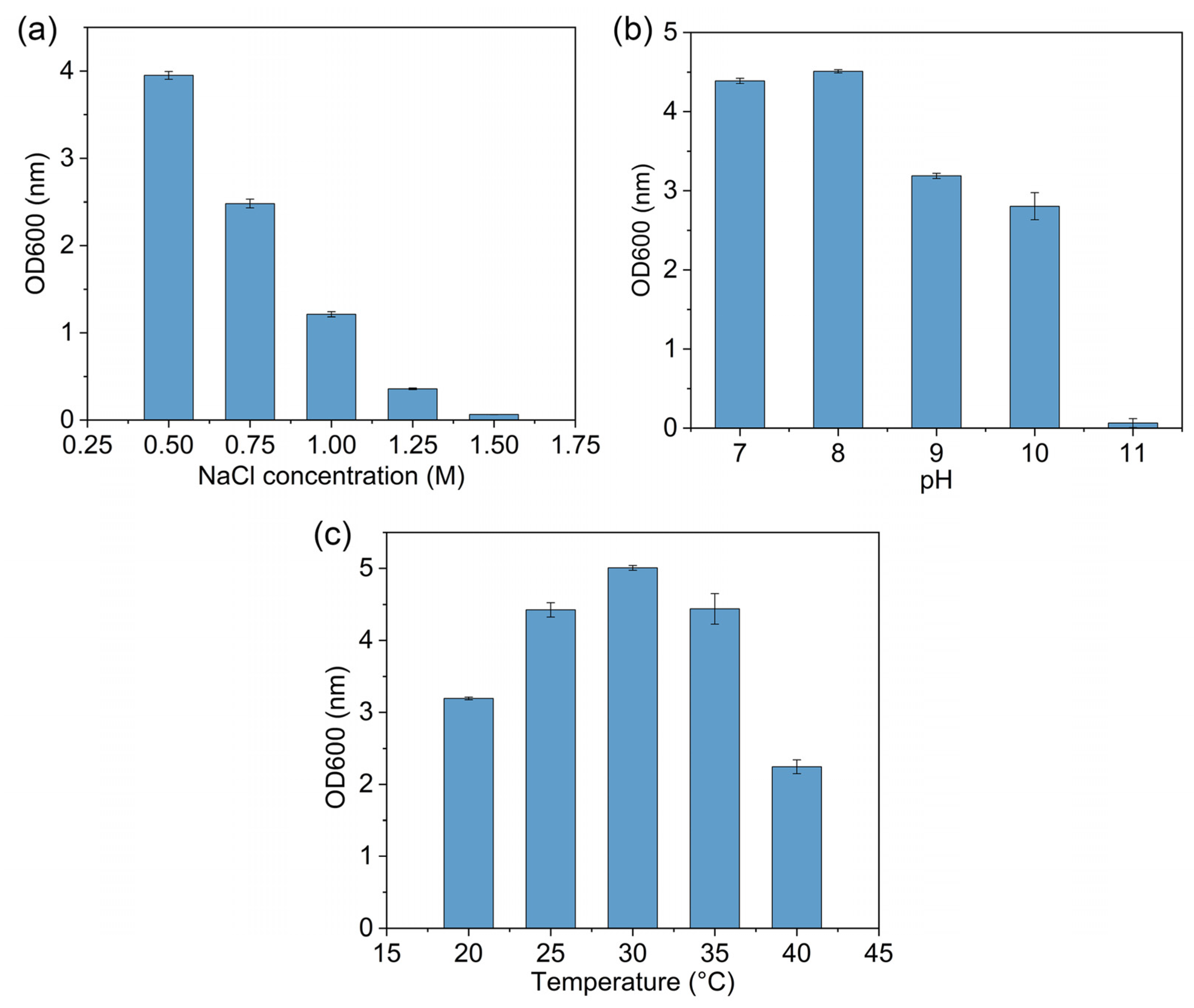
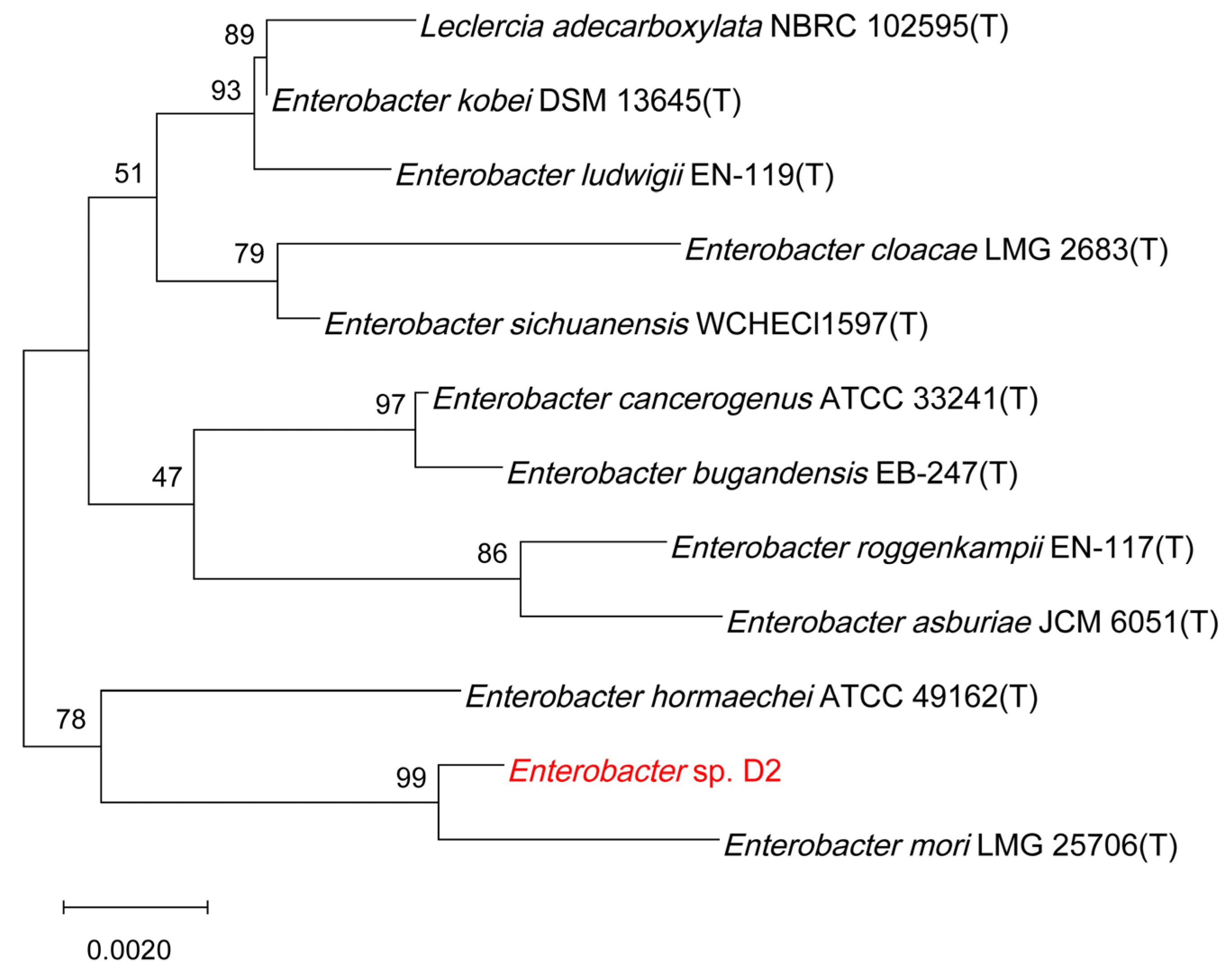
3.1. Isolation, Characterization and Identification of Strain D2
3.2. Genome Analysis of Strain D2
3.2.1. General Characteristics of the D2 Genome
3.2.2. Genes Involved in Plant Growth Promotion and Stress Response
3.3. Evaluation of the PGP Properties of Strain D2
3.4. Effect of Strain D2 Inoculation on the Growth of Rice under Salt Stress
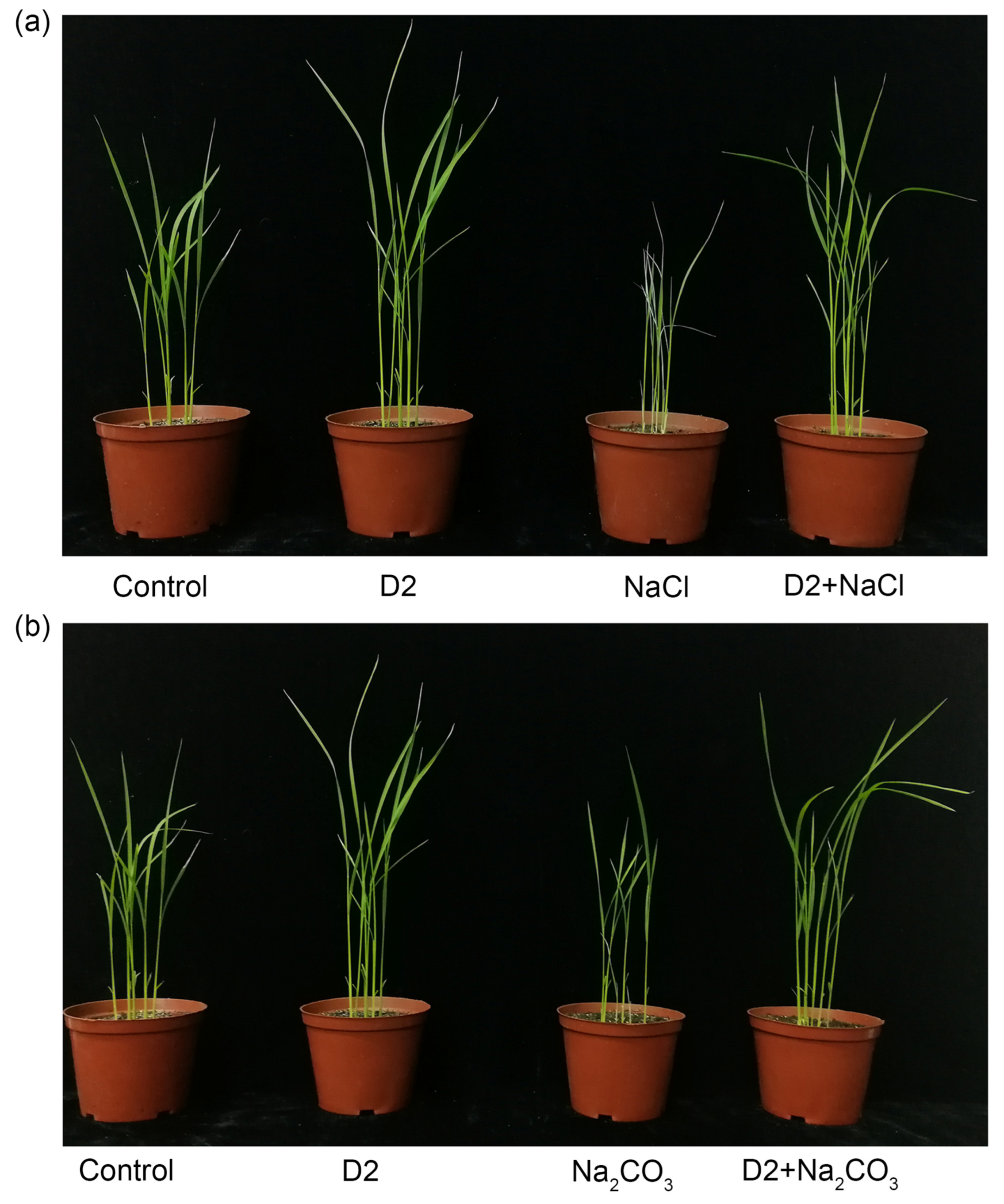
3.4.1. Growth Parameters
3.4.2. Contents of Chlorophyll, Total Soluble Protein, Proline, and MDA
3.4.3. Antioxidant Enzyme Activities
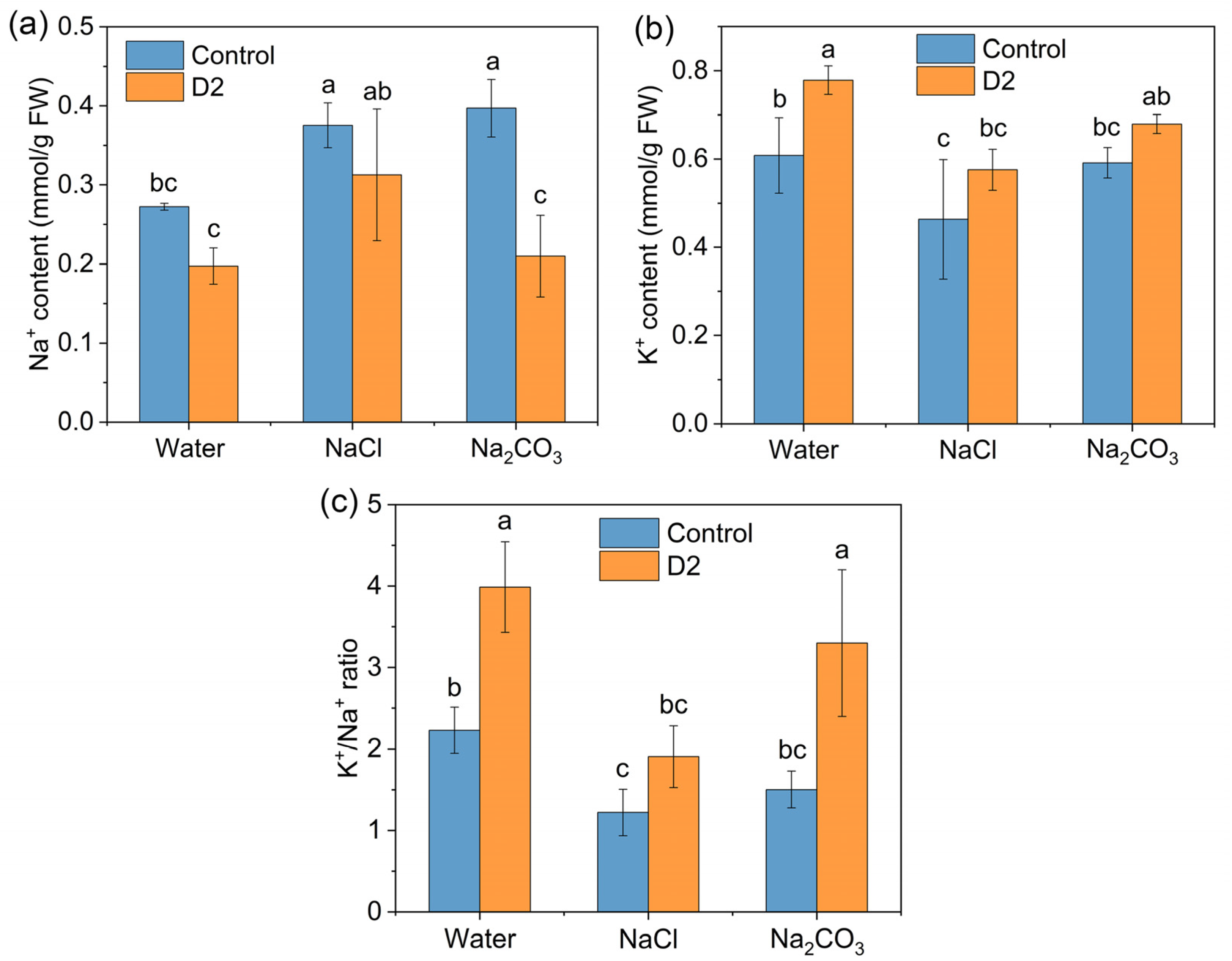
3.4.4. Na+ and K+ Concentrations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kruthika, N.; Jithesh, M.N. Response of rice to salinity risk-from a physiological outlook to laboratory focussed experimental approach. Cereal Res. Commun. 2023, 51, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Mao, B.; Yuan, D.; Chu, C.; Duan, M. Salt tolerance in rice: Physiological responses and molecular mechanisms. Crop J. 2022, 10, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganie, S.A.; Wani, S.H.; Henry, R.; Hensel, G. Improving rice salt tolerance by precision breeding in a new era. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2021, 60, 101996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, A.A.; Murtaza, G.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M.; Waraich, E.A. Application of gypsum or sulfuric acid improves physiological traits and nutritional status of rice in calcareous saline-sodic soils. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nut. 2022, 22, 1846–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khumairah, F.H.; Setiawati, M.R.; Fitriatin, B.N.; Simarmata, T.; Akfaraj, S.; Ansari, M.J.; Enshasy, J.A.E.; Sayyed, R.Z.; Najafi, S. Halotolerant plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria isolated from saline soil improve nitrogen fixation and alleviate salt stress in rice plants. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 905210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumawat, K.C.; Sharma, B.; Nagpal, S.; Kumar, A.; Tiwari, S.; Nair, R.M. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria: Salt stress alleviators to improve crop productivity for sustainable agriculture development. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 13, 1101862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, B.A.; Tariq, L.; Nissar, S.; Islam, S.T.; Islam, S.U.; Mangral, Z.; Ilyas, N.; Sayyed, R.Z.; Muthusamy, G.; Kim, W.; et al. The role of plant-associated rhizobacteria in plant growth, biocontrol and abiotic stress management. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 133, 2717–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Raghuvanshi, N.; Pandey, A.K.; Kumar, A.; Thoday-Kennedy, E.; Kant, S. Role of halotolerant plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria in mitigating salinity stress: Recent advances and possibilities. Agriculture 2023, 13, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, A.; Sayyed, R.Z.; Ramteke, P.W.; Sharma, S.; Marraiki, N.; Elgorban, A.M.; Syed, A. ACC deaminase and antioxidant enzymes producing halophilic Enterobacter sp. PR14 promotes the growth of rice and millets under salinity stress. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2020, 26, 1847–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, S.; Mukherjee, A.; Rastogi, R.P.; Verma, J.P. Salt-tolerant plant growth-promoting Bacillus pumilus strain JPVS11 to enhance plant growth attributes of rice and improve soil health under salinity stress. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 242, 126616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarker, P.K.; Karmoker, D.; Shohan, M.U.S.; Saha, A.K.; Rima, F.S.; Begum, R.A.; Islam, M.R.; Seraj, Z.I. Effects of multiple halotolerant rhizobacteria on the tolerance, growth, and yield of rice plants under salt stress. Folia Microbiol. 2023, 68, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, C.; Gao, D.; Bai, T.; Geng, Y.; Shao, X.; Guo, L. Straw return alleviates the negative effects of saline sodic stress on rice by improving soil chemistry and reducing the accumulation of sodium ions in rice leaves. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 342, 108253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passari, A.K.; Mishra, V.K.; Leo, V.V.; Gupta, V.K.; Singh, B.P. Phytohormone production endowed with antagonistic potential and plant growth promoting abilities of culturable endophytic bacteria isolated from Clerodendrum colebrookianum Walp. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 193, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bal, H.B.; Nayak, L.; Das, S.; Adhya, T.K. Isolation of ACC deaminase producing PGPR form rice rhizosphere and evaluating their plant growth promoting activity under salt stress. Plant Soil 2013, 366, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisburg, W.G.; Barns, S.M.; Pelletier, D.A.; Lane, D.J. 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.H.; Ha, S.M.; Kwon, S.; Lim, J.; Kim, Y.; Seo, H.; Chun, J. Introducing EzBioCloud: A taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 1613–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Yu, G.; Shi, C.; Liu, L.; Guo, Q.; Han, C.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, L.; Liu, B.; Gao, H.; et al. Majorbio Cloud: A one-stop, comprehensive bioinformatic platform for multiomics analyses. iMeta 2022, 1, e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bric, J.M.; Bostock, R.M.; Silverstone, S.E. Rapid in situ assay for indoleacetic acid production by bacteria immobilized on a nitrocellulose membrane. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1991, 57, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwyn, B.; Neilands, J.B. Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal. Biochem. 1987, 160, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nautiyal, C.S. An efficient microbiological growth medium for screening phosphate solubilizing microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1999, 170, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.; Riley, J.P. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 1962, 27, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penrose, D.M.; Glick, B.R. Methods for isolating and characterizing ACC deaminase-containing plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Physiol. Plantarum 2003, 118, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, P.; Kanagendran, A.; Samaddar, S.; Pazouki, L.; Sa, T.M.; Niinemets, Ü. Inoculation of Brevibacterium linens RS16 in Oryza sativa genotypes enhanced salinity resistance: Impacts on photosynthetic traits and foliar volatile emissions. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnon, D.I. Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 1949, 24, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, L.S.; Waldren, R.P.; Teare, I.D. Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 1973, 39, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagriffoul, A.; Mocquot, B.; Mench, M.; Vangronsveld, J. Cadmium toxicity effects on growth, mineral and chlorophyll contents, and activities of stress related enzymes in young maize plants (Zea mays L.). Plant Soil 1998, 200, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, F.X.; Rossi, M.J.; Soares, C.R.F.S.; McConkey, B.J.; Glick, B.R. New insights into 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) deaminase phylogeny, evolution and ecological significance. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prittesh, P.; Avnika, P.; Kinjal, P.; Jinal, H.N.; Sakthivel, K.; Amaresan, N. Amelioration effect of salt-tolerant plant growth-promoting bacteria on growth and physiological properties of rice (Oryza sativa) under salt-stressed conditions. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 2419–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, A.; Ghosh, P.K.; Pramanik, K.; Mitra, S.; Soren, T.; Pandey, S.; Mondal, M.H.; Maiti, T.K. A halotolerant Enterobacter sp. displaying ACC deaminase activity promotes rice seedling growth under salt stress. Res. Microbiol. 2018, 169, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, S.; Djedidi, S.; Ohkama-Ohtsu, N.; Sarhadi, W.A.; Kojima, K.; Rallos, R.V.; Ramirez, M.D.A.; Yamaya, H.; Sekimoto, H.; Yokoyama, T. Isolation and screening of indigenous plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria from different rice cultivars in Afghanistan soils. Microbes Environ. 2019, 34, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, K.M.; Pandey, P. Endophytic bacteria with host-supportive genetic determinants in their genomes induce growth and antioxidant activity related gene functions in transcriptome of black rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ. Exp. Bot. 2023, 213, 105396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkel, B.N.; Harper, C.P. The roles of auxin during interactions between bacterial plant pathogens and their hosts. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romasi, E.F.; Lee, J. Development of indole-3-acetic acid-producing Escherichia coli by functional expression of IpdC, AspC, and Iad1. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 23, 1726–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamalero, E.; Glick, B.R. Bacterial modulation of plant ethylene levels. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wu, Z.; Xiang, H.; He, Y.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, J. Whole genome analysis of Enterobacter cloacae Rs-2 and screening of genes related to plant-growth promotion. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 21548–21564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alori, E.T.; Glick, B.R.; Babalola, O.O. Microbial phosphorus solubilization and its potential for use in sustainable agriculture. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timofeeva, A.M.; Galyamova, M.R.; Sedykh, S.E. Bacterial siderophores: Classification, biosynthesis, perspectives of use in agriculture. Plants 2022, 11, 3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Nalwaya, S.; Jha, P.N. The draft genome sequence of the plant growth promoting rhizospheric bacterium Enterobacter cloacae SBP-8. Genom. Data 2017, 12, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, M.; Han, J.W.; Lee, C.; Choi, G.J.; Kim, H. Nematicidal and plant growth-promoting activity of Enterobacter asburiae HK169: Genome analysis provides insight into its biological activities. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 28, 968–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, R.T.; de Almeida, F.M.; Pappas, M.C.R.; Pappas, G.J.; Martins, K. Complete genome sequence of Pantoea stewartia RON18713 from Brazil nut tree phyllosphere reveals genes involved in plant growth promotion. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, M.A.; Sarkhosh, A.; Khan, N.; Balal, R.M.; Ali, S.; Rossi, L.; Gómez, C.; Mattson, N.; Nasim, W.; Garcia-Sanchez, F. Insights into the physiological and biochemical impacts of salt stress on plant growth and development. Agronomy 2020, 10, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Characteristics | Results | Characteristics | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oxidase | − | Hydrolysis of: | |
| Phenylalanine deaminase | − | Gelatin | − |
| Lysine decarboxylase | + | Starch | − |
| β-galactosidase | + | Acid production from: | |
| Arginine dihydrolase | + | Glucose | + |
| Urease | − | Lactose | − |
| Nitrate reduction | + | Fructose | + |
| H2S production | − | Mannitol | + |
| Indole production | − | Inositol | − |
| Voges-Proskauer test | + | Sorbitol | + |
| Methyl red test | − | Rhamnose | − |
| Utilization of: | Sucrose | − | |
| Malonate | + | Arabinose | − |
| Citrate | + | Melibiose | + |
| Treatment | Root Length (cm) | Shoot Length (cm) | Root Fresh Weight (mg) | Shoot Fresh Weight (mg) | Root Dry Weight (mg) | Shoot Dry Weight (mg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Control | 3.2 ± 0.3 b | 23.7 ± 2.0 b | 2.8 ± 0.3 c | 104.8 ± 6.1 b | 1.4 ± 0.3 b | 20.8 ± 3.8 b |
| D2 | 4.7 ± 0.3 a | 28.0 ± 2.4 a | 4.2 ± 0.4 a | 125.3 ± 8.2 a | 2.2 ± 0.1 a | 24.4 ± 2.3 a | |
| NaCl | Control | 2.1 ± 0.5 c | 18.2 ± 3.4 d | 1.1 ± 0.3 d | 55.3 ± 7.7 d | 0.8 ± 0.1 c | 13.1 ± 2.0 d |
| D2 | 3.3 ± 0.6 b | 21.8 ± 1.0 bc | 2.8 ± 0.3 c | 86.5 ± 7.2 c | 1.4 ± 0.1 b | 19.7 ± 1.3 bc | |
| Na2CO3 | Control | 2.7 ± 0.5 bc | 19.9 ± 2.7 cd | 2.5 ± 0.3 c | 92.8 ± 1.9 c | 0.8 ± 0.2 c | 16.7 ± 3.0 c |
| D2 | 3.4 ± 0.5 b | 26.8 ± 1.7 a | 3.7 ± 0.1 b | 103.3 ± 5.1 b | 2.0 ± 0.2 a | 21.8 ± 2.7 ab | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ning, Z.; Lin, K.; Gao, M.; Han, X.; Guan, Q.; Ji, X.; Yu, S.; Lu, L. Mitigation of Salt Stress in Rice by the Halotolerant Plant Growth-Promoting Bacterium Enterobacter asburiae D2. J. Xenobiot. 2024, 14, 333-349. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox14010021
Ning Z, Lin K, Gao M, Han X, Guan Q, Ji X, Yu S, Lu L. Mitigation of Salt Stress in Rice by the Halotolerant Plant Growth-Promoting Bacterium Enterobacter asburiae D2. Journal of Xenobiotics. 2024; 14(1):333-349. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox14010021
Chicago/Turabian StyleNing, Zican, Kexin Lin, Mengya Gao, Xiao Han, Qingjie Guan, Xiang Ji, Shuyu Yu, and Lei Lu. 2024. "Mitigation of Salt Stress in Rice by the Halotolerant Plant Growth-Promoting Bacterium Enterobacter asburiae D2" Journal of Xenobiotics 14, no. 1: 333-349. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox14010021
APA StyleNing, Z., Lin, K., Gao, M., Han, X., Guan, Q., Ji, X., Yu, S., & Lu, L. (2024). Mitigation of Salt Stress in Rice by the Halotolerant Plant Growth-Promoting Bacterium Enterobacter asburiae D2. Journal of Xenobiotics, 14(1), 333-349. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox14010021






