Irrigation Water Availability and Winter Wheat Abandonment in the North China Plain (NCP): Findings from a Case Study in Cangxian County of Hebei Province
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
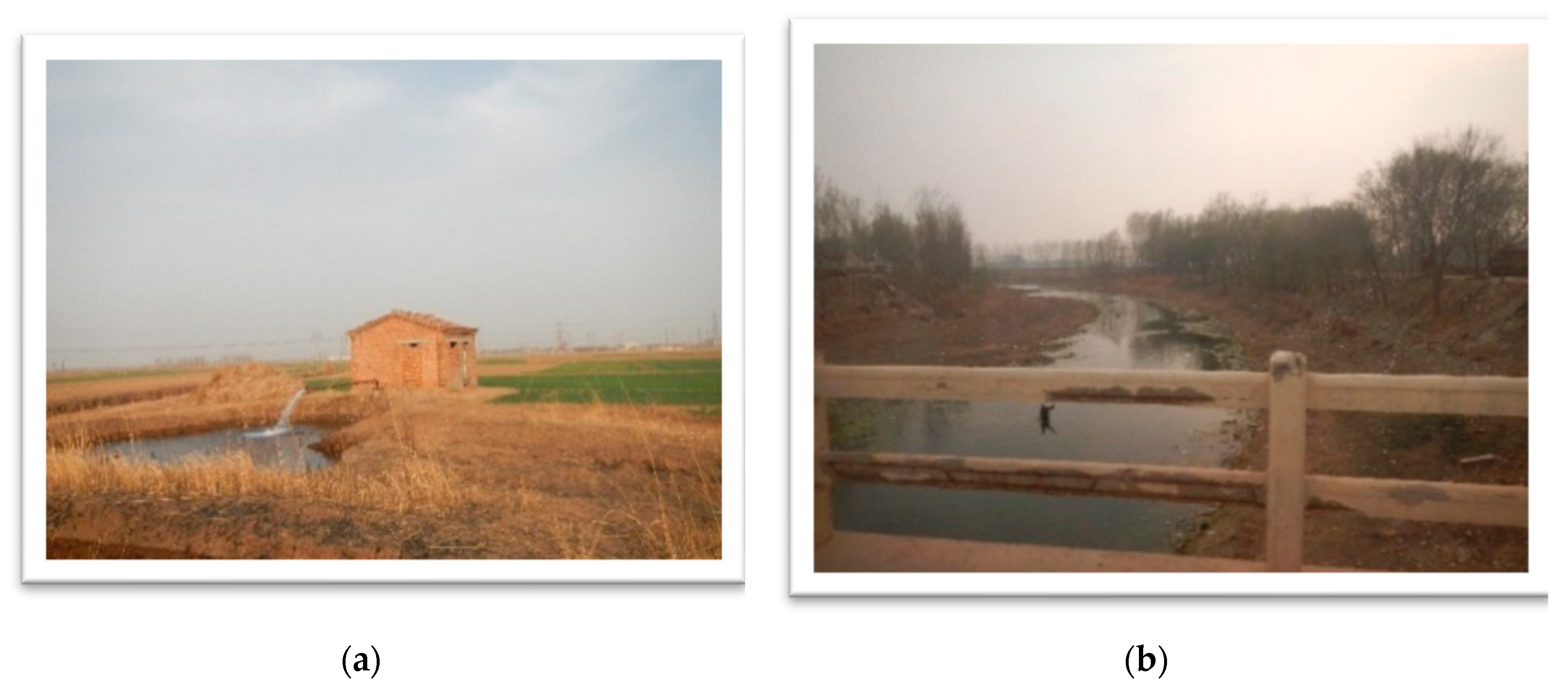
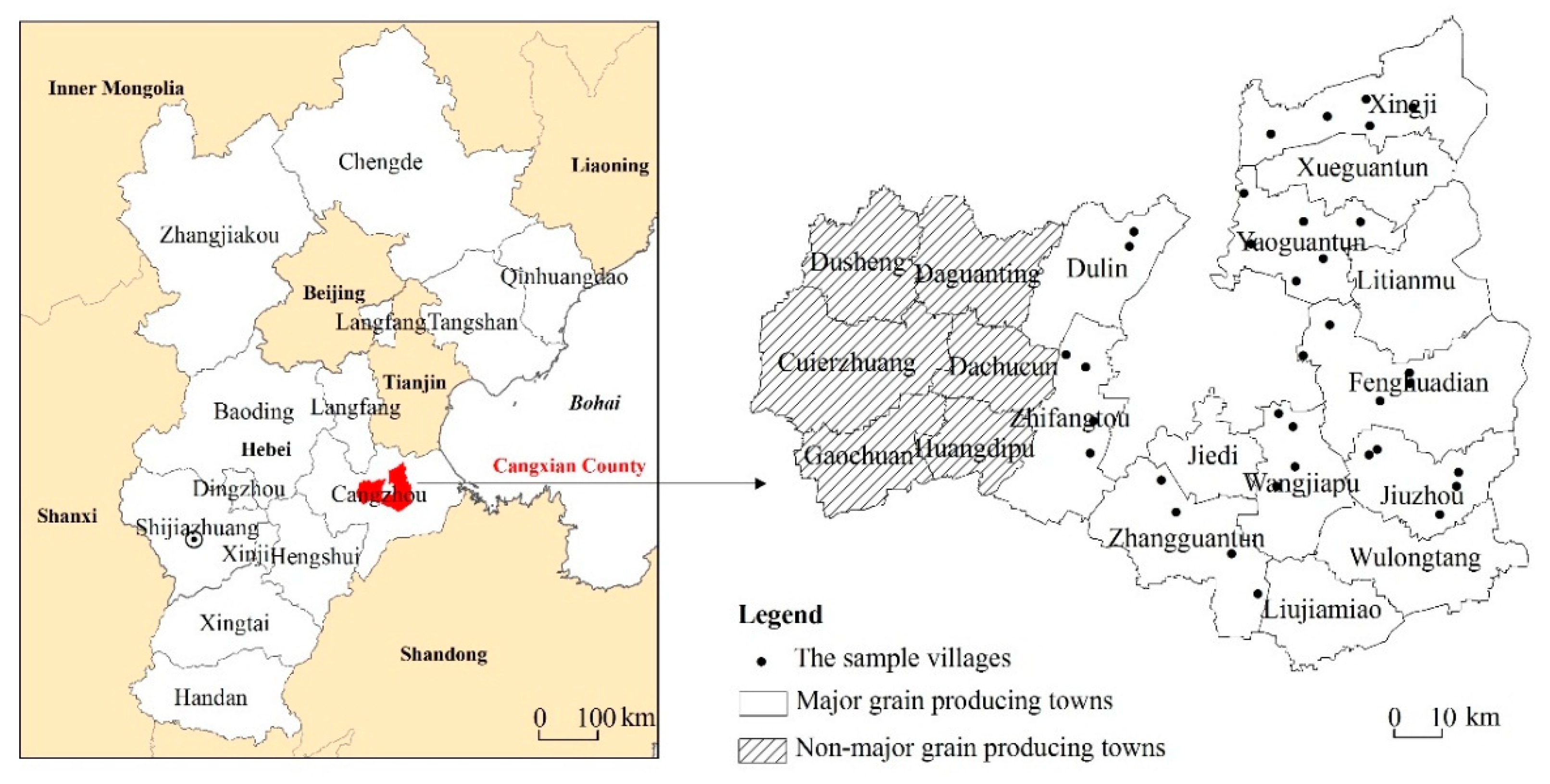
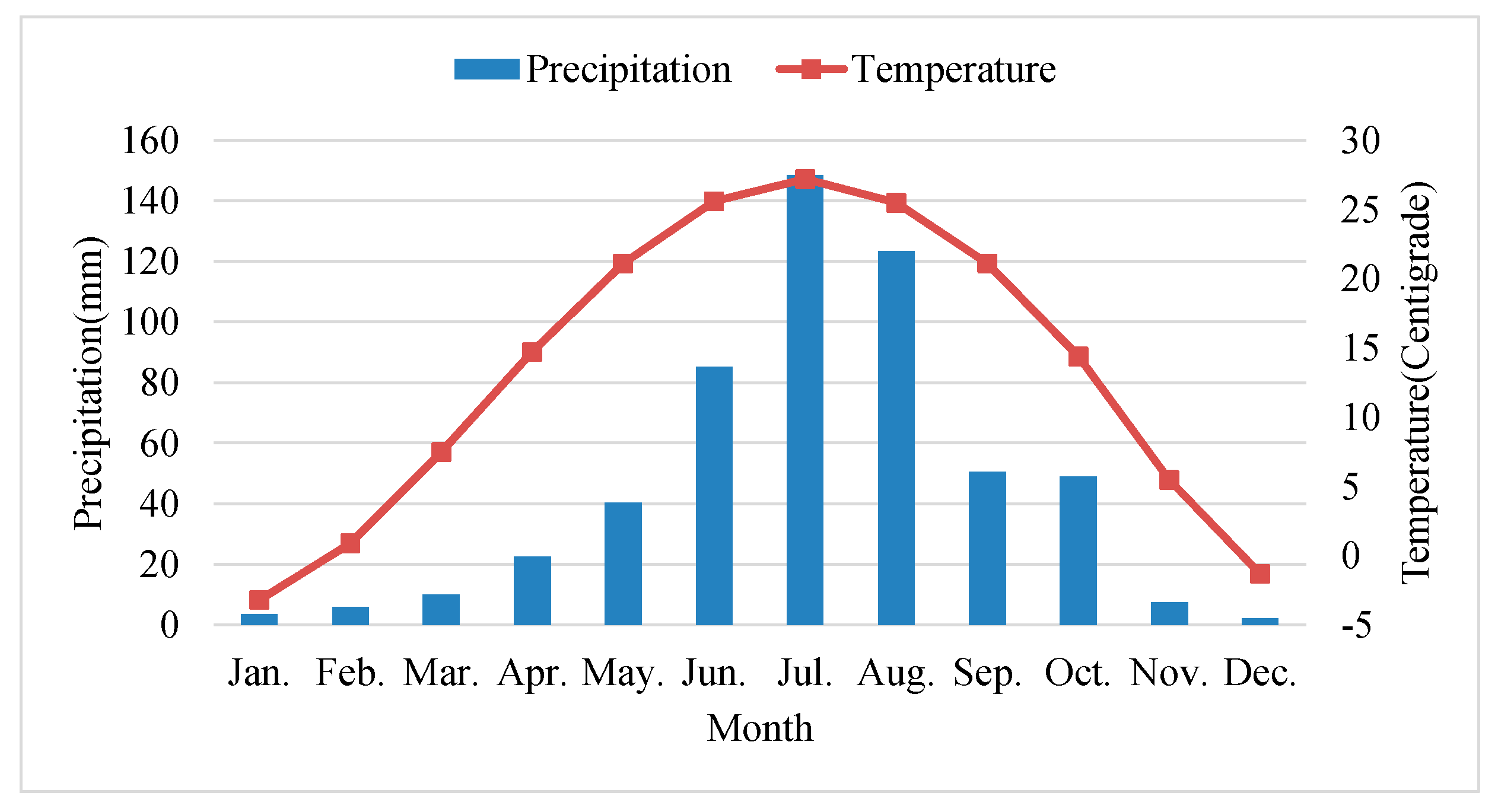
2.1. Study Area and Data Collection
2.2. IWA Assessment
2.3. Multilevel Modeling Specifications
3. Results
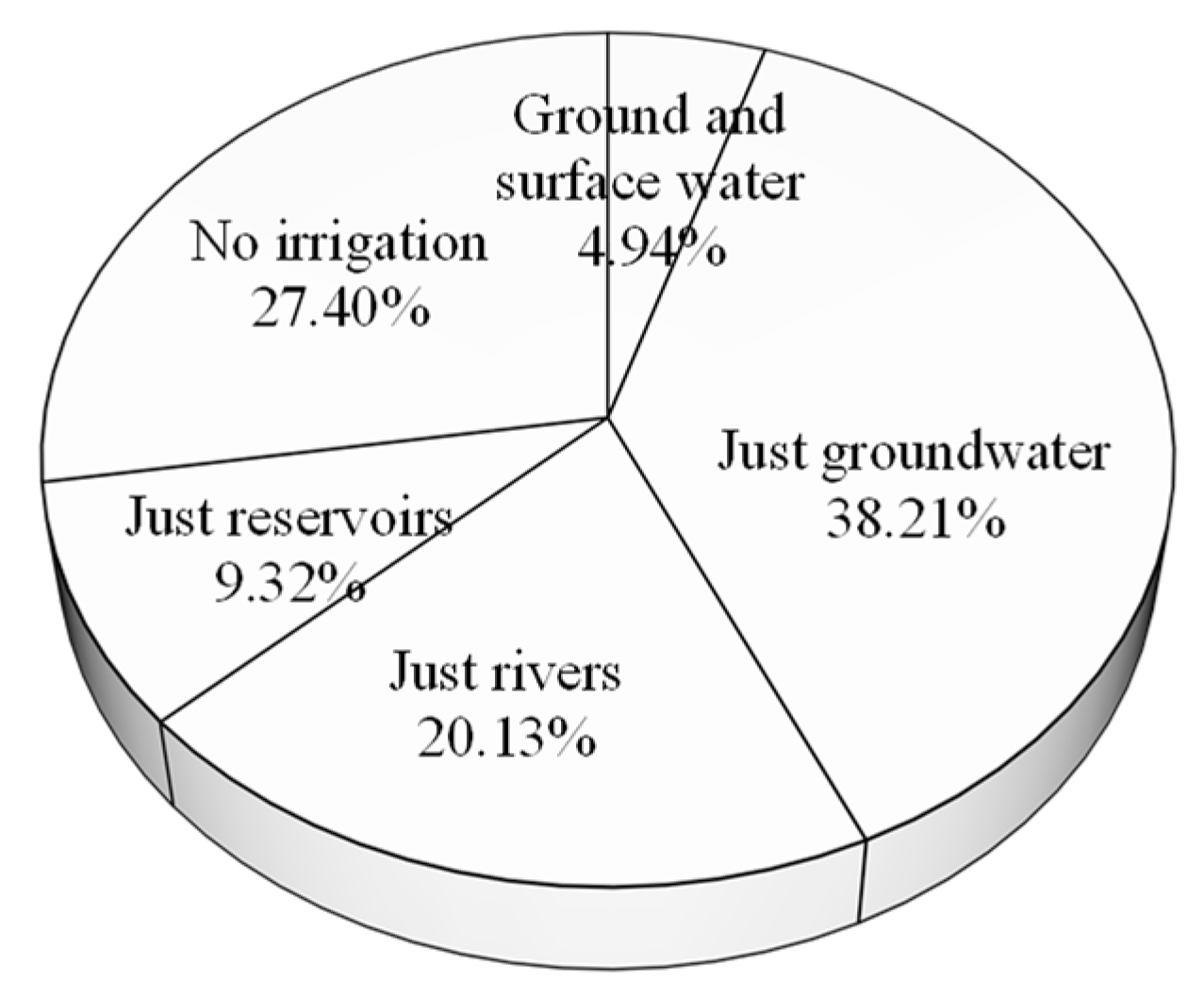
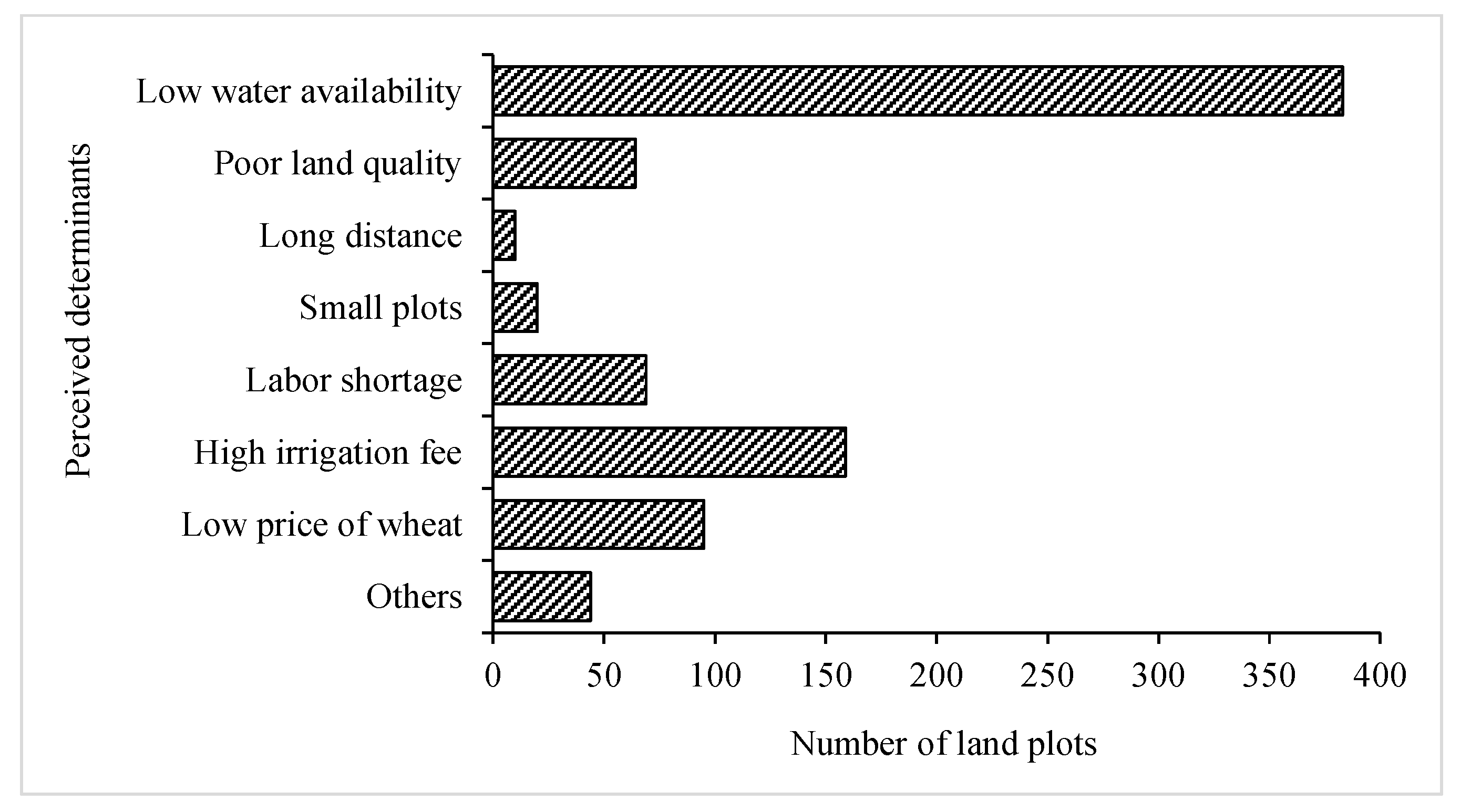
3.1. Background Information and the Determinants Perceived by Farmers for Winter Wheat Abandonment
3.2. Econometric Results from Multilevel Models
4. Discussion
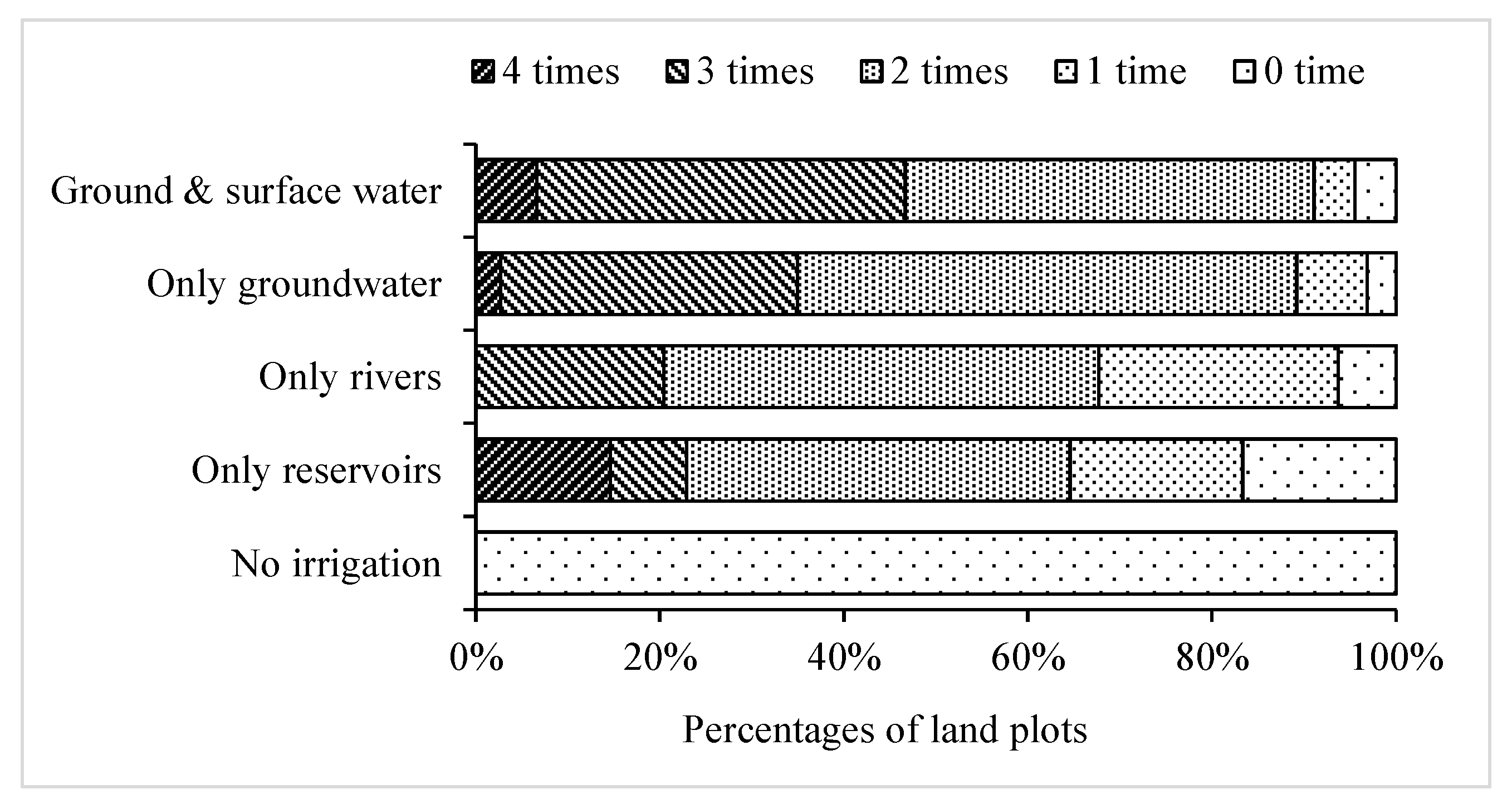
4.1. IWA and Irrigation Water Source
4.2. Policy Implications
4.3. The Main Shortcomings of This Study
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Variables | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 0.730 ** | 0.728 ** | 0.728 ** | 0.727 ** | 1.156 ** |
| Level 1 (Plot Level) | |||||
| Irrigation water source | |||||
| Ground and surface water | 1.163 ** | 1.212 ** | 1.272 ** | 1.190 ** | |
| Just groundwater | 1.132 ** | 1.168 ** | 1.214 ** | 1.118 ** | |
| Just rivers | 0.817 ** | 0.844 ** | 0.888 ** | 0.774 ** | |
| Just reservoirs | 0.985 ** | 1.027 ** | 1.062 ** | 0.943 ** | |
| (No irrigation) | |||||
| Soil quality | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.001 | ||
| Farming distance | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||
| Plot size | 0.223 | 0.223 | 0.195 | ||
| Level 2 (Household Level) | |||||
| Non-agricultural income per laborer | 0.003 | 0.008 | |||
| Agricultural labor availability | −0.011 | −0.009 | |||
| Age | −0.014 | −0.010 | |||
| Age squared | 0.000 | 0.000 | |||
| Education | 0.010 | 0.012 | |||
| Dependent ratio | −0.100 | −0.104 | |||
| Farming equipment | −0.051 | −0.059 | |||
| Land fragmentation | 0.015 | 0.014 | |||
| Level 3 (Village Level) | |||||
| Well depth | 0.000 | ||||
| Irrigation price | −0.084 | ||||
| Distance to county center | −0.033 | ||||
| Land rental rate | 0.271 | ||||
| Random effects | |||||
| Level 2 (Household Level) | |||||
| VAR (γ0) | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| ρh | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Level 3 (Village Level) | |||||
| VAR(μ00) | 0.036 ** | 0.037 ** | 0.037 ** | 0.036 ** | 0.007 ** |
| ρv | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.000 |
References
- Haney, N.; Cohen, S. Predicting 21st century global agricultural land use with a spatially and temporally explicit regression-based model. Appl. Geogr. 2015, 62, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vliet, J.; de Groot, H.L.F.; Rietveld, P.; Verburg, P.H. Manifestations and underlying drivers of agricultural land use change in Europe. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 133, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.J.; Ho, C.H.; Piao, S.; Kim, J.; Ciais, P.; Lee, Y.B.; Jhun, J.G.; Park, S.K. Effects of double cropping on summer climate of the North China Plain and neighbouring regions. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wang, H.; Cheng, Y.; Zheng, B.; Lu, Z. The impact of rural out-migration on arable land use intensity: Evidence from mountain areas in Guangdong, China. Land Use Policy 2016, 59, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakane, N.; van Wijk, M.T.; Langensiepen, M.; Becker, M. A quantitative model for understanding and exploring land use decisions by smallholder agrowetland households in rural areas of East Africa. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 197, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y.; Tang, C.Y.; Shen, Y.J.; Sakura, Y.; Kondoh, A.; Shimada, J. Use of water balance calculation and tritium to examine the dropdown of groundwater table in the piedmont of the North China Plain (NCP). Environ. Geol. 2003, 44, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Sun, Q.; Chen, X.; Cui, Z.; Yue, S.; Zhang, F.; Römheld, V. Alternative cropping systems for sustainable water and nitrogen use in the North China Plain. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 146, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Fischer, G.; Sun, L.; Tan, M.; Xin, L.; Liang, Z. Impact of the changing area sown to winter wheat on crop water footprint in the North China Plain. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 57, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W. Decoupling cultivated land loss by construction occupation from economic growth in Beijing. Habitat Int. 2014, 43, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Li, X.; Xie, H.; Lu, C. Urban land expansion and arable land loss in China—A case study of Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region. Land Use Policy 2005, 22, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.M.; Liu, D.W.; Zhang, Y.H. Water requirements and irrigation scheduling of spring maize using GIS and CropWat model in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2007, 17, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Xin, L. Impact of the shrinking winter wheat sown area on agricultural water consumption in the Hebei Plain. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 313–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, T.; Wada, Y.; Bierkens, M.F.P.; van Beek, L.P.H. Water balance of global aquifers revealed by groundwater footprint. Nature 2012, 488, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wiberg, D.; Zehnder, A.J.B.; Yang, H. Modeling the role of irrigation in winter wheat yield, crop water productivity, and production in China. Irrig. Sci. 2007, 26, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Inanaga, S.; Li, Z.; Eneji, A.E. Optimizing irrigation scheduling for winter wheat in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 76, 8–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Shen, Y.; Yu, Q.; Flerchinger, G.N.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, X. Effect of precipitation change on water balance and WUE of the winter wheat–summer maize rotation in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Kröbel, R.; Müller, T.; Römheld, V.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, F.; Chen, X. Optimization of yield and water-use of different cropping systems for sustainable groundwater use in North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 98, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grogan, D.S.; Zhang, F.; Prusevich, A.; Lammers, R.B.; Wisser, D.; Glidden, S.; Li, C.; Frolking, S. Quantifying the link between crop production and mined groundwater irrigation in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 511, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Chen, Y.; Pacenka, S.; Gao, W.; Ma, L.; Wang, G.; Yan, P.; Sui, P.; Steenhuis, T.S. Effect of diversified crop rotations on groundwater levels and crop water productivity in the North China Plain. J. Hydrol. 2015, 522, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.; Hayashi, S. Optimizing irrigation management for wheat to reduce groundwater depletion in the piedmont region of the Taihang Mountains in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 82, 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, H. Assessment of water supply reliability of different irrigation water sources. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2012, 22, 97–100. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Huang, J.; Chen, K. Information provision, policy support, and farmers’ adaptive responses against drought: An empirical study in the North China Plain. Ecol. Model. 2015, 318, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Scanlon, B.R.; Lei, H.; Yang, D.; Yang, F. Energy/water budgets and productivity of the typical croplands irrigated with groundwater and surface water in the North China Plain. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 181, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Zhou, X.; Wan, C.; Li, Y.; Kong, W. Land use changes to cash crop plantations: Crop types, multilevel determinants and policy implications. Land Use Policy 2016, 50, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Song, W. Determinants of cropland abandonment at the parcel, household and village levels in mountain areas of China: A multi-level analysis. Land Use Policy 2014, 41, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Deng, X.; Seto, K.C. Multi-level modeling of urban expansion and cultivated land conversion for urban hotspot counties in China. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 108, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snijders, T.A.B.; Boksker, R.J. (Eds.) Multilevel Analysis: An Introduction to Basic and Advanced Multilevel Modelling; Sage: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Raudenbush, S.W. (Ed.) Hierarchical Linear Models: Applications and Data Analysis Methods; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Moiwo, J.P.; Yang, Y.; Han, S.; Yang, Y. Agricultural water-saving and sustainable groundwater management in Shijiazhuang Irrigation District, North China Plain. J. Hydrol. 2010, 393, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aeschbach-Hertig, W.; Gleeson, T. Regional strategies for the accelerating global problem of groundwater depletion. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zehnder, A.J.B.; Yang, H. Global consumptive water use for crop production: The importance of green water and virtual water. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Radio Network. The Water Transfer Begins Today from the First Phase of the Middle Route of the Water Transfer Project. 2014. Available online: http://china.cnr.cn/ygxw/201412/t20141212_517092128.shtml (accessed on 12 December 2014). (In Chinese).
- Calow, R.C.; Howarth, S.E.; Wang, J. Irrigation Development and Water Rights Reform in China. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2009, 25, 227–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Q.; Hu, D.; Dou, M.; Zhang, X. Framework and core system of the most stringent water resource management system based on the concept of human-water harmony. Resour. Sci. 2014, 36, 906–912. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Jiang, C.; Lei, T.; Li, Y. Experimental study and simulation of water quality purification of urban surface runoff using non-vegetated bioswales. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 95, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overmars, K.P.; Verburg, P.H. Multilevel modelling of land use from field to village level in the Philippines. Agric. Syst. 2006, 89, 435–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variable | Definition | Mean | S.D. | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent Variable (Plot Level, n = 1416) | |||||
| Cropping system | 1: single-cropping system; 2: triple-cropping over 2 years; 3: double-cropping system | 2.00 | 0.91 | 1.00 | 3.00 |
| Explanatory Variables | |||||
| Level 1 (plot level, n = 1416) | |||||
| Irrigation water source | |||||
| Ground and surface water | Dummy variable (yes = 1; no = 0) | 0.05 | 0.22 | 0.00 | 1.00 |
| Just groundwater | Dummy variable (yes = 1; no = 0) | 0.38 | 0.49 | 0.00 | 1.00 |
| Just rivers | Dummy variable (yes = 1; no = 0) | 0.20 | 0.40 | 0.00 | 1.00 |
| Just reservoirs | Dummy variable (yes = 1; no = 0) | 0.09 | 0.29 | 0.00 | 1.00 |
| No irrigation | Reference group | ||||
| Soil quality | 1: good land; 2: relatively good land; 3: relatively poor land; 4: poor land | 2.05 | 0.96 | 1.00 | 4.00 |
| Farming distance | Distance from the land plot to household residence (km) | 0.92 | 0.65 | 0.05 | 4.00 |
| Plot size | Land plot area (ha) | 0.15 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 0.73 |
| Level 2 (household level, n = 350) | |||||
| Non-agricultural income per laborer | Total non-agricultural income divided by total non-agricultural laborers (103 yuan/capita) | 3.07 | 1.97 | 0.00 | 10.50 |
| Agricultural labor availability | Number of agricultural laborers per unit of farmland area (laborer/ha) | 4.50 | 3.24 | 0.60 | 24.52 |
| Age | Age of agricultural leader (years) | 57.00 | 10.55 | 24.00 | 87.00 |
| Educational level | Education status of the agricultural leader (1: illiterate; 2: primary school; 3: junior middle school; 4: senior middle school; 5: college or above) | 2.29 | 0.79 | 1.00 | 5.00 |
| Dependent ratio | Ratio of people older than 60 or younger than 16 to total laborers | 0.49 | 0.42 | 0.00 | 2.00 |
| Farming equipment | 1: tractors; 0: without tractors | 0.31 | 0.46 | 0.00 | 1.00 |
| Land fragmentation | Total number of plots divided by total farmland area (ha−1) | 7.15 | 2.82 | 2.50 | 20.27 |
| Level 3 (village level, n = 35) | |||||
| Well depth | Average depth of irrigation wells in the village (m) | 372.60 | 56.77 | 295.00 | 500.00 |
| Irrigation price | Electricity price for irrigation (yuan/kilowatt-hour) | 0.77 | 0.39 | 0.00 | 2.00 |
| Distance to county center | The nearest distance from the village to the county center (km) | 14.43 | 5.19 | 5.77 | 25.24 |
| Land rental rate | Ratio of leasing land to all cropland in the village | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.00 | 0.42 |
| Number | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cropping system | Single-cropping system/ha | 79.21 |
| Triple-cropping in 2 years/ha | 39.04 | |
| Double-cropping system/ha | 95.49 | |
| Others/ha | 6.39 | |
| Individuals | Male per capita | 924 |
| Female per capita | 858 | |
| Laborers | Agricultural laborer per capita | 637 |
| Part-time farming laborer per capita | 138 | |
| Off-farm laborer per capita | 674 | |
| Average number of land plots owned per household | 4.39 | |
| Average area of land owned per household/ha | 0.65 | |
| Average number of irrigation wells per village | 3.91 | |
| Average number of rivers per village | 0.89 | |
| Average number of reservoirs per village | 0.31 | |
| Variables | Single-Cropping System Versus Double-Cropping System | Two-Year Triple-Cropping Versus Double-Cropping System | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1A | Model 2A | Model 3A | Model 4A | Model 1B | Model 2B | Model 3B | Model 4B | |
| Fixed effects | ||||||||
| Intercept | −4.129 | −3.012 *** | −3.278 *** | −4.436 ** | −2.673 *** | −1.636 *** | −1.848 *** | −2.697 |
| Level 1 (Plot Level) | ||||||||
| Irrigation water source | ||||||||
| Ground and surface water | −7.798 *** | −7.138 *** | −7.479 *** | −7.536 *** | −3.163 *** | −2.836 *** | −3.262 *** | −3.282 *** |
| Just groundwater | −5.932 *** | −5.686 *** | −6.031 *** | −6.125 *** | −2.342 *** | −2.161 *** | −2.515 *** | −2.549 *** |
| Just rivers | −4.733 *** | −4.796 *** | −5.047 *** | −5.129 *** | −1.485 ** | −1.554 ** | −1.736 ** | −1.822 *** |
| Just reservoirs | −4.749 *** | −4.821 *** | −5.244 *** | −5.336 *** | −1.505 *** | −1.497 *** | −1.932 *** | −1.978 *** |
| (No irrigation) | ||||||||
| Soil quality | 0.781 *** | 0.814 *** | 0.818 *** | 0.357 *** | 0.377 ** | 0.379 ** | ||
| Farming distance | −0.052 | −0.073 | −0.068 | 0.529 *** | 0.525 *** | 0.528 ** | ||
| Plot size | −3.660 *** | −3.885 *** | −3.900 *** | −1.905 * | −2.115 * | −2.130 * | ||
| Level 2 (Household Level) | ||||||||
| Non-agricultural income per laborer | 0.092 * | 0.085 * | 0.036 | 0.049 | ||||
| Agricultural labor availability | −0.223 *** | −0.225 *** | −0.131 ** | −0.115 * | ||||
| Age | −0.263 *** | −0.285 *** | −0.327 ** | −0.308 ** | ||||
| Age squared | 0.002 *** | 0.003 *** | 0.003 ** | 0.003 ** | ||||
| Education | 0.305 ** | 0.324 ** | 0.126 | 0.081 | ||||
| Dependent ratio | 0.206 | 0.220 | −0.530 | −0.503 | ||||
| Farming equipment | −1.231 *** | −1.298 *** | −1.361 *** | −1.398 *** | ||||
| Land fragmentation | 0.167 *** | 0.175 *** | 0.015 | 0.041 | ||||
| Level 3 (Village Level) | ||||||||
| Well depth | −0.005 | −0.004 | ||||||
| Irrigation price | 2.730 *** | 1.834 ** | ||||||
| Distance to county center | 0.069 | 0.090 | ||||||
| Land rental rate | −3.085 | −10.799 ** | ||||||
| Random effects | ||||||||
| Level 2 (Household Level) | ||||||||
| VAR(γ0) | 0.430 a | 1.504 | 1.138 *** | 1.222 *** | 3.629 a,*** | 3.799 *** | 3.613 *** | 3.616 *** |
| ρh | 0.075 a | 0.183 | 0.149 | 0.186 | 0.399 a | 0.389 | 0.376 | 0.424 |
| Level 3 (Village Level) | ||||||||
| VAR(μ00) | 2.021 a,*** | 3.409 *** | 3.229 *** | 2.056 *** | 2.173 a,*** | 2.680 *** | 2.710 *** | 1.631 *** |
| ρv | 0.352 a | 0.416 | 0.422 | 0.313 | 0.239 a | 0.274 | 0.282 | 0.191 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Li, X. Irrigation Water Availability and Winter Wheat Abandonment in the North China Plain (NCP): Findings from a Case Study in Cangxian County of Hebei Province. Sustainability 2018, 10, 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10020354
Wang X, Li X. Irrigation Water Availability and Winter Wheat Abandonment in the North China Plain (NCP): Findings from a Case Study in Cangxian County of Hebei Province. Sustainability. 2018; 10(2):354. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10020354
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xue, and Xiubin Li. 2018. "Irrigation Water Availability and Winter Wheat Abandonment in the North China Plain (NCP): Findings from a Case Study in Cangxian County of Hebei Province" Sustainability 10, no. 2: 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10020354
APA StyleWang, X., & Li, X. (2018). Irrigation Water Availability and Winter Wheat Abandonment in the North China Plain (NCP): Findings from a Case Study in Cangxian County of Hebei Province. Sustainability, 10(2), 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10020354





