Increasing Weekend Effect in Ground-Level O3 in Metropolitan Areas of Mexico during 1988–2016
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Metropolitan Areas Description
2.2. O3 Measurements, Instrumentation, and Calibration
2.3. Calculation of the Weekend Effect (WE)
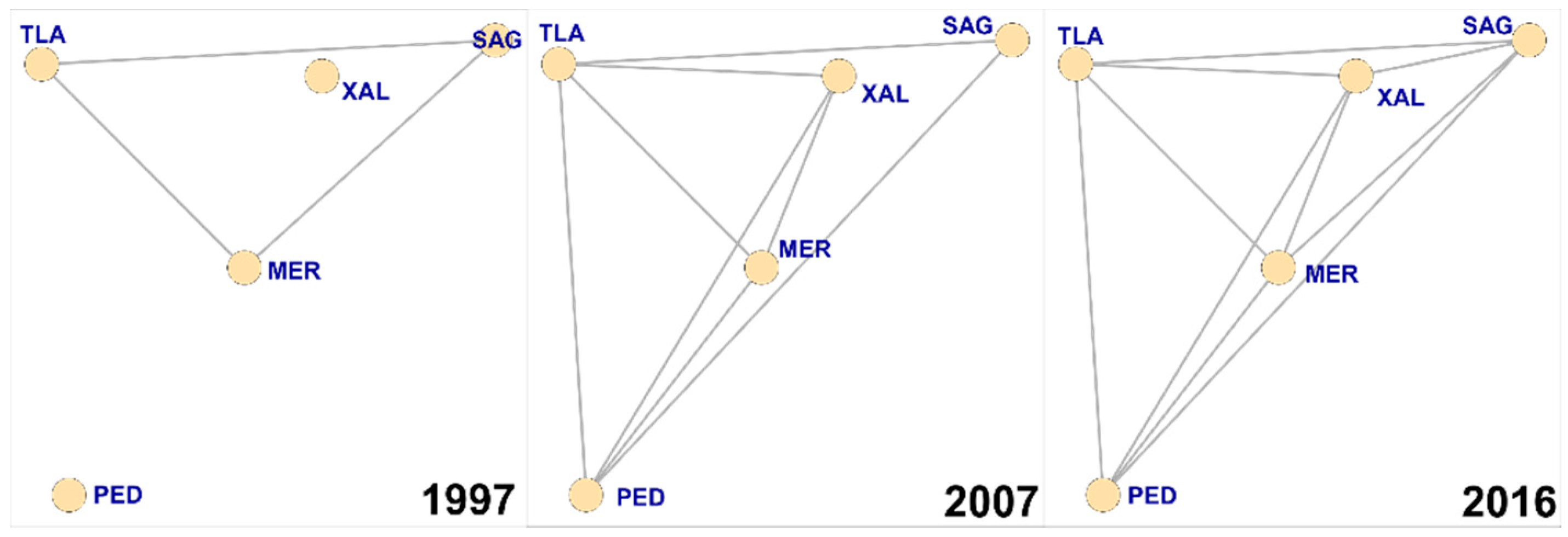
2.4. Spatial Interaction Calculation
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
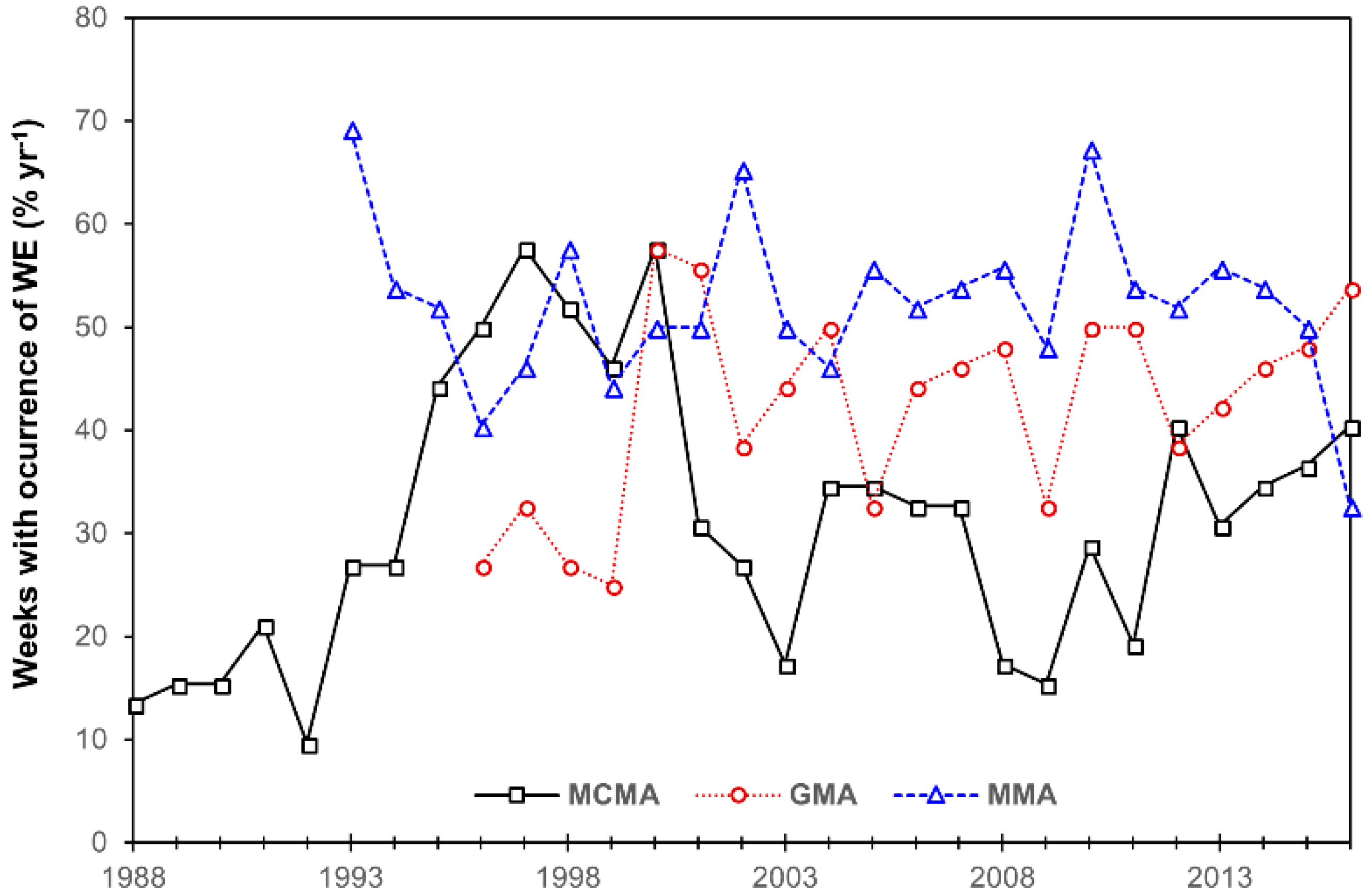
3.1. The WE Occurrence
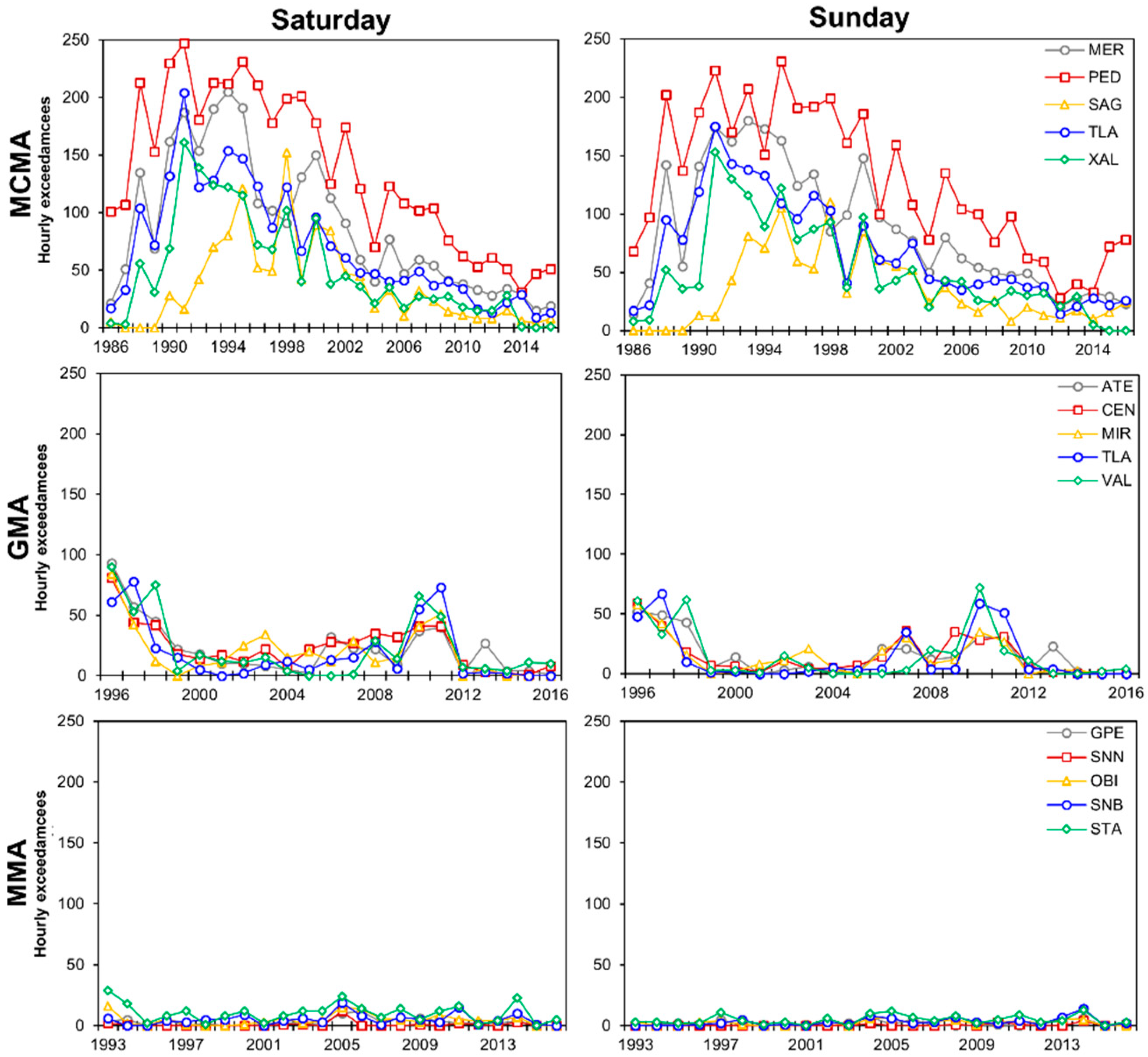
3.2. Weekend/Weekday Differences in the O3 Peaks
3.3. Long-Term Trends in the WE
3.4. Compliance with the Mexican Official Standards for O3
4. Discussion and Conclusions
4.1. Changes in the O3 Precursor Emissions
4.2. Long-Term and Spatial Distribution of the WE Occurrence
4.3. Policy Implications
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Monks, P.S.; Archibald, A.T.; Colette, A.; Cooper, O.; Coyle, M.; Derwent, R.; Fowler, D.; Granier, C.; Law, K.S.; Mills, G.E.; et al. Tropospheric ozone and its precursors from the urban to the global scale from air quality to short-lived climate forcer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 8889–8973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lelieveld, J.; Evans, J.S.; Fnais, M.; Giannadaki, D.; Pozzer, A. The contribution of outdoor air pollution sources to premature mortality on a global scale. Nature 2015, 525, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, D.S.; Dentener, F.J.; Schultz, M.G.; Ellingsen, K.; Van Noije, T.P.C.; Wild, O.; Zeng, G.; Amann, M.; Atherton, C.S.; Bell, N.; et al. Multimodel ensemble simulations of present-day and near-future tropospheric ozone. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D08301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2013. The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013; 1535p. [Google Scholar]
- Parrish, D.D.; Singh, H.B.; Molina, L.; Madronich, S. Air quality progress in North American megacities: A review. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 7015–7025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusede, S.E.; Cohen, R.C. On the observed response of ozone to NOx and VOC reactivity reductions in San Joaquin Valley California 1995–present. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 8323–8339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pugliese, S.C.; Murphy, J.G.; Geddes, J.A.; Wang, J.M. The impacts of precursor reduction and meteorology on ground-level ozone in the Greater Toronto Area. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 8197–8207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiménez, P.; Parra, R.; Gasso, S.; Baldasano, J.M. Modeling the ozone weekend effect in very complex terrains: A case study in the Northeastern Iberian Peninsula. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, W.S.; Graedel, T.E.; Kleiner, B.; Warner, J.L. Sunday and workday variations in photochemical air pollutants in New Jersey and New York. Science 1974, 186, 1037–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labron, F. A comparison of weekend and weekday ozone and hydrocarbon concentrations on the Baltimore-Washington Metropolitan Area. Atmos. Environ. 1975, 9, 861–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitt, S.B.; Chock, D.P. Weekday–weekend pollutant studies of the Los Angeles Basin. J. Air Pollut. Control Assoc. 1976, 26, 1091–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, G.T.; Kahlbaum, D.F.; Heuss, J.M. The vanishing ozone weekday/weekend effect. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2013, 63, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marr, L.C.; Harley, R.A. Spectral analysis of weekday–weekend differences in ambient ozone, nitrogen oxide, and non-methane hydrocarbon time series in California. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 2327–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riga-Karandinos, A.N.; Saitanis, C.; Arapis, G. Study of the weekday-weekend variation of air pollutants in a typical Mediterranean coastal town. Int. J. Environ. Poll. 2006, 27, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonse, S.R.; Brown, N.J.; Harley, R.A.; Jin, L. A process-analysis based study of the ozone weekend effect. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 7728–7736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seguel, R.J. Ozone weekend effect in Santiago, Chile. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 162, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, S.; Madronich, S.; Wu, F.; Olson, J.B.; Ramos, R.; Retama, A.; Muñoz, R. Weekly patterns of México City’s surface concentrations of CO, NOX, PM10 and O3 during 1986–2007. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 5313–5325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ProAire-MCMA (Programa para Mejorar la Calidad del Aire de la Zona Metropolitana del Valle de México 2002–2010), Mexico City Local Government-State of Mexico Government. 2011. Available online: http://www.aire.cdmx.gob.mx/descargas/publicaciones/flippingbook/proaire2011−2020/#p=1 (accessed on 28 August 2018).
- Jaimes, P.M.; Bravo, A.H.; Sosa, E.R.; Cureño, G.I.; Retama, H.A.; Granados, G.G.; Becerra, A.E. Surface ozone concentration trends in Mexico City Metropolitan Area. In Proceedings of the Air and Waste Management Association’s Annual Conference and Exhibition AWMA, San Antonio, TX, USA, 19–22 June 2012; Volume 3, pp. 2273–2284. [Google Scholar]
- Benítez-García, S.E.; Kanda, I.; Wakamatsu, S.; Okazaki, Y.; Kawano, M. Analysis of criteria air pollutant trends in three Mexican metropolitan areas. Atmosphere 2014, 5, 806–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Paniagua, I.Y.; Clemitshaw, K.C.; Mendoza, A. Observed trends in ground-level O3 in Monterrey, México, during 1993−2014: Comparison with Mexico City and Guadalajara. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco, E.; Retama, A. Ozone’s threat hits back Mexico city. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 31, 260–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Reynoso, A.; Jazcilevich, A.; Ruiz-Suarez, L.G.; Torres-Jardón, R.; Suárez Lastra, M.; Reséndiz Juárez, N.A. Ozone weekend effect analysis in México City. Atmósfera 2009, 22, 281–297. [Google Scholar]
- Sierra, A.; Vanoye, A.Y.; Mendoza, A. Ozone sensitivity to its precursor emissions in northeastern Mexico for a summer air pollution episode. J. Air Waste Manag. 2013, 63, 1221–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- INEGI (National Institute of Statistics and Geography): XIII Censo General de Población y Vivienda 2010, México. 2010. Available online: http://www.censo2010.org.mx/ (accessed on 22 August 2018).
- INE (Instituto Nacional de Ecologia). Cuarto Almanaque de datos y Tendencias de la Calidad del aire en 20 Ciudades Mexicanas 2000–2009; INE-SEMARNAT: México City, Mexico, 2011; 405p. [Google Scholar]
- SEDEMA (Secretaría del Medio Ambiente de la Ciudad de México). Inventario de Emisiones de la CDMX. Contaminantes Criterio, Tóxicos y de Efecto Invernadero. 2014. Available online: http://www.aire.cdmx.gob.mx/descargas/publicaciones/flippingbook/inventario-emisiones-cdmx2014−2/IE-CDMX−2014.pdf (accessed on 8 August 2018).
- ProAire-GDL (Programa para Mejorar la Calidad del Aire, Jalisco 2011–2020), SEMARNAT, Gobierno del estado de Jalisco). 2011. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/69282/ 13_ProAire_Jalisco.pdf (accessed on 24 August 2018).
- SEDEMA (Secretaría del Medio Ambiente—G.D.F.). Estimación de las concentraciones de ozono con la simulación de 13 medidas de control de emisiones, incluidas en el PROAIRE 2002−2010. 2005. Available online: http://www.aire.cdmx.gob.mx/descargas/publicaciones/gestion-ambiental-aire-memoria-documental−2001−2006/descargas/estimacion_ozono_proaire_dic2005.pdf (accessed on 10 August 2018).
- Davis, L.W. Saturday driving restrictions fail to improve air quality in Mexico City. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson-Palombo, C.M.; Miller, J.A.; Balling, R.C., Jr. Quantifying the ozone “weekend effect” at various locations in Phoenix, Arizona. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 7644–7658. [Google Scholar]
- Diestel, R. Graph Theory, Graduate Texts in Mathematics, 5th ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, German, 2017; ISBN 978-3-662-53621-6. [Google Scholar]
- Carslaw, D.C.; Ropkins, K. Openair—an R package for air quality data analysis. Environ. Model. Softw. 2012, 27–28, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013; ISBN 3-900051-07-0. Available online: www.R-project.org (accessed on 23 August 2018).
- Torres-Jardon, R.; García-Reynoso, J.A.; Jazcilevich, A.; Ruiz-Suárez, L.G.; Keener, T.C. Assessment of the ozone-nitrogen oxide-volatile organic compound sensitivity of Mexico City through an indicator-based approach: Measurements and numerical simulations comparison. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2009, 59, 1155–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, I.; Basaldud, R.; Magaña, M.; Retama, A.; Kubo, R.; Wakamatsu, S. Comparison of ozone production regimes between two Mexican cities: Guadalajara and Mexico City. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.O.; Niemeier, D.A. The impact of rush hour traffic and mix on the ozone weekend effect in southern California. Transp. Res. Transp. Environ. 2007, 12, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuss, J.M.; Kahlbaum, D.F.; Wolff, G.T. Weekday/weekend ozone differences: What can we learn from them? J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2003, 53, 772–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huryn, S.M.; Gough, W.A. Impact of urbanization on the ozone weekday/weekend effect in Southern Ontario, Canada. Urban Clim. 2014, 8, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SEMARNAT (Secretaría del Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales). Informe Nacional de Calidad del aire 2014. 2015. Available online: http://sinaica.inecc.gob.mx/archivo/informes/Informe2014.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2018).
- Cleveland, R.B.; Cleveland, W.S.; McRae, J.; Terpenning, I. STL: A seasonal-trend decomposition procedure based on Loess. J. Off. Stat. 1990, 6, 3–33. [Google Scholar]
- Salmi, T.; Määttä, A.; Anttila, P.; Ruoho-Airola, T.; Amnell, T. Detecting Trends of Annual Values of Atmospheric Pollutants by the Mann–Kendall Test and Sen’s Slope Estimates—the Excel Template Application MAKESENS; Publications on Air Quality Report code FMI-AQ−31; Finnish Meteorological Institute: Helsinki, Finland, 2002; Volume 31, pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- SEMARNAT (Secretaría del Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales). Inventario Nacional de Emisiones 2008, México, D.F. 2014. Available online: http://sinea.semarnat.gob.mx/sinae.php?steprep=5&process =UkVQT1JURUFET1I=&r=NC4gRnVlbnRlIHkgRW50aWRhZGVzIEZlZGVyYXRpdmFzIDIwMDgu (accessed on 5 August 2018).
- ProAire-MMA (Programa de Gestión para Mejorar la Calidad del Aire del Estado de Nuevo León 2016–2025), SEMARNAT, Gobierno del Estado de Nuevo León. 2016. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/250974/ProAire_Nuevo_Leon.pdf (accessed on 24 August 2018).
- Parrish, D.D. Critical evaluation of US on-road vehicle emission inventories. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 2288–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaimes-Palomera, M.; Retama, A.; Elias-Castro, G.; Neria-Hernández, A.; Rivera-Hernández, O.; Velasco, E. Nonmethane hydrocarbons in the atmosphere of Mexico City: Results of the 2012 ozone-season campaign. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 132, 258–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzón, J.P.; Huertas, J.I.; Magaña, M.; Huertas, M.E.; Cárdenas, B.; Watanabe, T.; Maeda, T.; Wakamatsu, S.; Blanco, S. Volatile organic compounds in the atmosphere of Mexico City. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 119, 415–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arriaga-Colina, J.L.; West, J.J.; Sosa, G.; Escalona, S.S.; Ordunez, R.M.; Cervantes, A.D.M. Measurements of VOCs in Mexico City (1992–2001) and evaluation of VOCs and CO in the emissions inventory. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 2523–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco, E.; Lamb, B.; Westberg, H.; Allwine, E.; Sosa, G.; Arriaga-Colina, J.L.; Jobson, B.T.; Alexander, M.L.; Prazeller, P.; Knighton, W.B.; et al. Distribution, magnitudes, reactivities, ratios and diurnal patterns of volatile organic compounds in the Valley of Mexico during the MCMA 2002 & 2003 field campaigns. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 329–353. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Carrillo-Torres, E.R.; Hernández-Paniagua, I.Y.; Mendoza, A. Use of combined observational-and model derived photochemical indicators to assess the O3-NOX-VOC system sensitivity in urban areas. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SEMARNAT (Secretaria del Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales). NOM−042 (Norma Oficial Mexicana NOM-042-ECOL-1993, que establece los límites máximos permisibles de emisión de hidrocarburos no quemados, monóxido de carbono, óxidos de nitrógeno y partículas suspendidas provenientes del escape de vehículos automotores nuevos en planta, así como de hidrocarburos evaporativos provenientes del sistema de combustible que usan gasolina, gas licuado de petróleo, gas natural y diésel de los mismos, con peso bruto vehicular que no exceda los 3,856 kilogramos). Diario Oficial de la Federación, 22 October 1993. [Google Scholar]





| Metropolitan Area | Site | Sat/Wed | Sun/Wed | Sat–Sun/Tue–Thu | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Average | Max | Min | Average | Max | Min | Average | Max | ||
| MCMA | MER | −188 | 3 | 186 | −191 | −2 | 180 | −73 | 1 | 46 |
| 1986–2016 | PED | −234 | 1 | 205 | −235 | −10 | 176 | −106 | 0 | 65 |
| SAG | −118 | 2 | 123 | −156 | 0 | 133 | −44 | 1 | 45 | |
| TLA | −232 | 2 | 190 | −213 | −1 | 148 | −53 | 1 | 51 | |
| XAL | −192 | 3 | 140 | −154 | 3 | 164 | −48 | 2 | 52 | |
| GMA | ATE | −129 | 0 | 131 | −114 | −4 | 116 | −56 | 0 | 56 |
| 1996–2016 | CEN | −143 | 3 | 169 | −166 | −3 | 106 | −46 | 1 | 54 |
| MIR | −145 | 1 | 125 | −145 | −2 | 105 | −59 | 0 | 57 | |
| TLA | −120 | 2 | 157 | −145 | −2 | 114 | −53 | 1 | 58 | |
| VAL | −190 | 1 | 144 | −169 | −4 | 143 | −46 | 1 | 54 | |
| MMA | GPE | −106 | −1 | 88 | −134 | −2 | 102 | −45 | 0 | 44 |
| 1993–2016 | SNN | −100 | −1 | 86 | −104 | −2 | 89 | −34 | 0 | 34 |
| OBI | −115 | 0 | 102 | −136 | 0 | 133 | −45 | 2 | 52 | |
| SNB | −104 | −1 | 113 | −109 | −2 | 84 | −47 | 0 | 45 | |
| STA | −116 | −1 | 125 | −143 | −3 | 138 | −41 | 1 | 45 | |
| Metropolitan Area | Site | Rates of Change | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sat/Wed | Sun/Wed | Sat–Sun/Tue–Thu | ||||||||
| ppb yr−1 | % yr−1 | p | ppb yr−1 | % yr−1 | p | ppb yr−1 | % yr−1 | p | ||
| MCMA | MER | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.64 | 0.06 | *** | 0.11 | 0.01 | ||
| PED | 0.42 | 0.04 | * | 1.29 | 0.13 | *** | 0.38 | 0.04 | *** | |
| SAG | −0.05 | −0.01 | 0.42 | 0.04 | + | 0.08 | 0.01 | |||
| TLA | −0.05 | 0.02 | 0.34 | 0.04 | * | 0.09 | 0.01 | |||
| XAL | −0.07 | −0.01 | 0.33 | 0.03 | * | 0.07 | 0.01 | |||
| GMA | ATE | −0.15 | −0.02 | 0.32 | 0.03 | + | 0.07 | 0.01 | ||
| CEN | −0.44 | −0.04 | 0.41 | 0.04 | + | 0.05 | 0.01 | |||
| MIR | −0.16 | −0.02 | −0.08 | −0.01 | 0.10 | 0.01 | ||||
| TLA | −0.37 | −0.03 | 0.26 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.01 | ||||
| VAL | −0.23 | −0.02 | 0.48 | 0.05 | * | −0.09 | −0.01 | |||
| MMA | GPE | −0.08 | −0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.00 | |||
| SNN | −0.17 | −0.03 | + | −0.11 | −0.02 | −0.08 | 0.01 | |||
| OBI | −0.12 | −0.01 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | ||||
| SNB | −0.16 | −0.03 | −0.08 | −0.01 | −0.04 | −0.01 | ||||
| STA | −0.05 | −0.01 | 0.33 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||||
| Metropolitan Area | Site | Rates of Change | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wednesday | Saturday | Sunday | Overall | ||||||||||
| ppb yr−1 | % yr−1 | p | ppb yr−1 | % yr−1 | p | ppb yr−1 | % yr−1 | p | ppb yr−1 | % yr−1 | p | ||
| MCMA | MER | −0.1 | −0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | −0.3 | −0.3 | * | −1.0 | −1.0 | *** | ||
| 1988–2016 | PED | −0.6 | −0.8 | *** | −0.4 | −0.7 | *** | −0.3 | −0.7 | *** | −1.0 | −1.7 | *** |
| SAG | 1.0 | 1.1 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | ** | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||
| TLA | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.6 | *** | 0.2 | 0.3 | * | −0.2 | −0.3 | * | ||
| XAL | −1.3 | 0.7 | *** | −0.2 | −0.1 | −1.0 | −0.9 | *** | −1.1 | −1.1 | *** | ||
| GMA | ATE | −1.1 | −0.9 | + | −1.6 | −1.4 | * | 0.0 | 0.0 | −0.9 | −1.4 | ||
| 1996–2016 | CEN | −2.8 | −2.0 | * | −3.1 | −2.2 | −2.2 | −2.0 | * | −2.0 | −2.1 | * | |
| MIR | 1.5 | 1.6 | * | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 0.1 | ||||
| TLA | −1.2 | −0.9 | −1.5 | −1.2 | −0.8 | −0.9 | −1.0 | −1.3 | |||||
| VAL | −3.2 | −2.7 | *** | −1.7 | −1.9 | * | −1.1 | −1.8 | *** | −1.6 | −2.6 | *** | |
| MMA | GPE | 0.6 | 1.6 | * | 0.4 | 1.1 | * | 0.4 | 1.1 | * | 0.2 | 0.1 | + |
| 1996–2016 | SNN | 1.1 | 3.3 | ** | 0.8 | 2.9 | ** | 0.8 | 2.8 | * | 0.4 | 1.8 | *** |
| OBI | −1.5 | −1.9 | ** | −0.9 | −1.6 | * | −0.9 | −1.6 | * | −0.9 | −1.8 | *** | |
| SNB | 1.2 | 6.6 | + | 0.9 | 5.6 | 0.9 | 5.6 | 0.5 | 3.4 | ||||
| STA | 1.5 | 3.5 | ** | 0.8 | 2.2 | + | 0.8 | 2.2 | + | 0.3 | 0.8 | ||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernández-Paniagua, I.Y.; Lopez-Farias, R.; Piña-Mondragón, J.J.; Pichardo-Corpus, J.A.; Delgadillo-Ruiz, O.; Flores-Torres, A.; García-Reynoso, A.; Ruiz-Suárez, L.G.; Mendoza, A. Increasing Weekend Effect in Ground-Level O3 in Metropolitan Areas of Mexico during 1988–2016. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3330. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10093330
Hernández-Paniagua IY, Lopez-Farias R, Piña-Mondragón JJ, Pichardo-Corpus JA, Delgadillo-Ruiz O, Flores-Torres A, García-Reynoso A, Ruiz-Suárez LG, Mendoza A. Increasing Weekend Effect in Ground-Level O3 in Metropolitan Areas of Mexico during 1988–2016. Sustainability. 2018; 10(9):3330. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10093330
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernández-Paniagua, Iván Y., Rodrigo Lopez-Farias, José J. Piña-Mondragón, Juan A. Pichardo-Corpus, Olivia Delgadillo-Ruiz, Arnoldo Flores-Torres, Agustín García-Reynoso, Luis G. Ruiz-Suárez, and Alberto Mendoza. 2018. "Increasing Weekend Effect in Ground-Level O3 in Metropolitan Areas of Mexico during 1988–2016" Sustainability 10, no. 9: 3330. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10093330
APA StyleHernández-Paniagua, I. Y., Lopez-Farias, R., Piña-Mondragón, J. J., Pichardo-Corpus, J. A., Delgadillo-Ruiz, O., Flores-Torres, A., García-Reynoso, A., Ruiz-Suárez, L. G., & Mendoza, A. (2018). Increasing Weekend Effect in Ground-Level O3 in Metropolitan Areas of Mexico during 1988–2016. Sustainability, 10(9), 3330. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10093330







