Inertia Provision and Small Signal Stability Analysis of a Wind-Power Generation System Using Phase-Locked Synchronized Equation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
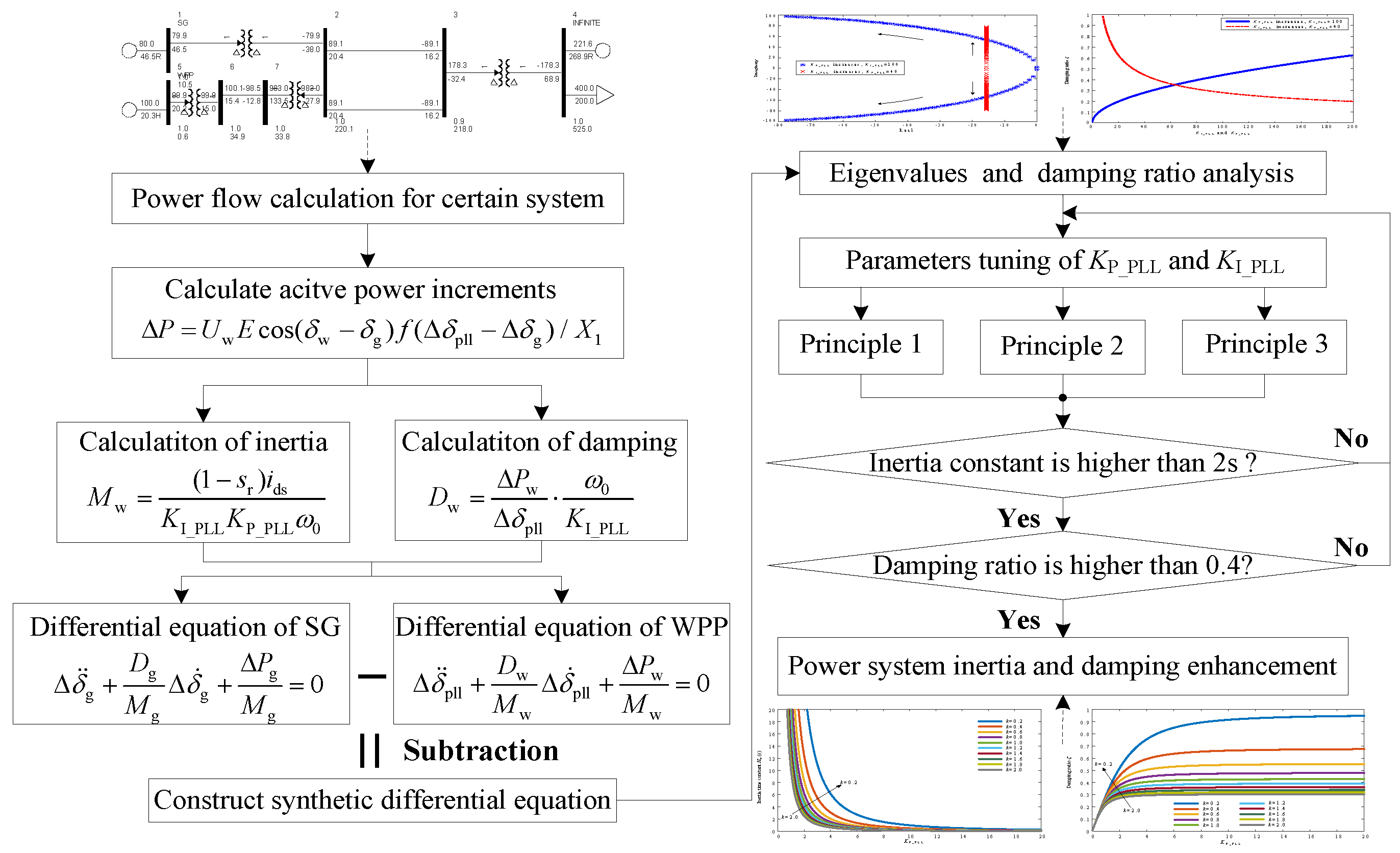
2. Materials and Methods
| KP_PLL, KI_PLL | Proportional plus integral (PI) control parameters of PLL. |
| uds, uqs | Stator voltage in the dq reference frame. |
| ids, iqs | Stator current in the dq reference frame. |
| δpll, ωpll | Phase angle of PLL, phase-locked angular velocity. |
| δg, ωg | Power angle of SG, rotor angular velocity of SG. |
| δw, θin | Phase angle of stator voltage, relative phase angle between Uw and E. |
| Uw, E, U | Stator voltage vector, internal voltage vector, voltage of infinite bus. |
| Hw, Hg | Inertia time constant of wind power plant (WPP), inertia time constant of SG. |
| Dw, Dg | Damping coefficient of WPP, damping coefficient of SG. |
| Pw, Pg | Active power output of WPP, active power output of SG. |
| sr, ω0 | Slip ratio of DFIG, reference angular velocity of the power system. |
2.1. Establishment of PLL-Synchronized Swing Equation of the DFIG
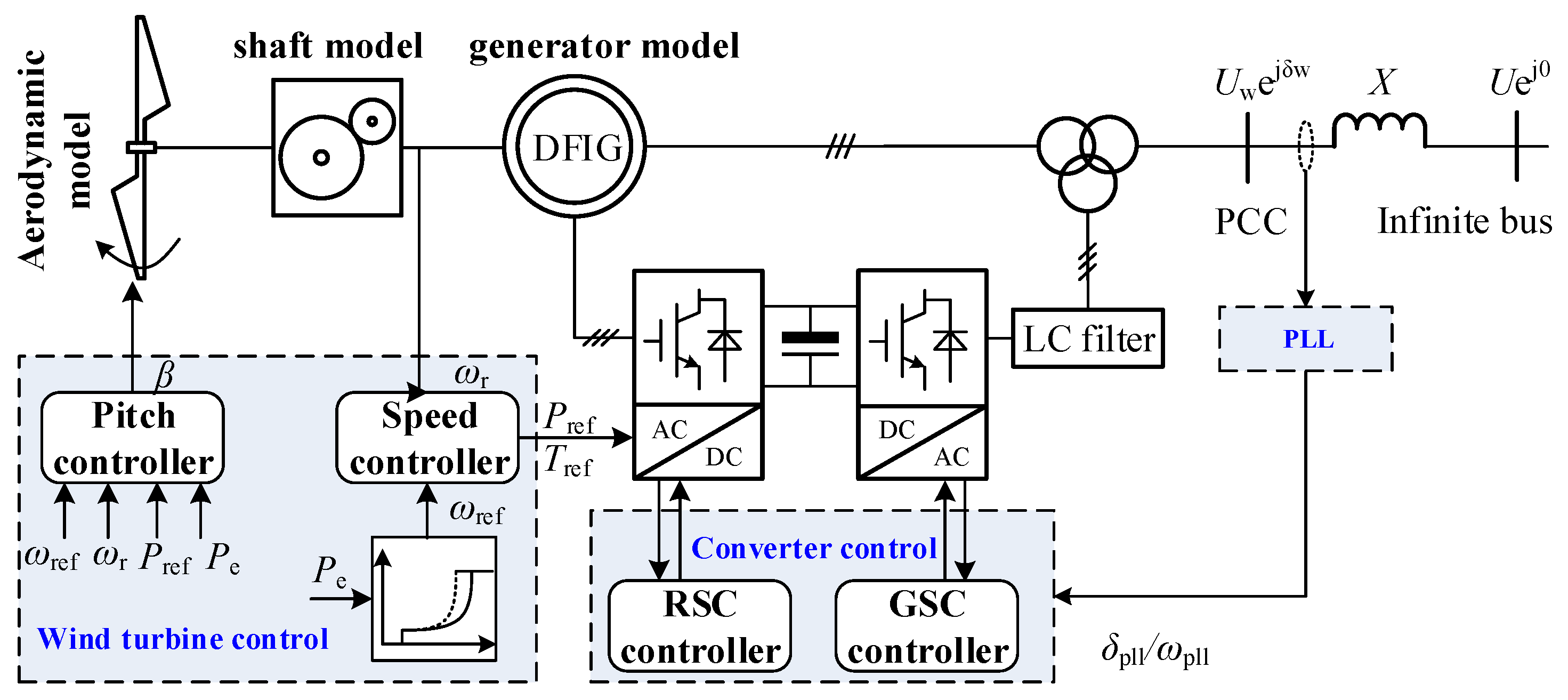
2.1.1. Introduction of the DFIG Control Structure
2.1.2. Establishment of Swing Equation of the DFIG Based on PLL
2.2. Inertia Provisions Using the PLL-Synchronized the DFIG Model
2.2.1. Physical Significance of the Proposed Swing Equation of the DFIG
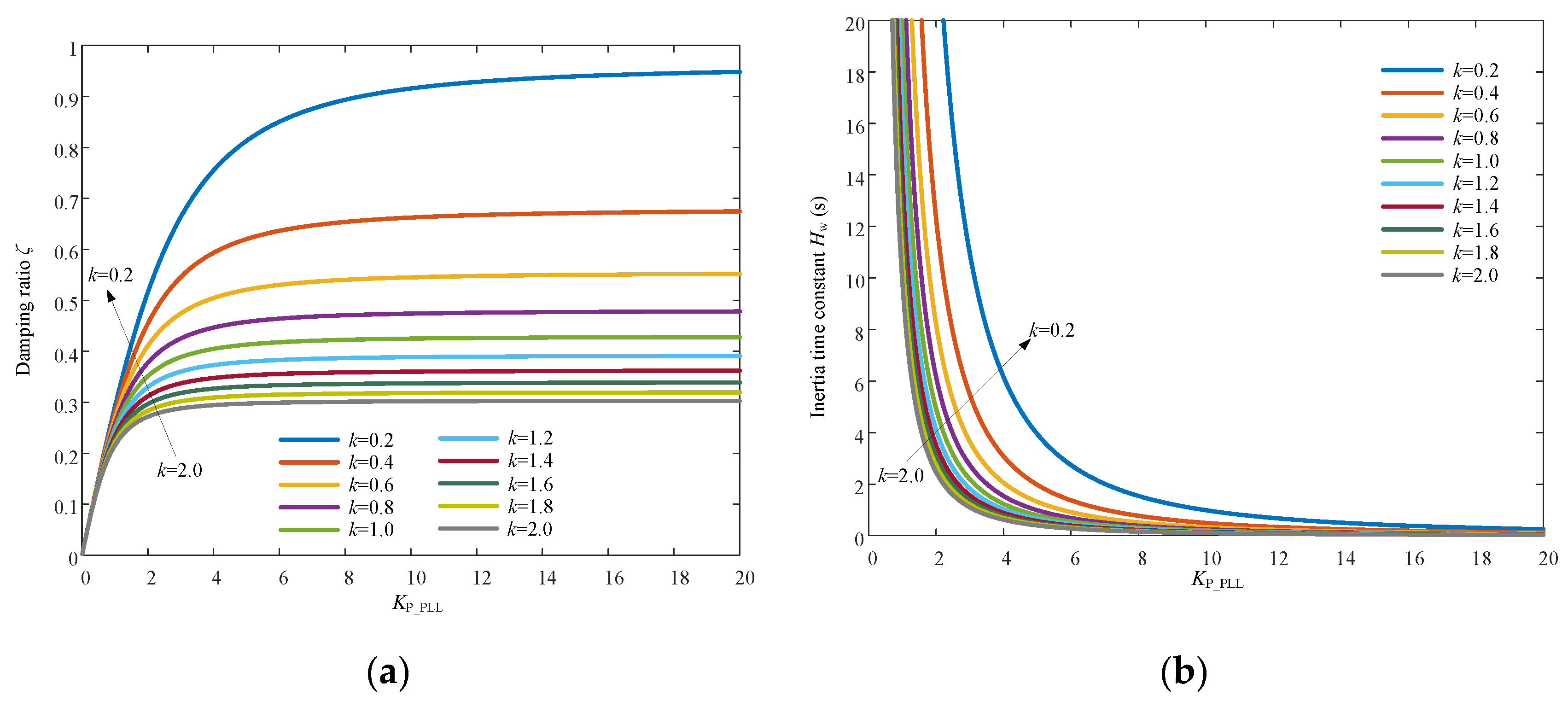
2.2.2. Inertia Emulation Using the PLL-Synchronized Swing Equation
2.3. Small Signal Stability Analysis Using PLL-synchronized Swing Equation
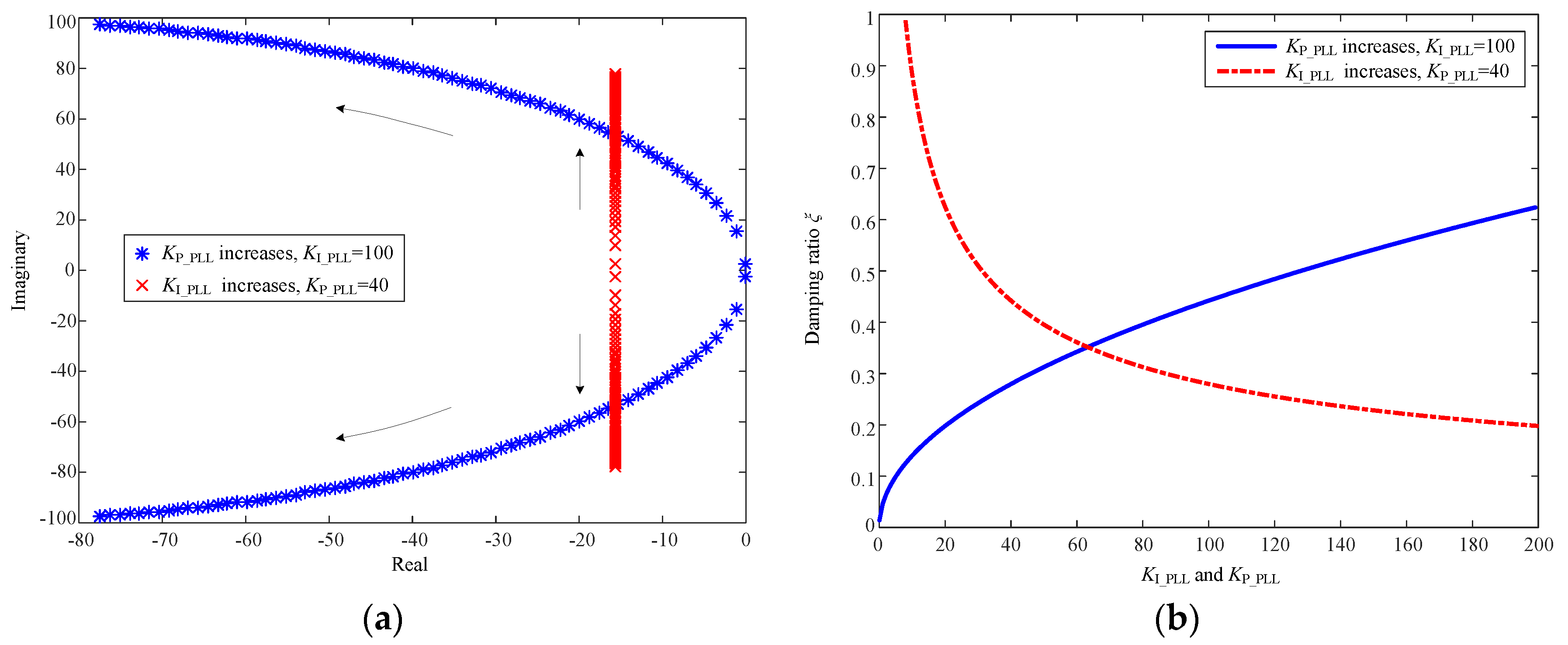
2.3.1. Internal Stability of PLL Model
2.3.2. Small Signal Stability of Wind-Integrated Power System
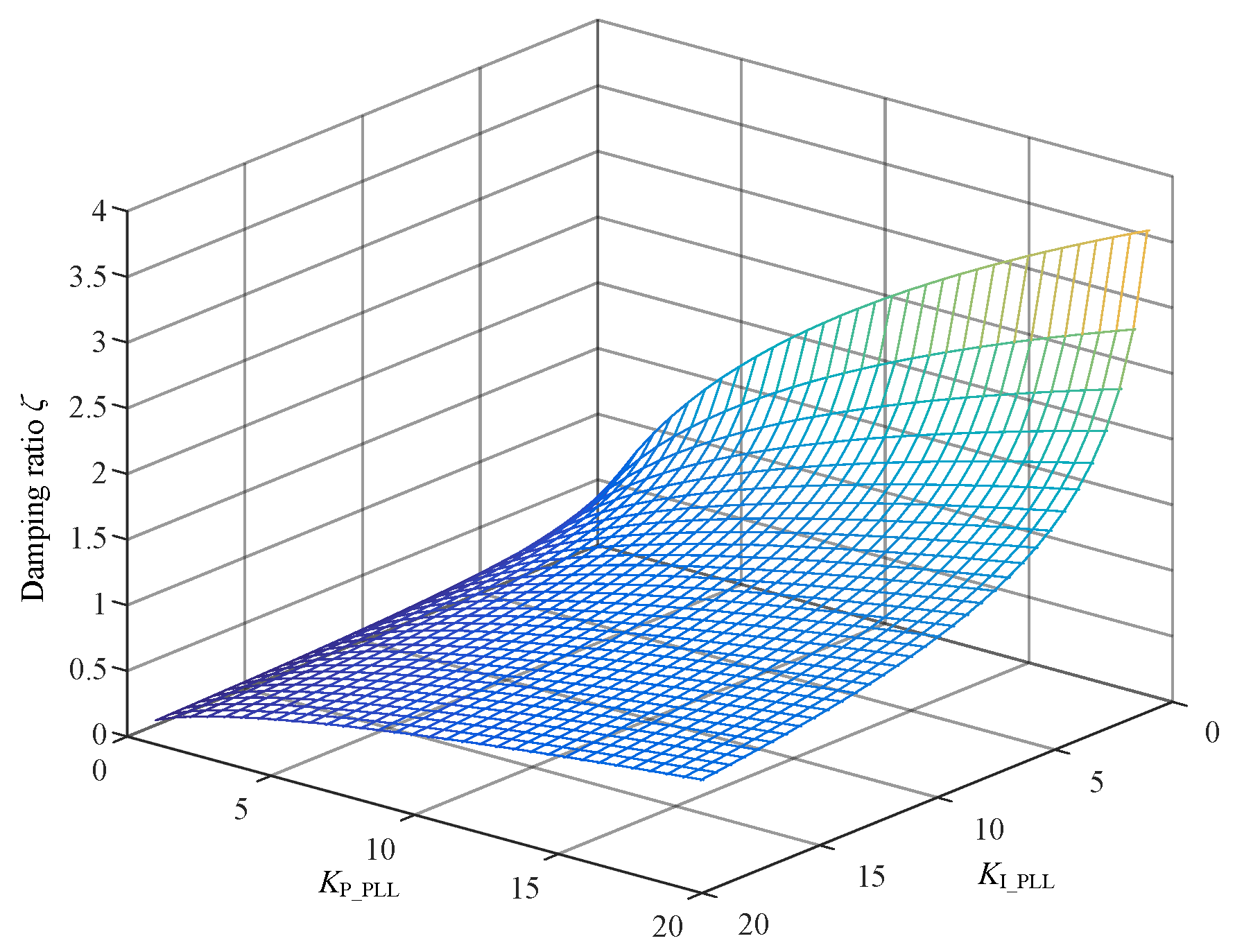
2.3.3. Parameters Optimization for Damping Enhancement and Inertia Provision
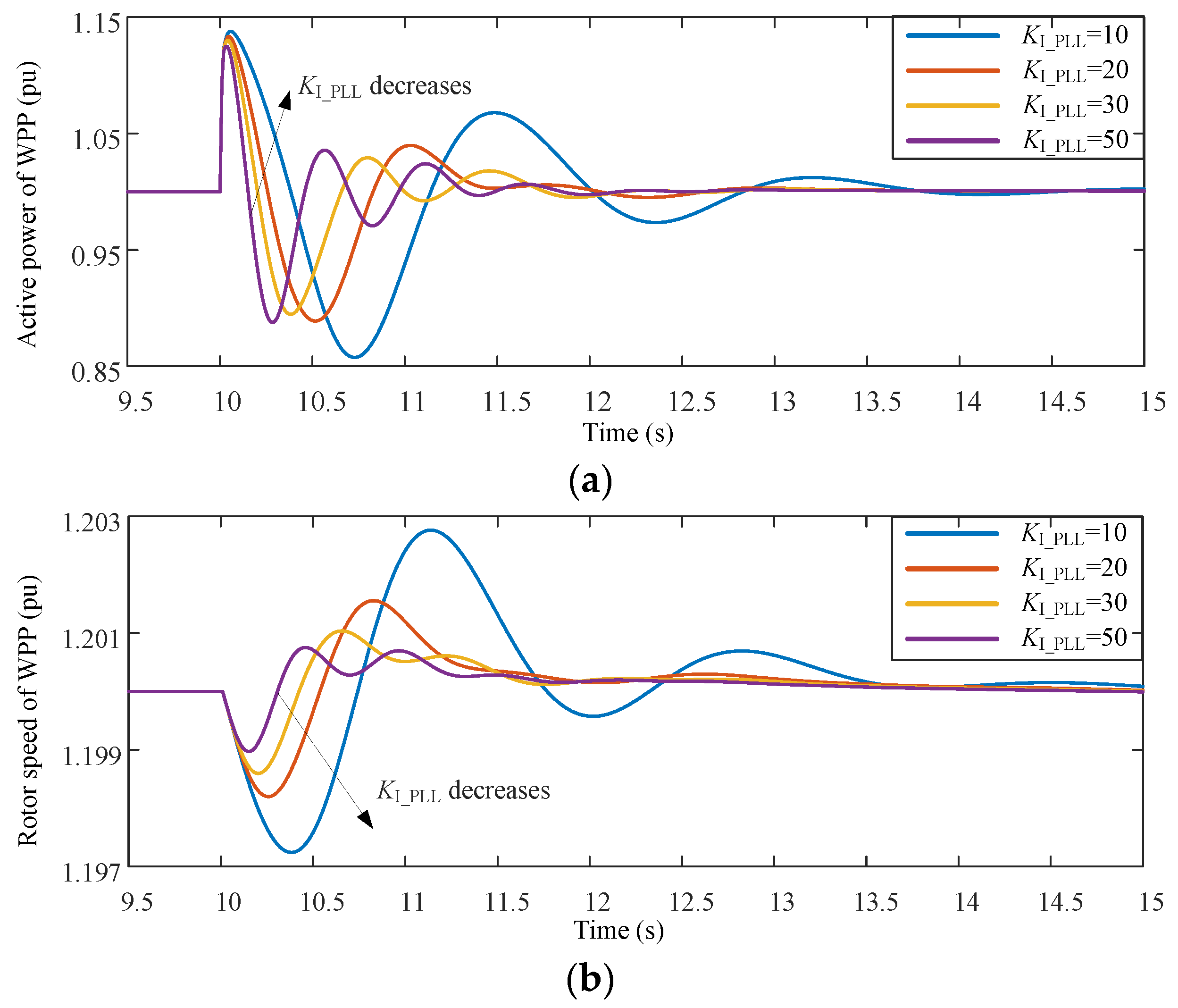
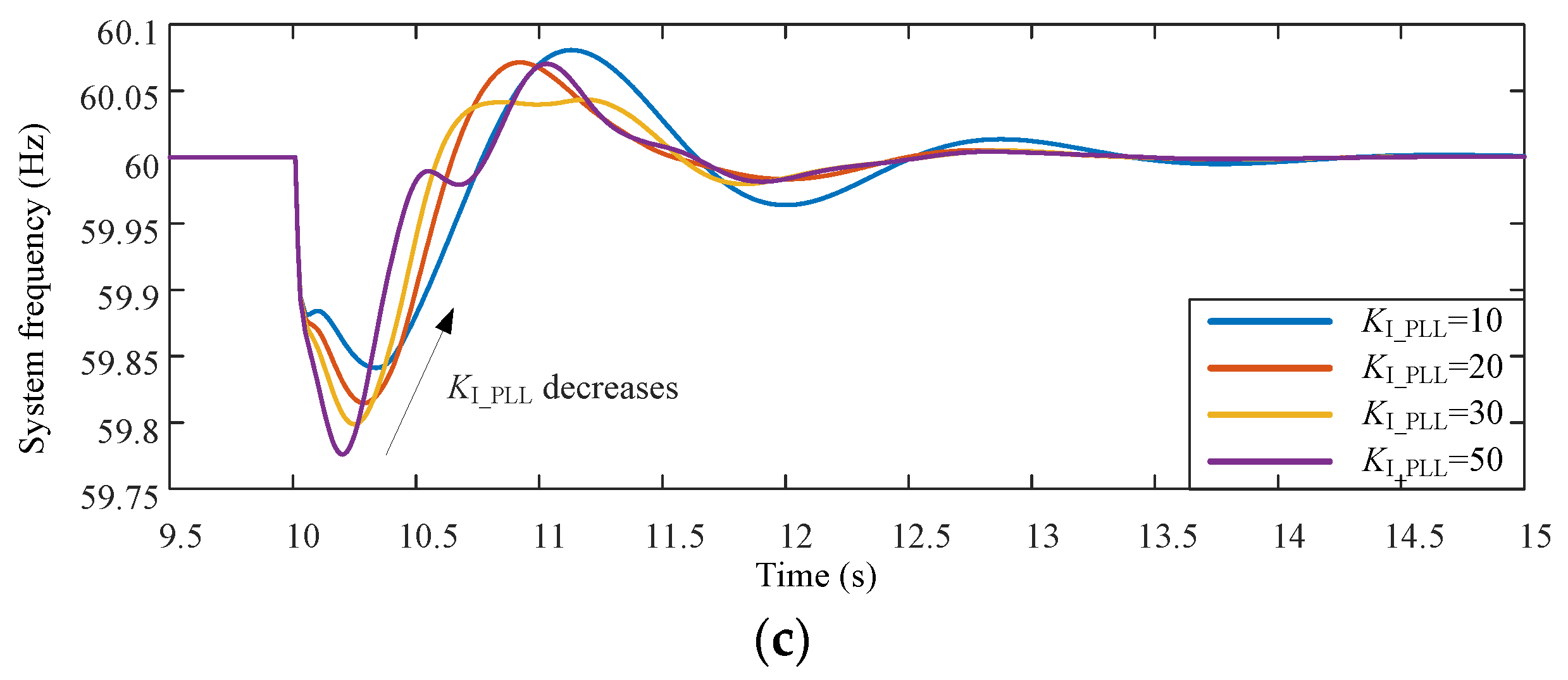
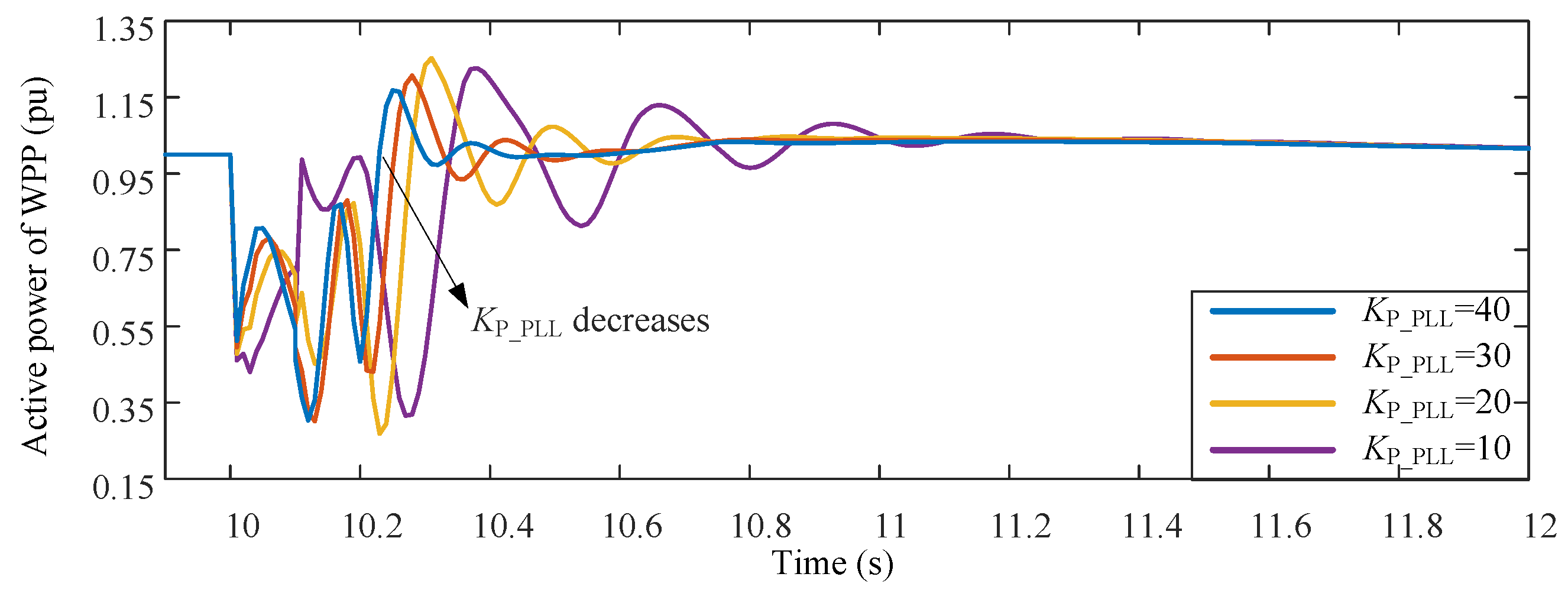
3. Simulation Results
3.1. Simulations in Single-Machine Infinite Bus System With a WPP
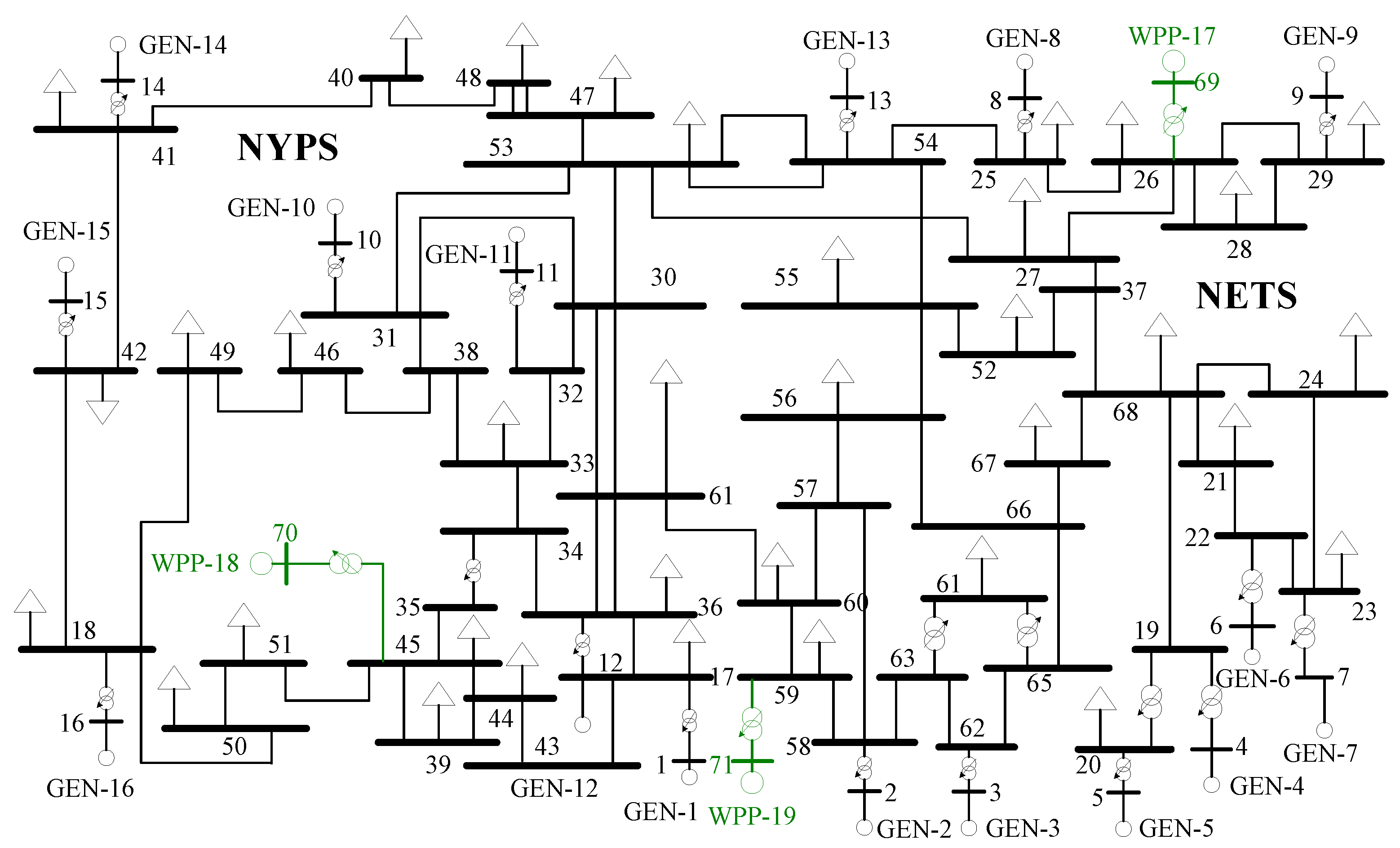
3.2. Simulations in NYPS-NETS Power System With WPPs Integration
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (i)
- The equivalent inertia of the DFIG is inversely proportional to both the proportional and integral gains of PLL. The proportional and integral gains should be small enough for providing the DFIG sufficient inertial response ability.
- (ii)
- The internal stability of PLL will not change if the proportional and integral gains decrease with the constant ratio. Whereas aiming at the multi-machine system, decreasing the parameters in PLL with the constant ratio cannot avoid deteriorating the damping characteristics of the whole system. The small proportional gain will also slow down the response rate and locking accuracy of PLL.
- (iii)
- The parameters optimization of PLL is proposed following three principles by decreasing the ratio of KI_PLL to KP_PLL for obtaining sufficient inertial response ability of the WPP and ideal damping properties of the system at the same.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| ids | iqs | sr | KP_PLL | KI_PLL | Mg | δg |
| 0.3122 | 0.95 | −0.2 | 40 | 100 | 0.0531 | 38.78° |
| Dg | Uw | E | U | X1 | X2 | δw |
| 0.001 | 0.998 | 0.995 | 1.000 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 33.99° |
References
- Islam, M.R.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, J.G. A review of offshore wind turbine nacelle: Technical challenges, and research and developmental trends. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 3, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Wind Energy Council. “Global Wind Report–Annual market update 2017”. Available online: http://files.gwec.net/register?file=/files/GWR2017.pdf (accessed on 5 April 2018).
- Yuan, T.J.; Wang, J.J.; Guan, Y.H.; Liu, Z.; Song, X.F.; Che, Y.; Cao, W.P. Virtual inertia adaptive control of a doubly fed induction generator wind power system with hydrogen energy storage. Energies 2018, 11, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.S.; Li, Y.J.; Zhu, Y.X.; Yang, P.; Xu, Z.R. Coordinated Control Schemes of Super-Capacitor and Kinetic Energy of DFIG for System Frequency Support. Energies 2018, 11, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.F.; Liu, J.; Liu, H.H.; Zhao, S.Q. Active-Reactive Additional Damping Control of a Doubly-Fed Induction Generator Based on Active Disturbance Rejection Control. Energies 2018, 11, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, K.; Altin, M.; Mikkelsen, L.M.; Olsen, R.L.; Lov, F. ICT Based Performance Evaluation of Primary Frequency Control Support from Renewable Power Plants in Smart Grids. Energies 2018, 11, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, J.G. Steady state characteristic simulation of DFIG for wind power system. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrical & Computer Engineering, Bursa, Turkey, 2–5 December 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Beltran, O.; Pena, R.; Segundo, J.; Esparza, A.; Muljadi, E.; Wenzhong, D. Inertia Estimation of Wind Power Plants Based on the Swing Equation and Phasor Measurement Units. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Dai, J.F.; Ning, J.; Dang, J.; Li, Y.; Tian, X.S. An Extended System Frequency Response Model Considering Wind Power Participation in Frequency Regulation. Energies 2018, 10, 1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.H.; Teng, Z.X.; Zhao, J.H.; Qiu, J. Small-Signal Performance of Type 4 Wind Turbine Generator-Based Clusters in Power Systems. Energies 2018, 11, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wen, F.S.; Zhao, H.W.; Chen, M.H.; Yang, Z.; Shang, H.Y. Stochastic Small Signal Stability of a Power System with Uncertainties. Energies 2018, 11, 2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamrakar, U.; Shrestha, D.; Maharjan, M.; Bhattarai, B.P.; Hansen, T.M.; Tonkoski, R. Virtual Inertia: Current Trends and Future Directions. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, M.; Muljadi, E.; Park, J.W.; Sorensen, P.; Kang, Y.C. Dynamic droop-based inertial control of a doubly-fed induction generator. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2016, 7, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerdphol, T.; Rahman, F.S.; Mitani, Y. Virtual Inertia Control Application to Enhance Frequency Stability of Interconnected Power Systems with High Renewable Energy Penetration. Energies 2018, 11, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morren, J.; Haan, S.W.H.D.; Kling, W.L.; Ferreira, J.A. Wind turbines emulating inertia and supporting primary frequency control. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2006, 21, 433–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Meng, J.; Zhang, X.; Xu, L. Control of PMSG-based wind turbines for system inertial response and power oscillation damping. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2015, 6, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musarrat, M.N.; Islam, M.R.; Muttaqi, K.M.; Sutanto, D. Enhanced Frequency Support From a PMSG-Based Wind Energy Conversion System Integrated with a High Temperature SMES in Standalone Power Supply Systems. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2019, 29, 3800206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, D.; Vittal, V. Impact of DFIG based Wind Turbine Generators on Transient and Small Signal Stability of Power Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2010, 24, 1426–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fu, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y. Effects of two-area variable inertia on transient stabilization in interconnected power system with DFIG-based wind turbines. IET Renew. Power Gen. 2017, 11, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.C. Virtual Synchronous Machines: A unified interface for grid integration. IEEE Power Electron. Mag. 2016, 3, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Ruan, X.; Yang, D.S.; Chen, X.R.; Zhao, W.X.; Lv, Z.P.; Zhong, Q.C. Small-Signal Modeling and Parameters Design for Virtual Synchronous Generators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 4292–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Bletterie, B.; Anta, A.; Gawlik, W. On Small Signal Frequency Stability under Virtual Inertia and the Role of PLLs. Energies 2018, 11, 2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Yuan, X.; Hu, J. Inertia Provision and Estimation of PLL-based DFIG Wind Turbines. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2016, 32, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Sun, L.; Yuan, X.M.; Wang, S. Modeling of Type 3 Wind Turbine with df/dt Inertia Control for System Frequency Response Study. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2017, 32, 2799–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, S.; Tang, W.; Xiong, X. Full-capacity wind turbine with inertial support by adjusting phase-locked loop response. IET Renew. Power Gen. 2016, 11, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Qiu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, W.; Song, Z.; Thorp, J.S. Research on the impact of WTG virtual inertia control on power system small-signal stability considering the phase-locked loop. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2017, 32, 20942105. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, S.; Geng, H.; Yang, G. Philips-Heffron model for current-controlled power electronic generation unit. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy. 2017, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.; Zhang, X.P.; Godfrey, K.; Ju, P. Small signal stability analysis and optimal control of a wind turbine with doubly fed induction generator. IET Gener. Transm. Dis. 2007, 1, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power Technologies International. PSS/E-33.4 Program Application Guide. 2013, Volume 2. Available online: https://www.scribd.com/document/241950119/POM-PSSE33-pdf (accessed on 6 March 2019).
- Zhong, Q.C.; Nguyen, P.L. Sinusoid-locked loops to detect the frequency, the amplitude and the phase of the fundamental component of a periodic signal. In Proceedings of the 24th Conference Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), Taiyuan, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.W.; Shen, C.; Liu, F. Impact of DFIG with Phase Lock Loop Dynamics on Power Systems Small Signal Stability. In Proceedings of the Pes General Meeting, Conference & Exposition IEEE, Washington, DC, USA, 27–31 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Abad, G.; Jesús, L.; Rodriguez, M.A.; Marroyo, L.; Iwanski, G. Doubly Fed Induction Machine: Modeling and Control for Wind Energy Generation; Wiley IEEE Press: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, P.M. Power System Control and Stability, 2nd ed.; Iowa State University Press: Ames, IA, USA, 1977; 40p. [Google Scholar]
- Gautam, D.; Goel, L.; Ayyanar, R.; Vittal, V.; Harbour, T. Control strategy to mitigate the impact of reduced inertia due to doubly fed induction generators on large power systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2011, 26, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.R.; Zhuang, X.Y. Principle of Automatic Control, 2nd ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 58–71. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.K.; Pal, B.C. IEEE PES Task Force on Benchmark Systems for Stability Controls Report on the 68-Bus, 16-Machine, 5-Area System. Available online: http://www.sel.eesc.usp.br/ieee/. (accessed on 1 August 2015).









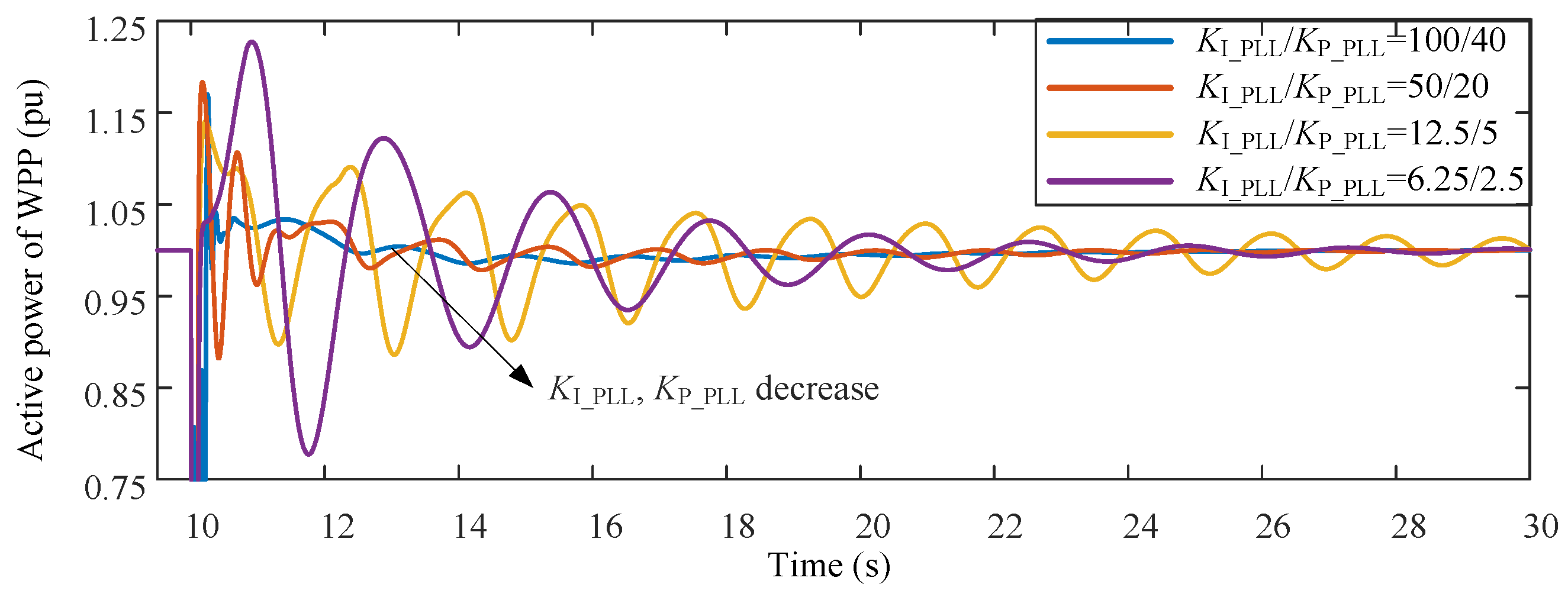


| Case1 | Case2 | Case3 | Case4 | Case5 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KI_PLL = 5 | KP_PLL = 4 | KI_PLL = 100 | KP_PLL = 1 | KI_PLL/KP_PLL = 2.5 | |||||
| KP_PLL | Hw (s) | KI_PLL | Hw (s) | KP_PLL | ξ | KI_PLL | ξ | KI_PLL/KP_PLL | ξ |
| 6 | 0.6572 | 10 | 0.4929 | 10 | 0.1798 | 100 | 0.0868 | 100/40 | 0.3139 |
| 10 | 0.3942 | 20 | 0.2465 | 20 | 0.2387 | 200 | 0.0712 | 50/20 | 0.3044 |
| 15 | 0.2629 | 30 | 0.1643 | 30 | 0.2803 | 300 | 0.0675 | 12.5/5 | 0.2603 |
| 25 | 0.1577 | 50 | 0.0986 | 40 | 0.3139 | 400 | 0.0664 | 6.25/2.5 | 0.1096 |
| PCC | WPP-Number | Capacity |
|---|---|---|
| Bus-69 | WPP-17 | 1110 MVA |
| Bus-45 | WPP-18 | 1110 MVA |
| Bus-59 | WPP-19 | 1110 MVA |
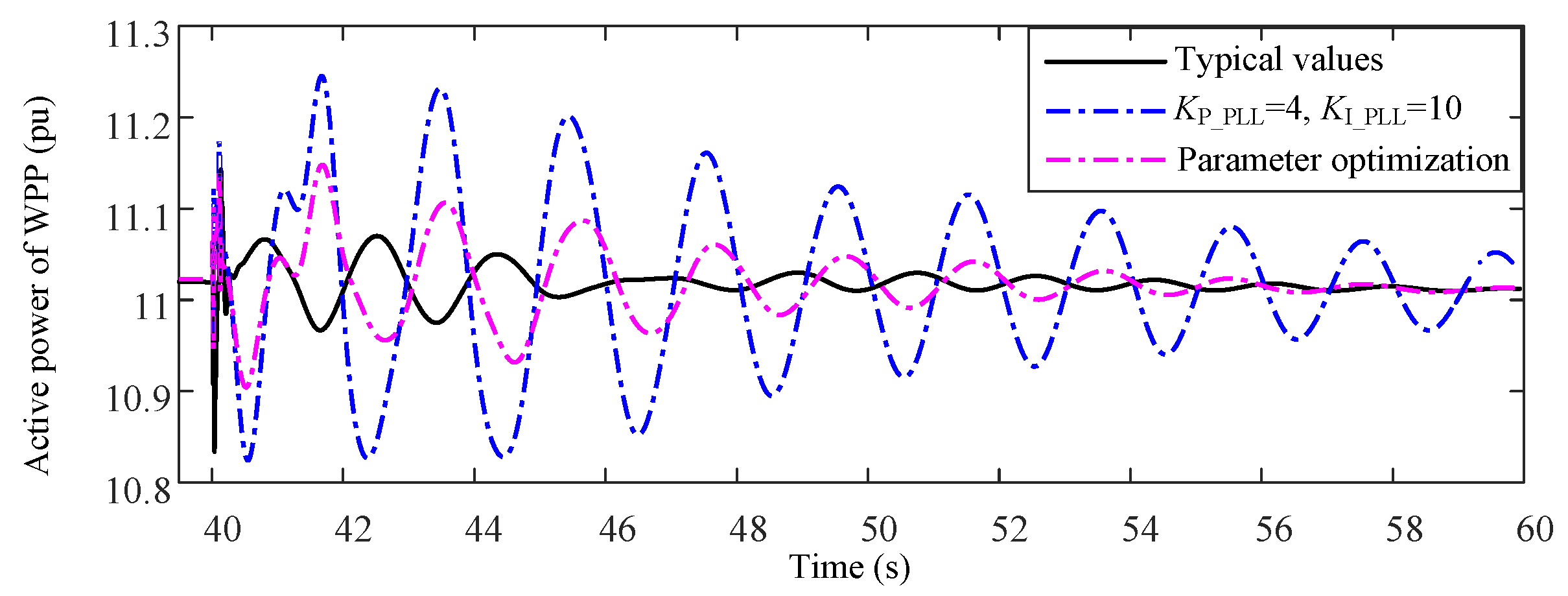
| KI_PLL, KP_PLL | Inertia Constant | Damping Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| 100, 40 | 0.0452 s | 0.68 |
| 10, 4 | 4.8183 s | 0.33 |
| 12, 2.5 | 6.0243 s | 0.69 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Yuan, Y. Inertia Provision and Small Signal Stability Analysis of a Wind-Power Generation System Using Phase-Locked Synchronized Equation. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11051400
Wang Y, Yuan Y. Inertia Provision and Small Signal Stability Analysis of a Wind-Power Generation System Using Phase-Locked Synchronized Equation. Sustainability. 2019; 11(5):1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11051400
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yifei, and Youxin Yuan. 2019. "Inertia Provision and Small Signal Stability Analysis of a Wind-Power Generation System Using Phase-Locked Synchronized Equation" Sustainability 11, no. 5: 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11051400
APA StyleWang, Y., & Yuan, Y. (2019). Inertia Provision and Small Signal Stability Analysis of a Wind-Power Generation System Using Phase-Locked Synchronized Equation. Sustainability, 11(5), 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11051400




