Analysis of Spatial-Temporal Characteristics of the PM2.5 Concentrations in Weifang City, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Materials and Methods
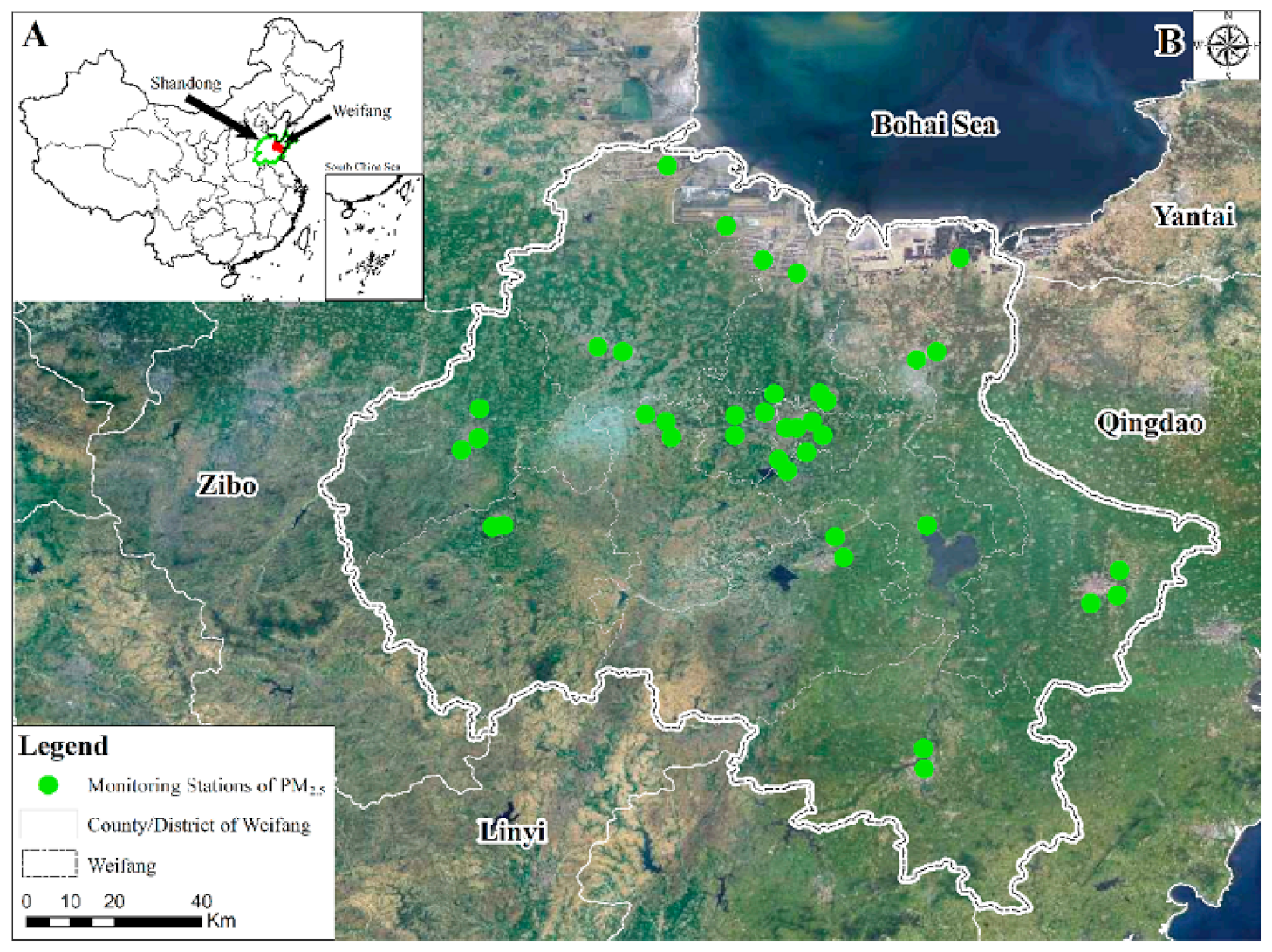
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Data Source and Processing
4. Results and Discussion
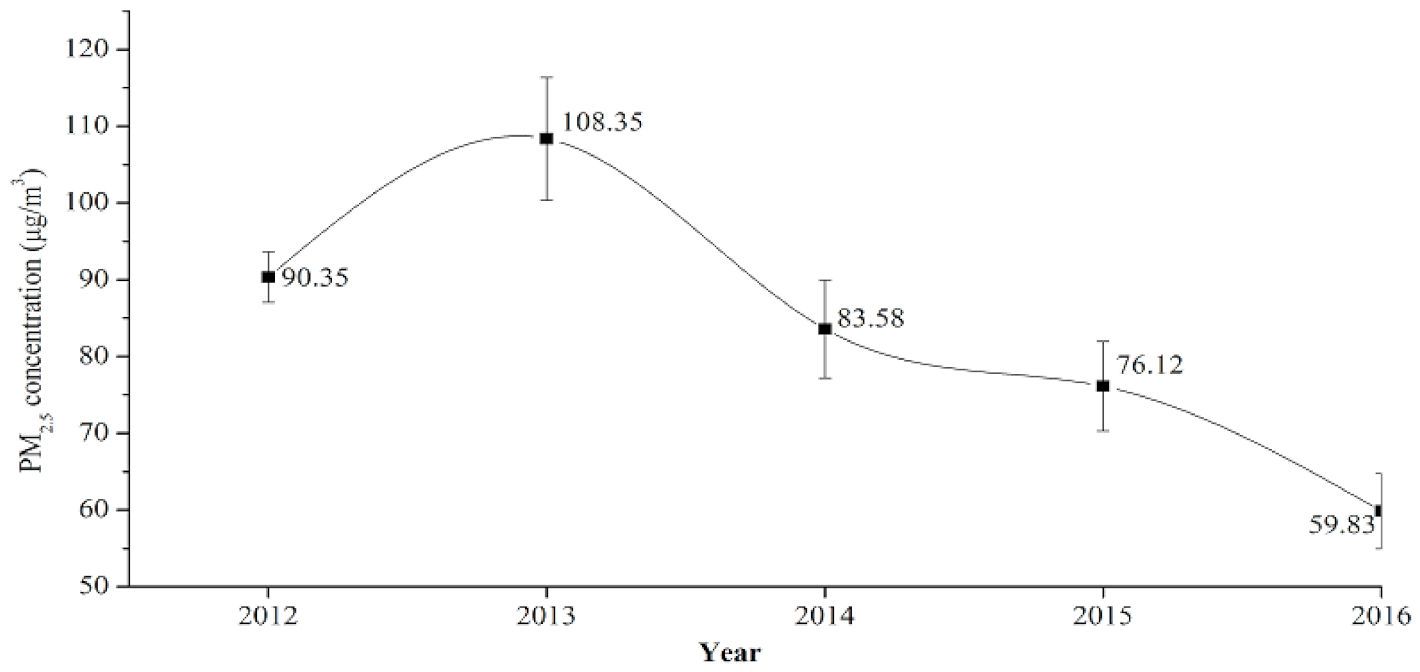
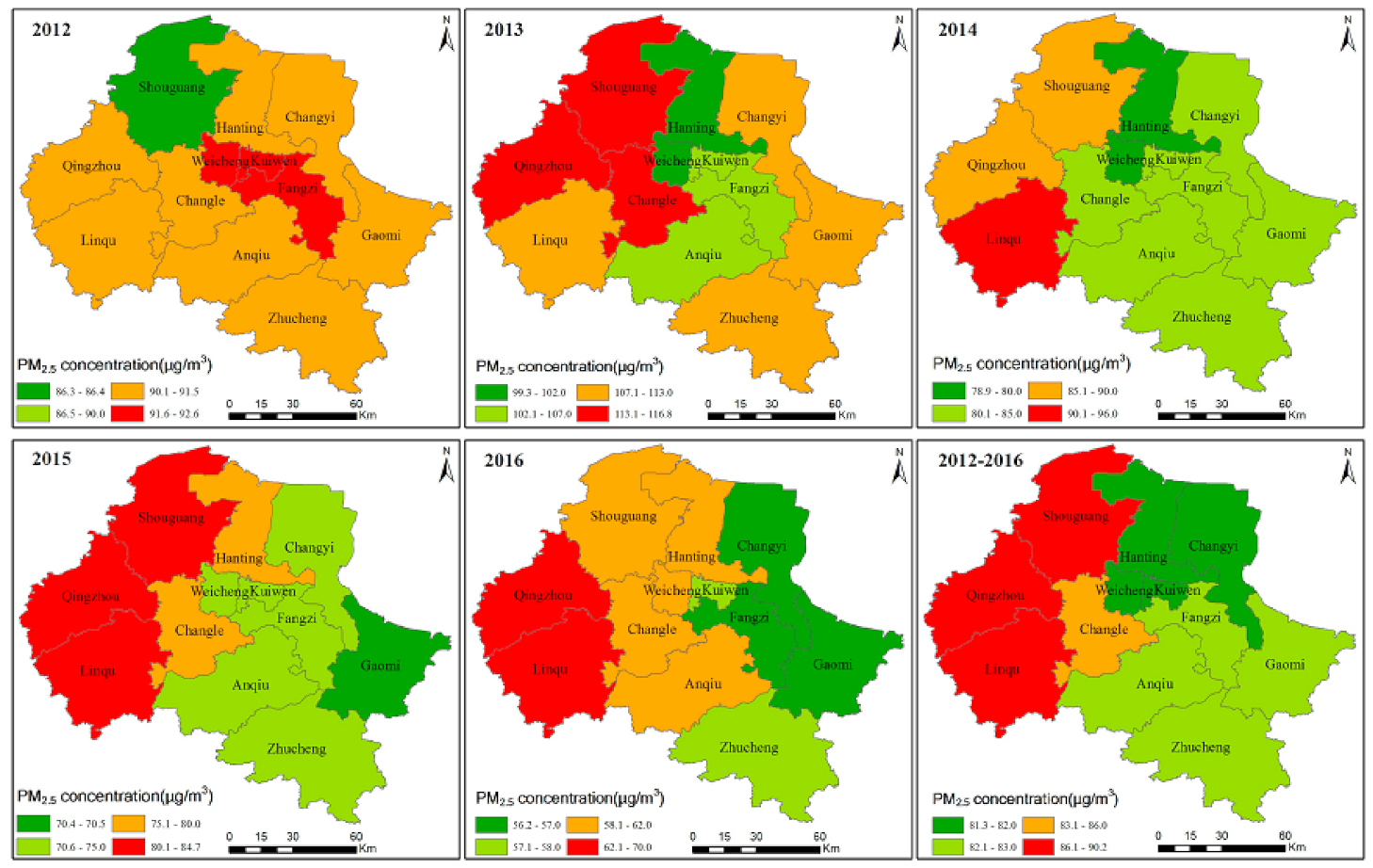
4.1. Annual Spatial-Temporal Characterization
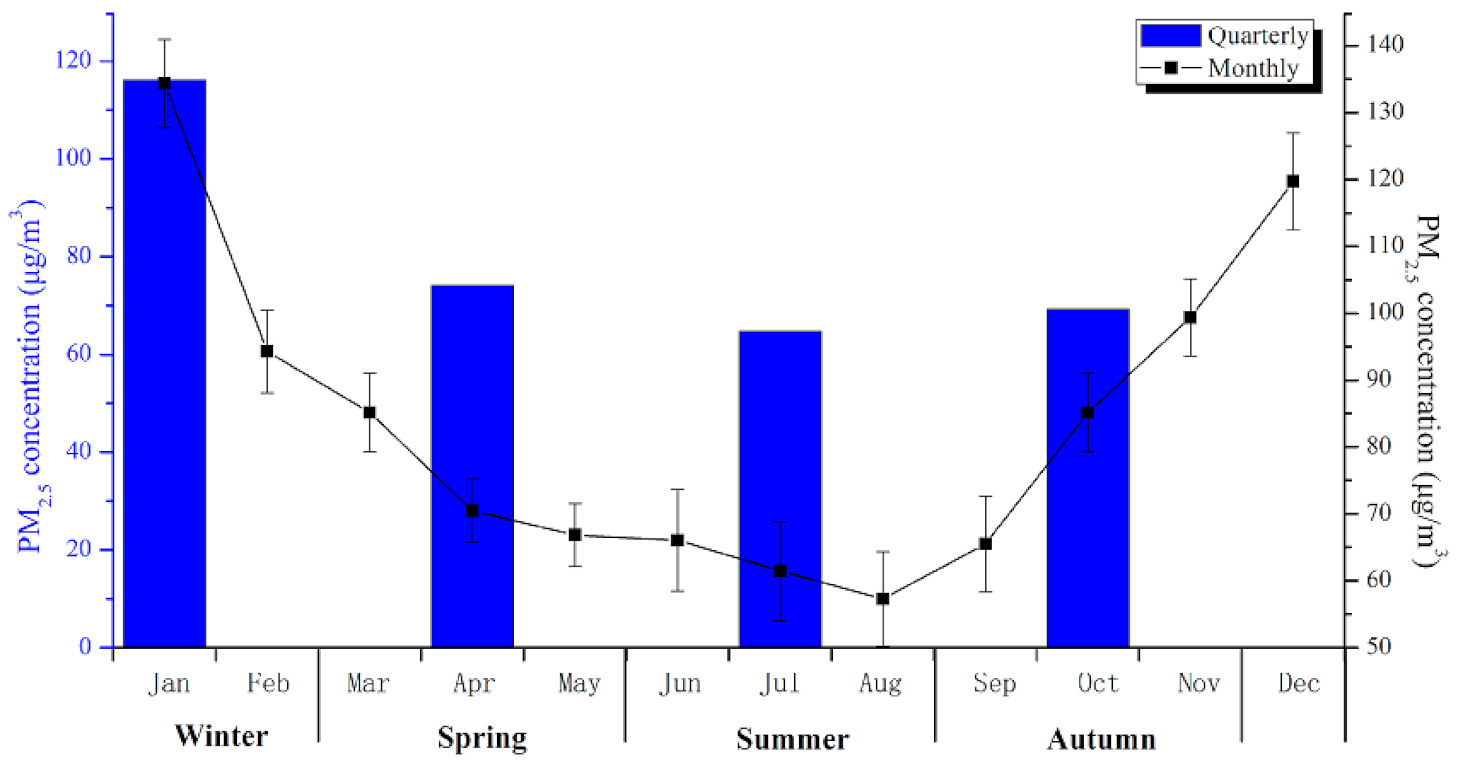
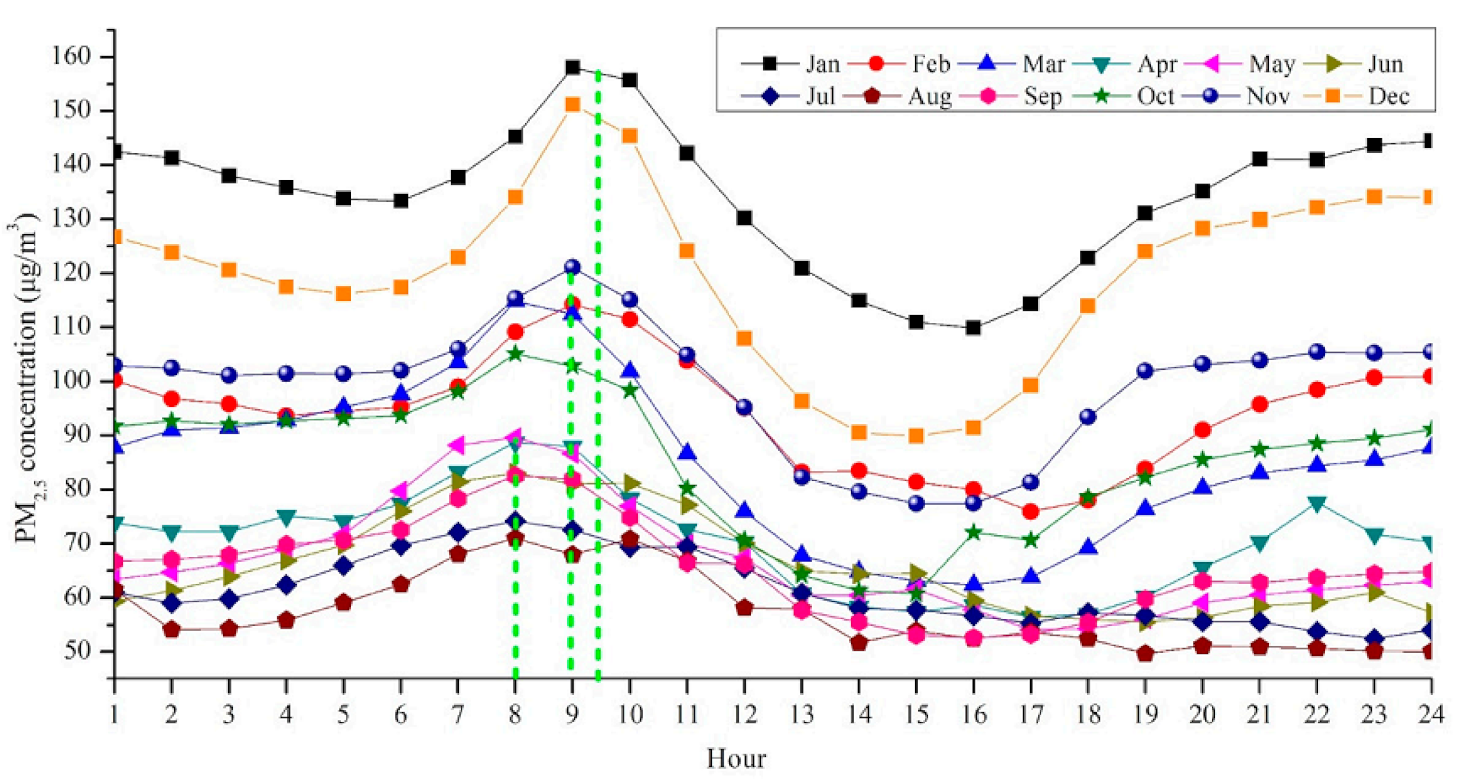
4.2. Seasonal and Monthly Spatial-Temporal Characterization
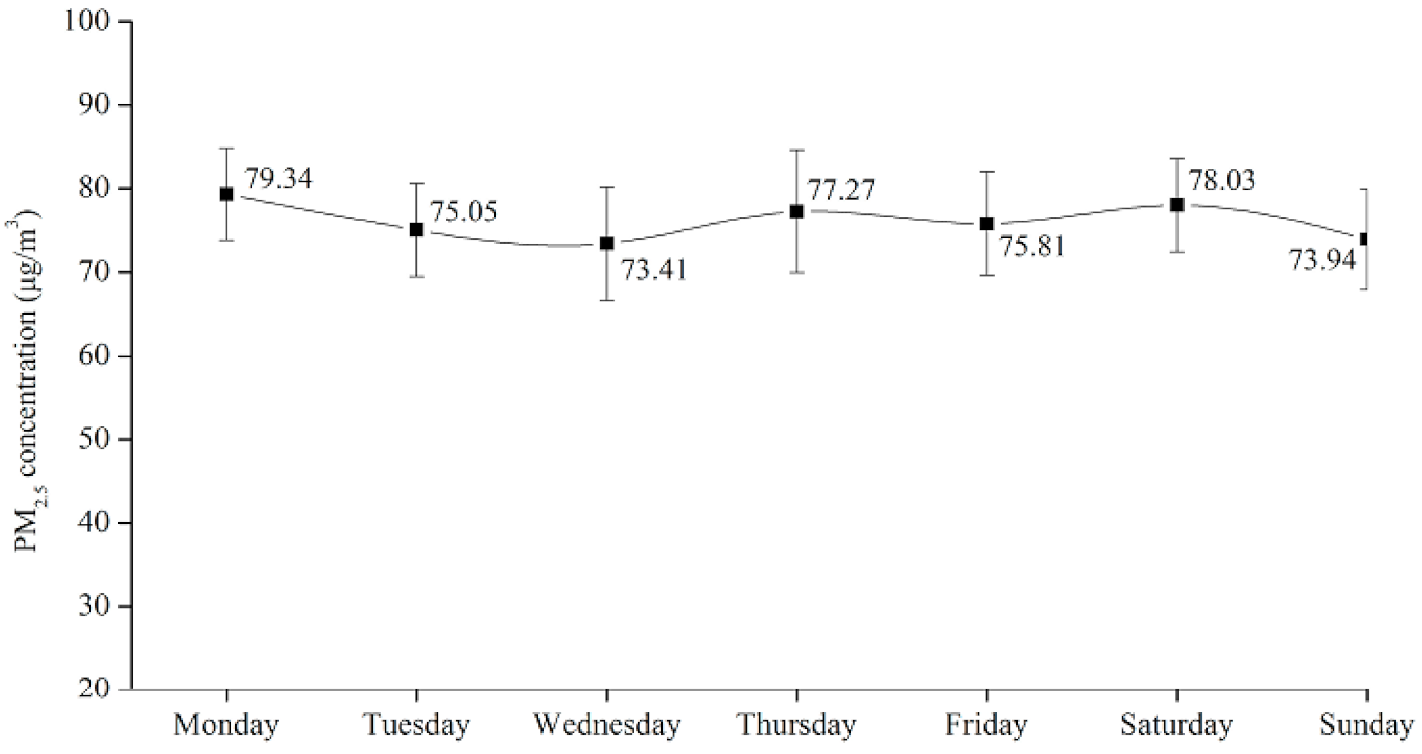
4.3. Daily Spatial-Temporal Characterization
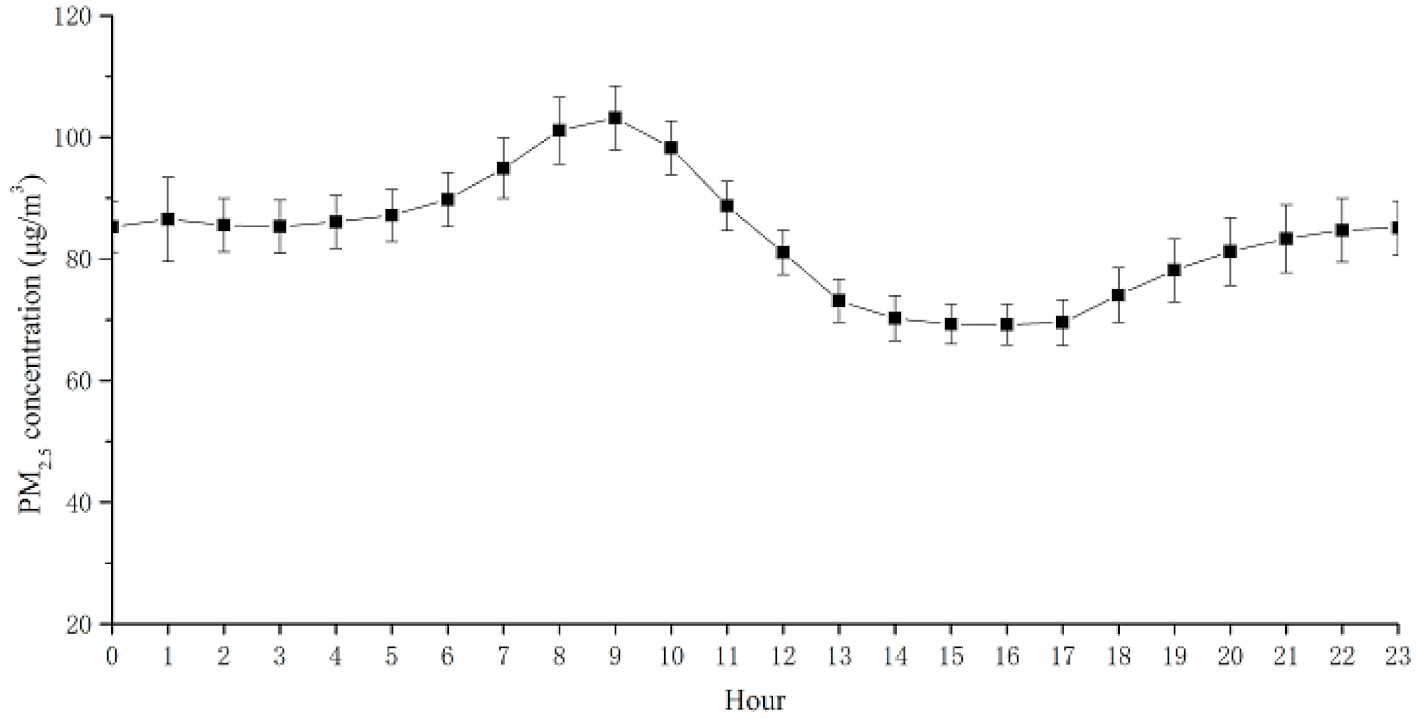
4.4. Hourly Spatial-Temporal Characterization
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhan, D.S.; Kwan, M.P.; Zhang, W.Z.; Yu, X.F.; Meng, B.; Liu, Q.Q. The driving factors of air quality index in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 197, 1342–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.X.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Hu, Y.F.; Yu, D. Spatial-temporal Characteristics of PM2.5 in Yangtze River Delta (YRD) Region Based on the Ground Monitoring Data from 2013 to 2015. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2016, 25, 813–821. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, L.; Lu, N.; Yue, X.F.; Du, J.; Yang, C.D. Comparison of Hourly PM2.5 Observations Between Urban and Suburban Areas in Beijing, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 12264–12276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Han, Y.Q.; Tang, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, T. Estimating adult mortality attributable to PM2.5 exposure in China with assimilated PM2.5 concentrations based on a ground monitoring network. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.Q.; Yu, X.N.; Zhu, B.; Zhu, J. Characteristics of aerosol extinction and low visibility in haze pollution. China Environ. Sci. 2016, 36, 1645–1653. [Google Scholar]
- Ming, L.L.; Jin, L.; Li, J.; Fu, P.Q.; Yang, W.Y.; Liu, D.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.F.; Li, X.D. PM2.5 in the Yangtze River Delta, China: Chemical compositions, seasonal Variations, and regional pollution events. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 233, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.H.; Chen, Y.F.; Guo, J.; Wang, G.Z.; Gong, Y.M. Spatial Concentration, Impact factors and Prevention-Control Measures of PM2.5 Pollution in China. Nat. Hazards 2017, 86, 393–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, G.; Heo, S.; Lee, J.T. Assessment of environmental injustice in Korea using synthetic air quality index and multiple indicators of socioeconomic status: A cross-sectional study. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2016, 66, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.Q.; Yuan, Q.Q.; Li, T.W.; Shen, H.F.; Zhang, L.P. The Relationships between PM2.5 and Meteorological Factors in China: Seasonal and Regional Variations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.S.; Geng, F.H.; Li, C.C.; Yang, S.Q.; Wang, Y.Y.; Mu, H.Z.; Zhou, G.Q.; Liu, X.B.; Gao, W.; et al. Long-term characteristics of satellite-based PM2.5 over East China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 612, 1417–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.Z.; Yang, H.L.; Peng, J.H.; Song, Y.R.; Sun, Q.; Li, Y. Estimating PM2.5 Concentrations in Xi’an City Using a Generalized Additive Model with Multi-Source Monitoring Data. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.F.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhang, W.Z. Exploring spatiotemporal patterns of PM2.5 in China based on ground-level observations for 190 cities. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, D.; Lei, Y.L.; Shi, Y.K.; Zhu, Q.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z.E. Evolution of the spatial-temporal pattern of PM2.5 concentrations in China—A case study from the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 183, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.L.; Wang, Y.G.; Ying, Q.; Zhang, H.L. Spatial and temporal variability of PM2.5 and PM10 over the North China Plain and the Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 95, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Cheng, T.H.; Gu, X.F.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Bao, F.W.; Shi, S.Y.; Xu, B.R.; Wang, W.N.; Zuo, X.; et al. Assessment of PM2.5 concentrations and exposure throughout China using ground observations. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 1024–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.M.; Han, X.L.; Li, X.; Yang, J.P.; Li, X.J. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Ground Monitored PM2.5 Concentrations in China in Recent Years. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.L.; Xue, J.J.; Zhang, J.Y. Analysis of Spatial-temporal distribution Characteristics and Main Cause of Air Pollution in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region in 2014. Meteorol. Environ. Sci. 2016, 39, 34–42. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, W.F.; Ma, Z.Y.; Ha, X.Z. Spatial-temporal patterns of PM2.5 concentrations for 338 Chinese Cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.M.; Fang, C.L.; Huang, J.J.; Zhu, X.D.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Z.B.; Zhang, Q. The Spatial Temporal Characteristics and influencing factors of air pollution in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration. J. Geog. Sci. 2018, 73, 177–191. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.L.; Hu, J.C.; Xu, B.H.; Hu, X.L.; Sun, P.; Han, W.L.; Gu, Z.P.; Yu, X.M.; Wu, M.H. Characteristics and seasonal variation of organic matter in PM2.5 at a regional background site of the Yangtze River Delta region, China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 123, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Sun, Q.M.; Zhong, M.Y.; Zuong, B.Q.; Luo, K.L. Temporal and Spatial Distribution Characteristics of PM2.5 in Chongqing Urban Areas. Environ. Sci. 2016, 37, 1219–1229. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, H.Y.; Liu, Y.L.; Li, T. Characteristics of Air Quality Index and its relationship with meteorological factors in key city of Heilongjiang Province. J. Nat. Resour. 2017, 32, 692–703. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.J.; Zhang, J.T.; Zhang, C.C.; Peng, X.J. Spatial and Temporal Variation of PM2.5 Concentrations Based on Thiessen Polygon and its Correlation with Land-use Patterns in Nanjing City. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 38, 293–298. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Q.; Fang, X.Y.; Wen, B.; Shan, A. Spatio-temporal variations of PM2.5 emission in China from 2005 to 2014. Chemosphere 2017, 183, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.P.; Hu, Y.M.; Liu, M.; Bu, R.C.; Chang, Y.; Li, C.L.; Wu, W. Characterization of air pollution index and its affecting factors in Industrial Urban Area in northeastern China. Technology 2015, 24, 1579–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.L.; Zhang, B.; Ai, N.S.; Liu, L.J. Wavelet analysis on SO2 pollution index changes of Shanghai in recent 10 years. Environ. Sci. 2009, 30, 2193–2198. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, G.; Qiao, Z.; Xu, X. Characteristic of particulate matter (PM10) and its relationship with meteorological factors during 2001-2012 in Beijing. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 192, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.S.; Matsunaga, T.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Zhao, A.; Li, Z.Q.; Gu, X.F. Long-term trends and spatial patterns of PM2.5-induced premature mortality in South and Southeast Asia from 1999 to 2014. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 1504–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.S.; Li, Y.T.; Chen, T.; Zhang, D.W.; Sun, F.; Pan, L.B. Spatial-Temporal characteristics of PM2.5 in Beijing in 2013. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2015, 70, 110–120. [Google Scholar]
- Nowak, D.J.; Hirabayashi, S.; Bodine, A.; Hoehn, R. Modeled PM2.5 removal by trees in ten U.S. cities and associated health effect. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.J.; Cao, H.; Chen, Y.; Wu, C.Z.; Hong, T.; Fan, H.L. Spatial and temporal characteristics of air quality and air pollutants in 2013 in Beijing. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 13996–14007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Qian, J.; Zhou, Y.X.; Guo, C.; Guo, Y. Spatial and temporal analysis of Air pollution Index and its timescale-dependent relationship with meteorological factor in Guangzhou, China, 2001–2011. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 190, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.H.; Zhou, Z.E.; Zhao, X.Y.; Yang, W.; Yin, B.H.; Bai, Z.P.; Ji, Y.Q. Source Apportionment of PM10 and PM2.5 in urban areas of Chongqing. Res. Environ. Sci. 2014, 27, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Dai, Z.; Liu, X. Analysis of Spatial-Temporal Characteristics of the PM2.5 Concentrations in Weifang City, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2960. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10092960
Li Y, Dai Z, Liu X. Analysis of Spatial-Temporal Characteristics of the PM2.5 Concentrations in Weifang City, China. Sustainability. 2018; 10(9):2960. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10092960
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yixiao, Zhaoxin Dai, and Xianlin Liu. 2018. "Analysis of Spatial-Temporal Characteristics of the PM2.5 Concentrations in Weifang City, China" Sustainability 10, no. 9: 2960. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10092960
APA StyleLi, Y., Dai, Z., & Liu, X. (2018). Analysis of Spatial-Temporal Characteristics of the PM2.5 Concentrations in Weifang City, China. Sustainability, 10(9), 2960. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10092960




